Android 15 では、デベロッパー向けに優れた機能と API が導入されました。以下のセクションでは、これらの機能の概要を説明し、関連する API を使い始めるうえで役立つ情報を提供します。
追加、変更、削除された API の詳細な一覧については、API 差分レポートをご覧ください。追加された API について詳しくは、Android API リファレンスをご覧ください。Android 15 の場合は、API レベル 35 で追加された API をご確認ください。プラットフォームの変更がアプリに影響する領域については、Android 15 の動作変更(Android 15 をターゲットとするアプリの場合とすべてのアプリの場合)をご確認ください。
カメラとメディア
Android 15 には、カメラとメディアのエクスペリエンスを向上させるさまざまな機能が含まれています。また、クリエイターが Android でビジョンを実現できるようサポートするツールやハードウェアにアクセスできます。
Android のメディアとカメラの最新機能とデベロッパー ソリューションについて詳しくは、Google I/O の Building modern Android media and camera experiences の講演をご覧ください。
Low Light Boost
Android 15 では、Camera 2 と夜間モードのカメラ拡張機能の両方で使用できる自動露出モードである Low Light Boost が導入されています。Low Light Boost は、暗い場所でプレビュー ストリームの露出を調整します。これは、夜間モードのカメラ拡張機能が静止画像を作成する方法とは異なります。夜間モードでは、連続撮影した写真を組み合わせて、1 枚の補正済み画像を作成します。夜間モードは静止画像の作成に非常に適していますが、連続したフレーム ストリームを作成することはできません。一方、低照度ブーストは連続したフレーム ストリームを作成できます。そのため、ローライト ブーストにより、次のようなカメラ機能が有効になります。
- 画像プレビューが強化され、暗い場所でも写真の構図を決めやすくなりました
- 暗い場所での QR コードのスキャン
Low Light Boost を有効にすると、明るさが低いときに自動的にオンになり、明るくなるとオフになります。
プレビュー ストリームをオフにして動画を録画することで、暗い場所でも明るい動画を保存できます。
詳しくは、Low Light Boost をご覧ください。
アプリ内カメラ コントロール
Android 15 では、サポート対象デバイスのカメラ ハードウェアとそのアルゴリズムをより細かく制御するための拡張機能が追加されました。
HDR ヘッドルーム制御
Android 15 は、基盤となるデバイスの機能とパネルのビット深度に適した HDR ヘッドルームを指定します。1 つの HDR サムネイルを表示するメッセージ アプリなど、SDR コンテンツが多いページでは、この動作により、SDR コンテンツの明るさが認識されなくなる可能性があります。Android 15 では、setDesiredHdrHeadroom を使用して HDR ヘッドルームを制御し、SDR コンテンツと HDR コンテンツのバランスをとることができます。
音量調節

Android 15 では、音量の不一致を回避し、コンテンツを切り替える際にユーザーが音量を絶えず調整する必要がないように、CTA-2075 音量標準のサポートが導入されました。このシステムは、出力デバイス(ヘッドフォンとスピーカー)の既知の特性と、AAC オーディオ コンテンツで利用可能なラウドネス メタデータを利用して、音声のラウドネスとダイナミック レンジ圧縮レベルをインテリジェントに調整します。
この機能を有効にするには、
AAC コンテンツを編集して、アプリでプラットフォーム機能を有効にします。そのために、
LoudnessCodecController オブジェクトをインスタンス化する
音声とともに create ファクトリ メソッドを呼び出す
関連付けられている AudioTrack のセッション ID。
自動的にオーディオ アップデートの適用が開始されます。OnLoudnessCodecUpdateListener を渡して、ラウドネス パラメータを変更またはフィルタリングしてから、MediaCodec に適用できます。
// Media contains metadata of type MPEG_4 OR MPEG_D
val mediaCodec = …
val audioTrack = AudioTrack.Builder()
.setSessionId(sessionId)
.build()
...
// Create new loudness controller that applies the parameters to the MediaCodec
try {
val lcController = LoudnessCodecController.create(mSessionId)
// Starts applying audio updates for each added MediaCodec
}
また、AndroidX media3 ExoPlayer もアップデートされ、
シームレスなアプリ統合のための LoudnessCodecController API。
仮想 MIDI 2.0 デバイス
Android 13 では、ユニバーサル MIDI パケット(UMP)を使用して通信する USB 経由の MIDI 2.0 デバイスへの接続のサポートが追加されました。Android 15 では、UMP のサポートを仮想 MIDI アプリに拡張し、コンポーズ アプリが USB MIDI 2.0 デバイスと同様に、仮想 MIDI 2.0 デバイスとしてシンセサイザー アプリを制御できるようにしました。
AV1 ソフトウェア デコードの効率化

dav1d は、VideoLAN の人気の高い AV1 ソフトウェア デコーダで、ハードウェアで AV1 デコードをサポートしていない Android デバイスで利用できます。dav1d は従来の AV1 ソフトウェア デコーダよりも最大 3 倍のパフォーマンスを発揮し、一部のローエンド デバイスやミッドレンジ デバイスを含む、より多くのユーザーが HD AV1 を再生できるようになります。
アプリは、dav1d の名前 "c2.android.av1-dav1d.decoder" で呼び出して、dav1d の使用をオプトインする必要があります。dav1d は、今後のアップデートでデフォルトの AV1 ソフトウェア デコーダになります。このサポートは標準化され、Google Play システム アップデートを受信する Android 11 デバイスにバックポートされています。
デベロッパーの生産性とツール
生産性向上のための取り組みのほとんどは、Android Studio、Jetpack Compose、Android Jetpack ライブラリなどのツールを中心に行われていますが、プラットフォームでビジョンをより簡単に実現できる方法も常に探しています。
OpenJDK 17 の更新
Android 15 では、最新の OpenJDK LTS リリースの機能に合わせて Android のコアライブラリを更新する取り組みが引き続き行われています。
主な機能と改善点は次のとおりです。
- NIO バッファに関する利便性の向上
- ストリーム
- 追加の
mathメソッドとstrictmathメソッド utilパッケージの更新(順序付きのcollection、map、setなど)DeflaterでのByteBufferのサポートX500PrivateCredentialやセキュリティ キーの更新などのセキュリティ アップデート
これらの API は、Android 12(API レベル 31)以降を搭載し、Google Play システム アップデートを受け取っている 10 億台を超えるデバイスで更新されるため、最新のプログラミング機能をターゲットにできます。
PDF の改善
Android 15 では、PdfRenderer が大幅に改善されています。
APIアプリには、パスワードで保護されたファイルのレンダリング、アノテーション、フォームの編集、検索、コピー付きの選択などの高度な機能を組み込むことができます。リニア化された PDF の最適化がサポートされているため、ローカル PDF の表示が高速化され、リソースの使用量が削減されます。Jetpack PDF ライブラリでは、これらの API を使用して PDF を簡単に追加できます。
表示機能を追加できます。
PdfRenderer は、プラットフォームのリリースに依存せずに Google Play システム アップデートを使用して更新できるモジュールに移動されました。また、Android 15 より前のバージョンの API サーフェス(PdfRendererPreV)を作成することで、Android 11(API レベル 30)へのこれらの変更をサポートしています。
言語の自動切り替えの改善
Android 14 では、言語間の自動切り替えによる音声でのオンデバイスの複数言語認識が追加されましたが、特に 2 つの発話の間に短い休止時間がある場合、単語が欠落する可能性があります。Android 15 では、アプリがユースケースに合わせてこの切り替えを調整できるように、追加のコントロールが追加されています。EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_INITIAL_ACTIVE_DURATION_TIME_MILLIS は自動切り替えを音声セッションの開始に限定します。EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_MATCH_SWITCHES は、指定した回数切り替えた後に言語切り替えを無効にします。これらのオプションは、セッション中に自動検出される単一の言語が話されることが予想される場合に特に便利です。
OpenType 可変フォント API の改善
Android 15 では、OpenType 可変フォントのユーザビリティが改善されています。新しい
重み軸を指定しない可変フォントからの FontFamily インスタンス
buildVariableFamily API の場合。テキスト レンダラが値をオーバーライドする
の wght 軸を、表示テキストに合わせて調整します。
API を使用すると、Typeface の作成コードが大幅に簡素化されます。
Kotlin
val newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build()
Java
Typeface newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build();
以前は、同じ Typeface を作成するには、より多くのコードが必要でした。
Kotlin
val oldTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build()) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ).build() ).build()
Java
Typeface oldTypeface = new Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ) .build() ).build();
新旧両方の API を使用して Typeface を作成する方法の例を次に示します。
レンダリング:
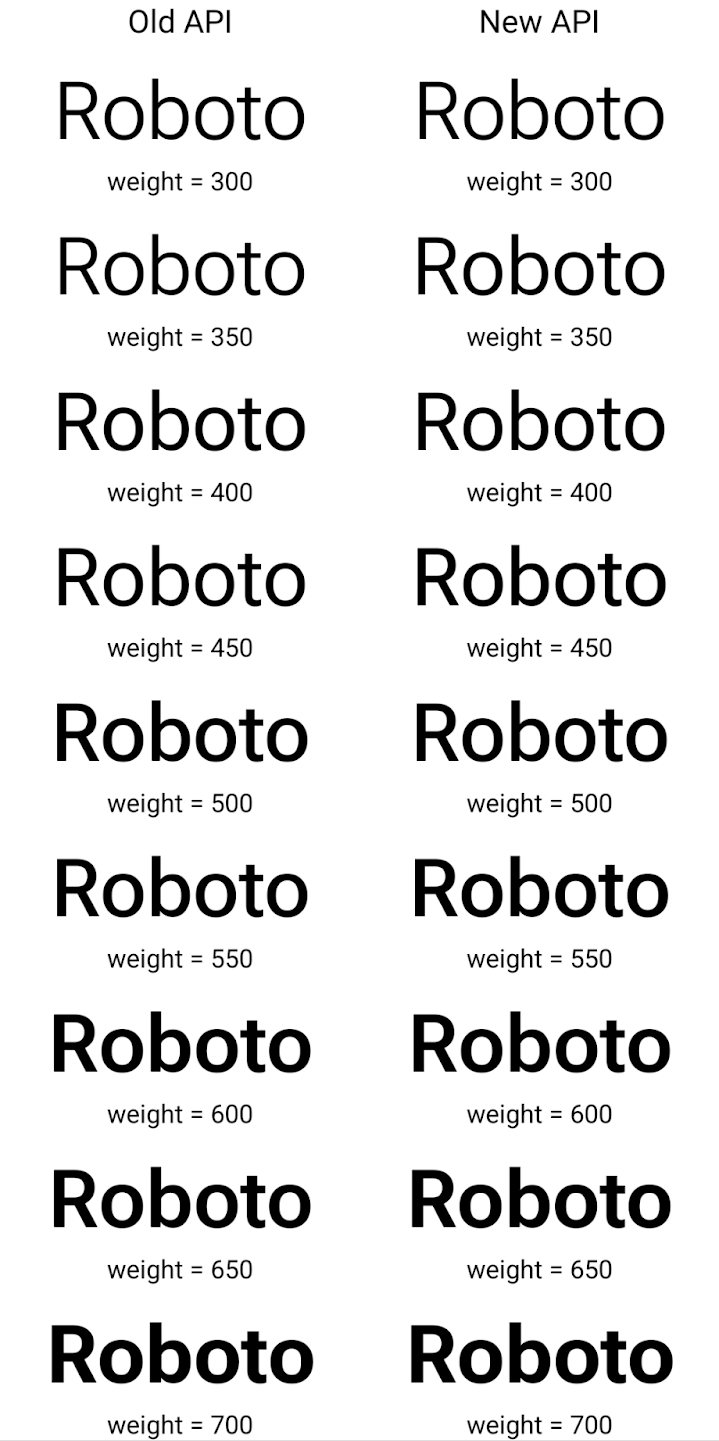
この例では、古い API で作成された Typeface に
350、450、550、650 のフォント ウェイトを正確に作成
Font インスタンスなので、レンダラは最も近い重みにフォールバックします。たとえば
この場合、350 ではなく 300 がレンダリングされ、450 ではなく 400 がレンダリングされます。
できます。一方、新しい API で作成された Typeface は、
指定された重みに対する Font インスタンス。350 度は正確な重みがレンダリングされます。
450、550、650 も選択できます
きめ細かい改行制御
Android 15 以降では、TextView と基盤となる行ブレーカーは、テキストの特定の部分を同じ行に保持して読みやすさを向上させることができます。この改行のカスタマイズを利用するには、文字列リソースまたは createNoBreakSpan で <nobreak> タグを使用します。同様に、<nohyphen> タグまたは createNoHyphenationSpan を使用して、単語をハイフネーションから除外することもできます。
たとえば、次の文字列リソースには改行が含まれていないため、「Google Pixel 8 Pro」というテキストが望ましくない場所で改行されてレンダリングされます。
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind Pixel 8 Pro.</string>
</resources>
一方、この文字列リソースには <nobreak> タグが含まれています。このタグは「Google Pixel 8 Pro」というフレーズを折り返し、改行を防ぎます。
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind <nobreak>Pixel 8 Pro.</nobreak></string>
</resources>
次の図に、これらの文字列のレンダリング方法の違いを示します。

<nobreak> タグを使用して折り返されていないテキスト行のレイアウト。
<nobreak> タグを使用して折り返されている、同じ行のテキストのレイアウト。アプリのアーカイブ
Android と Google Play は最後に、アプリのアーカイブのサポートを発表しました。 年間で、ユーザーは部分的削除によって空き容量を増やすことができます。 Android アプリを使用して公開された、デバイスの使用頻度の低いアプリ Google Play でセット購入。Android 15 はアプリのアーカイブを OS レベルでサポート アーカイブ解除が可能になり、すべてのアプリストアで容易に実装できるようになります。
REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES 権限を持つアプリは、
PackageInstaller requestArchive メソッドを使用して、メッセージの
インストール済みのアプリ パッケージ。APK とキャッシュされたファイルは削除されるが、
保護します。アーカイブされたアプリは、
LauncherApps APIそうしたケースがあることを強調する UI が
アプリがアーカイブされます。ユーザーがアーカイブされたアプリをタップすると、担当インストーラにアーカイブを解除するようリクエストが送信されます。復元プロセスは ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED ブロードキャストによってモニタリングできます。
開発者向けオプションを使用してデバイスで 16 KB モードを有効にする
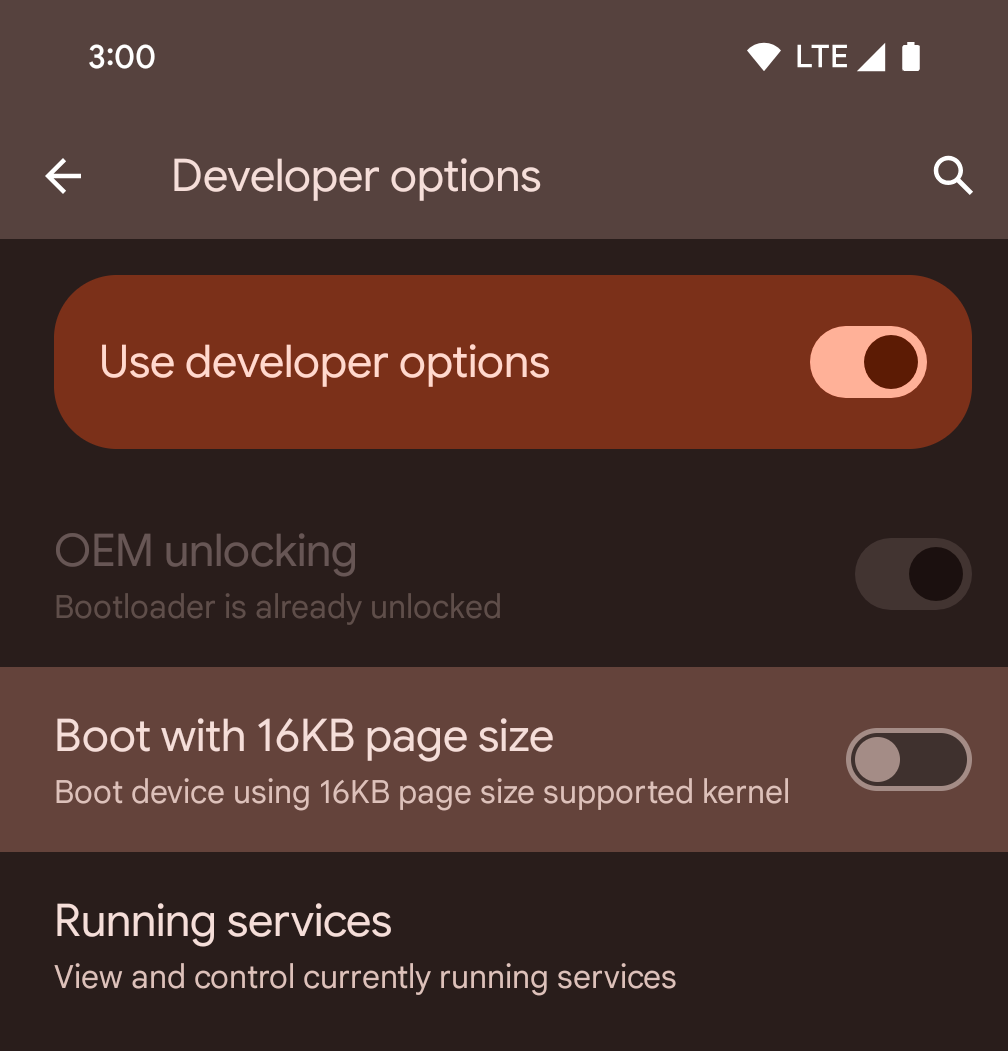
[16 KB ページサイズで起動する] デベロッパー オプションを切り替えて、デバイスを 16 KB モードで起動します。
Android 15 の QPR バージョンでは、特定のデバイスで利用可能なデベロッパー オプションを使用して、デバイスを 16 KB モードで起動し、オンデバイス テストを実行できます。開発者向けオプションを使用する前に、[設定] > [システム] > [ソフトウェア アップデート] に移動して、利用可能なアップデートを適用します。
この開発者向けオプションは、次のデバイスで利用できます。
Google Pixel 8、Google Pixel 8 Pro(Android 15 QPR1 以降)
Google Pixel 8a(Android 15 QPR1 以降)
Google Pixel 9、Google Pixel 9 Pro、Google Pixel 9 Pro XL(Android 15 QPR2 ベータ版 2 以降)
グラフィック
Android 15 では、ANGLE や Canvas グラフィック システムの追加など、最新のグラフィックの改善が導入されています。
Android の GPU アクセスの近代化

Android ハードウェアは、コア OS が単一の CPU で実行され、GPU に固定関数パイプラインに基づく API を使用してアクセスされていた初期の頃からかなり進化しています。Vulkan® グラフィック API は、Android 7.0(API レベル 24)以降、NDK で利用可能になりました。最新の GPU ハードウェアをより適切に反映する低レベルの抽象化により、複数の CPU コアをサポートするようにスケーリングが改善され、CPU ドライバのオーバーヘッドが削減され、アプリのパフォーマンスが向上します。Vulkan は、すべての最新のゲームエンジンでサポートされています。
Vulkan は、Android の GPU への優先インターフェースです。そのため、Android 15 には、Vulkan 上で OpenGL® ES を実行するためのオプション レイヤとして ANGLE が含まれています。ANGLE に移行することで、Android OpenGL の実装が標準化され、互換性が向上し、場合によってはパフォーマンスも向上します。Android 15 で [設定] -> [システム] -> [開発者向けオプション] -> [試験運用版: ANGLE を有効にする] で開発者向けオプションを有効にすると、ANGLE で OpenGL ES アプリの安定性とパフォーマンスをテストできます。
Android ANGLE on Vulkan のロードマップ
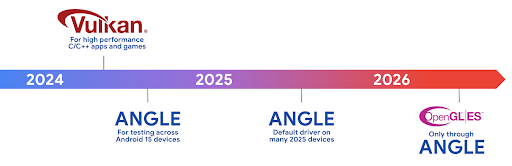
GPU スタックの効率化の一環として、今後はさらに多くの新しいデバイスで GL システム ドライバとして ANGLE を搭載する予定です。今後、OpenGL/ES は ANGLE でのみ利用可能になる見込みです。ただし、すべてのデバイスで OpenGL ES のサポートを継続する予定です。
推奨される次のステップ
デベロッパー オプションを使用して OpenGL ES の ANGLE ドライバを選択し、アプリをテストします。新しいプロジェクトでは、C/C++ に Vulkan を使用することを強くおすすめします。
キャンバスの改善点
Android 15 では、Android の Canvas グラフィック システムのモダナイゼーションを継続し、次の機能を追加しました。
Matrix44は、3D でキャンバスを操作するときに使用する座標変換用の 4x4 行列を提供します。clipShaderは現在のクリップと指定されたシェーダーを交差させ、clipOutShaderは現在のクリップとシェーダーの差分にクリップを設定します。どちらもシェーダーをアルファマスクとして扱います。これにより、複雑な形状を効率的に描画できます。
パフォーマンスとバッテリー
Android は、アプリのパフォーマンスと品質の向上を支援することに引き続き注力しています。Android 15 では、アプリ内のタスクの実行を効率化し、アプリのパフォーマンスを最適化し、アプリに関する分析情報を収集するのに役立つ API が導入されています。
バッテリー効率に関するベスト プラクティス、ネットワークと電力の使用量のデバッグ、Android 15 と最近のバージョンの Android でバックグラウンド作業のバッテリー効率を改善する方法について詳しくは、Google I/O の Android でのバックグラウンド作業のバッテリー効率の改善に関するトークをご覧ください。
ApplicationStartInfo API
以前のバージョンの Android では、アプリの起動は少し謎めいたものでした。アプリ内で、アプリがコールド スタート、ウォーム スタート、ホットスタートのいずれから開始されたかを判断することは困難でした。また、プロセスのフォーク、onCreate の呼び出し、最初のフレームの描画など、さまざまな起動フェーズでアプリが費やした時間を把握することも困難でした。Application クラスがインスタンス化されたときに、アプリがブロードキャスト、コンテンツ プロバイダ、ジョブ、バックアップ、起動完了、アラーム、Activity のいずれから開始されたかを把握する方法はありませんでした。
Android 15 の ApplicationStartInfo API には、これらに加えて多くの機能が用意されています。独自のタイムスタンプをフローに加えて、タイミング データを 1 か所で収集することもできます。指標の収集に加えて、ApplicationStartInfo を使用してアプリの起動を直接最適化することもできます。たとえば、ブロードキャストによりアプリの起動時に Application クラス内の UI 関連ライブラリをインスタンス化する必要がなくなります。
アプリサイズの詳細情報
Android 8.0(API レベル 26)以降、Android には、アプリのインストール サイズを 1 つのバイト数として要約する StorageStats.getAppBytes API が含まれています。これは、APK のサイズ、APK から抽出されたファイルのサイズ、デバイスで生成されたファイル(事前(AOT)コンパイル済みコードなど)の合計です。この数値は、アプリがストレージをどのように使用しているかを把握するうえではあまり有用ではありません。
Android 15 では StorageStats.getAppBytesByDataType([type]) API が追加され、APK ファイルの分割、AOT と高速化関連のコード、dex メタデータ、ライブラリ、ガイド付きプロファイルなど、アプリがそのスペースをどのように使用しているかを把握できるようになります。
アプリ管理のプロファイリング
Android 15 には ProfilingManager クラスが含まれています。これにより、ヒープダンプ、ヒープ プロファイル、スタック サンプリングなどのプロファイリング情報をアプリ内から収集できます。出力ファイルを識別するタグが指定されたコールバックがアプリに提供され、アプリのファイル ディレクトリに配信されます。この API は、パフォーマンスへの影響を最小限に抑えるためにレート制限を行います。
アプリでのプロファイリング リクエストの作成を簡素化するには、Core 1.15.0-rc01 以降で利用可能な、対応する Profiling AndroidX API を使用することをおすすめします。
SQLite データベースの改善
Android 15 では、Android の高度な機能を公開する SQLite API が導入されています。 基本的な SQLite エンジンを使用して、特定のパフォーマンスの問題をターゲットにできます。 使用しないでください。これらの API は、バージョンへの SQLite のアップデートに含まれています。 3.44.3。
特に大規模なデータベースを操作する場合や、レイテンシに敏感なクエリを実行する場合は、SQLite データベースを最大限に活用するために、SQLite パフォーマンスのベスト プラクティスを参照してください。
- 読み取り専用の遅延トランザクション:
読み取り専用(write ステートメントは含みません)、
beginTransactionReadOnly()、beginTransactionWithListenerReadOnly(SQLiteTransactionListener)読み取り専用のDEFERREDトランザクションを発行します。このようなトランザクションは相互に同時に実行できます。データベースが WAL モードの場合、IMMEDIATEトランザクションまたはEXCLUSIVEトランザクションと同時に実行できます。 - 行数と ID: 変更された行数を取得するための API が追加されました。
行または最後に挿入された行 ID のみを取得できます。
getLastChangedRowCount()は、現在のトランザクション内の最新の SQL ステートメントによって挿入、更新、削除された行の数を返します。getTotalChangedRowCount()は、現在の接続のカウントを返します。getLastInsertRowId()は、最後の行のrowidを返します。 現在の接続に挿入します。 - 未加工ステートメント: 便利なラッパーと、ラッパーで発生する追加の処理のオーバーヘッドをバイパスして、未加工の SQlite ステートメントを発行します。
Android Dynamic Performance Framework の更新
Android 15 では、Android Dynamic Performance Framework(ADPF)への投資が継続されています。ADPF は、ゲームやパフォーマンスを必要とするアプリが Android デバイスの電力システムや温度システムをより直接的に操作できるようにする API のセットです。サポートされているデバイスでは、Android 15 に ADPF 機能が追加されます。
- ヒント セッションの省電力モード。関連するスレッドでパフォーマンスよりも省電力を優先すべきことを示します。長時間実行されるバックグラウンド ワークロードに適しています。
- GPU と CPU の作業時間はヒント セッションで報告できるため、システムはワークロードの需要に最適に合わせて CPU と GPU の周波数を調整できます。
- サーマル ヘッドルームしきい値: ヘッドルーム予測に基づいて、サーマル スロットリングが発生する可能性のあるステータスを解釈します。
アプリやゲームで ADPF を使用する方法について詳しくは、ドキュメントをご覧ください。
プライバシー
Android 15 には、アプリ デベロッパーがユーザーのプライバシーを保護するのに役立つさまざまな機能が含まれています。
スクリーン レコーダーの検出
Android 15 では、それを検出するアプリのサポートが追加されています。 表示されます。アプリが遷移するたびにコールバックが呼び出される 画面録画内で表示 / 非表示の切り替えができます。アプリは 登録プロセスの UID が所有するアクティビティが、 表示されます。これにより、アプリが機密性の高い操作を実行している場合に、 録画中であることをユーザーに知らせることができます。
val mCallback = Consumer<Int> { state ->
if (state == SCREEN_RECORDING_STATE_VISIBLE) {
// We're being recorded
} else {
// We're not being recorded
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val initialState =
windowManager.addScreenRecordingCallback(mainExecutor, mCallback)
mCallback.accept(initialState)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
windowManager.removeScreenRecordingCallback(mCallback)
}
IntentFilter の機能の拡張
Android 15 では、UriRelativeFilterGroup を通じて、より正確な Intent 解決のサポートが組み込まれています。これには、それぞれ満たす必要がある一連の Intent マッチング ルール(URL クエリ パラメータ、URL フラグメント、ブロックルールや除外ルールなど)を形成する UriRelativeFilter オブジェクトのセットが含まれています。
これらのルールは、AndroidManifest XML ファイルで <uri-relative-filter-group> タグを使用して定義できます。必要に応じて、android:allow タグを含めることができます。これらのタグには、既存のデータタグ属性や android:query 属性、android:fragment 属性を使用する <data> タグを含めることができます。
AndroidManifest 構文の例を次に示します。
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="astore.com" />
<uri-relative-filter-group>
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="region=na" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="mobileoptout=true" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:fragmentPrefix="faq" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
</intent-filter>
プライベート スペース
プライベート スペースを利用すると、追加の認証が必要な独立した空間をデバイス上に作成し、そこにプライベートなアプリを配置することでセキュリティを確保することができます。プライベート スペースでは、独立したユーザー プロファイルを使用します。プライベート スペースにデバイスロックを使うか別のロックを使うかは、ユーザーが選択できます。
プライベート スペース内のアプリはランチャーの別のコンテナに表示され、プライベート スペースがロックされているときは、[最近] ビュー、通知、設定、および他のアプリで非表示になります。ユーザーが生成したりダウンロードしたりしたコンテンツ(メディアやファイルなど)やアカウントは、プライベート スペースとメインスペースで分離されます。プライベート スペースのロックが解除されている場合、システムの Sharesheet と写真選択ツールを使用すると、アプリは全スペースのコンテンツにアクセスできます。
ユーザーは、既存のアプリとそのデータをプライベート スペースに移動することはできません。代わりに、ユーザーはプライベート スペースでインストール オプションを選択し、任意のアプリストアを使用してアプリをインストールします。プライベート スペースのアプリは、メインスペースのアプリとは別のコピーとしてインストールされます(同じアプリの新しいコピー)。
ユーザーがプライベート スペースをロックすると、プロファイルは停止します。プロファイルが停止している間、プライベート スペース内のアプリはアクティブではなく、通知の表示など、フォアグラウンド アクティビティやバックグラウンド アクティビティを実行できません。
アプリが次のいずれかのカテゴリに該当する場合は特に、アプリが想定どおりに動作することを確認するために、プライベート スペースでアプリをテストすることをおすすめします。
- 仕事用プロファイル用のロジックを含むアプリ: メイン プロファイルにないアプリのインストール済みコピーが仕事用プロファイルにあることを前提としています。
- 医療アプリ
- ランチャー アプリ
- アプリストアのアプリ
選択した写真へのアクセスに関するユーザーの最新の選択をクエリする
アプリでは、最近選択した写真や動画のみが、
メディア権限への部分的なアクセスが付与されている。この機能を使用すると、
アプリが頻繁に写真へのアクセスをリクエストする場合、
できます。アプリでこの機能を使用するには、ContentResolver を介して MediaStore をクエリするときに QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY 引数を有効にします。
Kotlin
val externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external") val mediaColumns = arrayOf( FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE, ) val queryArgs = bundleOf( // Return only items from the last selection (selected photos access) QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY to true, // Sort returned items chronologically based on when they were added to the device's storage QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER to "${FileColumns.DATE_ADDED} DESC", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION to "${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ? OR ${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ?", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS to arrayOf( FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE.toString(), FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.toString() ) )
Java
Uri externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external"); String[] mediaColumns = { FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE }; Bundle queryArgs = new Bundle(); queryArgs.putBoolean(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, true); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER, FileColumns.DATE_ADDED + " DESC"); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION, FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ? OR " + FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ?"); queryArgs.putStringArray(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS, new String[] { String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE), String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) });
Android 版プライバシー サンドボックス
Android 15 には、最新バージョンの Android 版プライバシー サンドボックスが組み込まれた最新の Android Ad Services 拡張機能が含まれています。この追加は、ユーザーのプライバシーを保護し、モバイルアプリで効果的なパーソナライズド広告のエクスペリエンスを可能にする技術を開発するための取り組みの一環です。プライバシー サンドボックスのページでは、Android 版プライバシー サンドボックスのデベロッパー プレビュー プログラムとベータ版プログラムについて詳しく説明しています。
ヘルスコネクト
Android 15 では、 Android のヘルスコネクト: 安全で一元化された アプリが収集した健康とフィットネスに関するデータを管理、共有するプラットフォームです。今回の更新 フィットネス全体に対応するデータ型のサポートを追加します。 栄養、皮膚温、トレーニング計画など。
皮膚温の測定では、ウェアラブル デバイスなどの測定デバイスからより正確な温度データを保存して共有できます。
トレーニング プランは、ユーザーがフィットネスの目標を達成できるようにするための体系的なワークアウト プランです。トレーニング プランのサポートには、さまざまな達成目標とパフォーマンス目標が含まれます。
Android のヘルスコネクトの最新アップデートについて詳しくは、以下をご覧ください。 Android で適応性の高いエクスペリエンスを構築する Google I/O の健康に関するトピックです。
アプリの画面共有
Android 15 ではアプリの画面共有がサポートされているため、デバイスの画面全体ではなく、アプリのウィンドウのみを共有または録画できます。この機能は Android 14 QPR2 で初めて有効になり、アプリでアプリの画面共有エクスペリエンスをカスタマイズできる MediaProjection コールバックが含まれています。Android 14(API レベル 34)以降をターゲットとするアプリの場合、MediaProjection キャプチャ セッションごとにユーザーの同意が必要になります。
ユーザー エクスペリエンスとシステム UI
Android 15 では、アプリ デベロッパーとユーザーがニーズに合わせてデバイスを構成するための制御と柔軟性が向上しています。
Android 15 の最新の改善点を使用してアプリのユーザー エクスペリエンスを向上させる方法について詳しくは、Google I/O の Android アプリのユーザー エクスペリエンスを高めるをご覧ください。
Generated Previews API によるリッチなウィジェット プレビュー
Android 15 より前では、ウィジェット ピッカーのプレビューを提供する唯一の方法は、 静的な画像リソースやレイアウト リソース。これらのプレビューは、ホーム画面に配置された実際のウィジェットの外観と大きく異なる場合があります。また、Jetpack Glance では静的リソースを作成できないため、 デベロッパーは、ウィジェットのスクリーンショットか、XML レイアウトを作成して、 ウィジェットのプレビュー。
Android 15 では、生成されたプレビューのサポートが追加されています。つまりアプリウィジェットは
代わりに、プロバイダが選択ツールプレビューとして使用する RemoteViews を生成できます。
学びます。
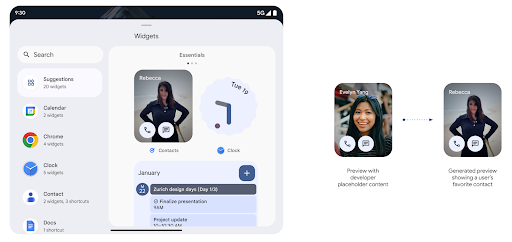
Push API
アプリは、生成されたプレビューを push API 経由で提供できます。アプリが提供できるもの
ライフサイクルのどの時点でもプレビューであり、明示的なリクエストが
プレビューが表示されます。プレビューは AppWidgetService に保持され、ホストはオンデマンドでリクエストできます。次の例では、XML ウィジェットを読み込みます。
それをプレビューとして設定します。
AppWidgetManager.getInstance(appContext).setWidgetPreview(
ComponentName(
appContext,
SociaLiteAppWidgetReceiver::class.java
),
AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN,
RemoteViews("com.example", R.layout.widget_preview)
)
想定されるフローは次のとおりです。
- ウィジェット プロバイダはいつでも
setWidgetPreviewを呼び出します。提供された プレビューは他のプロバイダ情報とともにAppWidgetServiceに保持されます。 setWidgetPreviewは、AppWidgetHost.onProvidersChangedコールバックを介して、更新されたプレビューをホストに通知します。これに対してウィジェットは ホストがすべてのプロバイダ情報を再読み込みします。- ウィジェットのプレビューを表示するとき、ホストは
AppWidgetProviderInfo.generatedPreviewCategories、 カテゴリが使用可能である場合は、AppWidgetManager.getWidgetPreviewを呼び出して このプロバイダ用に保存したプレビューを返します。
setWidgetPreview を呼び出すタイミング
プレビューを提供するためのコールバックがないため、アプリは プレビューの実行時に いつでもプレビューを表示できますプレビューの更新頻度は、ウィジェットのユースケースによって異なります。
次のリストは、プレビューのユースケースの 2 つの主なカテゴリを示しています。
- ウィジェットのプレビューに実際のデータ(パーソナライズされた情報や最新情報など)を表示するプロバイダ。これらのプロバイダは、ユーザーがログインした後、またはアプリで初期設定を行った後にプレビューを設定できます。その後、選択した頻度でプレビューを更新する定期タスクを設定できます。このタイプのウィジェットには、写真、カレンダー、天気、ニュースなどがあります 追加します。
- プレビューまたはクイック アクション ウィジェットに静的な情報を表示するプロバイダで、データを表示しないプロバイダ。これらのプロバイダは、アプリの初回起動時にプレビューを 1 回設定できます。このタイプのウィジェットの例としては、ドライブのクイック アクション ウィジェットや Chrome ショートカット ウィジェットなどがあります。
一部のプロバイダでは、ハブモード選択ツールに静的プレビューが表示される場合がありますが、 選択することもできます。これらのプロバイダは、これらの両方のユースケースのガイダンスに沿ってプレビューを設定する必要があります。
ピクチャー イン ピクチャー
Android 15 では、ピクチャー イン ピクチャー(PIP)の変更により、 PIP モードへの切り替え時のスムーズな遷移。これは、メイン UI の上に UI 要素がオーバーレイされているアプリ(PiP に移行するアプリ)に役立ちます。
デベロッパーが onPictureInPictureModeChanged コールバックを使用してロジックを定義する
オーバーレイ UI 要素の表示 / 非表示を切り替えます。このコールバックは、
PIP の開始または終了のアニメーションが完了したときにトリガーされます。開始まであと
Android 15 では、PictureInPictureUiState クラスに別の状態が含まれています。
この UI 状態では、Android 15(API レベル 35)をターゲットとするアプリは、
Activity#onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged コールバックが呼び出される
PIP アニメーションが開始されたらすぐに isTransitioningToPip() にします。他にも
PIP モードのアプリに関係のない多くの UI 要素
提案や今後の予定などの情報を含む、サンプルのビューやレイアウト
タイトル、動画、評価、タイトルなどですアプリを PIP モードにしたら、
これらの UI 要素を非表示にする onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged コールバック。アプリが PiP ウィンドウから全画面モードに移行すると、次の例に示すように、onPictureInPictureModeChanged コールバックを使用してこれらの要素を非表示から表示にします。
override fun onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged(pipState: PictureInPictureUiState) {
if (pipState.isTransitioningToPip()) {
// Hide UI elements
}
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean) {
if (isInPictureInPictureMode) {
// Unhide UI elements
}
}
(PIP ウィンドウ用の)無関係な UI 要素の表示をすばやく切り替えられるため、 スムーズでちらつきのない PIP 開始アニメーションにできます。
サイレント モード ルールの改善
AutomaticZenRule を使用すると、アプリでアテンションをカスタマイズできます。
管理(サイレント モード)ルールを設定し、有効化 / 無効化のタイミングを決定
できます。Android 15 では、これらのルールを大幅に強化し、
向上させることができます次の機能強化が含まれています。
AutomaticZenRuleに型を追加して、システムが特殊な 一部のルールが適用されます。AutomaticZenRuleにアイコンを追加し、モードをより見やすくしました 認識できるようにします。- 記述する
triggerDescription文字列をAutomaticZenRuleに追加する ユーザーに対してルールを有効にする条件を指定します。 - 追加済み
ZenDeviceEffectsAutomaticZenRuleに変更し、ルールによってグレースケールなどをトリガーできるようにする ディスプレイ、夜間モード、壁紙の暗さなどを設定できます。
通知チャンネルの VibrationEffect を設定する
Android 15 では、着信通知に対するリッチ バイブレーションの設定がサポートされています。
NotificationChannel.setVibrationEffect を使用してチャンネルを作成するので、
ユーザーは通知の種類を
区別できるように
ユーザーがデバイスを見る必要はありません
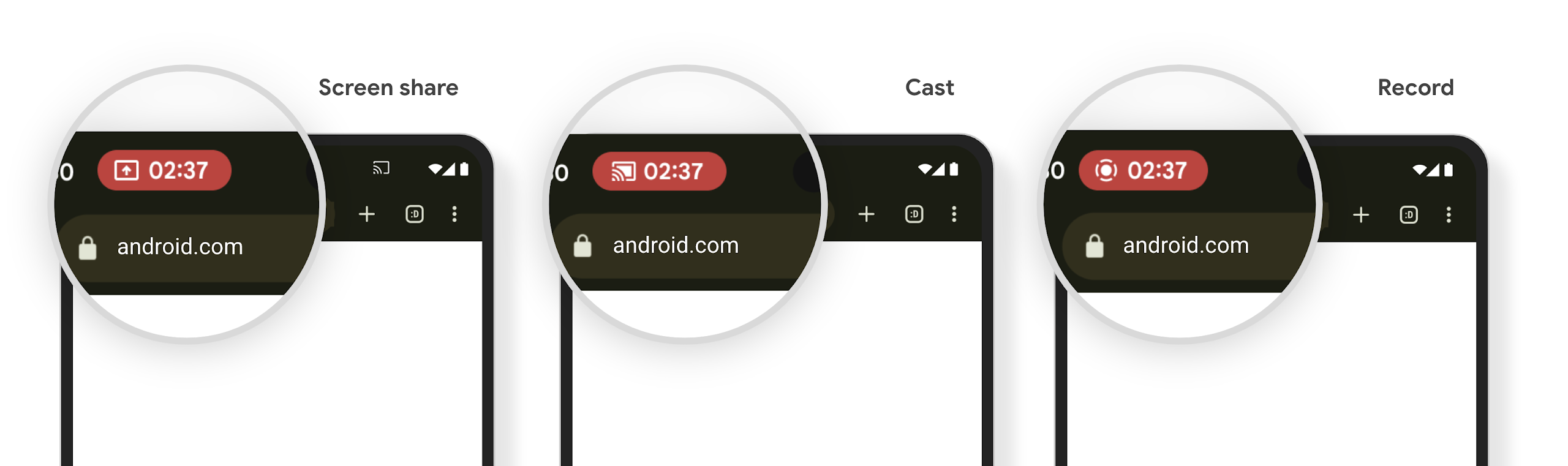
メディア プロジェクションのステータスバー チップと自動停止
メディア プロジェクションでは、ユーザーの個人情報が公開される可能性があります。新しい目立つステータスバー チップにより、画面投影が進行中であることをユーザーに知らせます。ユーザーはチップをタップして、画面のキャスト、共有、録画を停止できます。また、より直感的なユーザー エクスペリエンスを実現するため、デバイスの画面がロックされると、進行中の画面投影が自動的に停止されるようになりました。
大画面とフォーム ファクタ
Android 15 では、大画面、フリップ式、折りたたみ式など、Android のフォーム ファクタを最大限に活用するためのサポートがアプリに提供されます。
大画面でのマルチタスクを改善
Android 15 では、大画面デバイスでのマルチタスク機能が改善されています。対象 たとえば、ユーザーはお気に入りの分割画面のアプリの組み合わせを保存して、 画面上のタスクバーにアクセスしたり、固定したりすることで、アプリをすばやく切り替えられます。つまり アプリをアダプティブにすることの重要性が これまで以上に高まっています
Google I/O では、アダプティブな Android の構築に関するセッションを開催しています。 およびマテリアル 3 を使用した UI の作成 アダプティブ ライブラリ また、Google のドキュメントでは大規模な できます。
カバー画面のサポート
アプリは、Android 15 で使用されるプロパティを宣言して、対応するフリップ可能なデバイスの小さなカバー画面に Application または Activity を表示できます。これらの画面は小さすぎて、Android アプリの実行対象として互換性のあるターゲットと見なすことはできませんが、アプリでこれらの画面のサポートを有効にすることで、アプリをより多くのデバイスで利用できるようになります。
接続
Android 15 では、プラットフォームが更新され、アプリで最新の通信技術やワイヤレス技術を利用できるようになります。
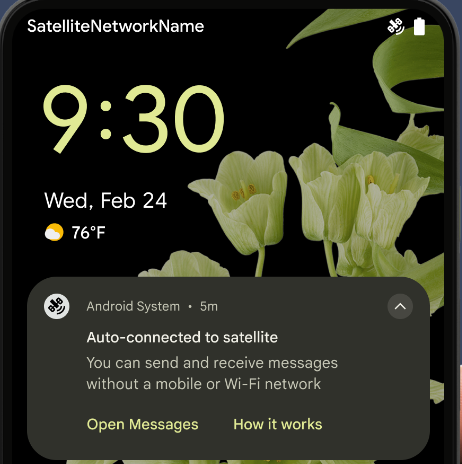
衛星通信のサポート
Android 15 では、衛星通信のプラットフォーム サポートをさらに拡張し、衛星通信の全域で一貫したユーザー エクスペリエンスを実現するための UI 要素を追加しています。
アプリは ServiceState.isUsingNonTerrestrialNetwork() を使用して次のことを行えます。
デバイスが衛星に接続されていることを検出し、
フル ネットワーク サービスが利用できない理由。さらに Android 15 では
SMS および MMS アプリや、プリロードされた RCS アプリに対応しています。
衛星回線で送受信されています
NFC エクスペリエンスの向上
Android 15 では、Android の堅牢な NFC アプリ エコシステムを引き続きサポートしながら、タッチ決済のエクスペリエンスをよりシームレスで信頼性の高いものにする取り組みを進めています。サポートされているデバイスでは、アプリは NfcAdapter に観察モードに入るようリクエストできます。このモードでは、デバイスはリッスンしますが NFC リーダーには応答せず、アプリの NFC サービス PollingFrame
オブジェクトを送信して処理します。PollingFrame オブジェクトを使用すると、NFC リーダーへの最初の通信の前に認証を行うことができ、多くの場合、ワンタップ取引が可能になります。
さらに、アプリはサポートされているデバイスにフィルタを登録して、ポーリング ループ アクティビティを通知できます。これにより、複数の NFC 対応アプリケーションでスムーズに動作できます。
ウォレットの役割
Android 15 では、ユーザーが優先するウォレット アプリとの統合を強化できるウォレット ロールが導入されています。このロールは、NFC のデフォルトの非接触型決済設定に代わるものです。ウォレットのロールホルダーを管理するには、[設定] > [アプリ] > [デフォルト アプリ] に移動します。
ウォレットのロールを使用するのは、支払いカテゴリに登録されている AID の NFC タップを転送する場合です。タップは、同じ AID に登録されている別のアプリがフォアグラウンドで実行されていない限り、常にウォレットのロール所有者に送信されます。
このロールは、ウォレットのクイック アクセス タイルが有効になったときに配置する場所を決定するためにも使用されます。ロールが [なし] に設定されている場合、クイック アクセス タイルを使用できず、支払いカテゴリの NFC タップはフォアグラウンド アプリにのみ配信されます。
セキュリティ
Android 15 では、アプリのセキュリティを強化し、アプリのデータを保護し、ユーザーがデータをより透明性をもって管理できるようになります。ユーザーの保護を強化し、アプリを新たな脅威から保護するために Google が行っている取り組みについて詳しくは、Google I/O のトーク「Android でのユーザー セキュリティの保護」をご覧ください。
認証情報マネージャーを自動入力と統合する
Android 15 以降では、デベロッパーはユーザー名やパスワード フィールドなどの特定のビューを認証情報マネージャー リクエストにリンクできるため、ログイン プロセス中にカスタマイズされたユーザー エクスペリエンスを簡単に提供できます。ユーザーがこれらのビューのいずれかにフォーカスすると、対応するリクエストが認証情報マネージャーに送信されます。生成された認証情報はプロバイダ間で集約され、インライン候補やプルダウン候補などの自動入力のフォールバック UI に表示されます。Jetpack androidx.credentials ライブラリは、デベロッパーが使用するエンドポイントとして推奨されます。このライブラリはまもなく Android 15 以降で利用可能になり、この機能をさらに強化できるようになります。
シングルタップ登録とログインを生体認証プロンプトと統合する
認証情報マネージャー: 生体認証プロンプトを認証情報作成に統合 ログイン プロセスがシンプルになり、プロバイダがログイン プロセスを管理する必要がなくなります。 プロンプトが表示されます。そのため、認証情報プロバイダは create フローと get フローの結果。生体認証フローの結果で拡張されます。 この簡素化されたプロセスにより、認証情報の作成と取得プロセスがより効率的で合理化されます。
エンドツーエンドの暗号化の鍵管理
Android 15 では E2eeContactKeysManager が導入されます。これは、暗号公開鍵の保存用の OS レベルの API を提供することで、Android アプリでのエンドツーエンドの暗号化(E2EE)を容易にします。
E2eeContactKeysManager は、プラットフォームの連絡先アプリと統合するように設計されており、ユーザーが連絡先の公開鍵を一元的に管理および検証できるようにします。
コンテンツ URI の権限チェック
Android 15 では、コンテンツ URI に対する権限チェックを実行する一連の API が導入されています。
Context.checkContentUriPermissionFull: コンテンツ URI に対する完全な権限チェックを実行します。Activityマニフェスト属性requireContentUriPermissionFromCaller: アクティビティの起動時に、指定された権限が指定されたコンテンツ URI に適用されます。Activity呼び出し元のComponentCallerクラス: アクティビティを起動したアプリを表します。
ユーザー補助
Android 15 では、ユーザー補助機能を改善する機能が追加されています。
Better Braille
Android 15 では、TalkBack が USB とセキュア Bluetooth の両方で HID 標準を使用している点字ディスプレイをサポートできるようになりました。
この標準は、マウスやキーボードで使用されている標準とよく似ており、Android が今後、より幅広い点字ディスプレイをサポートするのに役立ちます。
多言語対応
Android 15 では、デバイスが異なる言語で使用される場合のユーザー エクスペリエンスを補完する機能が追加されています。
CJK 可変フォント
Android 15 以降、中国語、日本語、韓国語(CJK)言語のフォント ファイル NotoSansCJK が可変フォントになりました。可変フォントにより、CJK 言語でのクリエイティブなタイポグラフィの可能性が広がります。デザイナーは、より幅広いスタイルを試し、これまで実現が難しかった、または不可能だった視覚的に魅力的なレイアウトを作成できます。

文字間隔の調整
Android 15 以降では、文字間隔を使用してテキストを両端揃えできます。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER を使用します。変更前の単語間の両端揃え:
Android 8.0(API レベル 26)で初めて導入されました。
同様の機能は、
空白文字(中国語、日本語など)

JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE を使用した日本語テキストのレイアウト。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE を使用した英語テキストのレイアウト。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD を使用した日本語テキストのレイアウト。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD を使用した英語テキストのレイアウト。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER を使用した日本語テキストのレイアウト。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER を使用した英語テキストのレイアウト。自動改行の設定
Android 13(API レベル 33)では、日本語と韓国語のフレーズベースの改行がサポートされるようになりました。ただし、フレーズベースの改行は短い行のテキストの読みやすさを向上させますが、長い行のテキストには適していません。Android 15 では、アプリは短い行にのみフレーズベースの改行を適用できます。
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO を使用
選択します。このオプションを選択すると、テキストに最適な単語スタイル オプションが選択されます。
短いテキストにはフレーズベースの改行を使用し、
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE のようにします。
次の画像:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
テキストが読みやすくなるように、フレーズベースの改行を適用します。
これは
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE。長いテキスト行の場合、LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO は改行なしの単語スタイルを使用します。これは、次の図に示すように、LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE と同じように機能します。

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
テキストが読みやすくなるように、改行の単語スタイルが適用されません。
これは
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE。追加の日本語変体仮名フォント
Android 15 では、古い日本のひらがな(変形がな)のフォント ファイルが追加されました。 デフォルトではバンドルされています変形がなキャラのユニークな形は、 アート作品やデザインとの特徴的なセンスを活かしながら、精度の高い 古代日本の文書の伝達と理解を 支援してきました

VideoLAN cone Copyright (c) 1996-2010 VideoLAN. このロゴまたはその変更版は、VideoLAN プロジェクトまたは VideoLAN チームによって開発された製品を参照するために、誰でも使用または変更できますが、プロジェクトによる推奨を示すものではありません。
Vulkan および Vulkan のロゴは、Khronos Group Inc.の登録商標です。
OpenGL は登録商標であり、OpenGL ES ロゴは Khronos の許可を得て使用している Hewlett Packard Enterprise の商標です。

