O Android 14 introduz ótimos recursos e APIs para desenvolvedores. As seções a seguir ajudam você a conhecer os recursos disponíveis para os apps e a começar a usar as APIs relacionadas.
Para uma lista detalhada das APIs adicionadas, modificadas e removidas, leia o Relatório de diferenças da API. Para mais detalhes sobre as APIs adicionadas, acesse a Referência da API do Android. No Android 14, procure APIs que foram adicionadas no nível 34 da API. Para saber mais sobre as áreas em que as mudanças na plataforma podem afetar seus apps, confira as mudanças de comportamento do Android 14 para apps destinados ao Android 14 e para todos os apps.
Internacionalização
Seleção de idioma por app
O Android 14 expande os recursos de linguagem por app lançados no Android 13 (API de nível 33) com estes recursos extras:
Gerar automaticamente o
localeConfigde um app: a partir do Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 e do AGP 8.1.0-alpha07, é possível configurar seu app para oferecer suporte a seleção de idioma por app automaticamente. Com base nos recursos do projeto, o Plug-in do Android para Gradle gera o arquivoLocaleConfige adiciona uma referência a ele no arquivo de manifesto final. Assim, não é mais necessário criar ou atualizar o arquivo manualmente. O AGP usa os recursos nas pastasresdos módulos do app e qualquer dependência de módulos de biblioteca para determinar as localidades que serão incluídas no arquivoLocaleConfig.Atualizações dinâmicas para o
localeConfigde um app: use os métodossetOverrideLocaleConfig()egetOverrideLocaleConfig()emLocaleManagerpara atualizar dinamicamente a lista de idiomas com suporte no app nas configurações do sistema do dispositivo. Use essa flexibilidade para personalizar a lista de idiomas com suporte por região, executar experimentos A/B ou fornecer uma lista atualizada de localidades se o app usar pushes do lado do servidor para localização.Visibilidade do idioma do app para Editores de método de entrada (IMEs): os IMEs podem usar o método
getApplicationLocales()para conferir o idioma do app atual e associar o idioma do IME a ele.
API Grammatical Inflection
Três bilhões de pessoas falam idiomas com marcação de gênero: idiomas em que categorias gramaticais, como substantivos, verbos, adjetivos e preposições, mudam de acordo com o gênero das pessoas e os objetos sobre os quais elas falam. Tradicionalmente, vários idiomas com marcação de gênero usam o gênero gramatical masculino como padrão ou genérico.
Referir-se a usuários no gênero gramatical errado, como falar com uma mulher no gênero gramatical masculino, pode afetar negativamente o desempenho e a atitude dela. Por outro lado, uma interface com linguagem que reflete corretamente o gênero gramatical do usuário pode melhorar o engajamento e fornecer uma experiência do usuário mais personalizada e natural.
Para ajudar a criar uma interface focada no usuário para idiomas com flexão de gênero, o Android 14 apresenta a API Grammatical Inflection, que permite adicionar suporte aos gêneros gramaticais sem refatorar o app.
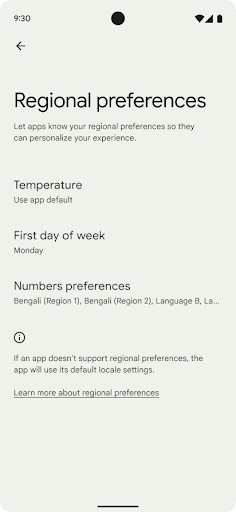
Preferências regionais
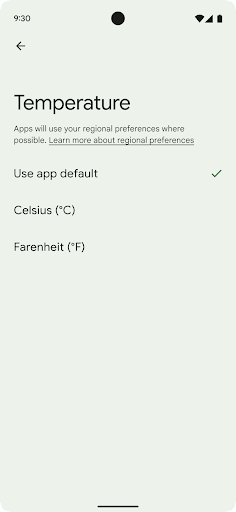
As preferências regionais permitem que os usuários personalizem unidades de temperatura, o primeiro dia da semana e sistemas de numeração. Um europeu que mora nos Estados Unidos pode preferir que as unidades de temperatura estejam em Celsius em vez de Fahrenheit e que apps tratem a segunda-feira como o início da semana, em vez do padrão dos EUA de usar o domingo.
Os novos menus de configurações do Android para essas preferências oferecem aos usuários um
local detectável e centralizado para mudar as preferências do app. Essas
preferências também são mantidas com backup e restauração. Várias APIs e
intents (como
getTemperatureUnit
e
getFirstDayOfWeek)
permitem que o app acesse as preferências do usuário, ajustando a forma como as informações
são exibidas. Também é possível registrar um
BroadcastReceiver em
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED
para processar mudanças de configuração de localidade quando as preferências regionais mudam.
Para encontrar essas configurações, abra o app Configurações e navegue até Sistema > Idiomas e entrada > Preferências regionais.
Acessibilidade
Dimensionamento de fonte não linear para 200%
No Android 14 e versões mais recentes, o sistema oferece suporte a escala de fonte de até 200%, oferecendo usuários com deficiência visual com opções de acessibilidade adicionais alinhadas com a Web Diretrizes de Acessibilidade de Conteúdo (WCAG, na sigla em inglês).
Para evitar que elementos de texto grandes na tela fiquem grandes demais, o sistema aplica uma curva de dimensionamento não linear. Essa estratégia significa que textos grandes não são dimensionados na mesma taxa que os menores. O dimensionamento de fontes não linear ajuda a preservar a hierarquia proporcional entre elementos de tamanhos diferentes, reduzindo problemas com dimensionamento linear em graus elevados, como cortes de texto ou dificuldade para ler um texto devido a tamanhos muito grandes de tela.
Testar o app com dimensionamento de fontes não linear
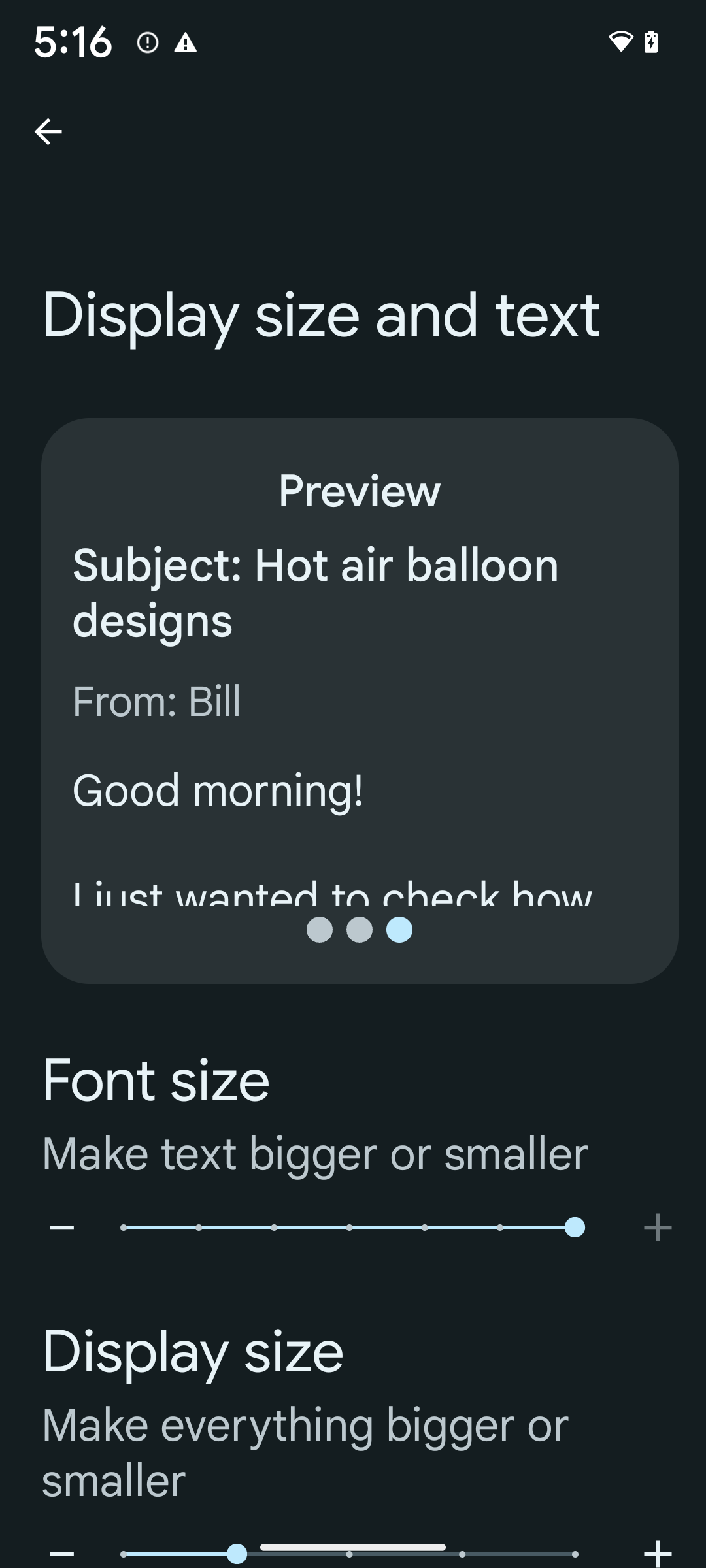
Se você já usa unidades de pixels dimensionados (sp) para definir o dimensionamento de texto, então essas opções extras e melhorias de escalonamento são aplicadas automaticamente texto em seu aplicativo. No entanto, você ainda deve realizar testes de interface com o máximo tamanho de fonte ativado (200%) para garantir que o app aplique os tamanhos de fonte corretamente e podem acomodar tamanhos de fonte maiores sem afetar a usabilidade.
Para ativar o tamanho de fonte de 200%, siga estas etapas:
- Abra o app Configurações e navegue até Acessibilidade > Texto e tamanho de exibição.
- Na opção Tamanho da fonte, toque no ícone de adição (+) até ativar a configuração de tamanho máximo de fonte, conforme mostrado na imagem que acompanha esta seção.
Usar unidades de pixels dimensionados (sp) para tamanhos de texto
Sempre especifique tamanhos de texto em unidades de sp. Quando seu app usa unidades sp, o Android pode aplicar o tamanho de texto preferencial do usuário e dimensioná-lo adequadamente.
Não use unidades sp para preenchimento ou defina alturas de visualização assumindo o preenchimento implícito: com o dimensionamento não linear, as dimensões de sp podem não ser proporcionais. Portanto, 4sp + 20sp podem não ser iguais a 24sp.
Converter unidades de pixels dimensionados
Usar TypedValue.applyDimension() para converter de unidades de sp
em pixels, e use TypedValue.deriveDimension() para
converter pixels em sp. Esses métodos aplicam o escalonamento não linear apropriado
curva automaticamente.
Evite equações fixadas no código usando
Configuration.fontScale ou
DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity Como o dimensionamento da fonte é
não linear, o campo scaledDensity não é mais preciso. O campo fontScale
deve ser usado apenas para fins informativos, porque as fontes não são mais
dimensionadas com um único valor escalar.
Usar unidades de sp para lineHeight
Sempre defina android:lineHeight usando unidades sp em vez
de dp para que a altura da linha seja dimensionada junto com o texto. Caso contrário, se o texto
é sp, mas lineHeight está em dp ou px. Ele não é dimensionado e parece apertado.
A TextView corrige automaticamente o lineHeight para que o objeto
proporções são preservadas, mas somente se textSize e lineHeight forem
definido em unidades de sp.
Câmera e mídia
Ultra HDR para imagens

O Android 14 adiciona suporte a imagens de High Dynamic Range (HDR) que retêm mais informações do sensor ao tirar uma foto, o que permite cores vibrantes e maior contraste. O Android usa o formato Ultra HDR, que é totalmente compatível com versões anteriores de imagens JPEG, permitindo que os apps interajam perfeitamente com imagens HDR, exibindo-as no intervalo dinâmico padrão (SDR, na sigla em inglês) conforme necessário.
A renderização dessas imagens na interface em HDR é feita automaticamente pelo framework
quando o app opta por usar a interface HDR para a janela de atividade, seja por uma
entrada de manifesto ou no momento da execução, chamando
Window.setColorMode(). Também é possível capturar imagens estáticas Ultra
HDR compactadas em dispositivos compatíveis. Com mais cores recuperadas
do sensor, a edição na pós-produção pode ser mais flexível. O
Gainmap associado a imagens Ultra HDR pode ser usado para renderizá-las
usando OpenGL ou Vulkan.
Zoom, foco, pós-visualização e muito mais nas extensões de câmera
O Android 14 atualiza e melhora as extensões de câmera, permitindo que os apps processem imagens em tempos mais longos, o que melhora as imagens usando algoritmos de computação intensiva, como a fotografia com pouca luz em dispositivos compatíveis. Esses recursos oferecem aos usuários uma experiência ainda mais robusta ao usar os recursos de extensão da câmera. Confira alguns exemplos dessas melhorias:
- A estimativa de latência de processamento de captura estática dinâmica fornece estimativas de latência de captura estática muito mais precisas com base nas condições atuais da cena e do ambiente. Chame
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()para receber um objetoStillCaptureLatencycom dois métodos de estimativa de latência. O métodogetCaptureLatency()retorna a latência estimada entreonCaptureStartedeonCaptureProcessStarted(), e o métodogetProcessingLatency()retorna a latência estimada entreonCaptureProcessStarted()e o frame processado final que está disponível. - Suporte a callbacks de progresso de captura para que os apps possam mostrar o progresso
atual de operações de processamento de captura de longa duração. É possível verificar
se esse recurso está disponível com
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailable. Se estiver, implemente o callbackonCaptureProcessProgressed(), que tem o progresso (de 0 a 100) transmitido como um parâmetro. Metadados específicos da extensão, como
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTHpara discar a quantidade de um efeito de extensão, como a quantidade de desfoque do plano de fundo comEXTENSION_BOKEH.Recurso de visualização pós-captura para captura de fotos em extensões de câmera, que fornece uma imagem menos processada mais rapidamente do que a imagem final. Se uma extensão aumentar a latência de processamento, uma imagem pós-visualização poderá ser fornecida como um marcador de posição para melhorar a UX e ser trocada posteriormente pela imagem final. Você pode verificar se esse recurso está disponível com
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable. Em seguida, você pode transmitir umOutputConfigurationparaExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration.Compatibilidade com
SurfaceView, permitindo um caminho de renderização de visualização mais otimizado e eficiente em termos de energia.Suporte a toque para focar e zoom durante o uso da extensão.
Zoom no sensor
Quando REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE em
CameraCharacteristics contém
SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW, o app
pode usar recursos avançados do sensor para fornecer a um fluxo RAW cortado os mesmos
pixels do campo de visão completo usando um CaptureRequest
com um destino RAW que tenha o caso de uso do fluxo definido como
CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW.
Ao implementar os controles de substituição de solicitação, a câmera atualizada oferece aos usuários
o controle de zoom antes mesmo que outros controles da câmera estejam prontos.
Áudio USB sem perdas
O Android 14 oferece suporte a formatos de áudio sem perda para experiências
de áudio de alta qualidade com fones de ouvido com fio USB. É possível consultar um dispositivo USB para saber os
atributos de mixer preferidos, registrar um listener para mudanças nos atributos
de mixer preferidos e configurar atributos de mixer usando a
classe AudioMixerAttributes. Essa classe representa o
formato, como máscara de canal, taxa de amostragem e comportamento do mixer de áudio. A
classe permite que o áudio seja enviado diretamente, sem mixagem,
ajuste de volume ou efeitos de processamento.
Produtividade e ferramentas para desenvolvedores
Credential Manager
O Android 14 adiciona o Gerenciador de credenciais como uma API da plataforma, com suporte adicional para dispositivos com o Android 4.4 (nível 19 da API) por meio de uma biblioteca Jetpack que usa o Google Play Services. O objetivo do Gerenciador de credenciais é facilitar o login para os usuários com APIs que extraem e armazenam credenciais com provedores de credenciais configurados pelo usuário. O Gerenciador de credenciais oferece suporte a vários métodos de login, incluindo nome de usuário e senha, chaves de acesso e soluções de login federadas (como o recurso Fazer login com o Google) em uma única API.
As chaves de acesso oferecem muitas vantagens. Por exemplo, as chaves de acesso são criadas com base nos padrões do setor, podem funcionar em diferentes sistemas operacionais e ecossistemas de navegadores e podem ser usadas em sites e apps.
Para mais informações, consulte a documentação do Gerenciador de credenciais e das chaves de acesso e o post do blog sobre o Gerenciador de credenciais e as chaves de acesso.
Conexão Saúde
A Conexão Saúde é um repositório no dispositivo para dados de saúde e condicionamento físico do usuário. Ele permite que os usuários compartilhem dados entre os apps favoritos, com um único lugar para controlar quais dados eles querem compartilhar com esses apps.
Em dispositivos com versões anteriores ao Android 14, o app Conexão Saúde está disponível para download na Google Play Store. A partir do Android 14, a Conexão Saúde faz parte da plataforma e recebe atualizações por meio das atualizações do sistema do Google Play sem precisar de um download separado. Com isso, a Conexão Saúde pode ser atualizada com frequência, e seus apps podem contar com a Conexão Saúde disponível em dispositivos com o Android 14 ou mais recente. Os usuários podem acessar a Conexão Saúde nas configurações do dispositivo, com controles de privacidade integrados às configurações do sistema.
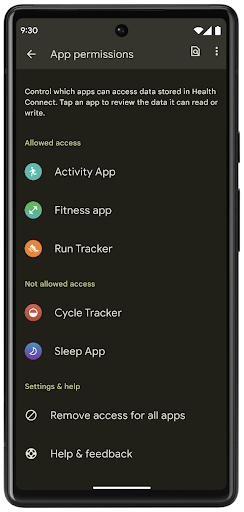
A Conexão Saúde inclui vários novos recursos no Android 14, como rotas de exercícios, permitindo que os usuários compartilhem uma rota do treino que pode ser visualizada em um mapa. Uma rota é definida como uma lista de locais salvos em um período de tempo, e o app pode inserir rotas em sessões de exercício, vinculando-as uma à outra. Para garantir que os usuários tenham controle total sobre esses dados sensíveis, eles precisam permitir o compartilhamento de rotas individuais com outros apps.
Para mais informações, consulte a documentação da Conexão Saúde e a postagem do blog Novidades no Android Health.
Atualizações do OpenJDK 17
O Android 14 continua o trabalho de atualizar as principais bibliotecas do Android para se alinhar aos recursos das versões mais recentes do LTS do OpenJDK, incluindo atualizações de bibliotecas e suporte à linguagem Java 17 para desenvolvedores de apps e plataformas.
Os seguintes recursos e melhorias estão incluídos:
- Aproximadamente 300 classes
java.baseforam atualizadas para oferecer suporte ao Java 17. - Blocos de texto, que introduzem literais de string de várias linhas à linguagem de programação Java.
- Correspondência de padrão para instanceof, que permite que um objeto
seja tratado como um tipo específico em uma
instanceofsem nenhuma outra variável. - Classes seladas, que permitem restringir quais classes e interfaces podem estender ou implementar essas classes.
Graças às atualizações do sistema do Google Play (Projeto Mainline), mais de 600 milhões de dispositivos podem receber as atualizações mais recentes do Android Runtime (ART), que incluem essas mudanças. Isso faz parte do nosso compromisso de oferecer aos apps um ambiente mais consistente e seguro em todos os dispositivos, com novos recursos para os usuários, independente da versão da plataforma.
Java e OpenJDK são marcas registradas da Oracle e/ou afiliadas.
Melhorias para app stores
O Android 14 apresenta várias APIs PackageInstaller que
permitem que as app stores melhorem a experiência do usuário.
Solicitar aprovação da instalação antes do download
A instalação ou atualização de um app pode exigir a aprovação do usuário.
Por exemplo, quando um instalador que usa a permissão
REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES tenta instalar um
novo app. Nas versões anteriores do Android, as app stores só podem solicitar a aprovação do usuário
depois que os APKs são gravados na sessão de instalação e a
sessão é confirmada.
A partir do Android 14, o método requestUserPreapproval()
permite que os instaladores solicitem a aprovação do usuário antes de confirmar a sessão
de instalação. Essa melhoria permite que a app store adie o download de APKs até
que a instalação seja aprovada pelo usuário. Além disso, depois que um usuário
aprova a instalação, a app store pode fazer o download e instalar o app em
segundo plano sem interromper o usuário.
Reivindicar a responsabilidade por atualizações futuras
O método setRequestUpdateOwnership() permite que um instalador
indique ao sistema que pretende ser responsável por futuras atualizações
de um app que ele está instalando. Esse recurso permite a aplicação da propriedade
da atualização, ou seja, apenas o proprietário da atualização pode
instalar atualizações automáticas no app. A aplicação da propriedade da atualização ajuda a
garantir que os usuários recebam atualizações apenas da app store esperada.
Qualquer outro instalador, incluindo aqueles que usam a permissão
INSTALL_PACKAGES, precisa receber aprovação explícita do usuário
para instalar uma atualização. Se um usuário decidir continuar com uma
atualização de outra fonte, a propriedade da atualização será perdida.
Atualizar apps em momentos menos incômodos
Geralmente, as app stores não querem atualizar um app que está em uso, porque isso encerra os processos em execução e pode interromper o que o usuário está fazendo.
A partir do Android 14, a API InstallConstraints
oferece aos instaladores uma maneira de garantir que as atualizações do app ocorram em um
momento oportuno. Por exemplo, uma app store pode chamar o método
commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet()
para garantir que uma atualização só será confirmada quando o usuário não estiver mais
interagindo com o app em questão.
Instalar divisões opcionais de forma simples
Com os APKs divididos, os recursos de um app podem ser enviados em arquivos APK separados
em vez de como um APK monolítico. Os APKs divididos permitem que as app stores otimizem a
entrega de diferentes componentes do app. Por exemplo, app stores podem otimizar
com base nas propriedades do dispositivo de destino. A
API PackageInstaller oferece
suporte a divisões desde a
apresentação no nível 22 da API.
No Android 14, o método setDontKillApp() permite que um
instalador indique que os processos em execução do app não serão encerrados quando
novas divisões forem instaladas. As app stores podem usar esse recurso para instalar
novos recursos enquanto o usuário está usando o app.
Pacotes de metadados do app
A partir do Android 14, o instalador do pacote do Android permite que você especifique os metadados do app, como práticas de segurança de dados, que serão incluídos em páginas de app stores, como o Google Play.
Detectar quando usuários fazem capturas de tela no dispositivo
Para criar uma experiência mais padronizada para detectar capturas de tela, o Android 14 apresenta uma API de detecção de capturas de tela que preserva a privacidade. Ela permite que os apps registrem callbacks por atividade. Esses callbacks são invocados, e o usuário é notificado quando faz uma captura de tela enquanto a atividade está visível.
Experiência do usuário
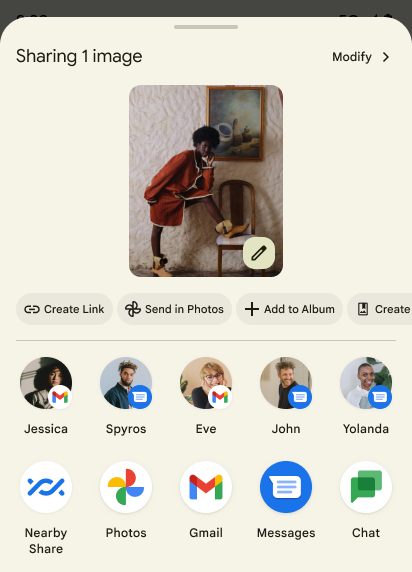
Ações personalizadas e melhoria na classificação do Sharesheet
O Android 14 atualiza o Sharesheet do sistema para oferecer suporte a ações personalizadas do app e resultados de visualização mais informativos para os usuários.
Adicionar ações personalizadas
Com o Android 14, o app pode adicionar ações personalizadas ao Sharesheet do sistema que ele invoca.
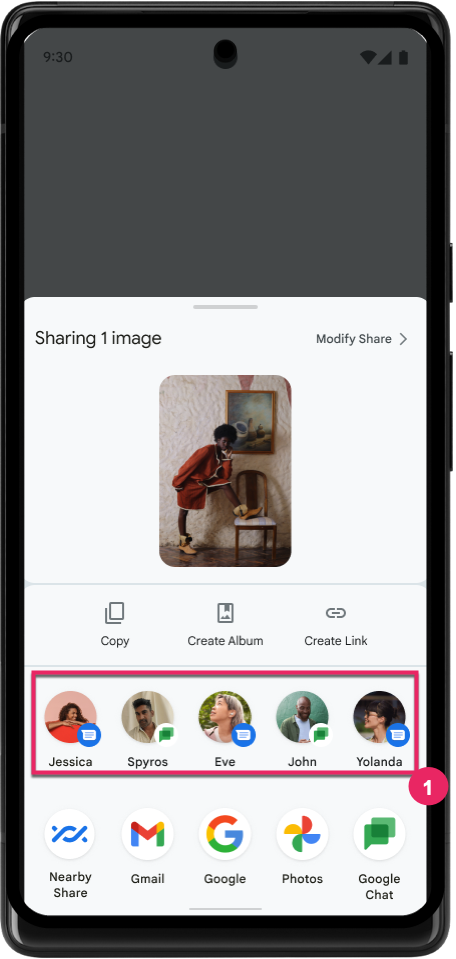
Melhorar a classificação dos alvos de compartilhamento direto
O Android 14 usa mais indicadores de apps para determinar a classificação dos alvos de compartilhamento diretos a fim de apresentar resultados mais úteis para o usuário. Para fornecer o indicador mais útil para a classificação, siga as orientações para melhorar a classificação dos seus alvos de compartilhamento direto. Os apps de comunicação também podem informar o uso de atalhos para mensagens de entrada e saída.
Suporte a animações de voltas preditivas integradas e personalizadas
O Android 13 introduziu a animação de volta preditiva à tela inicial por trás de uma opção do desenvolvedor. Quando usada em um app com suporte para a opção para desenvolvedor ativada, deslizar para trás mostra uma animação indicando que o gesto de retorno sai do app de volta à tela inicial.
O Android 14 inclui várias melhorias e novas orientações para a volta preditiva:
- Você pode configurar
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=truepara ativar as animações do sistema de volta preditiva por atividade em vez de para todo o app. - Adicionamos novas animações do sistema para acompanhar a animação de retorno à tela inicial do Android 13. As novas animações do sistema são entre atividades e tarefas, que são recebidas automaticamente após a migração para a volta preditiva.
- Adicionamos novas animações do componente Material Design para páginas inferiores, páginas laterais e pesquisa.
- Desenvolvemos orientações de design para a criação de transições e animações personalizadas no app.
- Adicionamos novas APIs para oferecer suporte a animações de transição personalizadas no app:
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- Use
overrideActivityTransitionem vez deoverridePendingTransitionpara transições que respondem à medida que o usuário desliza de volta.
Com esta versão de pré-lançamento do Android 14, todos os recursos de volta preditiva permanecem por trás de uma opção para desenvolvedores. Consulte o guia do desenvolvedor para migrar seu app para a volta preditiva e o guia do desenvolvedor para criar transições personalizadas no app.
Substituições por app do fabricante de dispositivos de tela grande
As substituições por app permitem que os fabricantes mudem o comportamento dos apps em dispositivos de tela grande. Por exemplo, a substituição FORCE_RESIZE_APP instrui o sistema a redimensionar o app para que se ajuste às dimensões de exibição (evitando o modo de compatibilidade de tamanho), mesmo que resizeableActivity="false" esteja definido no manifesto do app.
As substituições têm como objetivo melhorar a experiência do usuário em telas grandes.
As novas propriedades do manifesto permitem desativar algumas substituições do fabricante do dispositivo para o app.
Substituições por app para usuários de telas grandes
As substituições por app mudam o comportamento dos apps em dispositivos de tela grande. Por exemplo, a substituição do fabricante do dispositivo OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE define a proporção do app como 16:9, independente da configuração dele.
O Android 14 QPR1 permite que os usuários apliquem substituições por app usando um novo menu de configurações em dispositivos de tela grande.
Compartilhamento de tela de app
O compartilhamento de tela de apps permite que os usuários compartilhem uma janela de app em vez de toda a tela do dispositivo durante a gravação do conteúdo da tela.
Com o compartilhamento de tela do app, a barra de status, a barra de navegação, as notificações e outros elementos da interface do sistema são excluídos da tela compartilhada. Somente o conteúdo do app selecionado é compartilhado.
O compartilhamento de tela de apps melhora a produtividade e a privacidade, permitindo que os usuários executem vários apps, mas limitem o compartilhamento de conteúdo a um único app.
Resposta inteligente com tecnologia de LLM no Gboard do Pixel 8 Pro
Em dispositivos Pixel 8 Pro com a versão de dezembro, os desenvolvedores podem testar respostas inteligentes de maior qualidade no Gboard com modelos de linguagem grandes (LLMs) no dispositivo em execução no Google Tensor.
Esse recurso está disponível como uma prévia limitada para o inglês dos EUA no WhatsApp, no Line e no KakaoTalk. É necessário usar um dispositivo Pixel 8 Pro com o Gboard como teclado.
Para testar, primeiro ative o recurso em Configurações > Opções do desenvolvedor > Configurações do AICore > Ativar o AICore persistente.
Em seguida, abra uma conversa em um app compatível para conferir a resposta inteligente com LLM na faixa de sugestões do Gboard em resposta às mensagens recebidas.
Gráficos
Os caminhos podem ser consultados e interpolados
A API Path do Android é um mecanismo avançado e flexível para
criar e renderizar gráficos vetoriais, com a capacidade de traçar ou preencher um
caminho, construir um caminho a partir de segmentos de linha ou curvas quadráticas ou cúbicas, realizar
operações booleanas para conseguir formas ainda mais complexas ou todas essas
formas simultaneamente. Uma limitação é a capacidade de descobrir o que está
presente em um objeto de caminho. Os componentes internos do objeto são opacos para autores de chamadas
após a criação.
Para criar um Path, chame métodos como
moveTo(), lineTo() e
cubicTo() para adicionar segmentos de caminho. Mas não há uma maneira de perguntar a esse caminho quais são os segmentos. Portanto, você precisa manter essas informações no momento da criação.
A partir do Android 14, é possível consultar caminhos para descobrir o que há dentro deles.
Primeiro, você precisa conseguir um objeto PathIterator usando a API Path.getPathIterator:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
Em seguida, chame PathIterator para iterar os segmentos um por um, recuperando todos os dados necessários para cada segmento. Este exemplo
usa objetos PathIterator.Segment, que empacotam os dados
para você:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
O PathIterator também tem uma versão não alocada de next(), em que é possível transmitir
um buffer para armazenar os dados dos pontos.
Um dos casos de uso importantes para consultar os dados Path é a interpolação. Por
exemplo, você pode querer animar (ou transformar) entre dois caminhos diferentes. Para
simplificar ainda mais esse caso de uso, o Android 14 também inclui o
método interpolate() em Path. Supondo que os dois caminhos tenham
a mesma estrutura interna, o método interpolate() cria um novo Path
com esse resultado interpolado. Este exemplo retorna um caminho com um formato que está
na metade do caminho (uma interpolação linear de 0,5) entre path e otherPath:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
A biblioteca graphics-path do Jetpack também permite APIs semelhantes em versões anteriores do Android.
Malhas personalizadas com shaders de vértice e fragmento
O Android já oferece suporte a renderização de malhas triangulares com sombreamento personalizado, mas o formato de malha de entrada foi limitado a algumas combinações de atributos predefinidas. O Android 14 adiciona suporte a malhas personalizadas, que podem ser definidas como triângulos ou faixas de triângulo, e podem ser indexadas, se necessário. Essas malhas são especificadas com atributos personalizados, incrementos de vértice, variação e sombreadores de vértice e fragmento escritos em AGSL.
O sombreador de vértice define as variações, como posição e cor, enquanto o
sombreador de fragmentos pode definir a cor do pixel, normalmente
usando as variações criadas pelo sombreador de vértice. Se a cor for fornecida pelo
shader de fragmentos, ela será mesclada com a cor Paint
atual usando o modo de mesclagem selecionado ao
desenhar a malha. Os uniformes podem ser transmitidos
para os sombreadores de fragmentos e vértices para mais flexibilidade.
Renderizador de buffer de hardware para Canvas
Para ajudar no uso da API Canvas do Android para desenhar com
aceleração de hardware em um HardwareBuffer, Android 14
apresenta o HardwareBufferRenderer. Essa API é
particularmente útil quando seu caso de uso envolve a comunicação com o compositor
do sistema usando SurfaceControl para renderização
de baixa latência.

