1. 准备工作
在此实践 Codelab 中,您将学习双屏设备和可折叠设备的应用开发方面的基础知识。完成后,应用可支持 Pixel Fold、Microsoft Surface Duo、Samsung Galaxy Z Fold 5 等可折叠设备。
前提条件
为完成此 Codelab,您需要:
- 拥有构建 Android 应用的经验
- 拥有使用 activity、fragment、视图绑定和 xml-layout 的经验
实践内容
创建一款具有以下功能的简单应用:
- 显示设备功能
- 检测应用何时在可折叠设备或双屏设备上运行
- 确定设备状态
- 借助 Jetpack WindowManager 支持采用新的外形规格的设备。
所需条件
- Android Studio Arctic Fox 或更高版本
- 可折叠设备或模拟器
Android 模拟器 v30.0.6 及更高版本支持可折叠设备,以及虚拟合页传感器和 3D 视图。您可以使用下图中所示的几种可折叠设备模拟器:
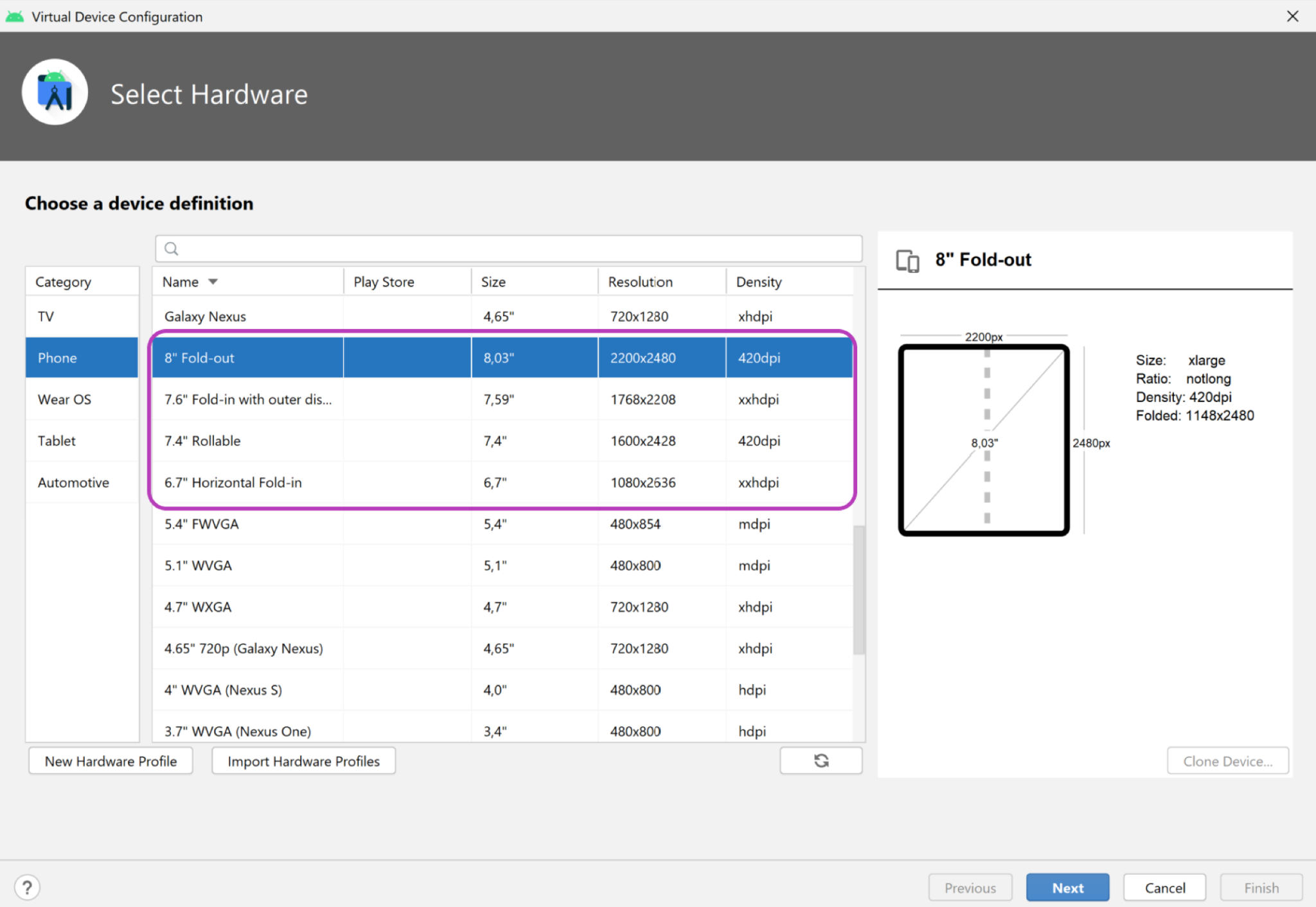
- 如需使用双屏设备模拟器,请点击下载适用于您的平台(Windows、MacOS 或 GNU/Linux)的 Microsoft Surface Duo 模拟器。
2. 单屏设备和可折叠设备
与以前的移动设备相比,可折叠设备为用户提供了更大的屏幕及更灵活多变的界面。在折叠后,此类设备的尺寸通常小于普通平板电脑的尺寸,便于携带且实用。
在撰写本文时,共有两种可折叠设备:
- 单屏可折叠设备,配备一个可折叠的屏幕。在
multi-window模式下,用户可以在同一屏幕上同时运行多个应用。 - 双屏可折叠设备,两个屏幕由合页相连。此类设备也可以折叠,但具有两个不同的逻辑显示区域。
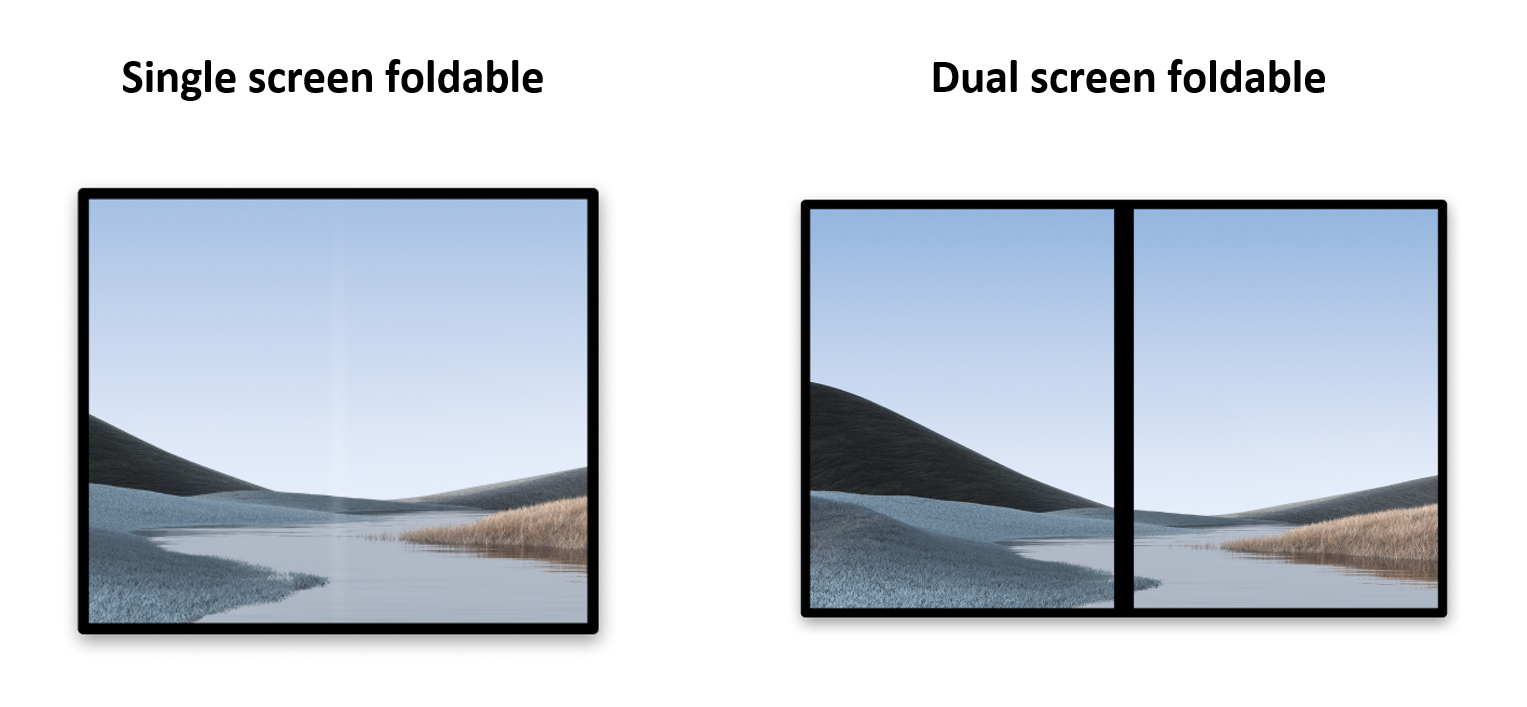

与平板电脑及其他单屏移动设备一样,可折叠设备可以:
- 在其中一个显示区域中运行一个应用。
- 同时运行两个应用,各位于一个显示区域中(在
multi-window模式下)。
与单屏设备不同的是,可折叠设备还支持不同的折叠状态。折叠状态可用来以不同的方式显示内容。
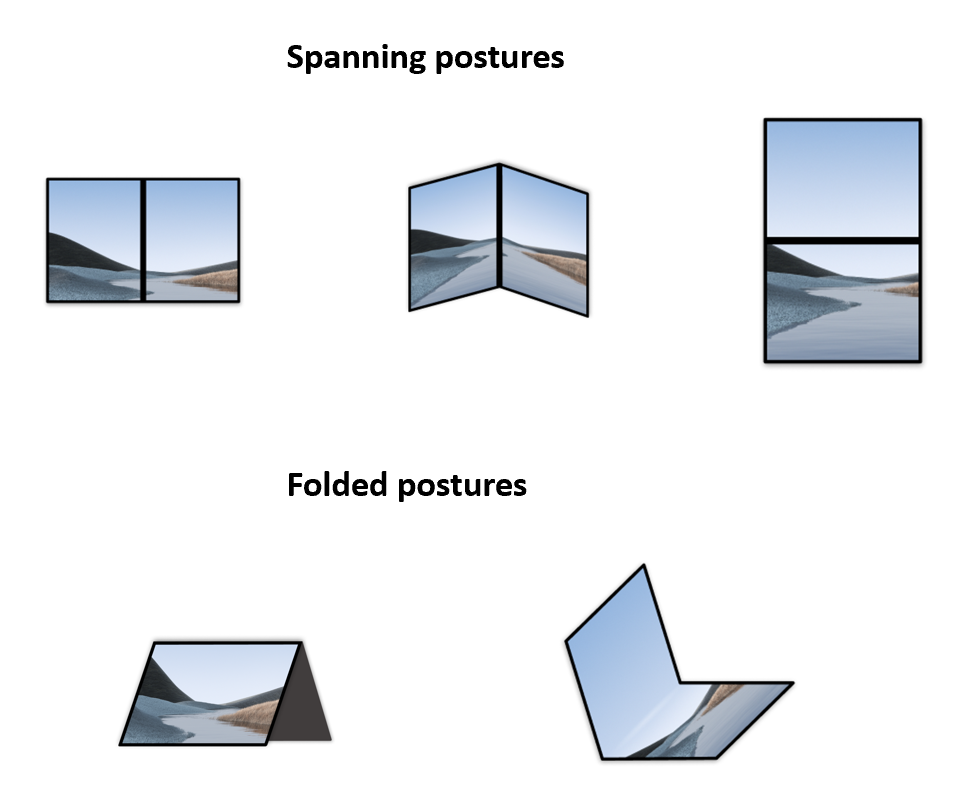
当应用跨整个显示区域(使用双屏可折叠设备上的所有显示区域)显示时,可折叠设备可提供不同的跨屏折叠状态。
可折叠设备还支持不同的折叠状态,例如,在桌面模式下,您可以在放平的屏幕和朝向您倾斜的屏幕之间进行逻辑拆分;在帐篷模式下,您可以像用小支架支起设备一样来观看内容。
3. Jetpack WindowManager
Jetpack WindowManager 库可帮助应用开发者支持新的设备外形规格,并为新旧版本平台上的各种 WindowManager 功能提供通用的 API Surface。
主要功能
Jetpack WindowManager 版本 1.1.0 包含 FoldingFeature 类,该类用于描述柔性显示屏的折叠状态或两个物理显示面板之间的合页状态。您可通过其 API 访问与设备相关的重要信息:
state():提供设备当前的折叠状态,该状态为已定义的折叠状态(FLAT和HALF_OPENED)列表中的一种isSeparating():计算是否应将FoldingFeature视为将窗口拆分为多个物理区域,而用户可以将这些区域视为逻辑上互相独立的区域occlusionType():计算遮挡模式,以确定FoldingFeature是否遮挡窗口的一部分。orientation():如果FoldingFeature宽度大于高度,则返回FoldingFeature.Orientation.HORIZONTAL;否则,返回FoldingFeature.Orientation.VERTICAL。bounds():提供一个Rect实例,其中包含设备功能的边界,例如物理合页的边界。
借助 WindowInfoTracker 接口,您可以访问 windowLayoutInfo() 以收集包含所有可用 DisplayFeature 的 WindowLayoutInfo 的 Flow。
4. 设置
创建一个新项目,然后选择“Empty Activity”模板:
将所有参数保留为默认值。
声明依赖项
为了能够使用 Jetpack WindowManager,请在应用或模块的 build.gradle 文件中添加相关依赖项:
app/build.gradle
dependencies {
ext.windowmanager_version = "1.1.0"
implementation "androidx.window:window:$windowmanager_version"
androidTestImplementation "androidx.window:window-testing:$windowmanager_version"
// Needed to use lifecycleScope to collect the WindowLayoutInfo flow
implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-runtime-ktx:2.6.2"
}
使用 WindowManager
您可通过 WindowManager 的 WindowInfoTracker 接口访问窗口功能。
打开 MainActivity.kt 源文件并调用 WindowInfoTracker.getOrCreate(this@MainActivity),以初始化与当前 activity 相关联的 WindowInfoTracker 实例:
MainActivity.kt
import androidx.window.layout.WindowInfoTracker
private lateinit var windowInfoTracker: WindowInfoTracker
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
windowInfoTracker = WindowInfoTracker.getOrCreate(this@MainActivity)
}
借助 WindowInfoTracker 实例,获取有关设备当前窗口状态的信息。
5. 设置应用界面
从 Jetpack WindowManager 中,获取窗口指标、布局和显示配置的相关信息。在主 activity 布局中显示这些信息,并针对每项信息使用 TextView。
创建一个包含三个 TextView 并在屏幕上居中显示的 ConstraintLayout。
打开 activity_main.xml 文件,然后粘贴以下内容:
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/constraint_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/window_metrics"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="20dp"
tools:text="Window metrics"
android:textSize="20sp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/layout_change"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintVertical_chainStyle="packed" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/layout_change"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="20dp"
tools:text="Layout change"
android:textSize="20sp"
app:layout_constrainedWidth="true"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/configuration_changed"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/window_metrics" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/configuration_changed"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="20dp"
tools:text="Using one logic/physical display - unspanned"
android:textSize="20sp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/layout_change" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
现在,我们将使用视图绑定功能在代码中关联这些界面元素。为此,我们首先在应用的 build.gradle 文件中启用该功能:
app/build.gradle
android {
// Other configurations
buildFeatures {
viewBinding true
}
}
按照 Android Studio 的建议同步 Gradle 项目,并使用以下代码在 MainActivity.kt 中使用视图绑定:
MainActivity.kt
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var windowInfoTracker: WindowInfoTracker
private lateinit var binding: ActivityMainBinding
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
setContentView(binding.root)
windowInfoTracker = WindowInfoTracker.getOrCreate(this@MainActivity)
}
}
6. 直观呈现 WindowMetrics 信息
在 MainActivity 的 onCreate 方法中,调用一个函数来获取并显示 WindowMetrics 信息。在 onCreate 方法中添加 obtainWindowMetrics() 调用:
MainActivity.kt
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
setContentView(binding.root)
windowInfoTracker = WindowInfoTracker.getOrCreate(this@MainActivity)
obtainWindowMetrics()
}
实现 obtainWindowMetrics 方法:
MainActivity.kt
import androidx.window.layout.WindowMetricsCalculator
private fun obtainWindowMetrics() {
val wmc = WindowMetricsCalculator.getOrCreate()
val currentWM = wmc.computeCurrentWindowMetrics(this).bounds.flattenToString()
val maximumWM = wmc.computeMaximumWindowMetrics(this).bounds.flattenToString()
binding.windowMetrics.text =
"CurrentWindowMetrics: ${currentWM}\nMaximumWindowMetrics: ${maximumWM}"
}
通过伴生函数 getOrCreate() 获取 WindowMetricsCalculator 的实例。
借助该 WindowMetricsCalculator 实例,将信息设置到 windowMetrics TextView 中。使用由函数 computeCurrentWindowMetrics.bounds 和 computeMaximumWindowMetrics.bounds 返回的值。
这些值会提供有关窗口所占区域各项指标的实用信息。
运行应用。在双屏设备模拟器中(如下图所示),您会得到与模拟器所镜像的设备尺寸对应的 CurrentWindowMetrics。您还可以查看应用在单屏模式下运行时的指标:
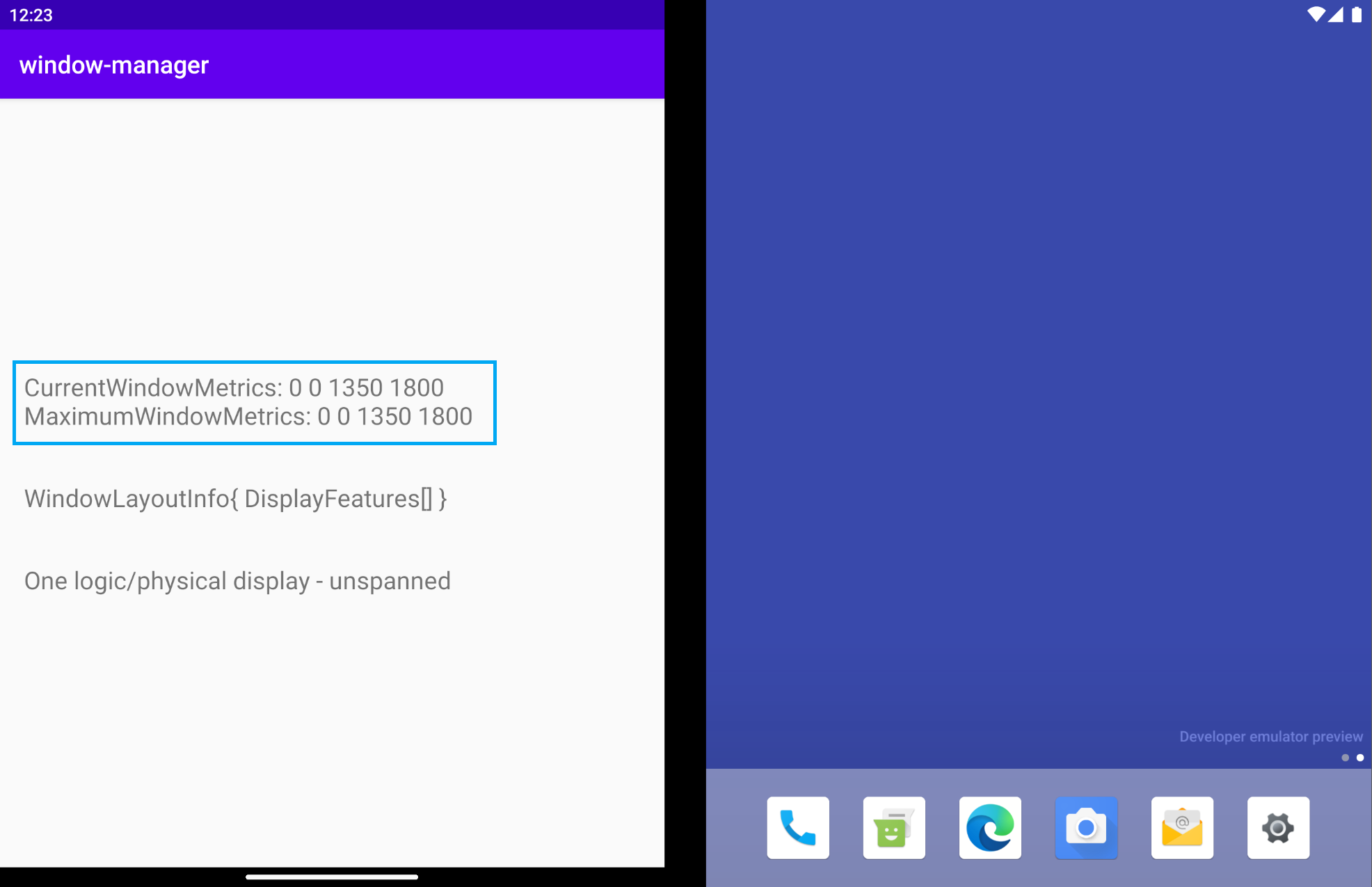
当应用跨显示屏显示时,窗口指标会发生变化(如下图所示),因此它们现在反映的应用所用窗口区域比之前大:
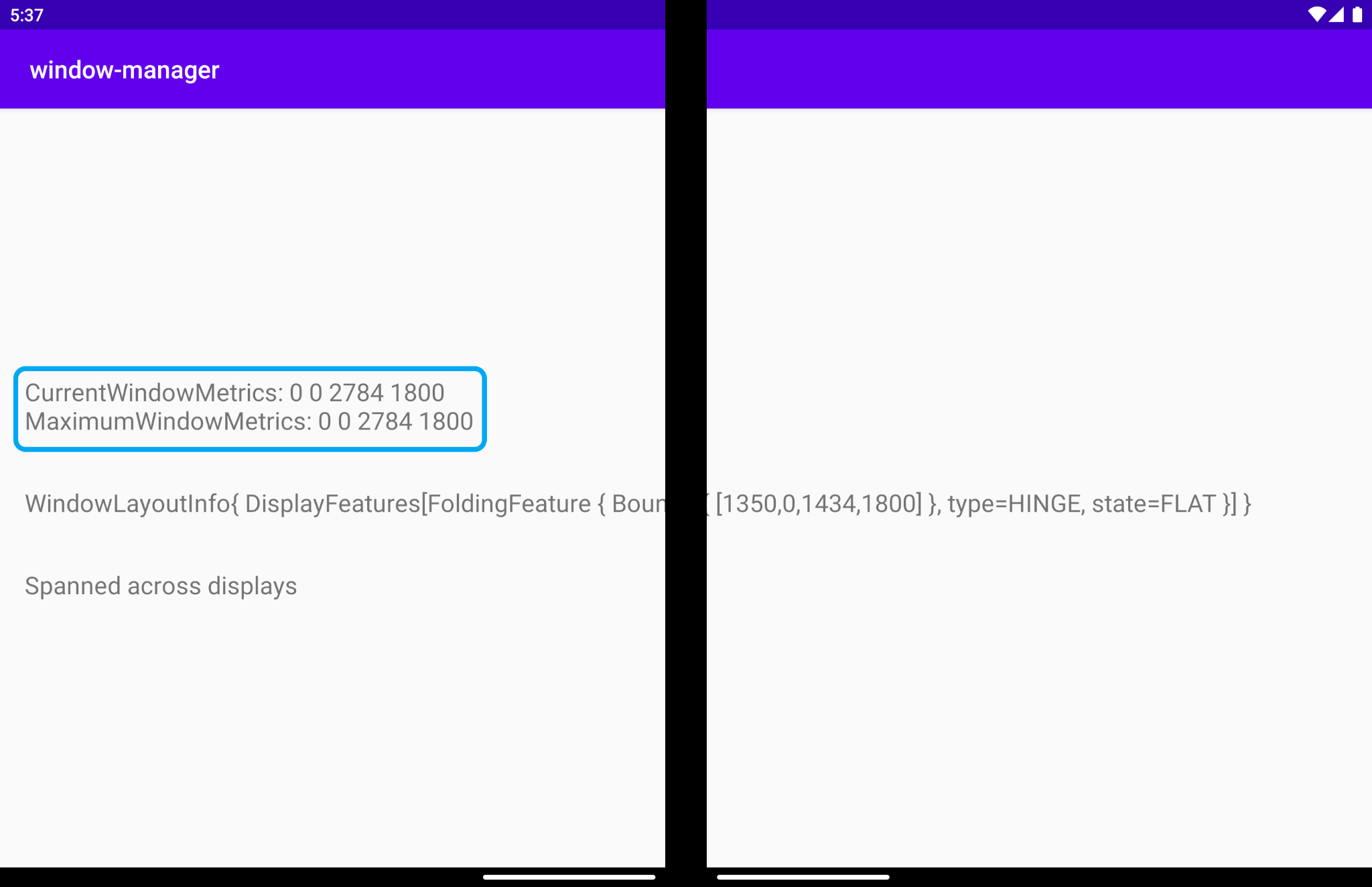
由于该应用在单屏和双屏设备上始终运行并占满整个显示区域,因此当前窗口指标和最大窗口指标的值相同。
在有水平折叠边的可折叠设备模拟器中,这些值在应用跨整个物理显示屏运行时和在多窗口模式下运行时会有所不同:
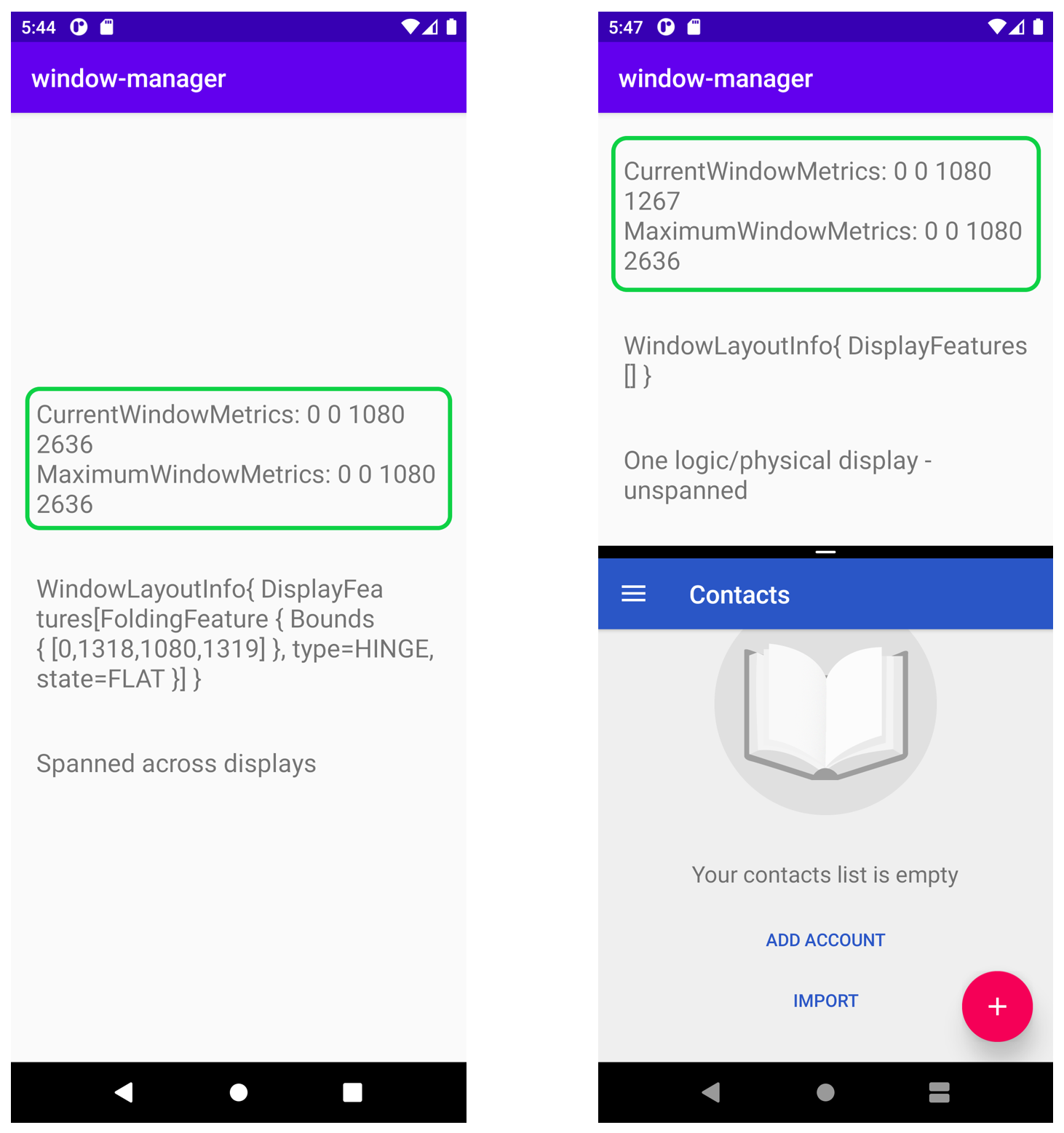
如左图所示,这两个指标的值相同,这是因为运行的应用占满了整个显示区域,该区域既是当前的显示区域,也是最大显示区域。
但在右图中,应用在多窗口模式下运行,您可看到当前指标如何显示应用在分屏模式下的特定区域(顶部)运行时所占区域的尺寸,还可看到最大指标如何显示设备的最大显示区域。
WindowMetricsCalculator 提供的指标对于确定应用当前使用或可以使用的窗口区域非常有用。
7. 直观呈现 FoldingFeature 信息
现在进行注册,以便接收窗口布局变化,以及模拟器或设备 DisplayFeatures 的特性和边界。
为了能从 WindowInfoTracker#windowLayoutInfo() 收集信息,使用为每个 Lifecycle 对象定义的 lifecycleScope。在此作用域内启动的协程会在 Lifecycle 被销毁时取消。您可以通过 lifecycle.coroutineScope 或 lifecycleOwner.lifecycleScope 属性访问 Lifecycle 的协程作用域。
在 MainActivity 的 onCreate 方法中,调用一个函数来获取并显示 WindowInfoTracker 信息。首先,在 onCreate 方法中添加 onWindowLayoutInfoChange() 调用:
MainActivity.kt
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
setContentView(binding.root)
windowInfoTracker = WindowInfoTracker.getOrCreate(this@MainActivity)
obtainWindowMetrics()
onWindowLayoutInfoChange()
}
每当新的布局配置发生变化时,都使用该函数的实现来获取信息。
定义函数签名和框架。
MainActivity.kt
private fun onWindowLayoutInfoChange() {
}
借助该函数收到的参数 WindowInfoTracker,获取其 WindowLayoutInfo 数据。WindowLayoutInfo 包含位于窗口内的 DisplayFeature 列表。例如,合页或显示屏折叠边可以穿过窗口,在这种情况下,可能有必要将视觉内容和互动元素分为两组(例如列表详情或视图控件)。
系统只会报告当前窗口边界内显示的功能。如果窗口在屏幕上移动或调整大小,其位置和大小可能会发生变化。
通过 lifecycle-runtime-ktx 依赖项中定义的 lifecycleScope,获取 WindowLayoutInfo 的 flow,其中包含所有显示功能的列表。添加 onWindowLayoutInfoChange 的正文:
MainActivity.kt
import androidx.lifecycle.Lifecycle
import androidx.lifecycle.lifecycleScope
import androidx.lifecycle.repeatOnLifecycle
import kotlinx.coroutines.Dispatchers
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.collect
import kotlinx.coroutines.launch
private fun onWindowLayoutInfoChange() {
lifecycleScope.launch(Dispatchers.Main) {
lifecycle.repeatOnLifecycle(Lifecycle.State.STARTED) {
windowInfoTracker.windowLayoutInfo(this@MainActivity)
.collect { value ->
updateUI(value)
}
}
}
}
正在从 collect 调用 updateUI 函数。实现此函数,以便显示和输出从 WindowLayoutInfo 的 flow 收到的信息。检查 WindowLayoutInfo 数据是否具有显示功能。如果是,则显示功能会以某种方式与应用的界面进行互动。如果 WindowLayoutInfo 数据没有任何显示功能,则表示应用正在单屏设备/模式或多窗口模式下运行。
MainActivity.kt
import androidx.window.layout.WindowLayoutInfo
private fun updateUI(newLayoutInfo: WindowLayoutInfo) {
binding.layoutChange.text = newLayoutInfo.toString()
if (newLayoutInfo.displayFeatures.isNotEmpty()) {
binding.configurationChanged.text = "Spanned across displays"
} else {
binding.configurationChanged.text = "One logic/physical display - unspanned"
}
}
运行应用。在双屏设备模拟器中,您将得到以下结果:
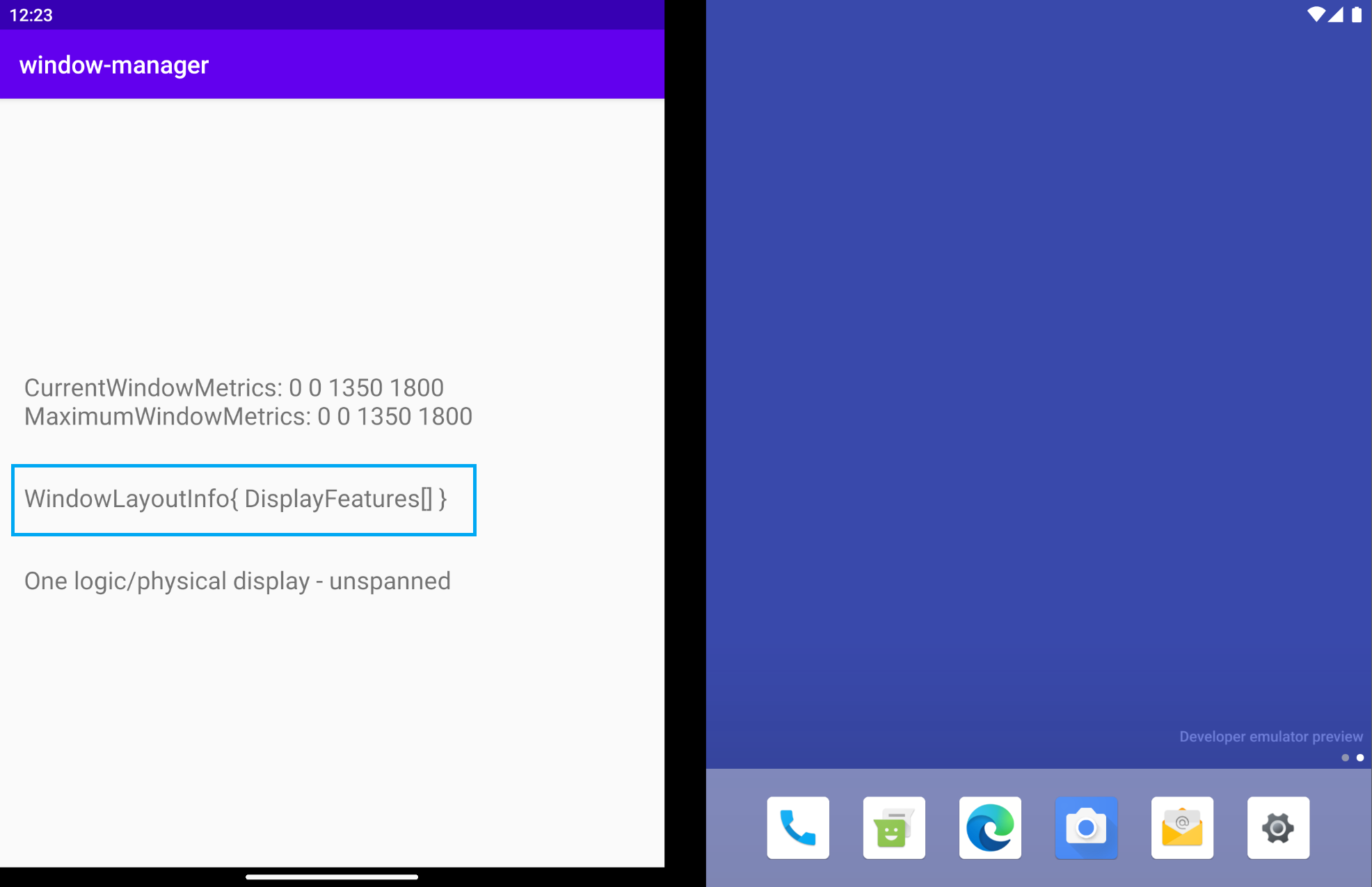
WindowLayoutInfo 为空,其中包含一个空的 List<DisplayFeature>。但如果模拟器的中间位置有合页,为什么不从 WindowManager 获取信息呢?
WindowManager 会(通过 WindowInfoTracker)在应用跨屏显示(以物理或虚拟方式)时提供 WindowLayoutInfo 数据(设备功能类型、设备功能边界和设备折叠状态)。因此,在上图中,应用在单屏模式下运行时,WindowLayoutInfo 为空。
掌握这些信息后,您就知道应用是在哪种模式(单屏模式还是跨屏模式)下运行,以便更改界面/用户体验,从而根据这些特定配置提供更好的用户体验。
在没有两个物理显示屏的设备(通常没有物理合页)上,应用可以在多窗口模式下并排运行。在此类设备上,当应用在多窗口模式下运行时,其行为将与上例中在单屏模式下的行为一样。当应用在运行时占满逻辑显示屏时,其行为就像跨屏一样。请看下图:
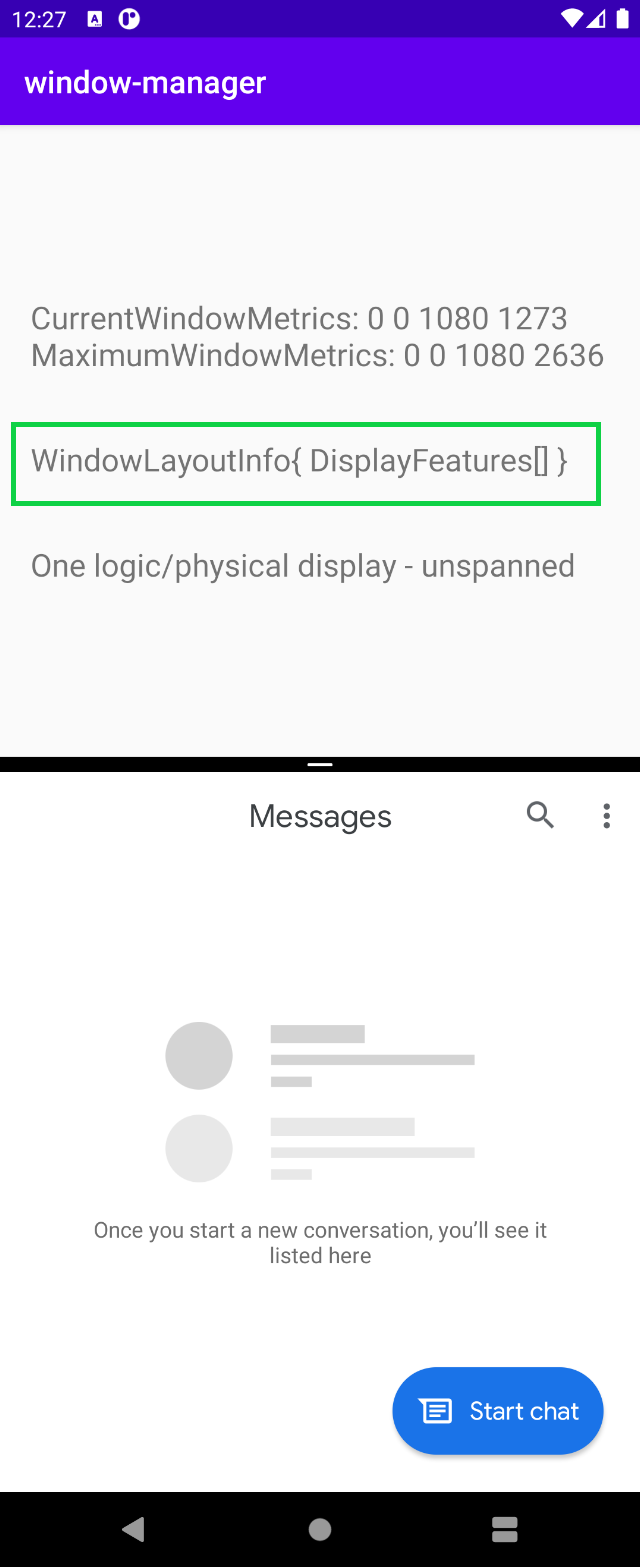
当应用在多窗口模式下运行时,WindowManager 会提供一个空的 List<LayoutInfo>。
简而言之,只有在应用在运行时占满逻辑显示屏、与设备功能(折叠边或合页)互动的情况下,您才会获得 WindowLayoutInfo 数据。在所有其他情况下,您都无法获得任何信息。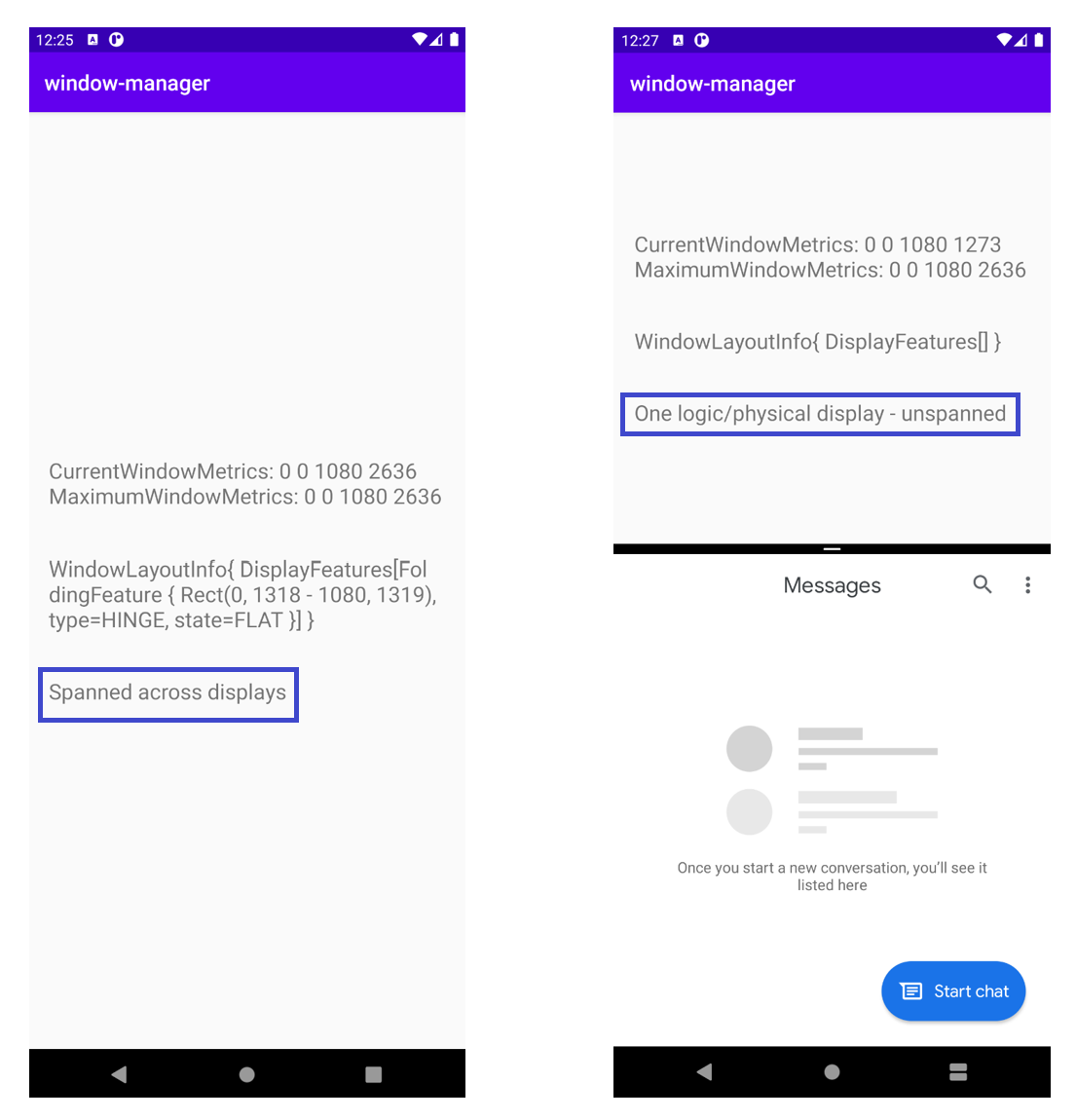
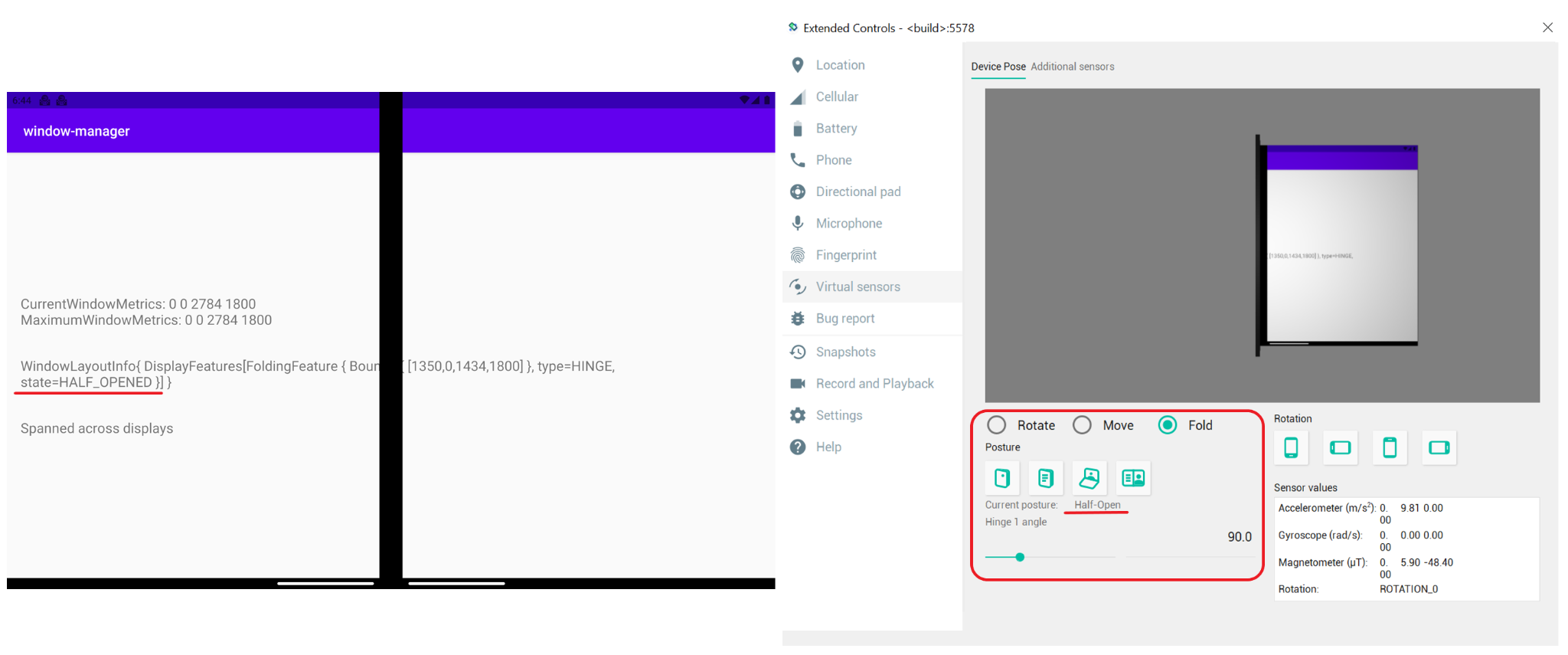
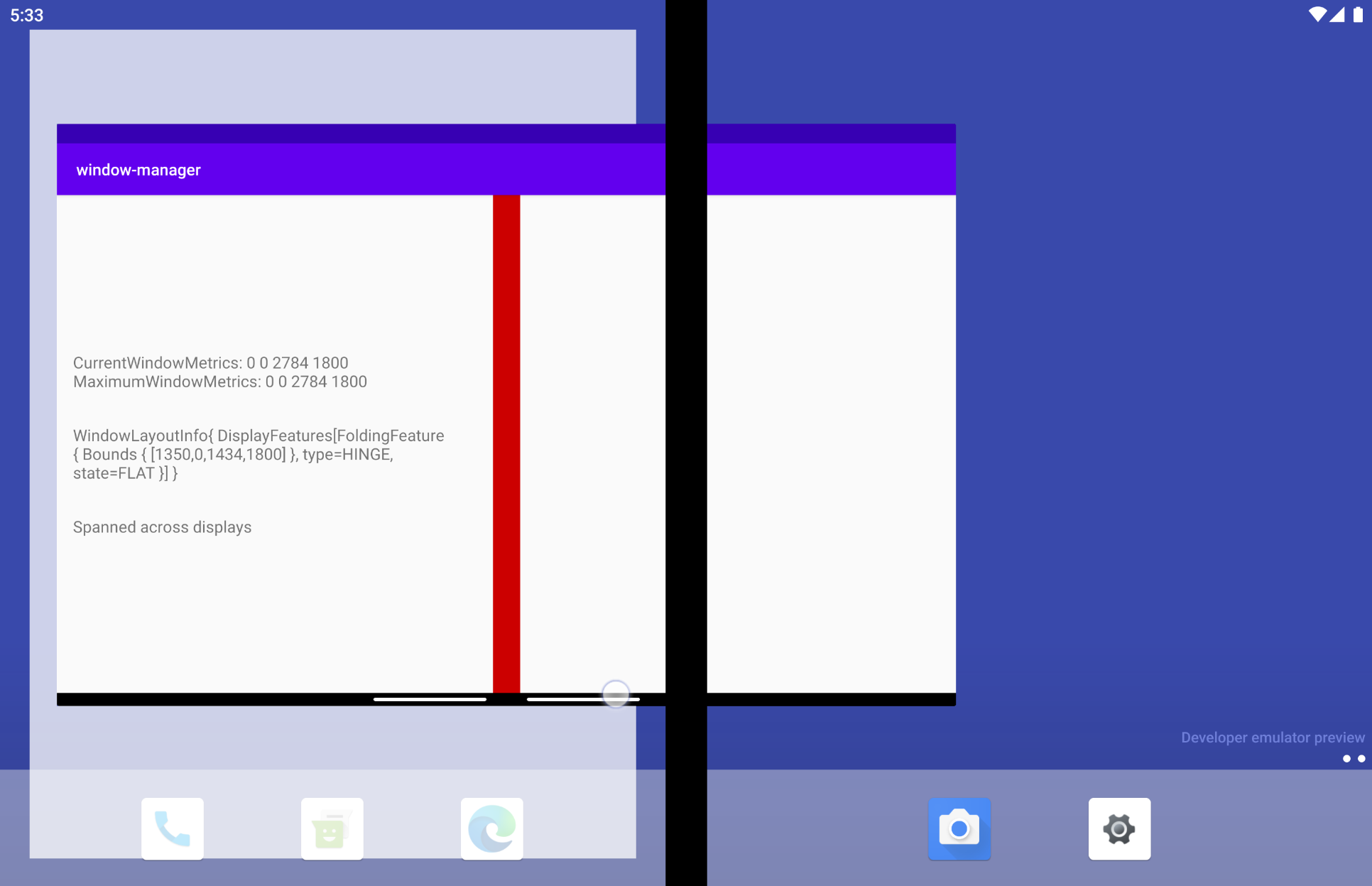
应用跨屏显示时会出现什么情况?在双屏设备模拟器中,WindowLayoutInfo 的 FoldingFeature 对象将提供以下数据:设备功能 (HINGE)、该功能的边界 (Rect [0, 0 - 1434, 1800]),以及设备的折叠状态 (FLAT)。

让我们来看看每个字段的含义:
type = TYPE_HINGE:此双屏设备模拟器镜像的是具有物理合页的真实 Surface Duo 设备,WindowManager 报告的结果也是如此。Bounds[0, 0 - 1434, 1800]:表示窗口坐标空间中应用窗口内功能的边界矩形。如果您已阅读 Surface Duo 设备的尺寸规范,便会发现合页的位置与这些边界(左、上、右、下)报告的情况完全一致。State:表示设备的折叠状态的值有三个。HALF_OPENED:可折叠设备的合页处于展开状态和闭合状态的中间位置,且柔性屏幕的各部分之间或物理屏幕之间的夹角不是平角。FLAT:可折叠设备处于完全打开状态,且呈现给用户的屏幕区域是平面。
模拟器默认处于打开 180 度的状态,因此 WindowManager 返回的折叠状态为 FLAT。
如果您使用虚拟传感器选项将模拟器的折叠状态更改为半开状态,WindowManager 会通知新位置:HALF_OPENED。
通过 WindowManager 调整界面/用户体验
如显示窗口布局信息的图所示,显示的信息被显示功能裁剪,同样的情况也发生在这里:
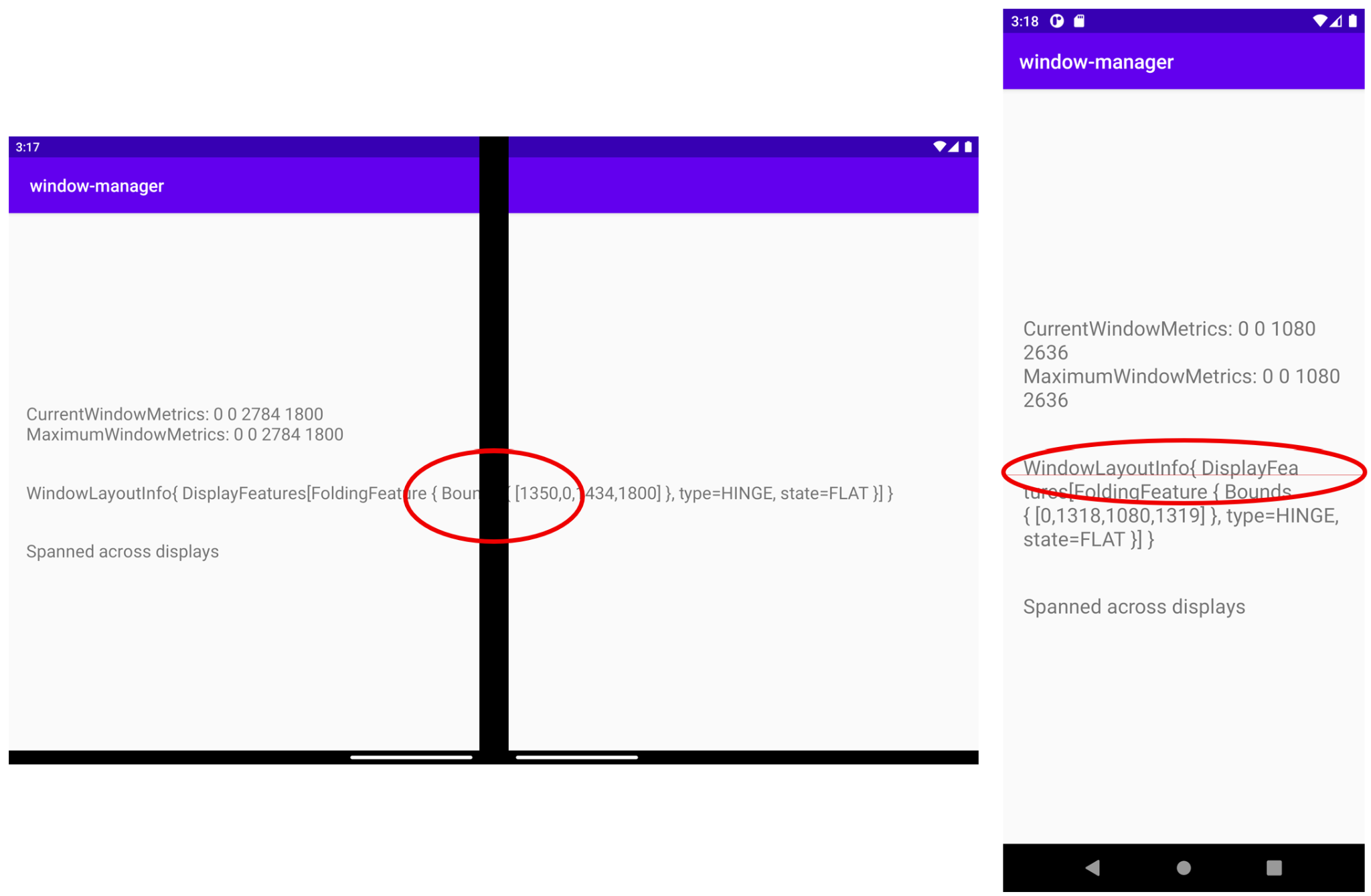
这并非最佳用户体验。您可以利用 WindowManager 提供的信息来调整界面/用户体验。
如前所述,当您的应用跨越不同的显示区域时,也是您的应用与设备功能互动时,WindowManager 会提供窗口布局信息作为显示状态和显示的边界。因此,当应用跨屏显示时,您便需要根据这些信息来调整界面/用户体验。
接下来,您要做的就是调整目前应用在运行时跨屏显示的界面/用户体验,确保任何重要信息都不会被显示功能裁剪或隐藏。您将创建一个镜像设备显示功能的视图,并将其作为约束 TextView 的参考,确保任何信息都不会再被剪裁或隐藏。
为便于学习,请设置此新视图的颜色,以便用户能够轻松看出该视图的位置与真实的设备显示功能的位置完全一致,且尺寸相同。
在 activity_main.xml 中添加将用作设备功能参考的新视图:
activity_main.xml
<!-- It's not important where this view is placed by default, it will be positioned dynamically at runtime -->
<View
android:id="@+id/folding_feature"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_red_dark"
android:visibility="gone"
tools:ignore="MissingConstraints" />
在 MainActivity.kt 中,找到用于显示给定 WindowLayoutInfo 信息的 updateUI() 函数,并添加一个在应用具有显示功能的 if-else 情况下进行的新函数调用:
MainActivity.kt
private fun updateUI(newLayoutInfo: WindowLayoutInfo) {
binding.layoutChange.text = newLayoutInfo.toString()
if (newLayoutInfo.displayFeatures.isNotEmpty()) {
binding.configurationChanged.text = "Spanned across displays"
alignViewToFoldingFeatureBounds(newLayoutInfo)
} else {
binding.configurationChanged.text = "One logic/physical display - unspanned"
}
}
您已添加函数 alignViewToFoldingFeatureBounds,该函数会接收 WindowLayoutInfo 作为参数。
创建相应函数。在该函数内,创建 ConstraintSet 以对您的视图应用新的约束条件:然后,使用 WindowLayoutInfo 获取显示功能的边界。由于 WindowLayoutInfo 会返回一个仅用作接口的 DisplayFeature 的列表,因此应将其转换为 FoldingFeature 以便访问所有信息:
MainActivity.kt
import androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintSet
import androidx.window.layout.FoldingFeature
private fun alignViewToFoldingFeatureBounds(newLayoutInfo: WindowLayoutInfo) {
val constraintLayout = binding.constraintLayout
val set = ConstraintSet()
set.clone(constraintLayout)
// Get and translate the feature bounds to the View's coordinate space and current
// position in the window.
val foldingFeature = newLayoutInfo.displayFeatures[0] as FoldingFeature
val bounds = getFeatureBoundsInWindow(foldingFeature, binding.root)
// Rest of the code to be added in the following steps
}
定义一个 getFeatureBoundsInWindow() 函数,以将功能边界转换为视图在窗口中的坐标空间和当前位置。
MainActivity.kt
import android.graphics.Rect
import android.view.View
import androidx.window.layout.DisplayFeature
/**
* Get the bounds of the display feature translated to the View's coordinate space and current
* position in the window. This will also include view padding in the calculations.
*/
private fun getFeatureBoundsInWindow(
displayFeature: DisplayFeature,
view: View,
includePadding: Boolean = true
): Rect? {
// Adjust the location of the view in the window to be in the same coordinate space as the feature.
val viewLocationInWindow = IntArray(2)
view.getLocationInWindow(viewLocationInWindow)
// Intersect the feature rectangle in window with view rectangle to clip the bounds.
val viewRect = Rect(
viewLocationInWindow[0], viewLocationInWindow[1],
viewLocationInWindow[0] + view.width, viewLocationInWindow[1] + view.height
)
// Include padding if needed
if (includePadding) {
viewRect.left += view.paddingLeft
viewRect.top += view.paddingTop
viewRect.right -= view.paddingRight
viewRect.bottom -= view.paddingBottom
}
val featureRectInView = Rect(displayFeature.bounds)
val intersects = featureRectInView.intersect(viewRect)
// Checks to see if the display feature overlaps with our view at all
if ((featureRectInView.width() == 0 && featureRectInView.height() == 0) ||
!intersects
) {
return null
}
// Offset the feature coordinates to view coordinate space start point
featureRectInView.offset(-viewLocationInWindow[0], -viewLocationInWindow[1])
return featureRectInView
}
利用有关显示功能边界的信息,您可以据此为参考视图设置正确的高度大小,并相应地移动参考视图。
alignViewToFoldingFeatureBounds 的完整代码如下所示:
MainActivity.kt - alignViewToFoldingFeatureBounds
private fun alignViewToFoldingFeatureBounds(newLayoutInfo: WindowLayoutInfo) {
val constraintLayout = binding.constraintLayout
val set = ConstraintSet()
set.clone(constraintLayout)
// Get and Translate the feature bounds to the View's coordinate space and current
// position in the window.
val foldingFeature = newLayoutInfo.displayFeatures[0] as FoldingFeature
val bounds = getFeatureBoundsInWindow(foldingFeature, binding.root)
bounds?.let { rect ->
// Some devices have a 0px width folding feature. We set a minimum of 1px so we
// can show the view that mirrors the folding feature in the UI and use it as reference.
val horizontalFoldingFeatureHeight = (rect.bottom - rect.top).coerceAtLeast(1)
val verticalFoldingFeatureWidth = (rect.right - rect.left).coerceAtLeast(1)
// Sets the view to match the height and width of the folding feature
set.constrainHeight(
R.id.folding_feature,
horizontalFoldingFeatureHeight
)
set.constrainWidth(
R.id.folding_feature,
verticalFoldingFeatureWidth
)
set.connect(
R.id.folding_feature, ConstraintSet.START,
ConstraintSet.PARENT_ID, ConstraintSet.START, 0
)
set.connect(
R.id.folding_feature, ConstraintSet.TOP,
ConstraintSet.PARENT_ID, ConstraintSet.TOP, 0
)
if (foldingFeature.orientation == FoldingFeature.Orientation.VERTICAL) {
set.setMargin(R.id.folding_feature, ConstraintSet.START, rect.left)
set.connect(
R.id.layout_change, ConstraintSet.END,
R.id.folding_feature, ConstraintSet.START, 0
)
} else {
// FoldingFeature is Horizontal
set.setMargin(
R.id.folding_feature, ConstraintSet.TOP,
rect.top
)
set.connect(
R.id.layout_change, ConstraintSet.TOP,
R.id.folding_feature, ConstraintSet.BOTTOM, 0
)
}
// Set the view to visible and apply constraints
set.setVisibility(R.id.folding_feature, View.VISIBLE)
set.applyTo(constraintLayout)
}
}
现在,曾与设备显示功能冲突的 TextView 会将该功能的位置考虑在内,以确保其内容不会再被裁剪或隐藏:
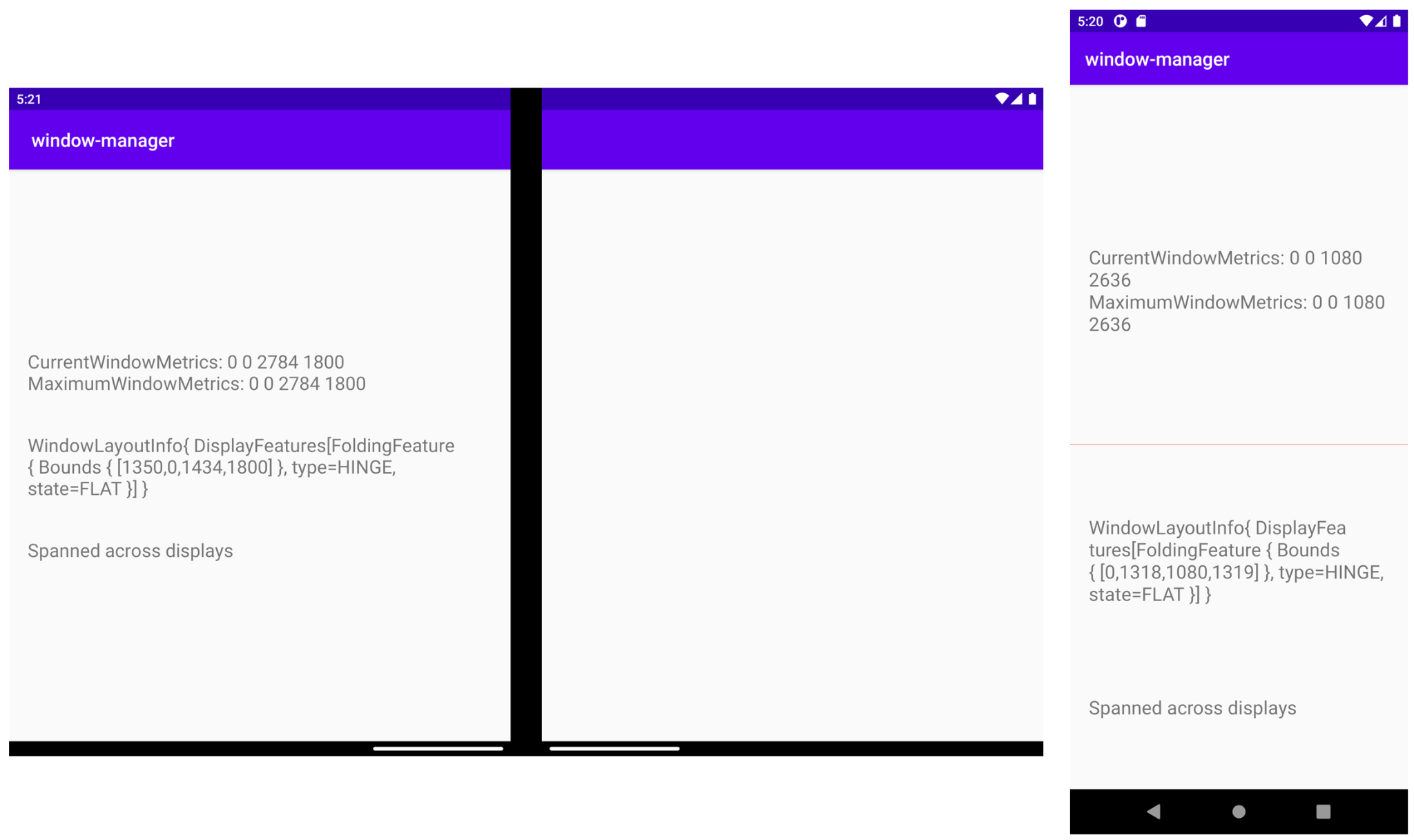
在双屏模拟器中(上方左图),您可以看到 TextView 如何跨屏显示内容,曾被合页裁剪的内容已正常显示,任何信息都没有缺失。
在可折叠设备模拟器中(上方右图),您会看到一条表示折叠显示功能所在位置的浅红色线,现在 TextView 显示在该功能下方。因此当设备处于折叠状态时(例如,笔记本电脑处于 90 度折叠状态),该功能不会影响任何信息的显示。
如果您想知道显示功能在双屏设备模拟器上的位置(由于这是一种合页型设备),用于展示该功能的视图是被合页隐藏了。但是,如果应用从跨屏显示更改为不跨屏显示,您就会在功能所在位置看到该视图,且视图高度和宽度正确无误。
8. 其他 Jetpack WindowManager 工件
除了主要组件之外,WindowManager 还附带其他实用工件,这些工件可帮助您在构建应用时考虑当前使用的环境,从而以不同的方式与组件互动。
Java 工件
如果您使用的是 Java 编程语言而非 Kotlin,或者通过回调来监听事件对您的架构而言是更好的方法,则 WindowManager 的 Java 工件可能会很有用,因为它提供了适合 Java 的 API,以便通过回调来注册和取消注册事件的监听器。
RxJava 工件
如果您已经在使用 RxJava(版本 2 或 3),则无论您使用的是 Observables 还是 Flowables,都可以使用特定工件来帮助您在代码中保持一致性。
9. 使用 Jetpack WindowManager 进行测试
在任何模拟器或设备上测试可折叠设备的折叠状态,对于测试如何将界面元素放置在 FoldingFeature 周围是非常有用的。
为此,WindowManger 附带了一个非常实用的工件,以用于进行插桩测试。
我们来看看该工件的使用方式。
在应用 build.gradle 文件中,我们不仅添加了主 WindowManager 依赖项,还添加了测试工件:androidx.window:window-testing
window-testing 工件附带有一个名为 WindowLayoutInfoPublisherRule 的实用的新 TestRule,它可以帮助您使用一系列 WindowLayoutInfo 值进行测试。借助 WindowLayoutInfoPublisherRule,您可以按需推送不同的 WindowLayoutInfo 值。
为了使用它,并在此基础上创建一个示例以帮助您使用此新工件来测试界面,请更新由 Android Studio 模板创建的测试类。将 ExampleInstrumentedTest 类中的所有代码替换为以下代码:
ExampleInstrumentedTest.kt
import androidx.test.ext.junit.rules.ActivityScenarioRule
import androidx.test.ext.junit.runners.AndroidJUnit4
import androidx.window.testing.layout.WindowLayoutInfoPublisherRule
import org.junit.Rule
import org.junit.rules.RuleChain
import org.junit.rules.TestRule
import org.junit.runner.RunWith
@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4::class)
class MainActivityTest {
private val activityRule = ActivityScenarioRule(MainActivity::class.java)
private val publisherRule = WindowLayoutInfoPublisherRule()
@get:Rule
val testRule: TestRule
init {
testRule = RuleChain.outerRule(publisherRule).around(activityRule)
}
}
上述规则已与 ActvityScenarioRule 链接。
为了模拟 FoldingFeature,此新工件附带有几个非常有用的函数用于实现此目的。下方是最简单的函数,它提供了一些默认值。
在 MainActivity 中,TextView 与折叠功能对齐到左侧。创建一个用于检查相应实现是否正确的测试。
创建一项名为 testText_is_left_of_Vertical_FoldingFeature 的测试:
ExampleInstrumentedTest.kt
import androidx.window.layout.FoldingFeature.Orientation.Companion.VERTICAL
import androidx.window.layout.FoldingFeature.State.Companion.FLAT
import androidx.window.testing.layout.FoldingFeature
import androidx.window.testing.layout.TestWindowLayoutInfo
import org.junit.Test
@Test
fun testText_is_left_of_Vertical_FoldingFeature() {
activityRule.scenario.onActivity { activity ->
val hinge = FoldingFeature(
activity = activity,
state = FLAT,
orientation = VERTICAL,
size = 2
)
val expected = TestWindowLayoutInfo(listOf(hinge))
publisherRule.overrideWindowLayoutInfo(expected)
}
// Add Assertion with EspressoMatcher here
}
测试 FoldingFeature 的状态为 FLAT,且屏幕方向为 VERTICAL。我们之所以定义特定尺寸,是因为我们希望在测试界面中显示模拟 FoldingFeature,以便了解它在设备上的位置。
我们使用之前实例化的 WindowLayoutInfoPublishRule 来发布模拟 FoldingFeaure,然后便可以像获取真实 WindowLayoutInfo 数据一样获取它:
最后一个步骤很简单,就是测试界面元素是否位于应该对齐且能避开 FoldingFeature 的位置。为此,我们只需使用 EspressoMatchers,并在我们刚刚创建的测试的末尾添加断言即可:
ExampleInstrumentedTest.kt
import androidx.test.espresso.assertion.PositionAssertions
import androidx.test.espresso.matcher.ViewMatchers.withId
onView(withId(R.id.layout_change)).check(
PositionAssertions.isCompletelyLeftOf(withId(R.id.folding_feature))
)
完整的测试将如下所示:
ExampleInstrumentedTest.kt
@Test
fun testText_is_left_of_Vertical_FoldingFeature() {
activityRule.scenario.onActivity { activity ->
val hinge = FoldingFeature(
activity = activity,
state = FoldingFeature.State.FLAT,
orientation = FoldingFeature.Orientation.VERTICAL,
size = 2
)
val expected = TestWindowLayoutInfo(listOf(hinge))
publisherRule.overrideWindowLayoutInfo(expected)
}
onView(withId(R.id.layout_change)).check(
PositionAssertions.isCompletelyLeftOf(withId(R.id.folding_feature))
)
}
val horizontal_hinge = FoldingFeature(
activity = activity,
state = FLAT,
orientation = HORIZONTAL,
size = 2
)
现在,您可以在设备或模拟器上运行测试,以检查应用的行为是否符合预期。请注意,此测试无需使用可折叠设备或模拟器即可运行。
10. 恭喜!
Jetpack WindowManager 可帮助开发者使用新型设备(例如可折叠设备)。
在使 Android 应用适应可折叠设备以提供更好的用户体验方面,WindowManager 提供的信息非常有用。
总结一下,在此 Codelab 中,您学习了以下内容:
- 什么是可折叠设备
- 不同的可折叠设备之间的区别
- 可折叠设备、单屏设备和平板电脑之间的区别
- Jetpack WindowManager API
- 如何使用 Jetpack WindowManager,以及如何针对新设备外形规格调整应用
- 使用 Jetpack WindowManager 进行测试
