פלטפורמת Android 16 כוללת שינויים בהתנהגות שעשויים להשפיע על האפליקציה שלכם. השינויים הבאים בהתנהגות חלים על כל האפליקציות כשהן פועלות ב-Android 16, ללא קשר ל-targetSdkVersion. מומלץ לבדוק את האפליקציה ואז לשנות אותה לפי הצורך כדי לתמוך בשינויים האלה, במקרים הרלוונטיים.
חשוב גם לעיין ברשימת השינויים בהתנהגות שמשפיעים רק על אפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 16.
פונקציונליות עיקרית
Android 16 (רמת API 36) כולל את השינויים הבאים, שמשנה או מרחיבים יכולות ליבה שונות של מערכת Android.
אופטימיזציה של מכסות ב-JobScheduler
החל מ-Android 16, אנחנו משנים את המכסה של זמן הריצה לביצוע משימות רגילות ומשימות מואצות על סמך הגורמים הבאים:
- הקטגוריה של האפליקציה במצב המתנה: ב-Android 16, קטגוריות פעילות של אפליקציות במצב המתנה יתחילו להיות מופעלות באמצעות מכסה נדיבה של זמן ריצה.
- אם המשימה מתחילה לפעול בזמן שהאפליקציה במצב 'מופעלת': ב-Android 16, משימות שהתחילו לפעול בזמן שהאפליקציה גלויה למשתמש והמשיכו לפעול אחרי שהאפליקציה הפכה לבלתי נראית, יתחייבו למכסת זמן הריצה של המשימה.
- אם המשימה פועלת בזמן הפעלת שירות שפועל בחזית: ב-Android 16, משימות שפועלות בו-זמנית עם שירות שפועל בחזית יתחייבו למכסת זמן הריצה של המשימה. אם אתם משתמשים במשימות להעברת נתונים שהמשתמשים יזמו, כדאי להשתמש במקום זאת במשימות של העברת נתונים שהמשתמשים יזמו.
השינוי הזה משפיע על משימות שתזמנתם באמצעות WorkManager, JobScheduler ו-DownloadManager. כדי לנפות באגים ולברר למה המשימה הופסקה, מומלץ לקרוא ל-WorkInfo.getStopReason() כדי לתעד את הסיבה להפסקה (במשימות של JobScheduler, צריך לקרוא ל-JobParameters.getStopReason()).
במאמר מגבלות משאבים לניהול צריכת החשמל מוסבר איך המצב של האפליקציה משפיע על המשאבים שבהם היא יכולה להשתמש. למידע נוסף על שיטות מומלצות לשמירה על אופטימיזציה של הסוללה, אפשר לעיין בהנחיות בנושא אופטימיזציה של השימוש בסוללה ב-API לניהול משימות.
מומלץ גם להשתמש ב-API החדש JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory שנוסף ב-Android 16 כדי להבין למה משימה לא בוצעה.
בדיקה
כדי לבדוק את ההתנהגות של האפליקציה, אפשר להפעיל שינוי של אופטימיזציות מסוימות של מכסות משימות, כל עוד האפליקציה פועלת במכשיר עם Android מגרסה 16 ואילך.
כדי להשבית את האכיפה של 'מצב העליון יתאים למכסה של זמן הריצה של המשימה', מריצים את הפקודה הבאה adb:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
כדי להשבית את האכיפה של 'משימות שפועלות בו-זמנית עם שירות בחזית יתחייבו למכסת זמן הריצה של המשימה', מריצים את הפקודה הבאה של adb:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
כדי לבדוק התנהגות מסוימת של קטגוריית האפליקציה במצב המתנה, אפשר להגדיר את קטגוריית האפליקציה במצב המתנה באמצעות הפקודה adb הבאה:
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
כדי להבין באיזו קטגוריה של אפליקציות במצב המתנה האפליקציה שלכם נמצאת, תוכלו לקבל את הקטגוריה של האפליקציה במצב המתנה באמצעות הפקודה adb הבאה:
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
הסיבה להפסקה של משימות ריקות שננטשו
משימה נטושה מתרחשת כשאובייקט JobParameters המשויך למשימה נאסף על ידי מנהל האשפה, אבל לא בוצע קריאה ל-JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) כדי לסמן את סיום המשימה. המשמעות היא שהמשימה עשויה לפעול ולהיבחר מחדש ללא ידיעת האפליקציה.
אפליקציות שמסתמכות על JobScheduler לא שומרות הפניה חזקה לאובייקט JobParameters, ועכשיו הסיבה החדשה להפסקת המשימה STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED תוקצה לתפוגה במקום STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT.
אם יהיו מקרים תדירים של הסיבה החדשה להפסקה, המערכת תבצע פעולות כדי לצמצם את תדירות המשימות.
באפליקציות צריך להשתמש בסיבה החדשה להפסקה כדי לזהות משימות שננטשו ולהפחית את מספרן.
אם אתם משתמשים ב-WorkManager, ב-AsyncTask או ב-DownloadManager, השינוי לא ישפיע עליכם כי ממשקי ה-API האלה מנהלים את מחזור החיים של המשימה בשם האפליקציה.
הוצאה משימוש מלאה של JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground
השיטה JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean) מציינת את מידת החשיבות של משימה בזמן שאפליקציית התזמון נמצאת בחזית או כשהיא פטורה באופן זמני מההגבלות על משימות ברקע.
השיטה הזו הוצאה משימוש בגרסה Android 12 (רמת API 31). החל מגרסה Android 16, היא כבר לא פועלת בצורה יעילה והקריאה לשיטה הזו תתעלם.
הסרת הפונקציונליות הזו חלה גם על JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground(). החל מגרסה Android 16, אם השיטה נקראת, היא מחזירה את הערך false.
היקף העדיפות של שידור ממוין כבר לא גלובלי
אפליקציות ל-Android יכולות להגדיר עדיפות למכשירי שידור כדי לקבוע את הסדר שבו המכשירים מקבלים את השידור ומעבדים אותו. במקרה של מקלטים שמוגדרים במניפסט, האפליקציות יכולות להשתמש במאפיין android:priority כדי להגדיר את העדיפות. במקרה של מקלטים שמתועדפים לפי הקשר, האפליקציות יכולות להשתמש ב-API IntentFilter#setPriority() כדי להגדיר את העדיפות. כשמפעילים שידור, המערכת מעבירה אותו לנמענים לפי סדר העדיפויות שלהם, מהגבוה לנמוך.
ב-Android 16, לא מובטח שהסדר של העברת השידורים באמצעות המאפיין android:priority או IntentFilter#setPriority() בתהליכים שונים יישמר. המערכת תתייחס לעדיפויות השידור רק באותו תהליך בקשה, ולא בכל התהליכים.
בנוסף, העדיפויות של השידורים יוגבלו באופן אוטומטי לטווח (SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1). רק רכיבי המערכת יוכלו להגדיר את SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY ו-SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY כעדיפות השידור.
יכול להיות שהאפליקציה שלכם תושפע אם היא מבצעת אחת מהפעולות הבאות:
- ב-Intent הרצוי של השידור יש כמה תהליכים ב-Intent הרצוי של השידור, ויש ציפיות לקבלת ה-Intent האלה בסדר מסוים על סמך העדיפות.
- תהליך הבקשה שלכם מתקשר עם תהליכים אחרים, ויש לו ציפיות לגבי קבלת כוונה לשידור בסדר מסוים.
אם התהליכים צריכים לתאם ביניהם, הם צריכים לתקשר באמצעות ערוצי תיאום אחרים.
שינויים פנימיים ב-ART
Android 16 כולל את העדכונים האחרונים ל-Android Runtime (ART), שמשפרים את הביצועים של Android Runtime (ART) ומספקים תמיכה בתכונות נוספות של Java. דרך עדכוני המערכת של Google Play, השיפורים האלה זמינים גם ליותר ממיליארד מכשירים עם Android 12 (רמת API 31) ואילך.
כשהשינויים האלה יפורסמו, יכול להיות שספריות וקוד של אפליקציות שמסתמכים על מבנים פנימיים של ART לא יפעלו כראוי במכשירים עם Android 16, וגם בגרסאות קודמות של Android שבהן מופעלים עדכוני מערכת של Google Play למודול ART.
תמיד יכולות להיות בעיות תאימות אם מסתמכים על מבנים פנימיים (כמו ממשקים שאינם SDK), אבל חשוב במיוחד להימנע מהסתמכות על קוד (או ספריות שמכילות קוד) שמשתמש במבנים פנימיים של ART, כי השינויים ב-ART לא קשורים לגרסה של הפלטפורמה שבה המכשיר פועל, והם מועברים ליותר ממיליארד מכשירים דרך עדכוני המערכת של Google Play.
כל המפתחים צריכים לבדוק אם האפליקציה שלהם מושפעת מהשינוי, על ידי בדיקה יסודית של האפליקציות ב-Android 16. בנוסף, כדאי לבדוק את הבעיות המוכרות כדי לראות אם האפליקציה שלכם תלויה בספריות שזיהינו שתלויה במבנים פנימיים של ART. אם יש לכם קוד אפליקציה או יחסי תלות בספרייה שמושפעים מהשינוי, כדאי לנסות למצוא חלופות לממשקי API ציבוריים כשהדבר אפשרי, ולבקש ממשקי API ציבוריים לתרחישי שימוש חדשים על ידי יצירת בקשה לתכונה באתר למעקב אחר בעיות.
מצב תאימות לגודל דף של 16KB
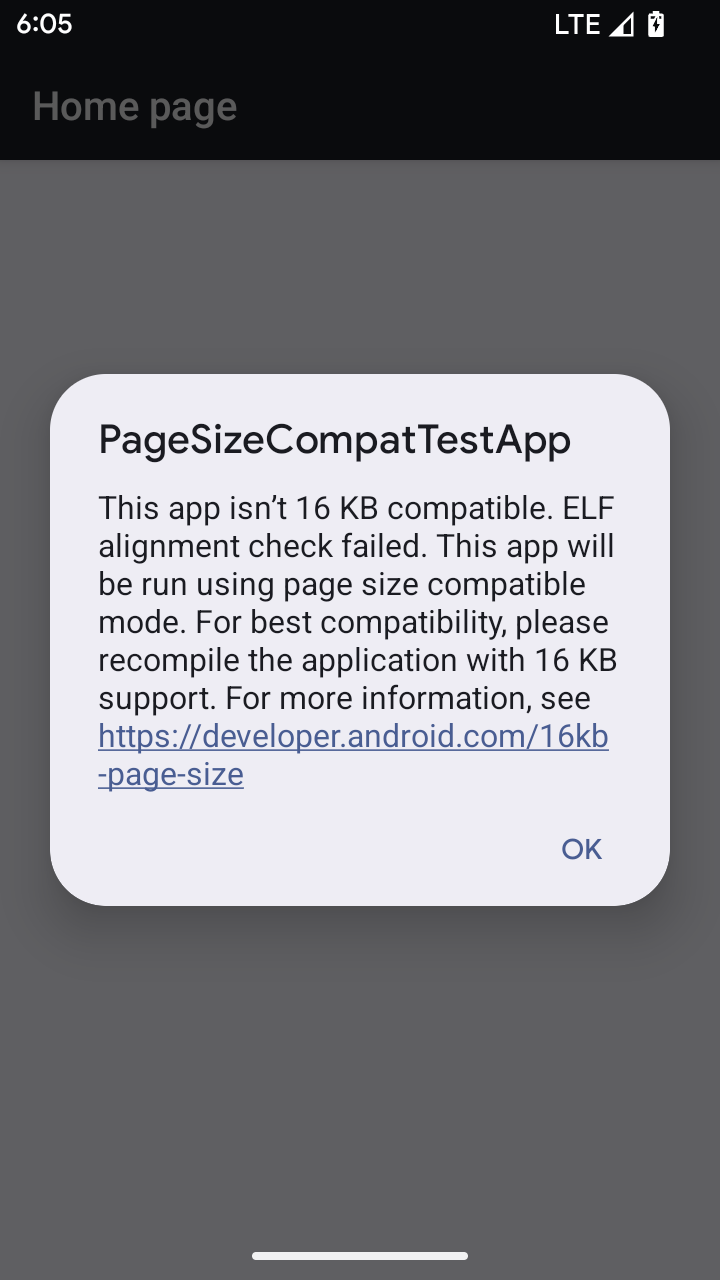
ב-Android 15 נוספה תמיכה בדפים בזיכרון בגודל 16KB כדי לייעל את הביצועים של הפלטפורמה. ב-Android 16 נוספה תמיכה במצב תאימות, שמאפשר לאפליקציות מסוימות שנוצרו לדפים בזיכרון בנפח 4KB לפעול במכשיר שמוגדר לדפים בזיכרון בנפח 16KB.
כשהאפליקציה פועלת במכשיר עם Android מגרסה 16 ואילך, אם מערכת Android מזהה שהאפליקציה כוללת דפי זיכרון בגודל 4KB, היא משתמשת באופן אוטומטי במצב תאימות ומציגה למשתמש תיבת דו-שיח עם התראה. הגדרת המאפיין android:pageSizeCompat בקובץ AndroidManifest.xml כדי להפעיל את מצב התאימות לאחור תמנע את הצגת תיבת הדו-שיח כשהאפליקציה מופעלת. כדי להשתמש בנכס android:pageSizeCompat, צריך לקמפל את האפליקציה באמצעות Android 16 SDK.
כדי לקבל את הביצועים, האמינות והיציבות הטובים ביותר, עדיין צריך לבצע התאמה של האפליקציה ל-16 KB. פרטים נוספים זמינים בפוסט האחרון שלנו בבלוג בנושא עדכון האפליקציות כך שיתמכו בדפי זיכרון בגודל 16KB.
חוויית משתמש וממשק המשתמש של המערכת
Android 16 (רמת API 36) כולל את השינויים הבאים, שנועדו ליצור חוויית משתמש עקבית ואינטואיטיבית יותר.
הוצאה משימוש של הודעות מפריעות בנושא נגישות
ב-Android 16 הופסקה התמיכה בהודעות נגישות, שמתאפיינות בשימוש ב-announceForAccessibility או בשליחת אירועי נגישות מסוג TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT. כתוצאה מכך, חוויית המשתמש של משתמשי TalkBack וקורא המסך של Android עשויה להיות לא עקבית. חלופות יכולות לעזור לטפל בטווח רחב יותר של צרכים של משתמשים במגוון טכנולוגיות העזרה של Android.
דוגמאות לחלופות:
- לשינויים משמעותיים בממשק המשתמש, כמו שינויים בחלונות, צריך להשתמש ב-
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)וב-setAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence). ב-Compose, משתמשים ב-Modifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" } - כדי להודיע למשתמש על שינויים בממשק המשתמש הקריטי, משתמשים ב-
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int). בחלונית הכתיבה, משתמשים ב-Modifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}. מומלץ להשתמש בהם במשורה, כי הם עלולים ליצור הודעות בכל פעם שנתונים מתעדכנים בתצוגה. - כדי להודיע למשתמשים על שגיאות, שולחים
AccessibilityEventמסוגAccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORומגדירים אתAccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence), או משתמשים ב-TextView#setError(CharSequence).
במסמכי העזרה של ממשק ה-API announceForAccessibility, שהוצא משימוש, מופיעים פרטים נוספים על חלופות מוצעות.
תמיכה בניווט ב-3 לחצנים
ב-Android 16 יש תמיכה בתכונה 'חזרה חזותית' בניווט ב-3 לחצנים באפליקציות שהועברו כראוי ל'חזרה חזותית'. לחיצה ארוכה על לחצן החזרה מפעילה אנימציה חזותית של תנועת החזרה, שמאפשרת לכם לראות תצוגה מקדימה של המקום שאליו תגיעו אם תמשיכו להחליק לאחור.
ההתנהגות הזו חלה על כל האזורים במערכת שתומכים באנימציות חיזוי של תנועת החזרה, כולל אנימציות המערכת (חזרה למסך הבית, בין משימות ובין פעילויות).
גורמי צורה של מכשירים
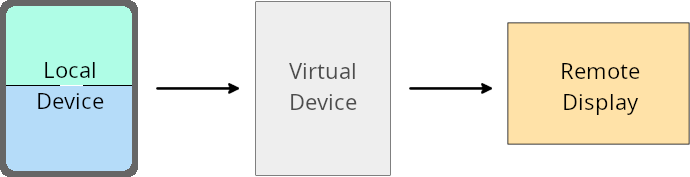
ב-Android 16 (רמת API 36) יש שינויים באפליקציות כשהבעלים של מכשירים וירטואליים מקרינים אותן למסכים.
שינויים מברירת המחדל של הבעלים של המכשיר הווירטואלי
הבעלים של מכשיר וירטואלי הוא אפליקציה מהימנה או בעלת הרשאות שמשמשת ליצירה ולניהול של מכשיר וירטואלי. בעלי מכשיר וירטואלי מריצים אפליקציות במכשיר וירטואלי, ואז מקרינים את האפליקציות במסך של מכשיר מרוחק, כמו מחשב אישי, מכשיר מציאות מדומה או מערכת בידור ברכב. הבעלים של המכשיר הווירטואלי נמצא במכשיר מקומי, כמו טלפון נייד.
שינויים מברירת המחדל לכל אפליקציה
במכשירים עם Android 16 (API ברמה 36), בעלי מכשירי וירטואליים יכולים לשנות את הגדרות האפליקציות במכשירים וירטואליים נבחרים שבבעלותם. לדוגמה, כדי לשפר את הפריסה של האפליקציות, בעלי המכשיר הווירטואלי יכולים להתעלם מהמגבלות על הכיוון, יחס הגובה-רוחב והיכולת לשנות את הגודל של האפליקציות כשהם מקרינים אותן למסך חיצוני.
שינויי תוכנה נפוצים שעלולים לגרום לכשלים
התנהגות Android 16 עשויה להשפיע על ממשק המשתמש של האפליקציה במכשירים עם מסכים גדולים, כמו מסכי רכב או Chromebooks, במיוחד בפריסות שתוכננו למסכים קטנים בכיוון לאורך. במאמר מידע על פריסות מסתגלות מוסבר איך להתאים את האפליקציה לכל גורמי הצורה של המכשירים.
קובצי עזר
אבטחה
Android 16 (רמת API 36) כולל שינויים שמקדמים את אבטחת המערכת כדי להגן על אפליקציות ועל משתמשים מפני אפליקציות זדוניות.
אבטחה משופרת מפני התקפות של הפניה אוטומטית של כוונה (Intent)
מערכת Android 16 מספקת אבטחה שמוגדרת כברירת מחדל מפני התקפות Intent כלליות של הפניה אוטומטית, עם תאימות מינימלית ושינויים מינימליים שצריך לבצע המפתחים.
אנחנו משיקים פתרונות לאבטחה מוגברת כברירת מחדל כדי למנוע ניצול לרעה של Intent
הפניות אוטומטיות. ברוב המקרים, אפליקציות שמשתמשות בכוונות לא יסבלו מבעיות תאימות. אספנו מדדים לאורך תהליך הפיתוח כדי לעקוב אחרי האפליקציות שעשויות להיתקל בבעיות.
הפניה אוטומטית של Intent ב-Android מתרחשת כשתוקף יכול לשלוט באופן חלקי או מלא בתוכן של Intent שמשמש להפעלת רכיב חדש בהקשר של אפליקציה פגיעה, בזמן שאפליקציית הקורבן מפעילה Intent ברמה משנית לא מהימנה בשדה 'תוספות' של Intent ('ברמה העליונה'). כתוצאה מכך, אפליקציית התוקף עשויה להפעיל רכיבים פרטיים בהקשר של אפליקציית הקורבן, להפעיל פעולות עם הרשאות או לקבל גישה לנתונים רגישים דרך URI, וכתוצאה מכך לגרום לגניבת נתונים ולהרצת קוד שרירותי.
ביטול ההסכמה לטיפול בהפניות אוטומטיות של כוונה
ב-Android 16 נוסף ממשק API חדש שמאפשר לאפליקציות לבטל את ההצטרפות להגנות האבטחה במהלך ההשקה. יכול להיות שתצטרכו לעשות זאת במקרים ספציפיים שבהם התנהגות האבטחה שמוגדרת כברירת מחדל מפריעה לתרחישי שימוש חוקיים באפליקציה.
לאפליקציות שעוברות הידור (compilation) עם SDK של Android 16 (רמת API 36) ואילך
אפשר להשתמש ישירות בשיטה removeLaunchSecurityProtection() באובייקט Intent.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
לאפליקציות שמתבצעת בהן הידור עבור Android 15 (רמת API 35) ואילך
לא מומלץ לעשות זאת, אבל אפשר להשתמש בהשתקפות (reflection) כדי לגשת לשיטה removeLaunchSecurityProtection().
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
אפליקציות נלוות לא מקבלות יותר התראות על זמן קצוב לתפוגה של גילוי
בגרסה 16 של Android נוספה התנהגות חדשה במהלך תהליך ההתאמה של מכשיר נלווה, כדי להגן על פרטיות המיקום של המשתמש מפני אפליקציות זדוניות. כל האפליקציות הנלוות שפועלות ב-Android 16 לא מקבלות יותר התראה ישירה על זמן הקצוב לגילוי באמצעות RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT. במקום זאת, המשתמש יקבל הודעה על אירועי זמן קצוב באמצעות תיבת דו-שיח חזותית. כשהמשתמש סוגר את תיבת הדו-שיח, האפליקציה מקבלת התראה על כישלון השיוך עם RESULT_USER_REJECTED.
משך החיפוש הוא עכשיו ארוך יותר מ-20 השניות המקוריות, והמשתמשים יכולים להפסיק את זיהוי המכשיר בכל שלב במהלך החיפוש. אם נמצא מכשיר אחד לפחות ב-20 השניות הראשונות של החיפוש, ה-CDM מפסיק לחפש מכשירים נוספים.
קישוריות
Android 16 (רמת API 36) כולל את השינויים הבאים ב-Bluetooth stack כדי לשפר את הקישוריות עם ציוד היקפי.
טיפול משופר באובדן אג"ח
החל מגרסה 16 של Android, סטאק ה-Bluetooth עודכן כדי לשפר את האבטחה ואת חוויית המשתמש במקרה של איבוד חיבור מרחוק. בעבר, המערכת הייתה מסירה את הקישור באופן אוטומטי ומתחילה תהליך התאמה חדש, שעלול להוביל להתאמה מחדש לא מכוונת. גילינו במקרים רבים שאפליקציות לא מטפלות באירוע של אובדן ההתחייבות בצורה עקבית.
כדי לאחד את חוויית השימוש, מערכת Android 16 עברה שיפורים בטיפול באובדן קישורים. אם לא ניתן לאמת מכשיר Bluetooth שהיה מקושר בעבר במהלך החיבור מחדש, המערכת תנתק את הקישור, תשמור את פרטי הקישור המקומיים ותציג תיבת דו-שיח של המערכת שבה תודיע למשתמשים על אובדן הקישור ותנחה אותם לבצע התאמה מחדש.

