בדומה לגרסאות קודמות, Android 15 כולל שינויים בהתנהגות שעשויים להשפיע על האפליקציה שלכם. שינויי ההתנהגות הבאים רלוונטיים רק לאפליקציות שמטרגטות את Android 15 ואילך. אם האפליקציה שלכם מטרגטת את Android מגרסה 15 ואילך, אתם צריכים לשנות את האפליקציה כדי שהיא תתמוך בהתנהגויות האלה, במקרים הרלוונטיים.
חשוב גם לבדוק את רשימת השינויים בהתנהגות שמשפיעים על כל האפליקציות שפועלות ב-Android 15, בלי קשר ל-targetSdkVersion של האפליקציה.
פונקציונליות עיקרית
Android 15 משנה או מרחיב יכולות ליבה שונות של מערכת Android.
שינויים בשירותים שפועלים בחזית
אנחנו מבצעים את השינויים הבאים בשירותים שפועלים בחזית ב-Android 15.
- התנהגות של זמן קצוב לתפוגה בשירות 'סנכרון נתונים' שפועל בחזית
- סוג חדש של שירות שפועל בחזית לעיבוד מדיה
- הגבלות על מקלטי שידורים מסוג
BOOT_COMPLETEDשמפעילים שירותים שפועלים בחזית - הגבלות על הפעלת שירותים שפועלים בחזית בזמן שאפליקציה מחזיקה בהרשאה
SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW
התנהגות זמן קצוב לתפוגה של שירות בחזית לסנכרון נתונים
ב-Android 15 נוספה התנהגות חדשה של זמן קצוב לתפוגה ל-dataSync באפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 15 (רמת API 35) ואילך. ההתנהגות הזו רלוונטית גם לסוג החדש של שירות mediaProcessing שפועל בחזית.
המערכת מאפשרת לשירותי dataSync של אפליקציה לפעול במשך 6 שעות בסך הכול בתקופה של 24 שעות, ולאחר מכן המערכת קוראת ל-method Service.onTimeout(int, int) של השירות שפועל (התכונה הזו נוספה ב-Android 15). בשלב הזה, לשירות יש כמה שניות לבצע קריאה ל-Service.stopSelf(). כשקוראים לפונקציה Service.onTimeout(), השירות כבר לא נחשב לשירות שפועל בחזית. אם השירות לא קורא ל-Service.stopSelf(), המערכת תיצור חריגה פנימית. החריגה מתועדת ב-Logcat עם ההודעה הבאה:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type dataSync did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
כדי למנוע בעיות שקשורות לשינוי הזה בהתנהגות, אפשר לבצע אחת או יותר מהפעולות הבאות:
- מטמיעים את השיטה החדשה
Service.onTimeout(int, int)בשירות. כשהאפליקציה תקבל את הקריאה החוזרת, חשוב להתקשר למספרstopSelf()תוך כמה שניות. (אם לא עוצרים את האפליקציה מיד, המערכת יוצרת כשל). - חשוב לוודא ששירותי
dataSyncשל האפליקציה לא פועלים במשך יותר מ-6 שעות בסך הכול בכל תקופה של 24 שעות (אלא אם המשתמש יוצר אינטראקציה עם האפליקציה, ומאפס את הטיימר). - הפעלת שירותים שפועלים בחזית
dataSyncרק כתוצאה מאינטראקציה ישירה של המשתמש. מכיוון שהאפליקציה פועלת בחזית כשהשירות מופעל, השירות פועל במשך 6 שעות בלבד אחרי שהאפליקציה עוברת לרקע. - במקום להשתמש בשירות
dataSyncשפועל בחזית, צריך להשתמש בAPI חלופי.
אם השירותים שפועלים בחזית ב-dataSync באפליקציה פועלים במשך 6 שעות ב-24 השעות האחרונות, לא ניתן להפעיל שירות נוסף שפועל בחזית של dataSync אלא אם המשתמש העביר את האפליקציה לחזית האפליקציה (הפעולה הזו מאפסת את הטיימר). אם תנסו להפעיל שירות אחר שפועל בחזית של dataSync, המערכת תגרור ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException הודעת שגיאה כמו "Time limit limit for data Sync type" (סוג שירות שפועל בחזית).
בדיקה
כדי לבדוק את התנהגות האפליקציה, אפשר להפעיל זמן קצוב לסיום הסנכרון של הנתונים גם אם האפליקציה לא מטרגטת ל-Android 15 (כל עוד האפליקציה פועלת במכשיר עם Android 15). כדי להפעיל זמן קצוב לתפוגה, מריצים את הפקודה הבאה ב-adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
אפשר גם לשנות את משך הזמן של הזמן הקצוב לתפוגה, כדי שיהיה קל יותר לבדוק איך האפליקציה מתנהגת כשמגיעים למגבלה. כדי להגדיר פרק זמן חדש לזמן קצוב, מריצים את הפקודה adb הבאה:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager data_sync_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
סוג חדש של שירות שפועל בחזית לעיבוד מדיה
ב-Android 15 מוצג סוג חדש של שירות שפועל בחזית, mediaProcessing. סוג השירות הזה מתאים לפעולות כמו המרת קידוד של קובצי מדיה. לדוגמה, אפליקציית מדיה עשויה להוריד קובץ אודיו ולהמיר אותו לפורמט אחר לפני ההפעלה. אתם יכולים להשתמש בשירות mediaProcessing שפועל בחזית כדי לוודא שההמרה תימשך גם כשהאפליקציה ברקע.
המערכת מאפשרת לשירותי mediaProcessing של אפליקציה לפעול במשך 6 שעות בסך הכול בתקופה של 24 שעות, ולאחר מכן המערכת קוראת ל-method Service.onTimeout(int, int) של השירות שפועל (הmethod הזה הוצג ב-Android 15). בשלב הזה, לשירות יש כמה שניות לבצע קריאה ל-Service.stopSelf(). אם השירות לא קורא ל-Service.stopSelf(), המערכת גורמת לחריגה פנימית. החריג מתועד ביומן Logcat עם ההודעה הבאה:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type mediaProcessing did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
כדי למנוע את החריגה, אפשר לבצע אחת מהפעולות הבאות:
- עליך להטמיע בשירות שלך את השיטה החדשה של
Service.onTimeout(int, int). כשהאפליקציה מקבלת את הקריאה החוזרת, חשוב להקפיד להתקשר ל-stopSelf()תוך מספר שניות. (אם לא מפסיקים את האפליקציה מיד, המערכת יוצרת כשל). - חשוב לוודא ששירותי
mediaProcessingשל האפליקציה לא פועלים במשך יותר מ-6 שעות בסך הכול בכל תקופה של 24 שעות (אלא אם המשתמש יוצר אינטראקציה עם האפליקציה, ומאפס את הטיימר). - כדאי להפעיל שירותים
mediaProcessingשפועלים בחזית רק כתוצאה מאינטראקציה ישירה של משתמש. מכיוון שהאפליקציה נמצאת בחזית כשהשירות מופעל, השירות מקבל את שש השעות המלאות אחרי שהאפליקציה עוברת לרקע. - במקום להשתמש בשירות שפועל בחזית
mediaProcessing, צריך להשתמש בAPI חלופי, כמו WorkManager.
אם שירותי mediaProcessing של האפליקציה פעלו בחזית במשך 6 שעות ב-24 השעות האחרונות, לא תוכלו להפעיל שירות mediaProcessing נוסף בחזית אלא אם המשתמש העביר את האפליקציה לחזית (פעולה שמאפסת את הטיימר). אם תנסו להפעיל שירות mediaProcessing שפועל בחזית, המערכת תשליך את הערך ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException עם הודעת שגיאה כמו "Time Limit כבר נשלחת לכל שירות שפועל בחזית מסוג mediaProcessing".
מידע נוסף על סוג השירות mediaProcessing זמין במאמר שינויים בסוגי שירותים בחזית במהדורת Android 15: עיבוד מדיה.
בדיקה
כדי לבדוק את התנהגות האפליקציה, אפשר להפעיל זמן קצוב לתפוגה של עיבוד מדיה גם אם האפליקציה לא מטרגטת ל-Android 15 (כל עוד האפליקציה פועלת במכשיר עם Android 15). כדי להפעיל זמן קצוב לתפוגה, מריצים את הפקודה הבאה ב-adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
אפשר גם לשנות את משך הזמן של הזמן הקצוב לתפוגה, כדי שיהיה קל יותר לבדוק איך האפליקציה מתנהגת כשמגיעים למגבלה. כדי להגדיר פרק זמן חדש לתפוגה, מריצים את הפקודה הבאה של adb:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager media_processing_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
הגבלות על מקלטי שידורים מסוג BOOT_COMPLETED שמפעילים שירותים שפועלים בחזית
יש הגבלות חדשות על השקת מקלטי שידור של BOOT_COMPLETED
שירותים שפועלים בחזית. למקלטי BOOT_COMPLETED אסור להפעיל את
הסוגים הבאים של שירותים שפועלים בחזית:
dataSynccameramediaPlaybackphoneCallmediaProjectionmicrophone(ההגבלה הזו חלה עלmicrophoneמאז Android 14)
אם מקלט BOOT_COMPLETED מנסה להפעיל אחד מהסוגים האלה של חזית
השירותים האלה, המערכת מטילה ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException.
בדיקה
כדי לבדוק את התנהגות האפליקציה, אפשר להפעיל את ההגבלות החדשות האלה גם אם
האפליקציה לא מטרגטת ל-Android 15 (כל עוד האפליקציה פועלת עם Android 15).
במכשיר). מריצים את הפקודה adb הבאה:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_BOOT_COMPLETED_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
כדי לשלוח שידור של BOOT_COMPLETED בלי להפעיל מחדש את המכשיר:
מריצים את הפקודה הבאה של adb:
adb shell am broadcast -a android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED your-package-name
הגבלות על הפעלת שירותים שפועלים בחזית בזמן שאפליקציה מחזיקה בהרשאה SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW
בעבר, אם לאפליקציה הייתה הרשאה SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW, היא הייתה יכולה להפעיל שירות שפועל בחזית גם אם האפליקציה הייתה כרגע ברקע (כפי שמתואר בקטע פטורים מהגבלות הפעלה ברקע).
אם אפליקציה מטרגטת את Android 15, הפטור הזה מצומצם יותר עכשיו. עכשיו האפליקציה צריכה לקבל את ההרשאה SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW וגם להציג חלון שכבת-על גלוי. כלומר, האפליקציה צריכה קודם להפעיל חלון TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY וגם החלון צריך להיות גלוי לפני שמפעילים שירות בחזית.
אם האפליקציה תנסה להפעיל שירות שפועל בחזית מהרקע בלי לעמוד בדרישות החדשות האלה (ואין לה פטור אחר), המערכת תשליך את השגיאה ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException.
אם האפליקציה שלכם מצהירה על ההרשאה SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW ומפעילה שירותים שפועלים בחזית מהרקע, היא עשויה להיות מושפעת מהשינוי הזה. אם האפליקציה מקבלת את השגיאה ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException, צריך לבדוק את סדר הפעולות של האפליקציה ולוודא שכבר יש לה חלון שכבת-על פעיל לפני שהיא מנסה להפעיל שירות בחזית מהרקע. תוכלו לבדוק אם החלון של שכבת-העל גלוי כרגע באמצעות קריאה ל-View.getWindowVisibility(), או לבטל את View.onWindowVisibilityChanged() כדי לקבל התראה בכל פעם שהחשיפה משתנה.
בדיקה
כדי לבדוק את התנהגות האפליקציה, אפשר להפעיל את ההגבלות החדשות האלה גם אם האפליקציה לא מטרגטת ל-Android 15 (כל עוד האפליקציה פועלת במכשיר עם Android 15). כדי להפעיל את ההגבלות החדשות האלה על הפעלת שירותים שפועלים בחזית מהרקע, מריצים את הפקודה הבאה של adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_SAW_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
שינויים במועד שבו אפליקציות יכולות לשנות את המצב הגלובלי של המצב 'נא לא להפריע'
אפליקציות שמטרגטות את Android מגרסה 15 ואילך (רמת API 35 ואילך) לא יכולות יותר לשנות את המצב או המדיניות הגלובלית של 'נא לא להפריע' במכשיר (על ידי שינוי ההגדרות של המשתמש או השבתת מצב 'נא לא להפריע'). במקום זאת, האפליקציות צריכות לספק AutomaticZenRule, שהמערכת משלבת במדיניות גלובלית לפי התוכנית הקיימת של 'המדיניות המחמירה ביותר מנצחת'. קריאות ל-APIs קיימים שקודם השפיעו על המצב הגלובלי (setInterruptionFilter, setNotificationPolicy) יוצרות או מעדכנות AutomaticZenRule משתנה נסתר, שמופעל או מושבת בהתאם למחזור הקריאות של קריאות ה-API האלה.
חשוב לזכור שהשינוי הזה משפיע על ההתנהגות הנצפית רק אם האפליקציה מבצעת קריאה ל-setInterruptionFilter(INTERRUPTION_FILTER_ALL) ומצפה שהקריאה הזו תשבית AutomaticZenRule שהבעלים שלו הפעילו בעבר.
שינויים ב-OpenJDK API
ב-Android 15 אנחנו ממשיכים את העבודה על רענון ספריות הליבה של Android כדי להתאים אותן לתכונות בגרסאות ה-LTS האחרונות של OpenJDK.
חלק מהשינויים האלה יכולים להשפיע על תאימות האפליקציה לאפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 15 (רמת API 35):
שינויים בממשקי API לעיצוב מחרוזות: האימות של אינדקס הארגומנט, הדגלים, הרוחב והדיוק הוא עכשיו מחמיר יותר כשמשתמשים בממשקי ה-API הבאים:
String.format()ו-Formatter.format():String.format(String, Object[])String.format(Locale, String, Object[])Formatter.format(String, Object[])Formatter.format(Locale, String, Object[])
לדוגמה, החריגה הבאה מופעלת כשמשתמשים באינדקס ארגומנט של 0 (
%0במחרוזת הפורמט):IllegalFormatArgumentIndexException: Illegal format argument index = 0במקרה כזה, אפשר לפתור את הבעיה באמצעות אינדקס ארגומנט של 1 (
%1במחרוזת הפורמט).שינויים בסוג הרכיב של
Arrays.asList(...).toArray(): כשמשתמשים ב-Arrays.asList(...).toArray(), סוג הרכיב של המערך שמתקבל הוא עכשיוObject– ולא הסוג של הרכיבים במערך הבסיסי. לכן הקוד הבא מחזיר את השגיאהClassCastException:String[] elements = (String[]) Arrays.asList("one", "two").toArray();במקרה כזה, כדי לשמור את
Stringכסוג הרכיב במערך שמתקבל, אפשר להשתמש במקום זאת ב-Collection.toArray(Object[]):String[] elements = Arrays.asList("two", "one").toArray(new String[0]);שינויים בטיפול בקודי שפה: כשמשתמשים ב-API
Locale, קודי השפה לעברית, יידיש ואינדונזית לא מומרים יותר לפורמטים שיצאו משימוש (עברית:iw, יידיש:jiואינדונזית:in). כשמציינים את קוד השפה לאחד מהלוקאלים האלה, צריך להשתמש בקודים מ-ISO 639-1 (עברית:he, יידיש:yiואינדונזית:id).שינויים ברצפים של מספרים שלמים אקראיים: בעקבות השינויים שבוצעו בכתובת https://bugs.openjdk.org/browse/JDK-8301574, השיטות הבאות
Random.ints()מחזירות עכשיו רצף שונה של מספרים מהשיטותRandom.nextInt():בדרך כלל, השינוי הזה לא אמור לגרום להתנהגות שמשבשת את האפליקציה, אבל הקוד לא אמור לצפות שהרצף שנוצר משיטות
Random.ints()יתאים ל-Random.nextInt().
ה-API החדש SequencedCollection יכול להשפיע על התאימות של האפליקציה אחרי עדכון compileSdk בהגדרות הבנייה של האפליקציה לשימוש ב-Android 15 (רמת API 35):
התנגשות עם פונקציות של התוספים
MutableList.removeFirst()ו-MutableList.removeLast()ב-kotlin-stdlibהסוג
Listב-Java ממופה לסוגMutableListב-Kotlin. ממשקי ה-APIList.removeFirst()ו-List.removeLast()הוצגו ב-Android 15 (רמת API 35), לכן קומפיילר Kotlin פותר קריאות לפונקציות, למשלlist.removeFirst(), באופן סטטי לממשקי ה-API החדשיםListבמקום לפונקציות ההרחבה ב-kotlin-stdlib.אם קומפלו מחדש אפליקציה עם
compileSdkשהוגדר ל-35ו-minSdkשהוגדר ל-34או לערך נמוך יותר, ואז האפליקציה מופעלת ב-Android 14 ובגרסאות קודמות, מוצגת שגיאת זמן ריצה:java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: No virtual method removeFirst()Ljava/lang/Object; in class Ljava/util/ArrayList;אפשר להשתמש באפשרות
NewApilint הקיימת ב-Android Gradle Plugin כדי לזהות את השימושים החדשים ב-API../gradlew lintMainActivity.kt:41: Error: Call requires API level 35 (current min is 34): java.util.List#removeFirst [NewApi] list.removeFirst()כדי לתקן את חריגת זמן הריצה ואת שגיאות ה-lint, אפשר להחליף את הקריאות לפונקציות
removeFirst()ו-removeLast()ב-Kotlin בפונקציותremoveAt(0)ו-removeAt(list.lastIndex)בהתאמה. אם אתם משתמשים ב-Android Studio Ladybug | 2024.1.3 ואילך, יש גם אפשרות לתיקון מהיר של השגיאות האלה.אם האפשרות lint מושבתת, כדאי להסיר את התווים
@SuppressLint("NewApi")ו-lintOptions { disable 'NewApi' }.התנגשות עם שיטות אחרות ב-Java
נוספו שיטות חדשות לסוגים הקיימים, לדוגמה,
Listו-Deque. יכול להיות שהשיטות החדשות האלה לא יהיו תואמות לשיטות עם אותו שם וסוגי ארגומנטים בממשקים ובמחלקות אחרים. במקרה של התנגשות בחתימת שיטה עם אי-תאימות, מהדרjavacמוציא שגיאה בזמן הבנייה. לדוגמה:דוגמה לשגיאה 1:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:135: error: removeLast() in MyList cannot implement removeLast() in List public void removeLast() { ^ return type void is not compatible with Object where E is a type-variable: E extends Object declared in interface Listדוגמה לשגיאה 2:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:7: error: types Deque<Object> and List<Object> are incompatible; public class MyList implements List<Object>, Deque<Object> { both define reversed(), but with unrelated return types 1 errorשגיאה לדוגמה 3:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:43: error: types List<E#1> and MyInterface<E#2> are incompatible; public static class MyList implements List<Object>, MyInterface<Object> { class MyList inherits unrelated defaults for getFirst() from types List and MyInterface where E#1,E#2 are type-variables: E#1 extends Object declared in interface List E#2 extends Object declared in interface MyInterface 1 errorכדי לתקן את שגיאות ה-build האלה, המחלקה שמטמיעה את הממשקים האלה צריכה לבטל את השיטה עם סוג החזרה תואם. לדוגמה:
@Override public Object getFirst() { return List.super.getFirst(); }
אבטחה
Android 15 כולל שינויים שמקדמים את אבטחת המערכת כדי לעזור להגן על אפליקציות ומשתמשים מפני אפליקציות זדוניות.
גרסאות TLS מוגבלות
ב-Android 15 יש הגבלה על השימוש ב-TLS בגרסאות 1.0 ו-1.1. הגרסאות האלה הוצאו משימוש ב-Android, אבל עכשיו אסור להשתמש בהן באפליקציות שמטרגטות את Android 15.
הפעלות מאובטחות של פעילות ברקע
Android 15 מגן על המשתמשים מפני אפליקציות זדוניות ומעניק להם יותר שליטה במכשירים שלהם. השינויים שנוספו מונעים מאפליקציות זדוניות שפועלות ברקע להעביר אפליקציות אחרות לחזית, להגדיל את ההרשאות שלהן ולנצל לרעה את האינטראקציה עם המשתמש. ההשקה של פעילות ברקע מוגבלת מאז Android 10 (רמת API 29).
שינויים אחרים
- שינוי ברירת המחדל של יוצרי
PendingIntentלחסימת הפעלות של פעילות ברקע. כך אפליקציות לא יוצרות בטעותPendingIntentשגורמים זדוניים יכולים לנצל לרעה. - אל תעבירו אפליקציה לחזית אלא אם
PendingIntentהשולח מאשר זאת. המטרה של השינוי הזה היא למנוע מאפליקציות זדוניות לנצל לרעה את היכולת להתחיל פעילויות ברקע. כברירת מחדל, לאפליקציות אסור להעביר את ערימת המשימות לחזית, אלא אם היוצר מאשר הרשאות להפעלת פעילות ברקע או שלשולח יש הרשאות להפעלת פעילות ברקע. - איך קובעים איך הפעילות העליונה בערימת המשימות יכולה לסיים את המשימה שלה. אם הפעילות העליונה מסיימת משימה, מערכת Android תחזור למשימה האחרונה שהייתה פעילה. בנוסף, אם פעילות שלא נמצאת בחלק העליון מסיימת את המשימה שלה, מערכת Android תחזור למסך הבית ולא תחסום את סיום הפעילות הזו.
- מניעת הפעלה של פעילויות שרירותיות מאפליקציות אחרות במשימה שלכם. השינוי הזה מונע מאפליקציות זדוניות לבצע פישינג על משתמשים על ידי יצירת פעילויות שנראות כאילו הן מגיעות מאפליקציות אחרות.
- חסימה של חלונות לא גלויים כך שלא ייכללו בהפעלות של פעילות ברקע. כך אפליקציות זדוניות לא יכולות לנצל לרעה הפעלות של פעילות ברקע כדי להציג למשתמשים תוכן לא רצוי או זדוני.
כוונות רכישה בטוחות יותר
Android 15 מציגה את StrictMode עבור כוונות.
כדי לראות יומנים מפורטים על הפרות של השימוש ב-Intent, משתמשים בשיטה הבאה:
Kotlin
fun onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build() ) }
Java
public void onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(new VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build()); }
חוויית המשתמש וממשק המשתמש של המערכת
Android 15 כוללת כמה שינויים שנועדו ליצור חוויית משתמש עקבית ואינטואיטיבית יותר.
שינויים בהזחה של חלון
יש שני שינויים שקשורים לחלונות מוטמעים ב-Android 15: תצוגה מקצה לקצה נאכפת כברירת מחדל, ויש גם שינויים בהגדרות, כמו הגדרת ברירת המחדל של שורת הסטטוס.
אכיפה מקצה לקצה
אפליקציות מוצגות מקצה לקצה כברירת מחדל במכשירים עם Android 15 אם האפליקציה מטרגטת ל-Android 15 (API ברמה 35).
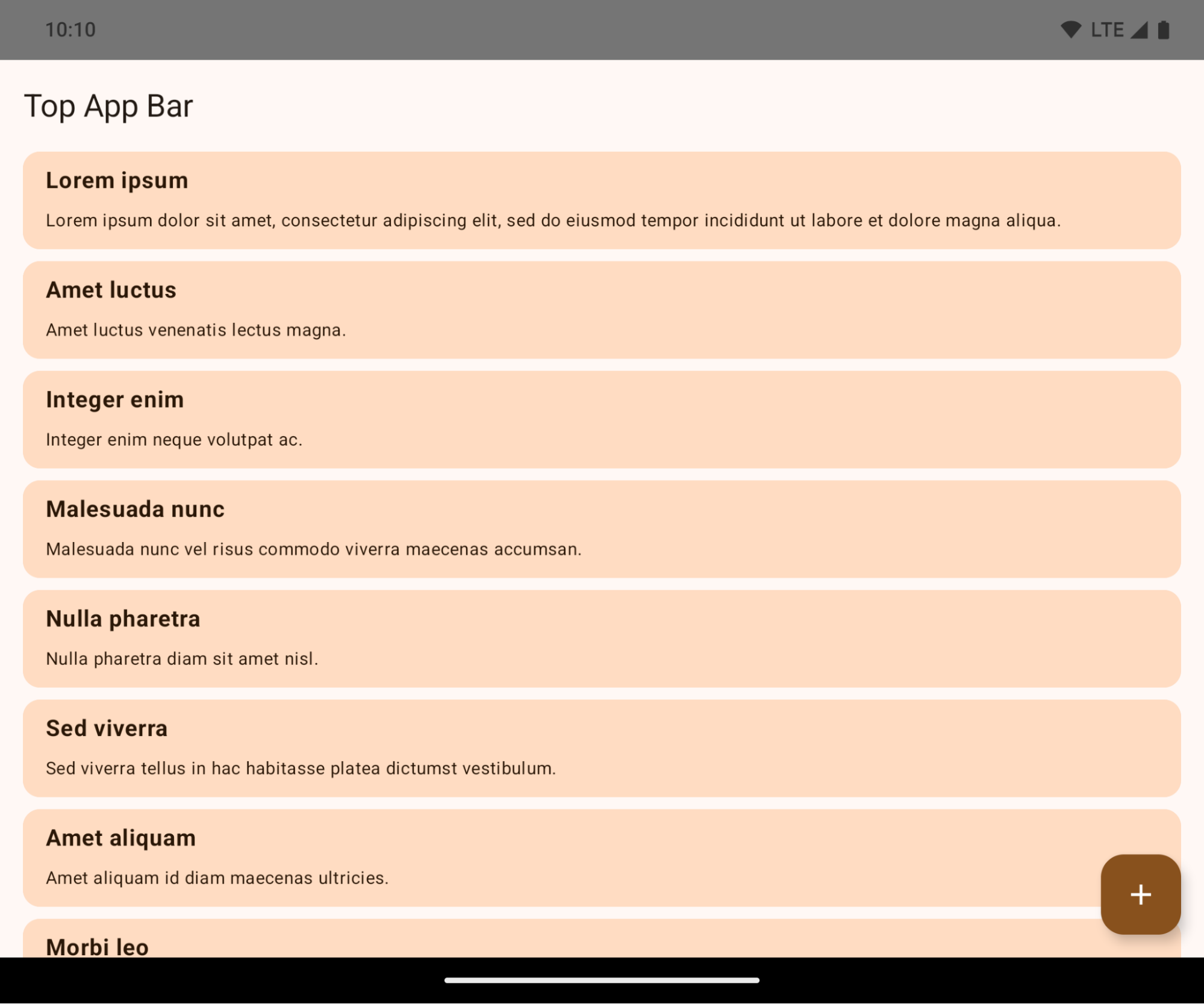
זהו שינוי משמעותי שעשוי להשפיע לרעה על ממשק המשתמש של האפליקציה. השינויים ישפיעו על האזורים הבאים בממשק המשתמש:
- סרגל ניווט עם ידית לתנועות
- שקוף כברירת מחדל.
- ההיסט התחתון מושבת, ולכן התוכן מוצג מאחורי סרגל הניווט של המערכת, אלא אם מוחלים שוליים פנימיים.
- האפשרויות
setNavigationBarColorו-R.attr#navigationBarColorהוצאו משימוש ולא משפיעות על הניווט באמצעות תנועות. setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedו-R.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedממשיכים שלא להשפיע על הניווט באמצעות מחוות.
- ניווט ב-3 לחצנים
- השקיפות מוגדרת כברירת מחדל ל-80%, והצבע יכול להיות זהה לצבע הרקע של החלון.
- ההיסט התחתון מושבת, כך שהתוכן מוצג מאחורי סרגל הניווט של המערכת, אלא אם מוחלים שוליים פנימיים.
- כברירת מחדל,
setNavigationBarColorו-R.attr#navigationBarColorמוגדרים להתאמה לרקע של החלון. כדי שברירת המחדל הזו תחול, הרקע של החלון צריך להיות פריט גרפי שניתן לשרטוט בצבע. ממשק ה-API הזה הוצא משימוש, אבל הוא ממשיך להשפיע על הניווט באמצעות 3 לחצנים. - הערך של
setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedושלR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedהוא True כברירת מחדל, מה שמוסיף רקע אטום ב-80% לניווט ב-3 לחצנים.
- שורת הסטטוס
- שקוף כברירת מחדל.
- ההיסט העליון מושבת, ולכן התוכן מוצג מאחורי שורת הסטטוס, אלא אם מוחלים שוליים פנימיים.
-
setStatusBarColorו-R.attr#statusBarColorהוצאו משימוש ואין להם השפעה על Android 15. -
setStatusBarContrastEnforcedו-R.attr#statusBarContrastEnforcedהוצאו משימוש, אבל עדיין יש להם השפעה ב-Android 15.
- חיתוך בתצוגה
- הערך של
layoutInDisplayCutoutModeבחלונות לא צפים צריך להיותLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS. הערכיםSHORT_EDGES,NEVERו-DEFAULTמתפרשים כ-ALWAYS, כדי שהמשתמשים לא יראו פס שחור שנוצר בגלל החיתוך של המסך, והאפליקציה תופיע מקצה לקצה.
- הערך של
בדוגמה הבאה מוצגת אפליקציה לפני ואחרי טירגוט ל-Android 15 (רמת API 35), ולפני ואחרי החלת אזורי inset. הדוגמה הזו לא מקיפה, והמראה שלה עשוי להיות שונה ב-Android Auto.
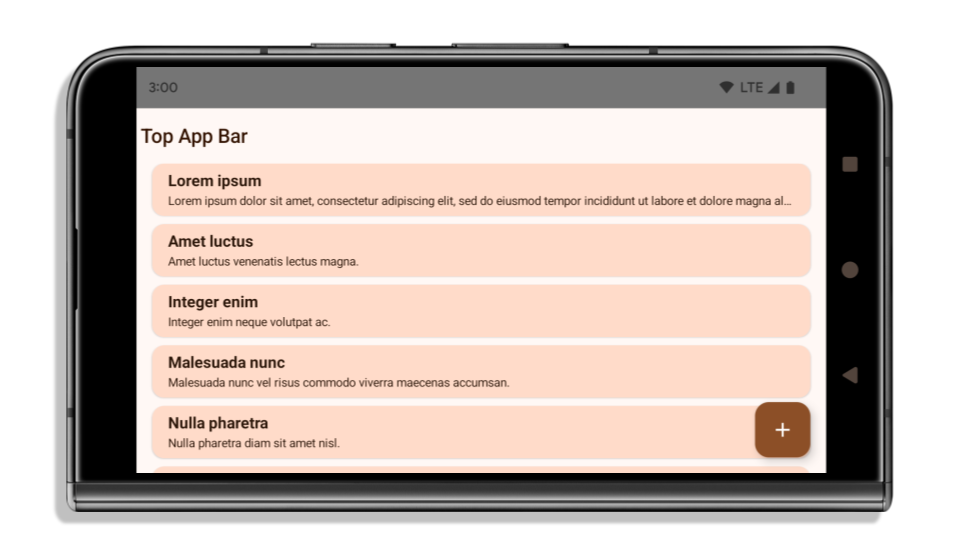
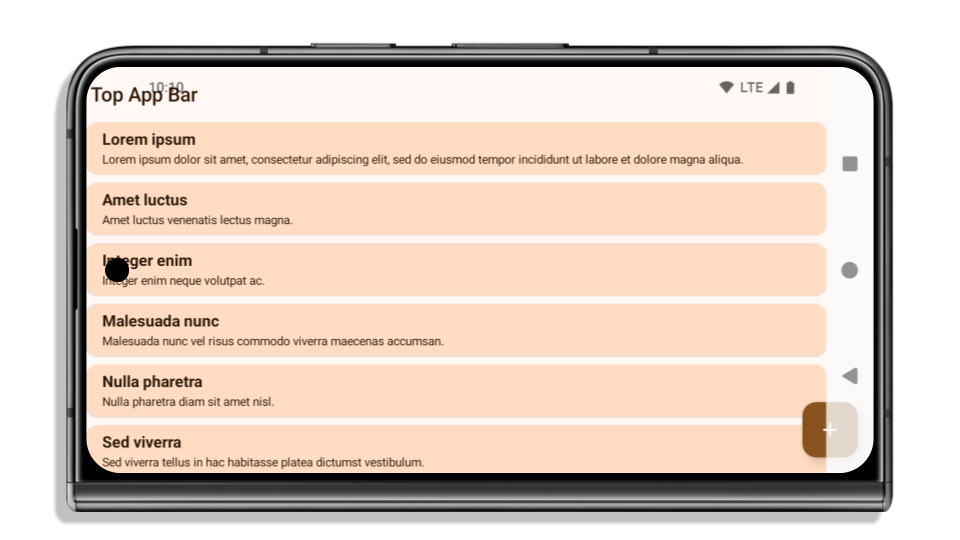

מה צריך לבדוק אם האפליקציה כבר מוצגת מקצה לקצה
אם האפליקציה שלכם כבר ממלאת את המסך מקצה לקצה ומוגדרים בה שוליים פנימיים, השינוי לא ישפיע עליה ברוב המקרים, למעט בתרחישים הבאים. עם זאת, גם אם אתם חושבים שהאפליקציה שלכם לא מושפעת, מומלץ לבדוק אותה.
- יש לכם חלון לא צף, כמו
Activityשמשתמש ב-SHORT_EDGES, ב-NEVERאו ב-DEFAULTבמקום ב-LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS. אם האפליקציה קורסת בזמן ההפעלה, יכול להיות שהבעיה היא במסך הפתיחה. אפשר לשדרג את התלות ב-core splashscreen לגרסה 1.2.0-alpha01 ומעלה או להגדיר אתwindow.attributes.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = WindowManager.LayoutInDisplayCutoutMode.always. - יכול להיות שיש מסכים עם תנועת גולשים נמוכה יותר שבהם ממשק המשתמש מוסתר. מוודאים שרכיבי ממשק המשתמש במסכים האלה, שפחות מבקרים בהם, לא מוסתרים. מסכים עם נפח תנועה נמוך יותר כוללים:
- מסכי צירוף או כניסה
- דפי הגדרות
מה צריך לבדוק אם האפליקציה עדיין לא מוצגת מקצה לקצה
אם האפליקציה שלכם עדיין לא מוצגת מקצה לקצה, סביר להניח שאתם מושפעים מהשינוי. בנוסף לתרחישים של אפליקציות שכבר מוצגות מקצה לקצה, כדאי לשקול את הדברים הבאים:
- אם האפליקציה שלכם משתמשת ברכיבי Material 3 (
androidx.compose.material3) ב-Compose, כמוTopAppBar,BottomAppBarו-NavigationBar, סביר להניח שלא תהיה השפעה על הרכיבים האלה כי הם מטפלים באופן אוטומטי ב-insets. - אם האפליקציה שלכם משתמשת ברכיבי Material 2 (
androidx.compose.material) ב-Compose, הרכיבים האלה לא מטפלים באופן אוטומטי ב-insets. עם זאת, אפשר לקבל גישה לתמונות הממוזערות ולהוסיף אותן באופן ידני. ב-androidx.compose.material 1.6.0 ואילך, משתמשים בפרמטרwindowInsetsכדי להחיל את השוליים הפנימיים באופן ידני עלBottomAppBar,TopAppBar,BottomNavigationו-NavigationRail. באופן דומה, משתמשים בפרמטרcontentWindowInsetsבשבילScaffold. - אם האפליקציה שלכם משתמשת בתצוגות ורכיבי Material (
com.google.android.material), רוב רכיבי Material מבוססי-תצוגות, כמוBottomNavigationView,BottomAppBar, NavigationRailViewאוNavigationView, מטפלים בשוליים ולא דורשים עבודה נוספת. עם זאת, אם משתמשים ב-AppBarLayout, צריך להוסיףandroid:fitsSystemWindows="true". - במקרה של קומפוזיציות מותאמות אישית, צריך להחיל את השוליים הפנימיים באופן ידני כריווח פנימי. אם התוכן נמצא בתוך
Scaffold, אפשר להשתמש בערכי הריווח הפנימי שלScaffoldכדי להגדיר שוליים פנימיים. אחרת, מוסיפים ריווח באמצעות אחת מהאפשרויות שלWindowInsets. - אם האפליקציה שלכם משתמשת בתצוגות וב-
BottomSheet,SideSheetאו במאגרי תגים מותאמים אישית, צריך להחיל ריווח פנימי באמצעותViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener. ב-RecyclerView, אפשר להחיל מרווח פנימי באמצעות מאזין כזה, וגם להוסיףclipToPadding="false".
מה צריך לבדוק אם האפליקציה חייבת להציע הגנה מותאמת אישית ברקע
אם האפליקציה שלכם צריכה להציע הגנה מותאמת אישית ברקע לניווט עם 3 לחצנים או לסרגל המצב, האפליקציה צריכה למקם רכיב שאפשר להרכיב או תצוגה מאחורי סרגל המערכת באמצעות WindowInsets.Type#tappableElement() כדי לקבל את הגובה של סרגל הניווט עם 3 הלחצנים או WindowInsets.Type#statusBars.
מקורות מידע נוספים בנושא תצוגה מקצה לקצה
במאמרים תצוגות מקצה לקצה ויצירת קומפוזיציה מקצה לקצה מפורטים שיקולים נוספים לגבי החלת שוליים פנימיים.
ממשקי API שהוצאו משימוש
ממשקי ה-API הבאים הוצאו משימוש אבל לא הושבתו:
R.attr#enforceStatusBarContrast-
R.attr#navigationBarColor(לניווט ב-3 לחצנים, עם אלפא של 80%) Window#isStatusBarContrastEnforced-
Window#setNavigationBarColor(לניווט ב-3 לחצנים, עם שקיפות של 80%) Window#setStatusBarContrastEnforced
ממשקי ה-API הבאים הוצאו משימוש והושבתו:
R.attr#navigationBarColor(לניווט באמצעות תנועות)R.attr#navigationBarDividerColorR.attr#statusBarColorWindow#setDecorFitsSystemWindowsWindow#getNavigationBarColorWindow#getNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#getStatusBarColorWindow#setNavigationBarColor(לניווט באמצעות תנועות)Window#setNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#setStatusBarColor
הגדרה יציבה
אם האפליקציה מטרגטת ל-Android 15 (רמת API 35) ומעלה, Configuration היא כבר לא מחריגה את סרגלי המערכת. אם אתם משתמשים בגודל המסך במחלקה Configuration לחישוב הפריסה, כדאי להחליף אותו בחלופות טובות יותר כמו ViewGroup, WindowInsets או WindowMetricsCalculator, בהתאם לצורך.
Configuration זמין החל מ-API 1. בדרך כלל הוא מתקבל מ-Activity.onConfigurationChanged. הוא מספק מידע כמו צפיפות החלונות, הכיוון והגדלים. מאפיין חשוב לגבי גדלי החלונות שמוחזרים מ-Configuration הוא שבעבר לא נכללו בהם סרגלי המערכת.
גודל ההגדרה משמש בדרך כלל לבחירת משאבים, כמו /res/layout-h500dp, וזה עדיין תרחיש שימוש תקף. עם זאת, תמיד המלצנו שלא להשתמש בה לחישוב פריסות. אם אתם עושים את זה, עליכם להתרחק ממנו עכשיו. צריך להחליף את השימוש ב-Configuration במשהו מתאים יותר בהתאם לתרחיש לדוגמה.
אם משתמשים בו כדי לחשב את הפריסה, צריך להשתמש ב-ViewGroup מתאים, כמו
CoordinatorLayout או ConstraintLayout. אם משתמשים בו כדי לקבוע את הגובה של סרגל הניווט של המערכת, צריך להשתמש ב-WindowInsets. אם רוצים לדעת מה הגודל הנוכחי של חלון האפליקציה, משתמשים ב-computeCurrentWindowMetrics.
ברשימה הבאה מפורטים השדות שיושפעו מהשינוי הזה:
- הגודל של
Configuration.screenWidthDpושלscreenHeightDpכבר לא כולל את סרגלי המערכת. Configuration.smallestScreenWidthDpמושפע באופן עקיף משינויים ב-screenWidthDpוב-screenHeightDp.- השינויים ב-
screenWidthDpוב-screenHeightDpמשפיעים באופן עקיף עלConfiguration.orientationבמכשירים שהיחס בין האורך לרוחב שלהם קרוב ל-1:1. - השינויים ב-
Configurationמשפיעים באופן עקיף עלDisplay.getSize(Point). החל מרמת API 30, השיטה הזו הוצאה משימוש. Display.getMetrics()כבר פועל כך מרמת API 33.
ערך ברירת המחדל של המאפיין elegantTextHeight הוא true
באפליקציות שמטרגטות את Android 15 (רמת API 35), המאפיין TextView של elegantTextHeight הופך ל-true כברירת מחדל, ומחליף את הגופן הקומפקטי שמשמש כברירת מחדל בסקריפטים מסוימים עם מדדים אנכיים גדולים, בגופן שקל יותר לקרוא אותו.
הגופן הקומפקטי הוצג כדי למנוע הפרעה לפריסות. בגרסה Android 13 (רמת API 33) מונעים הרבה מהפרעות כאלה על ידי מתן אפשרות לפריסת הטקסט להתמתח לגובה האנכי באמצעות המאפיין fallbackLineSpacing.
ב-Android 15, הגופן הקומפקטי עדיין נשאר במערכת, כך שהאפליקציה יכולה להגדיר את elegantTextHeight ל-false כדי לקבל את אותה התנהגות כמו קודם, אבל סביר להניח שהוא לא יקבל תמיכה בגרסאות הבאות. לכן, אם האפליקציה תומכת בסקריפטים הבאים: ערבית, לאוס, מיאנמר, טמילית, גוג'ראטית, קנאדה, מליאלאם, אודיה, טלוגו או תאית, צריך לבדוק את האפליקציה על ידי הגדרת elegantTextHeight לערך true.
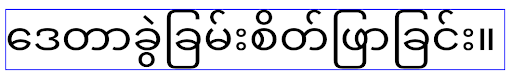 התנהגות של
התנהגות של elegantTextHeight באפליקציות שמיועדות ל-Android 14 (רמת API 34) וגרסאות ישנות יותר.
elegantTextHeight באפליקציות שמטרגטות את Android 15.רוחב TextView משתנה עבור צורות מורכבות של אותיות
בגרסאות קודמות של Android, חלק מגופנים או שפות עם כתב מחובר עם עיצוב מורכב עשויים לצייר את האותיות באזור של התו הקודם או הבא.
במקרים מסוימים, אותיות כאלה נחתכו בנקודת ההתחלה או הסיום.
החל מ-Android 15, TextView מקצה רוחב לציור מספיק מקום לאותיות כאלה ומאפשר לאפליקציות לבקש תוספת רווח שמימין כדי למנוע חיתוך.
מכיוון שהשינוי הזה משפיע על האופן שבו TextView מחליט על הרוחב, TextView מקצה יותר רוחב כברירת מחדל אם האפליקציה מטרגטת ל-Android 15 (רמת API 35) ואילך. אפשר להפעיל או להשבית את ההתנהגות הזו על ידי שליחת קריאה ל-API setUseBoundsForWidth ב-TextView.
הוספת רווח פנימי בצד ימין עלולה לגרום לחוסר התאמה של פריסות קיימות, ולכן הוא לא מתווסף כברירת מחדל גם לאפליקציות שמטרגטות את Android מגרסה 15 ואילך.
עם זאת, אפשר להוסיף עוד ריפוד כדי למנוע חיתוך על ידי קריאה ל-setShiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang.
הדוגמאות הבאות מראות איך השינויים האלה יכולים לשפר את פריסת הטקסט בגופנים ובשפות מסוימים.

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" />

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />
גובה שורה שמוגדר כברירת מחדל ב-EditText בהתאם ללוקאל
בגרסאות קודמות של Android, פריסת הטקסט הגדילה את גובה הטקסט כדי להתאים לגובה השורה של הגופן שתואם לאזור הנוכחי. לדוגמה, אם התוכן היה ביפנית, הגובה של הטקסט השתנה מעט כי גובה השורה של הגופן היפני גדול מעט מזה של גופן לטינית. עם זאת, למרות ההבדלים האלה בגובה השורות, הגודל של הרכיב EditText היה אחיד, ללא קשר לאזור הזמן שבו נעשה שימוש, כפי שמוצג בתמונה הבאה:

EditText שיכולים להכיל טקסט באנגלית (en), ביפנית (ja) ובבורמזית (my). הגובה של EditText זהה, למרות שלשפות האלה יש גובה שורות שונה זו מזו.באפליקציות שמטרגטות את Android 15 (רמת API 35), גובה שורה מינימלי מוקצה עכשיו ל-EditText כדי להתאים לגופן העזר של האזור הגיאוגרפי שצוין, כפי שמוצג בתמונה הבאה:

EditText שיכולים להכיל טקסט באנגלית (en), ביפנית (ja) ובבורמזית (my). הגובה של EditText כולל עכשיו מקום שמתאים לגובה השורה שמוגדר כברירת מחדל לגופנים של השפות האלה.אם צריך, אפשר לשחזר את ההתנהגות הקודמת של האפליקציה על ידי ציון הערך false למאפיין useLocalePreferredLineHeightForMinimum. אפשר גם להגדיר באפליקציה מדדים מינימליים מותאמים אישית של מודעות רגילות באמצעות ממשק ה-API setMinimumFontMetrics ב-Kotlin וב-Java.
מצלמה ומדיה
ב-Android 15 בוצעו השינויים הבאים בהתנהגות של המצלמה והמדיה באפליקציות שמטרגטות את Android 15 ואילך.
הגבלות על בקשת מיקוד אודיו
כדי לבקש את המיקוד באודיו, אפליקציות שמטרגטות את Android 15 (רמת API 35) צריכות להיות האפליקציה העליונה או להפעיל שירות בחזית. אם אפליקציה מנסה לבקש להתמקד בה כשהיא לא עומדת באחת מהדרישות האלה, הקריאה מחזירה את הערך AUDIOFOCUS_REQUEST_FAILED.
מידע נוסף על התכונה 'מיקוד אודיו' זמין במאמר ניהול התכונה 'מיקוד אודיו'.
הגבלות שאינן קשורות ל-SDK עודכנו
Android 15 כולל רשימות מעודכנות של ממשקי non-SDK מוגבלים, שמבוססות על שיתוף פעולה עם מפתחי Android ועל הבדיקות הפנימיות האחרונות. כשאפשר, אנחנו מוודאים שיש חלופות ציבוריות זמינות לפני שאנחנו מגבילים ממשקים שאינם SDK.
אם האפליקציה שלכם לא מטרגטת ל-Android 15, יכול להיות שחלק מהשינויים האלה לא ישפיעו עליכם באופן מיידי. עם זאת, יכול להיות שהאפליקציה שלך תוכל לגשת לחלק מממשקי ה-API שאינם חלק מ-SDK, בהתאם לרמת ה-API לטירגוט של האפליקציה, אבל שימוש בשיטה או בשדה כלשהם שלא נכללים ב-SDK תמיד כרוך בסיכון גבוה להפסקת פעולת האפליקציה.
אם אתם לא בטוחים אם האפליקציה שלכם משתמשת בממשקים שאינם SDK, אתם יכולים לבצע בדיקה לאפליקציה כדי לגלות זאת. אם האפליקציה שלך מסתמכת על ממשקים שאינם SDK, כדאי להתחיל לתכנן מעבר לחלופות SDK. עם זאת, אנחנו מבינים שיש אפליקציות שבהן יש תרחישי שימוש לגיטימיים בממשקים שאינם SDK. אם אין לך אפשרות להשתמש בממשק שאינו SDK עבור תכונה באפליקציה, עליך לשלוח בקשה ליצירת API ציבורי חדש.
מידע נוסף על השינויים בגרסה הזו של Android זמין במאמר עדכונים לגבי הגבלות על ממשקים שאינם SDK ב-Android 15. מידע נוסף על ממשקים שאינם ב-SDK זמין במאמר הגבלות על ממשקים שאינם ב-SDK.
