Die Android 15-Plattform umfasst Verhaltensänderungen, die sich auf Ihre App auswirken können.
Die folgenden Verhaltensänderungen gelten für alle Apps, wenn sie unter Android 15 ausgeführt werden, unabhängig von targetSdkVersion. Sie sollten Ihre App testen und sie bei Bedarf so anpassen, dass sie diese richtig unterstützt.
Sehen Sie sich auch die Liste der Verhaltensänderungen an, die sich nur auf Apps auswirken, die auf Android 15 ausgerichtet sind.
Hauptfunktion
In Android 15 werden verschiedene Kernfunktionen des Android-Systems geändert oder erweitert.
Änderungen am Status „Angehalten“ von Paketen
Der Status „Paket FLAG_STOPPED“ (den Nutzer in AOSP-Builds durch langes Drücken auf ein App-Symbol und Auswahl von „Zwangsweise beenden“ aktivieren können) soll Apps in diesem Status halten, bis der Nutzer die App explizit daraus entfernt, indem er sie direkt startet oder indirekt mit ihr interagiert (z. B. über das Freigabe-Menü oder ein Widget oder indem er die App als Live-Hintergrund auswählt). In Android 15 haben wir das Verhalten des Systems an dieses beabsichtigte Verhalten angepasst. Apps sollten nur durch eine direkte oder indirekte Nutzeraktion aus dem Status „Angehalten“ entfernt werden.
Um das beabsichtigte Verhalten zu unterstützen, werden zusätzlich zu den bestehenden Einschränkungen alle ausstehenden Intents abgebrochen, wenn die App auf einem Gerät mit Android 15 den Status „Angehalten“ einnimmt. Wenn die App durch die Aktionen des Nutzers aus dem angehaltenen Status entfernt wird, wird die ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED-Broadcast an die App gesendet. So können ausstehende Intents neu registriert werden.
Sie können die neue Methode ApplicationStartInfo.wasForceStopped() aufrufen, um zu prüfen, ob die App in den Status „Beendet“ versetzt wurde.
Unterstützung von Seitengrößen von 16 KB
Bisher wurden in Android nur Arbeitsspeicherseiten mit 4 KB unterstützt. Dadurch wurde die Leistung des Systemspeichers für die durchschnittliche Menge an Gesamtspeicher optimiert, die Android-Geräte in der Regel hatten. Ab Android 15 unterstützt AOSP Geräte, die für die Verwendung einer Seitengröße von 16 KB konfiguriert sind (16‑KB-Geräte). Wenn Ihre App NDK-Bibliotheken verwendet, entweder direkt oder indirekt über ein SDK, müssen Sie Ihre App neu erstellen, damit sie auf diesen 16‑KB-Geräten funktioniert.
Da Gerätehersteller weiterhin Geräte mit größeren Mengen an physischem Arbeitsspeicher (RAM) entwickeln, werden viele dieser Geräte 16‑KB-Seitengrößen (und schließlich noch größere) verwenden, um die Leistung des Geräts zu optimieren. Wenn Sie Unterstützung für Geräte mit einer Seitengröße von 16 KB hinzufügen, kann Ihre App auf diesen Geräten ausgeführt werden und von den damit verbundenen Leistungsverbesserungen profitieren. Ohne Neukompilierung funktionieren Apps in zukünftigen Android-Versionen nicht auf Geräten mit 16 KB.
Damit Sie Ihre App entsprechend anpassen können, haben wir Anleitungen dazu bereitgestellt, wie Sie prüfen, ob Ihre App betroffen ist, wie Sie Ihre App neu erstellen (falls zutreffend) und wie Sie Ihre App mit Emulatoren (einschließlich Android 15-Systemabbildern für den Android-Emulator) in einer 16‑KB-Umgebung testen.
Vorteile und Leistungssteigerungen
Geräte, die mit einer Seitengröße von 16 KB konfiguriert sind, benötigen im Durchschnitt etwas mehr Arbeitsspeicher, erzielen aber auch verschiedene Leistungsverbesserungen für das System und die Apps:
- Kürzere App-Startzeiten, während das System unter Speicherauslastung steht: im Durchschnitt 3,16 % niedriger, mit deutlicheren Verbesserungen (bis zu 30%) bei einigen von uns getesteten Apps
- Verringerter Stromverbrauch beim Starten der App: durchschnittlich 4,56% weniger
- Schnellerer Kamerastart: 4,48% schnellere Heißstarts und 6,60% schnellere Kaltstarts im Durchschnitt
- Verbesserte Systemstartzeit: durchschnittlich um 8% (ca. 950 Millisekunden)
Diese Verbesserungen basieren auf unseren ersten Tests. Die Ergebnisse auf tatsächlichen Geräten werden sich wahrscheinlich unterscheiden. Im Rahmen unserer Tests werden wir zusätzliche Analysen zu den potenziellen Vorteilen für Apps durchführen.
Prüfen, ob Ihre App betroffen ist
Wenn Ihre App nativen Code verwendet, sollten Sie Ihre App neu erstellen, um Geräte mit 16‑KB-Speicherseiten zu unterstützen. Wenn Sie sich nicht sicher sind, ob Ihre App nativen Code verwendet, können Sie mit dem APK Analyzer prüfen, ob nativer Code vorhanden ist, und dann die Ausrichtung von ELF-Segmenten für alle gefundenen gemeinsam genutzten Bibliotheken prüfen. Android Studio bietet auch Funktionen, mit denen Sie Ausrichtungsprobleme automatisch erkennen können.
Wenn Ihre App nur Code verwendet, der in der Programmiersprache Java oder in Kotlin geschrieben wurde, einschließlich aller Bibliotheken oder SDKs, unterstützt Ihre App bereits Geräte mit 16 KB. Wir empfehlen Ihnen jedoch, Ihre App in einer 16‑KB-Umgebung zu testen, um zu prüfen, ob es unerwartete Regressionen im App-Verhalten gibt.
Erforderliche Änderungen für einige Apps zur Unterstützung des vertraulichen Profils
Vertrauliche Profile sind eine neue Funktion in Android 15. Damit können Nutzer einen separaten Bereich auf ihrem Gerät erstellen, in dem sensible Apps durch eine zusätzliche Authentifizierung vor neugierigen Blicken geschützt werden. Da die Sichtbarkeit von Apps im vertraulichen Profil eingeschränkt ist, müssen bei einigen Arten von Apps zusätzliche Schritte ausgeführt werden, damit sie im vertraulichen Profil eines Nutzers angezeigt werden und damit Nutzer mit ihnen interagieren können.
Alle Apps
Da Apps im privaten Bereich in einem separaten Nutzerprofil gespeichert werden, ähnlich wie Arbeitsprofile, sollten Apps nicht davon ausgehen, dass installierte Kopien ihrer App, die sich nicht im Hauptprofil befinden, sich im Arbeitsprofil befinden. Wenn Ihre App Logik für Apps mit Arbeitsprofil enthält, die diese Annahme treffen, müssen Sie diese Logik anpassen.
Medizinische Apps
Wenn ein Nutzer das vertrauliche Profil sperrt, werden alle Apps darin angehalten. Diese Apps können dann keine Aktivitäten im Vordergrund oder Hintergrund ausführen, z. B. keine Benachrichtigungen anzeigen. Dieses Verhalten kann sich erheblich auf die Nutzung und Funktion von medizinischen Apps auswirken, die im vertraulichen Profil installiert sind.
Bei der Einrichtung des vertraulichen Profils werden Nutzer darauf hingewiesen, dass es sich nicht für Apps eignet, die wichtige Aktivitäten im Vordergrund oder Hintergrund ausführen müssen, z. B. die Anzeige von Benachrichtigungen von medizinischen Apps. Apps können jedoch nicht feststellen, ob sie im privaten Profil verwendet werden, und können dem Nutzer daher in diesem Fall keine Warnung anzeigen.
Wenn Sie also eine medizinische App entwickeln, sollten Sie prüfen, wie sich diese Funktion auf Ihre App auswirken könnte, und entsprechende Maßnahmen ergreifen, z. B. Ihre Nutzer darüber informieren, dass sie Ihre App nicht in einem vertraulichen Profil installieren sollen, um Unterbrechungen wichtiger App-Funktionen zu vermeiden.
Launcher-Apps
Wenn Sie eine Launcher-App entwickeln, müssen Sie Folgendes tun, damit Apps im privaten Bereich sichtbar sind:
- Ihre App muss als Standard-Launcher-App für das Gerät zugewiesen sein, d. h. sie muss die Rolle
ROLE_HOMEhaben. - Ihre App muss die normale Berechtigung
ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILESin der Manifestdatei Ihrer App deklarieren.
Launcher-Apps, die die Berechtigung ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILES angeben, müssen die folgenden Anwendungsfälle für vertrauliche Profile unterstützen:
- Ihre App muss einen separaten Launcher-Container für Apps haben, die im vertraulichen Profil installiert sind. Mit der Methode
getLauncherUserInfo()kannst du feststellen, welcher Nutzerprofiltyp verarbeitet wird. - Der Nutzer muss den Container für das vertrauliche Profil ausblenden und einblenden können.
- Der Nutzer muss den Container für das vertrauliche Profil sperren und entsperren können. Verwenden Sie die Methode
requestQuietModeEnabled(), um das vertrauliche Profil zu sperren (trueübergeben) oder zu entsperren (falseübergeben). Wenn das vertrauliche Profil gesperrt ist, sollten keine Apps im Container des vertraulichen Profils sichtbar sein oder über Mechanismen wie die Suche gefunden werden können. Ihre App sollte einen Empfänger für die Übertragungen von
ACTION_PROFILE_AVAILABLEundACTION_PROFILE_UNAVAILABLEregistrieren und die Benutzeroberfläche in Ihrer App aktualisieren, wenn sich der gesperrte oder entsperrte Status des Containers für den privaten Bereich ändert. Beide Streams enthaltenEXTRA_USER, mit dem sich in Ihrer App auf den Nutzer mit privatem Profil Bezug nehmen lässt.Sie können auch die Methode
isQuietModeEnabled()verwenden, um zu prüfen, ob das Profil des privaten Bereichs gesperrt ist.
App-Shop-Apps
Das vertrauliche Profil enthält die Schaltfläche „Apps installieren“, über die Apps implizit im vertraulichen Profil des Nutzers installiert werden. Damit Ihre App diese implizite Absicht erhält, müssen Sie in der Manifestdatei Ihrer App eine <intent-filter> mit einer <category> von CATEGORY_APP_MARKET deklarieren.
PNG-basierte Emoji-Schriftart entfernt
Die alte, PNG-basierte Emoji-Schriftdatei (NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf) wurde entfernt. Es bleibt nur die vektorbasierte Datei. Ab Android 13 (API-Ebene 33) wurde die Emoji-Schriftdatei, die vom System-Emoji-Renderer verwendet wird, von einer PNG-basierten Datei in eine vektorbasierte Datei geändert. Die alte Schriftdatei wurde in Android 13 und 14 aus Kompatibilitätsgründen beibehalten, damit Apps mit eigenen Schrift-Renderern die alte Schriftdatei weiter verwenden konnten, bis ein Upgrade möglich war.
Um zu prüfen, ob Ihre App betroffen ist, suchen Sie im Code Ihrer App nach Verweis auf die Datei NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf.
Sie haben verschiedene Möglichkeiten, Ihre App anzupassen:
- Verwenden Sie Plattform-APIs für das Text-Rendering. Sie können Text in eine bitmapfähige
Canvasrendern und bei Bedarf ein Rohbild daraus erstellen. - Fügen Sie Ihrer App die Schriftartenunterstützung COLRv1 hinzu. Die Open-Source-Bibliothek FreeType unterstützt COLRv1 ab Version 2.13.0.
- Als letzten Ausweg können Sie die alte Emoji-Schriftdatei (
NotoColorEmoji.ttf) in Ihr APK einbinden. In diesem Fall fehlen Ihrer App jedoch die neuesten Emoji-Updates. Weitere Informationen finden Sie auf der GitHub-Projektseite von Noto Emoji.
Die Mindest-SDK-Zielversion wurde von 23 auf 24 erhöht.
Android 15 baut auf der
die in Android 14 vorgenommene Änderungen
noch weiter zu verbessern. In Android 15 werden Apps mit einem
targetSdkVersion mit einer Version unter 24 können nicht installiert werden.
Wenn Anwendungen moderne API-Levels erfüllen müssen, können Sie die Sicherheit verbessern und
Datenschutz.
Malware zielt häufig auf niedrigere API-Level ab, um Sicherheit und Datenschutz zu umgehen
die in höheren Android-Versionen eingeführt wurden. Beispiel:
einige Malware-Apps einen targetSdkVersion von 22, um zu verhindern, dass sie
2015 durch Android 6.0 Marshmallow (API) eingeführtes Laufzeitberechtigungsmodell
Stufe 23). Durch diese Android 15-Änderung wird es Malware schwerer, Sicherheitsrisiken zu umgehen
und Verbesserungen beim Datenschutz. Versuch, eine App zu installieren, die auf eine niedrigere API ausgerichtet ist
führt zu einem Installationsfehler mit einer Meldung wie der folgenden
in Logcat angezeigt:
INSTALL_FAILED_DEPRECATED_SDK_VERSION: App package must target at least SDK version 24, but found 7
Auf Geräten mit einem Upgrade auf Android 15: alle Apps mit einem um targetSdkVersion niedrigeren
als 24 installiert sind.
Wenn du eine App testen musst, die auf ein älteres API-Level ausgerichtet ist, verwende den folgenden ADB-Code Befehl:
adb install --bypass-low-target-sdk-block FILENAME.apk
Sicherheit und Datenschutz
Mit Android 15 werden strenge Maßnahmen eingeführt, um Betrug mit Einmalpasswörtern (OTP) zu bekämpfen und die vertraulichen Inhalte der Nutzer zu schützen. Dabei liegt der Schwerpunkt auf der Verschärfung des Notification Listener Service und der Bildschirmfreigabe. Zu den wichtigsten Verbesserungen gehören das Entfernen von OTPs aus Benachrichtigungen, auf die nicht vertrauenswürdige Apps zugreifen können, das Ausblenden von Benachrichtigungen während der Bildschirmfreigabe und die Sicherung von App-Aktivitäten, wenn OTPs gepostet werden. Mit diesen Änderungen sollen die vertraulichen Inhalte der Nutzer vor unbefugten Zugriffen geschützt werden.
Entwickler müssen Folgendes beachten, damit ihre Apps mit den Änderungen in Android 15 kompatibel sind:
OTP-Entfernung
Android verhindert, dass nicht vertrauenswürdige Apps, die NotificationListenerService implementieren, nicht entfernte Inhalte aus Benachrichtigungen lesen, in denen ein OTP erkannt wurde. Vertrauenswürdige Apps wie Verknüpfungen mit Gerätemanagern für Begleitgeräte sind von diesen Einschränkungen ausgenommen.
Schutz bei der Bildschirmfreigabe
- Benachrichtigungsinhalte werden während der Bildschirmfreigabe ausgeblendet, um die Privatsphäre der Nutzer zu schützen. Wenn die App
setPublicVersion()implementiert, zeigt Android die öffentliche Version der Benachrichtigung an, die in unsicheren Kontexten als Ersatzbenachrichtigung dient. Andernfalls werden die Inhalte der Benachrichtigung ohne weiteren Kontext entfernt. - Vertrauliche Inhalte wie die Passworteingabe werden für externe Betrachter ausgeblendet, um zu verhindern, dass vertrauliche Informationen des Nutzers offengelegt werden.
- Aktivitäten von Apps, die während der Bildschirmfreigabe Benachrichtigungen senden, bei denen ein OTP erkannt wurde, werden ausgeblendet. App-Inhalte sind für den Remote-Betrachter ausgeblendet, wenn die App gestartet wird.
- Zusätzlich zur automatischen Erkennung sensibler Felder durch Android können Entwickler Teile ihrer App manuell mit
setContentSensitivityals sensibel kennzeichnen. Diese werden dann bei der Bildschirmfreigabe für Remote-Zuschauer ausgeblendet. - Entwickler können unter Entwickleroptionen die Option Schutzmaßnahmen für Bildschirmfreigabe deaktivieren aktivieren, um für Demo- oder Testzwecke von den Schutzmaßnahmen für die Bildschirmfreigabe ausgenommen zu werden. Der standardmäßige Bildschirmrekorder des Systems ist von diesen Änderungen ausgenommen, da die Aufnahmen auf dem Gerät verbleiben.
Kamera und Medien
Unter Android 15 werden die folgenden Änderungen am Kamera- und Medienverhalten für alle Apps vorgenommen.
Durch die direkte und ausgelagerte Audiowiedergabe werden zuvor geöffnete direkte oder ausgelagerte Audiotracks ungültig, wenn Ressourcenlimits erreicht werden.
Vor Android 15 konnte eine App, die eine direkte oder ausgelagerte Audiowiedergabe anforderte, während eine andere App Audio wiedergab und die Ressourcenlimits erreicht wurden, keine neue AudioTrack öffnen.
Ab Android 15 werden alle derzeit geöffneten AudioTrack-Objekte ungültig, wenn eine App die direkte oder Offload-Wiedergabe anfordert und die Ressourcenlimits erreicht werden. Dadurch wird verhindert, dass die neue Titelanfrage erfüllt wird.
(Direkte und Offload-Audiotracks werden in der Regel für die Wiedergabe komprimierter Audioformate geöffnet. Gängige Anwendungsfälle für die direkte Audiowiedergabe sind das Streaming von codiertem Audio über HDMI an einen Fernseher. Offload-Tracks werden in der Regel verwendet, um komprimierte Audioinhalte auf einem Mobilgerät mit Hardware-DSP-Beschleunigung abzuspielen.)
Nutzerfreundlichkeit und System-UI
Android 15 enthält einige Änderungen, die für eine einheitlichere und intuitivere User Experience sorgen sollen.
Animationen für die intelligente „Zurück“-Touchgeste für Apps aktiviert, die sich dafür angemeldet haben
Ab Android 15 wurde die Entwickleroption für intelligente „Zurück“-Touch-Gesten entfernt. Systemanimationen wie das Zurückgehen zum Startbildschirm, das Wechseln zwischen Aufgaben und das Wechseln zwischen Aktivitäten werden jetzt für Apps angezeigt, die die vorhersagende Geste zum Zurückgehen entweder vollständig oder auf Aktivitätsebene aktiviert haben. Wenn Ihre App betroffen ist, gehen Sie so vor:
- Prüfen Sie, ob Ihre App richtig migriert wurde, um die vorweggenommene Zurück-Geste zu verwenden.
- Achten Sie darauf, dass Ihre Fragmentübergänge mit der vorausschauenden Navigation zurück funktionieren.
- Verwenden Sie stattdessen Animator- und androidx-Übergänge.
- Migrieren Sie von Backstacks weg, die
FragmentManagernicht kennt. Verwenden Sie stattdessen Backstacks, die vonFragmentManageroder der Navigationskomponente verwaltet werden.
Widgets werden deaktiviert, wenn ein Nutzer eine App erzwingt, dass sie beendet wird
Wenn ein Nutzer eine App auf einem Gerät mit Android 15 erzwungen beendet, deaktiviert das System vorübergehend alle Widgets der App. Die Widgets sind ausgegraut und der Nutzer kann nicht mit ihnen interagieren. Das liegt daran, dass ab Android 15 alle ausstehenden Intents einer App vom System abgebrochen werden, wenn die App erzwungen beendet wird.
Das System aktiviert diese Widgets wieder, wenn der Nutzer die App das nächste Mal startet.
Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter Änderungen am Status „Angehalten“ für Pakete.
Chip in der Statusleiste für die Medienprojektion informiert Nutzer über Bildschirmfreigabe, Streaming und Aufzeichnung
Bei Ausnutzung von Bildschirmprojektion werden personenbezogene Nutzerdaten wie Finanzinformationen offengelegt, da Nutzer nicht wissen, dass ihr Gerätebildschirm geteilt wird.
Bei Apps, die auf Geräten mit Android 15 QPR1 oder höher ausgeführt werden, werden Nutzer über einen großen und gut sichtbaren Chip in der Statusleiste über eine laufende Bildschirmprojektion informiert. Nutzer können auf den Chip tippen, um zu verhindern, dass ihr Bildschirm geteilt, gestreamt oder aufgezeichnet wird. Außerdem wird die Bildschirmprojektion automatisch beendet, wenn das Display des Geräts gesperrt wird.
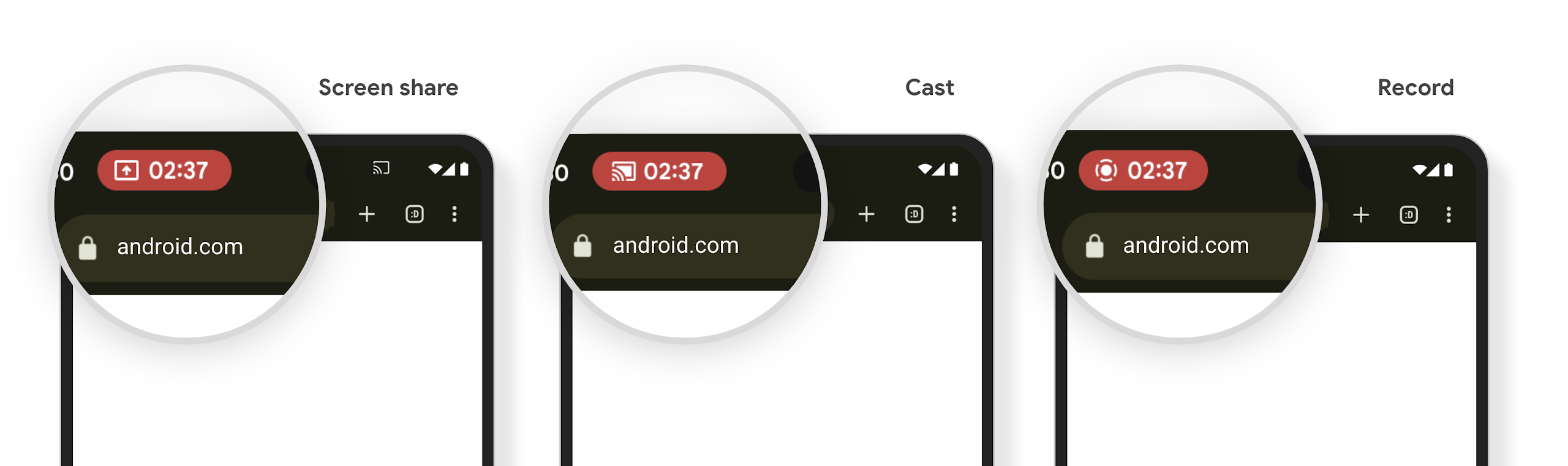
Prüfen, ob Ihre App betroffen ist
Ihre App enthält standardmäßig den Statusleisten-Chip und die Bildschirmprojektion wird automatisch pausiert, wenn der Sperrbildschirm aktiviert wird.
Weitere Informationen zum Testen Ihrer App für diese Anwendungsfälle finden Sie unter Statusleiste – Chip und automatischer Stopp.
Einschränkungen für den Netzwerkzugriff im Hintergrund
In Android 15 erhalten Apps, die eine Netzwerkanfrage außerhalb eines gültigen Prozesslebenszyklus starten, eine Ausnahme. In der Regel ist dies ein UnknownHostException oder ein anderer socketbezogener IOException. Netzwerkanfragen, die außerhalb eines gültigen Lebenszyklus erfolgen, sind in der Regel darauf zurückzuführen, dass Apps eine Netzwerkanfrage unwissentlich fortsetzen, auch wenn die App nicht mehr aktiv ist.
Um diese Ausnahme zu vermeiden, sollten Sie dafür sorgen, dass Ihre Netzwerkanfragen sitzungsorientiert sind und abgebrochen werden, wenn sie einen gültigen Prozesslebenszyklus verlassen. Verwenden Sie dazu sitzungsorientierte Komponenten. Wenn es wichtig ist, dass die Netzwerkanfrage auch dann erfolgt, wenn der Nutzer die Anwendung verlässt, können Sie die Netzwerkanfrage mit WorkManager planen oder eine für den Nutzer sichtbare Aufgabe mit einem Dienst im Vordergrund fortsetzen.
Einstellung
Mit jeder Veröffentlichung können bestimmte Android-APIs veraltet sein oder müssen refaktoriert werden, um ein besseres Entwicklererlebnis zu bieten oder neue Plattformfunktionen zu unterstützen. In diesen Fällen werden die veralteten APIs offiziell eingestellt und Entwickler werden auf alternative APIs verwiesen.
Das bedeutet, dass wir den offiziellen Support für die APIs eingestellt haben, sie aber weiterhin für Entwickler verfügbar sind. Weitere Informationen zu wichtigen Einstellungen in dieser Version von Android finden Sie auf der Seite zu Einstellungen.

