1. 准备工作
在此 Codelab 中,您将学习如何使用 Android for Cars 应用库面向 Android Auto 和 Android Automotive OS 构建经过防分心优化的应用。您首先要添加对 Android Auto 的支持,然后只需少量的额外工作,即可创建能够在 Android Automotive OS 上运行的应用变体。构建好能够在这两个平台上运行的应用后,您将构建一个额外的屏幕和一些基本的交互功能!
所需条件
- 最新版本的 Android Studio。
- 具备基本 Kotlin 使用经验。
- 了解 Android 服务的基础知识。
- 具备创建 Android 虚拟设备以及在 Android 模拟器中运行 Android 虚拟设备的经验。
- 了解 Android 应用模块化的基础知识。
- 了解构建器设计模式的基础知识。
构建内容
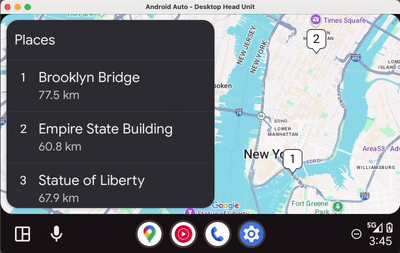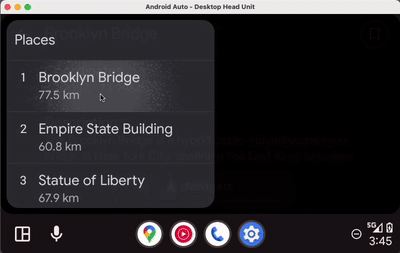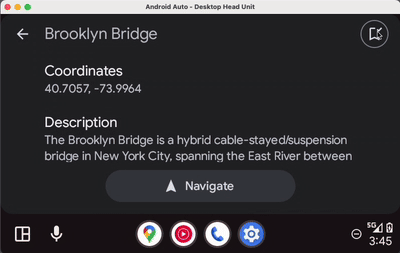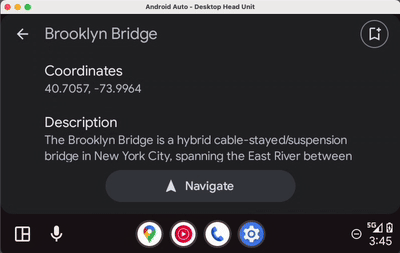
Android Auto | Android Automotive OS |
|
|
学习内容
- 汽车应用库的“客户端-主机”架构的工作原理。
- 如何编写您自己的
CarAppService、Session和Screen类。 - 如何在 Android Auto 与 Android Automotive OS 之间共享您的实现。
- 如何在开发机器上使用桌面车机运行 Android Auto。
- 如何运行 Android Automotive OS 模拟器。
2. 进行设置
获取代码
- 此 Codelab 的代码可以在
car-codelabsGitHub 存储库的car-app-library-fundamentals目录中找到。若要克隆该代码,请运行以下命令:
git clone https://github.com/android/car-codelabs.git
- 或者,您也可以下载代码库 Zip 文件。
打开项目
- 在启动 Android Studio 后,导入项目,仅选择
car-app-library-fundamentals/start目录。car-app-library-fundamentals/end目录包含解决方案代码,如果您遇到困难或只想查看完整项目,可以随时参考。
熟悉代码
- 在 Android Studio 中打开项目后,花些时间浏览起始代码。
请注意,此应用的起始代码分成两个模块::app 和 :common:data。
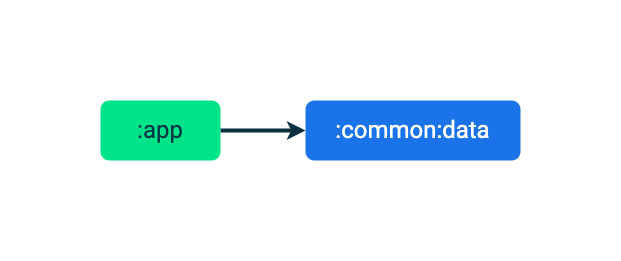
:app 模块包含移动应用的界面和逻辑,而 :common:data 模块包含 Place 模型数据类,以及用于读取 Place 模型的仓库。为了简单起见,该仓库从一个硬编码的列表中读取数据,但在实际应用中,它可以轻松地从数据库或后端服务器中读取数据。
:app 模块包括对 :common:data 模块的依赖项,这样就可以读取和呈现 Place 模型的列表。
3. 了解 Android for Cars 应用库
Android for Cars 应用库是一组 Jetpack 库,可助力开发者构建车载应用。该应用库提供了一个模板化框架,其中包含针对驾驶进行了优化的界面,并负责适应汽车中存在的各种硬件配置(例如输入法、屏幕尺寸和宽高比)。所有这一切让开发者能够轻松构建应用,并确信应用在搭载 Android Auto 和 Android Automotive OS 的各种汽车中都能顺畅运行。
了解工作原理
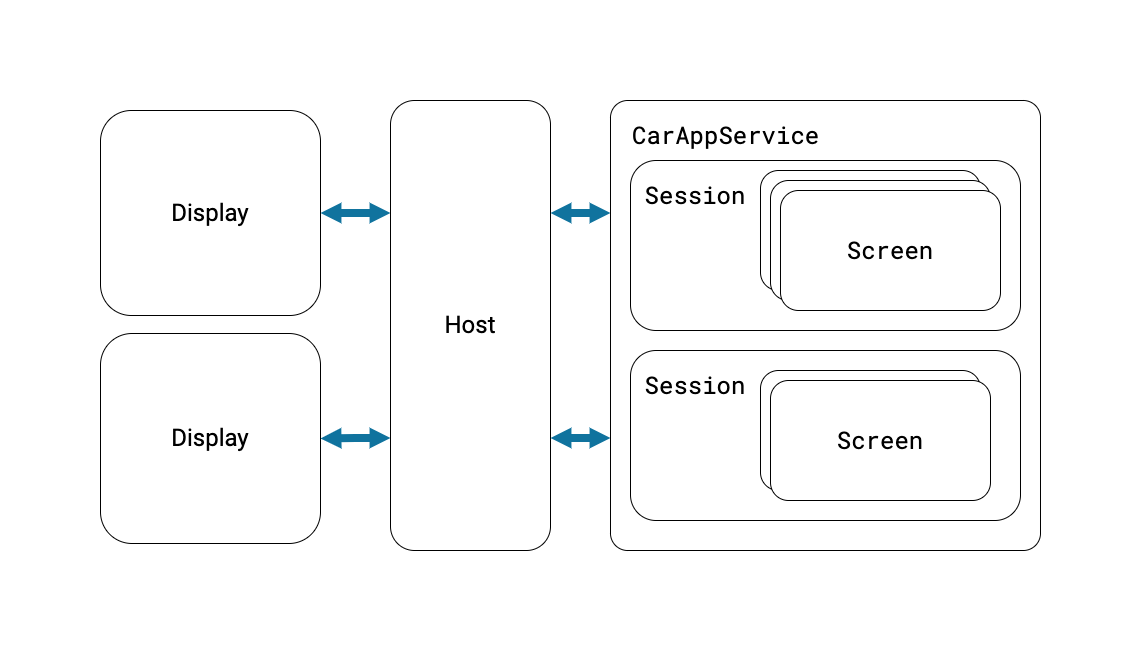
使用汽车应用库构建的应用不能直接在 Android Auto 或 Android Automotive OS 上运行。它们依赖于一个主机应用,并由该主机应用负责与客户端应用(您的应用)进行通信,并代为呈现客户端的界面。Android Auto 本身就是一个主机,而 Google Automotive App Host 则是在含 Google 预装的 Android Automotive OS 车辆上使用的主机。
下面列出了汽车应用库的一些关键类,在构建应用时,您必须要扩展这些类:
CarAppService
CarAppService 是 Android 的 Service 类的子类,充当主机应用与客户端应用(例如您在此 Codelab 中构建的应用)进行通信的入口点。其主要用途是创建与主机应用进行交互的 Session 实例。
会话
可以将 Session 视为在车辆内的显示屏中运行的客户端应用实例。与其他 Android 组件一样,它有自己的生命周期,可用于初始化和销毁在 Session 实例存在期间使用的资源。CarAppService 和 Session 之间是一对多关系。例如,对于支持仪表板屏幕的导航应用,一个 CarAppService 可以有两个 Session 实例,其中一个用于主显示屏,另一个用于仪表板显示屏。
屏幕截图
Screen 实例负责生成由主机应用渲染的界面。这些界面由 Template 类表示,每个类模拟特定类型的布局,例如 grid 或 list。每个 Session 管理一组 Screen 实例,这些实例用于处理应用不同部分之间的用户流。与 Session 一样,Screen 也有自己的生命周期,您可以在其中应用钩子。
在此 Codelab 的编写 CarAppService 部分中,您将编写 CarAppService、Session 和 Screen,届时您将详细了解这些类的方方面面。
4. 设置您的初始配置
首先,设置包含 CarAppService 的模块并声明其依赖项。
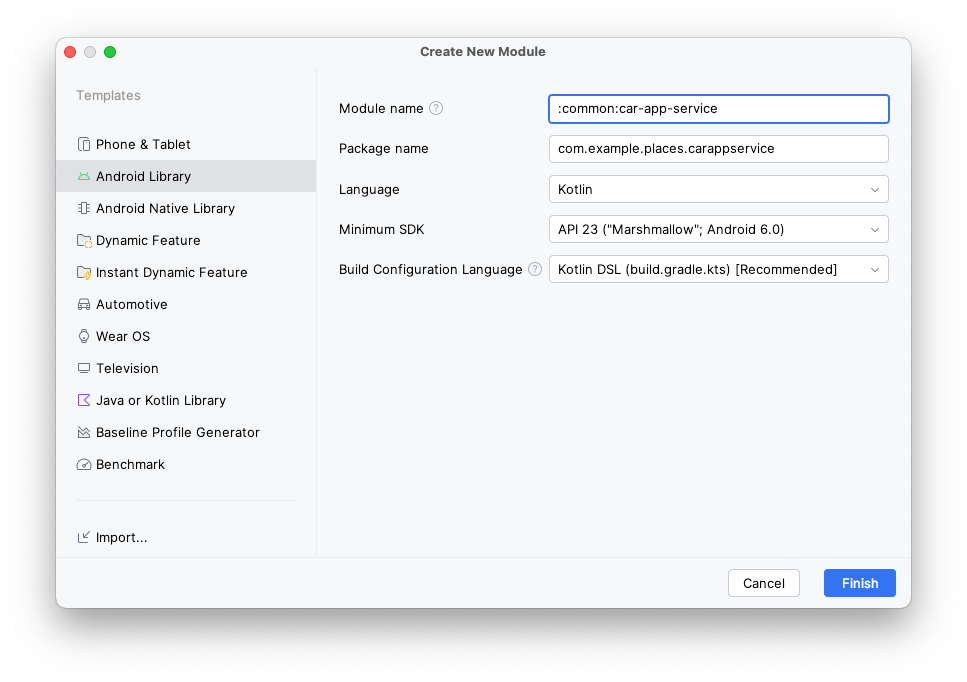
创建 car-app-service 模块
- 在“Project”窗口中选择
:common模块后,右键点击并选择 New > Module 选项。 - 在打开的模块向导中,从左侧列表中选择 Android Library 模板(这样该模块便可被其他模块用作依赖项),然后使用以下值:
- 模块名称:
:common:car-app-service - 软件包名称:
com.example.places.carappservice - 最低 SDK 版本:
API 23: Android 6.0 (Marshmallow)
设置依赖项
- 在
libs.version.toml文件中,为androidx.car.app:app制品添加条目。
libs.version.toml
[versions]
...
carApp = "1.7.0-rc01"
[libraries]
...
androidx-car-app = { group = "androidx.car.app", name = "app", version.ref = "carApp" }
- 接下来,在
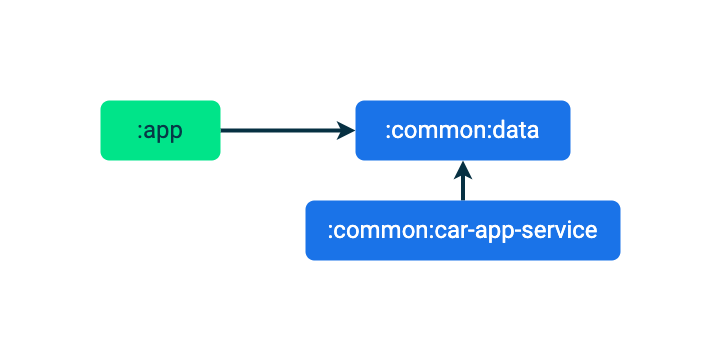
:common:car-app-service模块的build.gradle.kts文件中添加两个依赖项。
androidx.car.app:app。这是汽车应用库的主要工件,其中包含在构建应用时使用的所有核心类。该库中还包含另外三个工件:androidx.car.app:app-projected用于特定于 Android Auto 的功能,androidx.car.app:app-automotive用于 Android Automotive OS 功能代码,androidx.car.app:app-testing用于一些实用的单元测试辅助功能。您稍后会在此 Codelab 中使用app-projected和app-automotive。:common:data。这是现有移动应用使用的相同数据模块,允许为每个版本的应用体验使用相同的数据源。
build.gradle.kts(模块 :common:car-app-service)
dependencies {
...
implementation(libs.androidx.car.app)
implementation(project(":common:data"))
...
}
通过此项更改,应用各模块的依赖关系图如下所示:
现在已经设置好了依赖项,接下来可以开始编写 CarAppService 了。
5. 编写 CarAppService
- 首先在
carappservice软件包的:common:car-app-service模块内创建一个名为PlacesCarAppService.kt的文件。 - 在此文件中,创建一个名为
PlacesCarAppService的类,该类扩展了CarAppService。
PlacesCarAppService.kt
import androidx.car.app.CarAppService
import androidx.car.app.Session
import androidx.car.app.SessionInfo
import androidx.car.app.validation.HostValidator
...
class PlacesCarAppService : CarAppService() {
override fun createHostValidator(): HostValidator {
return HostValidator.ALLOW_ALL_HOSTS_VALIDATOR
}
override fun onCreateSession(sessionInfo: SessionInfo): Session {
// PlacesSession will be an unresolved reference until the next step
return PlacesSession()
}
}
CarAppService 抽象类为您实现了一些 Service 方法,例如 onBind 和 onUnbind,并可以防止进一步覆盖这些方法,以确保与主机应用之间实现适当的互操作性。您只需实现 createHostValidator 和 onCreateSession。
绑定 CarAppService 时会引用 createHostValidator 返回的 HostValidator,以确保主机是可信的,如果主机不符合您定义的参数,则绑定将失败。对于此 Codelab 以及在一般测试中,ALLOW_ALL_HOSTS_VALIDATOR 可以确保您的应用建立连接,但不应在生产环境中使用。如需详细了解如何为正式版应用配置此选项,请参阅 createHostValidator 的文档。
对于像这样简单的应用,onCreateSession 只需返回 Session 的实例即可。在更复杂的应用中,这非常适合用于初始化长期资源,例如当应用在车辆上运行时所使用的指标和日志记录客户端。
- 最后,您需要在
:common:car-app-service模块的AndroidManifest.xml文件中添加与PlacesCarAppService相对应的<service>元素,以便让操作系统(进而让主机等其他应用)知道它的存在。
AndroidManifest.xml (:common:car-app-service)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<!--
This AndroidManifest.xml will contain all of the elements that should be shared across the
Android Auto and Automotive OS versions of the app, such as the CarAppService <service> element
-->
<application>
<service
android:name="com.example.places.carappservice.PlacesCarAppService"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="androidx.car.app.CarAppService" />
<category android:name="androidx.car.app.category.POI" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
</application>
</manifest>
此处需要注意以下两个重要事项:
<action>元素允许主机(和启动器)应用找到该应用。<category>元素声明了应用的类别(在本例中为地图注点),用于确定必须满足的应用质量标准(稍后会详细介绍)。如需详细了解其他可能的值,请参阅支持的应用类别。
创建 PlacesSession 类
- 在
PlacesCarAppService.kt中,添加以下代码:
PlacesCarAppService.kt
import android.content.Intent
import androidx.car.app.Screen
...
class PlacesSession : Session() {
override fun onCreateScreen(intent: Intent): Screen {
// MainScreen will be an unresolved reference until the next step
return MainScreen(carContext)
}
}
对于像这样的简单应用,您只需在 onCreateScreen 中返回主屏幕。但是,由于此方法以 Intent 作为参数,因此功能更丰富的应用也可能会从中读取数据,并填充屏幕的返回堆栈或使用其他条件逻辑。
创建 MainScreen 类
接下来,创建一个名为 screen. 的新软件包。
- 右键点击
com.example.places.carappservice软件包并依次选择 New > Package(其完整软件包名称为com.example.places.carappservice.screen)。这是用来存放应用的所有Screen子类的位置。 - 在
screen软件包中,创建一个名为MainScreen.kt的文件来包含MainScreen类,该类扩展了Screen。目前,它将使用PaneTemplate显示简单的 Hello, world! 消息。
MainScreen.kt
import androidx.car.app.CarContext
import androidx.car.app.Screen
import androidx.car.app.model.Action
import androidx.car.app.model.Header
import androidx.car.app.model.Pane
import androidx.car.app.model.PaneTemplate
import androidx.car.app.model.Row
import androidx.car.app.model.Template
...
class MainScreen(carContext: CarContext) : Screen(carContext) {
override fun onGetTemplate(): Template {
val row = Row.Builder()
.setTitle("Hello, world!")
.build()
val pane = Pane.Builder()
.addRow(row)
.build()
return PaneTemplate.Builder(pane)
.setHeader(
Header.Builder()
.setStartHeaderAction(Action.APP_ICON)
.build()
).build()
}
}
6. 添加对 Android Auto 的支持
尽管您现在已经实现让应用正常运行所需的全部逻辑,但在 Android Auto 上运行应用之前,还需要完成两个方面的配置。
添加对 car-app-service 模块的依赖项
在 :app 模块的 build.gradle.kts 文件中,添加以下内容:
build.gradle.kts(模块 :app)
dependencies {
...
implementation(project(":common:car-app-service"))
...
}
通过此项更改,应用各模块的依赖关系图如下所示:
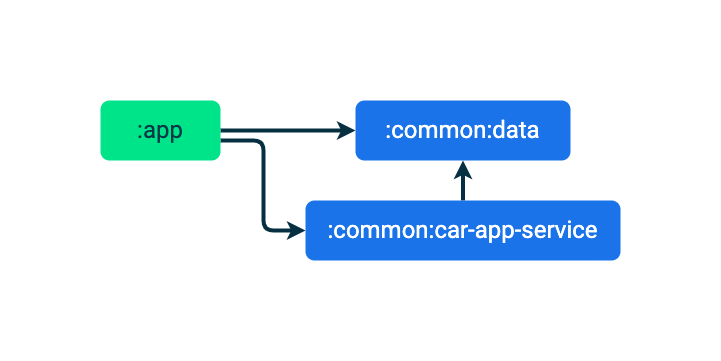
这会将您刚刚在 :common:car-app-service 模块中编写的代码与汽车应用库中包含的其他组件捆绑在一起,例如提供的权限授予 activity。
声明 com.google.android.gms.car.application 元数据
- 右键点击
:common:car-app-service模块并依次选择 New > Android Resource File 选项,然后覆盖以下值:
- 文件名:
automotive_app_desc.xml - 资源类型:
XML - 根元素:
automotiveApp
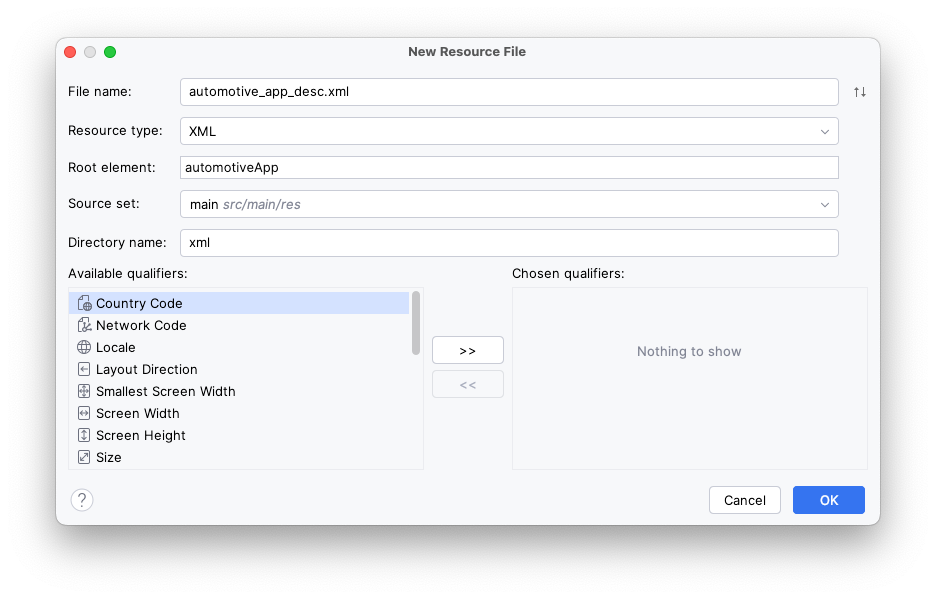
- 在该文件中,添加以下
<uses>元素以声明您的应用使用汽车应用库提供的模板。
automotive_app_desc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<automotiveApp>
<uses name="template"/>
</automotiveApp>
- 在
:app模块的AndroidManifest.xml文件中,添加以下<meta-data>元素,引用您刚刚创建的automotive_app_desc.xml文件。
AndroidManifest.xml (:app)
<application ...>
<meta-data
android:name="com.google.android.gms.car.application"
android:resource="@xml/automotive_app_desc" />
...
</application>
该文件由 Android Auto 读取,并让其知道您的应用支持哪些功能 - 在本例中,应用使用汽车应用库的模板系统。然后,系统会利用这些信息来处理行为,例如将应用添加到 Android Auto 启动器并从通知打开应用。
可选:监听投影变化
有时,您想知道用户的设备是否连接到汽车。您可以使用 CarConnection API 来完成此操作,该 API 提供了一个 LiveData,可让您观测连接状态。
- 若要使用
CarConnectionAPI,请先在:app模块中添加对androidx.car.app:app工件的依赖项。
build.gradle.kts(模块 :app)
dependencies {
...
implementation(libs.androidx.car.app)
...
}
- 出于演示目的,您可以创建一个简单的 Composable,如下所示,用于显示当前的连接状态。在实际应用中,此状态可能会被记录在某些日志中,用于在投影时禁用手机屏幕上的某些功能,或用于执行其他操作。
MainActivity.kt
import androidx.car.app.connection.CarConnection
...
@Composable
fun ProjectionState(carConnectionType: Int, modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
val text = when (carConnectionType) {
CarConnection.CONNECTION_TYPE_NOT_CONNECTED -> "Not projecting"
CarConnection.CONNECTION_TYPE_NATIVE -> "Running on Android Automotive OS"
CarConnection.CONNECTION_TYPE_PROJECTION -> "Projecting"
else -> "Unknown connection type"
}
Text(
text = text,
style = MaterialTheme.typography.bodyMedium,
modifier = modifier
)
}
- 现在已经可以显示数据、读取数据并将其传递到 Composable 中,如以下代码片段所示。
MainActivity.kt
import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue
import androidx.compose.runtime.livedata.observeAsState
...
setContent {
val carConnectionType by CarConnection(this).type.observeAsState(initial = -1)
PlacesTheme {
// A surface container using the 'background' color from the theme
Surface(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
color = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.background
) {
Column {
Text(
text = "Places",
style = MaterialTheme.typography.displayLarge,
modifier = Modifier.padding(8.dp)
)
ProjectionState(
carConnectionType = carConnectionType,
modifier = Modifier.padding(8.dp)
)
PlaceList(places = PlacesRepository().getPlaces())
}
}
}
}
- 如果您运行该应用,它应该会显示“Not projecting”.
7. 使用桌面车机 (DHU) 进行测试
实现 CarAppService 并完成 Android Auto 配置之后,接下来就可以运行应用并查看其外观了。
- 在手机上安装该应用,然后按照此处的说明安装并运行 DHU。
DHU 启动并运行后,您应该会在启动器中看到应用图标(如果没有,请仔细检查您是否已按照上一节中的所有步骤进行操作,然后在终端中退出并重新启动 DHU)。
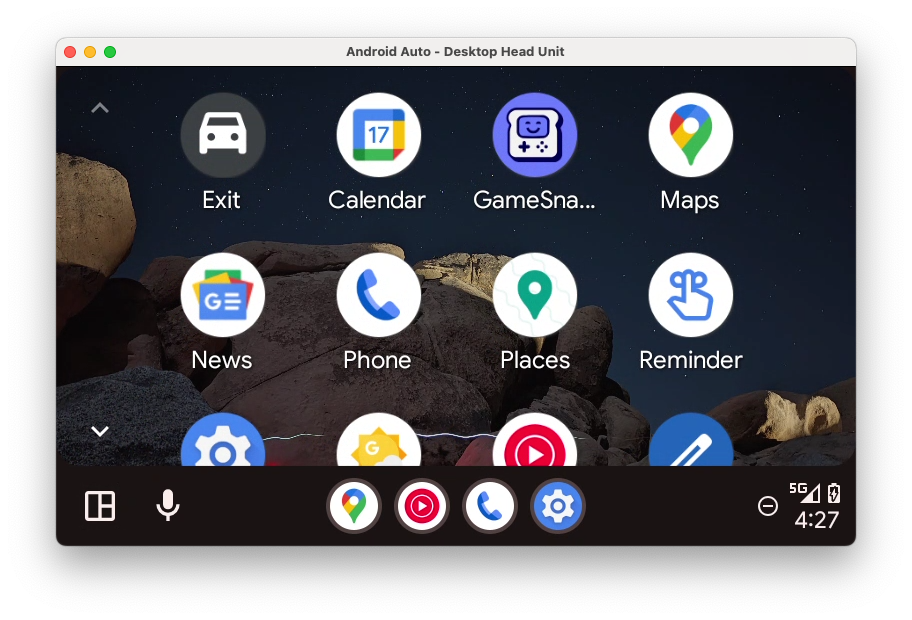
糟糕,应用崩溃了!
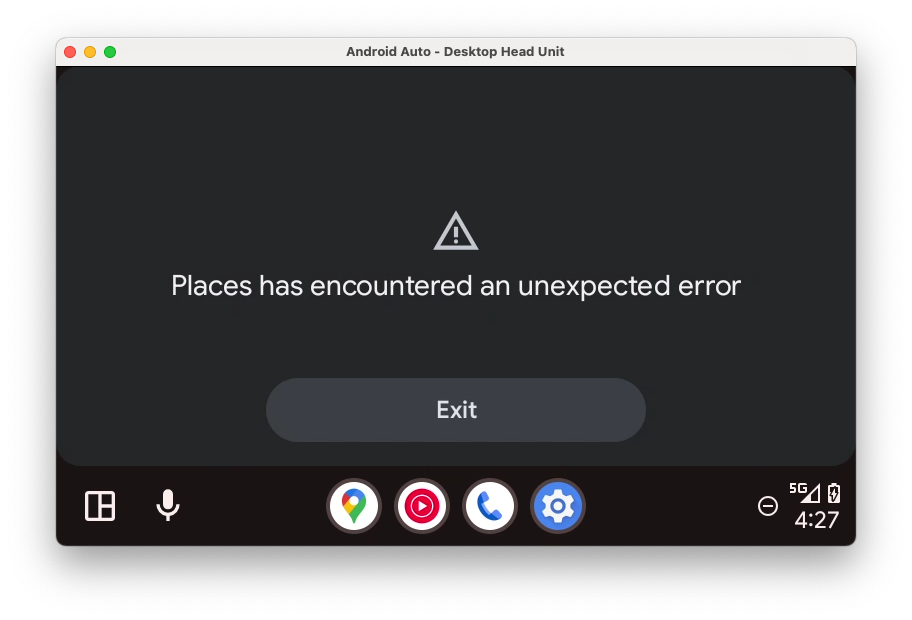
- 如需了解应用崩溃的原因,您可以查看 Android Studio 中的 Logcat(您可能需要移除
package:mine的默认 Logcat 过滤条件,并将其替换为is:error)。
Error: [type: null, cause: null, debug msg: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Min API level not declared in manifest (androidx.car.app.minCarApiLevel)
at androidx.car.app.AppInfo.retrieveMinCarAppApiLevel(AppInfo.java:143)
at androidx.car.app.AppInfo.create(AppInfo.java:91)
at androidx.car.app.CarAppService.getAppInfo(CarAppService.java:380)
at androidx.car.app.CarAppBinder.getAppInfo(CarAppBinder.java:255)
at androidx.car.app.ICarApp$Stub.onTransact(ICarApp.java:182)
at android.os.Binder.execTransactInternal(Binder.java:1285)
at android.os.Binder.execTransact(Binder.java:1244)
]
从日志中,您可以看到清单中缺少对应用支持的最低 API 级别的声明。在添加该项声明之前,最好先了解为什么需要它。
与 Android 一样,汽车应用库也有 API 级别的概念,因为主机与客户端应用之间需要达成一项合约才能进行通信。主机应用支持特定的 API 级别及其相关联的功能。此外,为了保持向后兼容性,还支持较早期级别的功能。例如,SignInTemplate 可以在运行 API 级别 2 或更高级别的主机上使用。但是,如果您尝试在仅支持 API 级别 1 的主机上使用它,该主机将不知道模板类型,也无法用它来执行任何有意义的操作。
在将主机绑定到客户端的过程中,所支持的 API 级别必须存在一定程度的重叠才能确保绑定成功。例如,如果主机仅支持 API 级别 1,但客户端应用在没有 API 级别 2 的功能的情况下无法运行(如此清单声明所示),则应用不应建立连接,因为客户端无法在主机上成功运行。因此,客户端必须在其清单中声明所需的最低 API 级别,以确保只有可支持该级别的主机才能与其绑定。
- 若要设置所支持的最低 API 级别,请在
:common:car-app-service模块的AndroidManfiest.xml文件中添加以下<meta-data>元素:
AndroidManifest.xml (:common:car-app-service)
<application>
<meta-data
android:name="androidx.car.app.minCarApiLevel"
android:value="1" />
<service android:name="com.example.places.carappservice.PlacesCarAppService" ...>
...
</service>
</application>
- 再次安装应用并在 DHU 上启动它,然后您应该会看到以下内容:
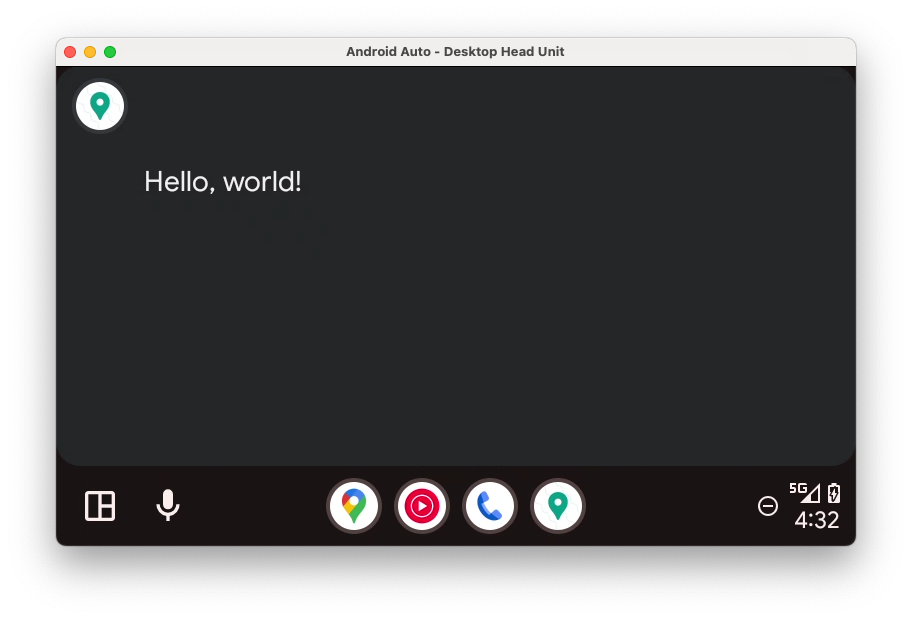
为了完整起见,您还可以尝试将 minCarApiLevel 设置为较大的值(例如 100),看看在主机与客户端不兼容的情况下启动应用会发生什么(提示:应用会崩溃,类似于未设置任何值的情形)。
另请注意,与 Android 一样,如果在运行时验证主机支持所需的 API 级别,则可以使用高于声明的最低 API 级别的 API 级别中的功能。
可选:监听投影变化
- 如果您在上一步中添加了
CarConnection侦听器,则当 DHU 运行时,您应该会在手机上看到状态更新,如下所示:

8. 添加对 Android Automotive OS 的支持
现在 Android Auto 已经正常运行,接下来再接再厉,添加对 Android Automotive OS 的支持。
创建 :automotive 模块
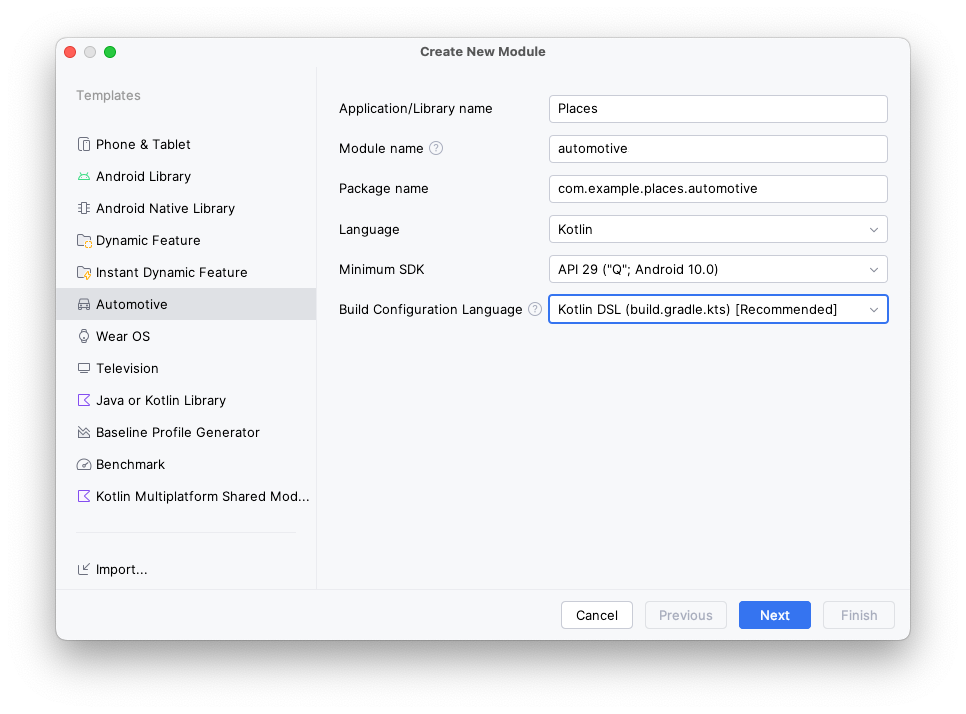
- 若要创建包含 Android Automotive OS 版本应用的相关代码的模块,请在 Android Studio 中依次打开 File > New > New Module...,从左侧模板类型列表中选择 Automotive 选项,然后使用以下值:
- 应用/库名称:
Places(与主应用相同,但如果需要,您也可以选择不同的名称) - 模块名称:
automotive - 软件包名称:
com.example.places.automotive - 语言:
Kotlin - 最低 SDK 版本:
API 29: Android 10.0 (Q),支持汽车应用库应用的所有 Android Automotive OS 车辆至少运行 API 29。
- 点击 Next,然后在下一个屏幕中选择 No Activity,最后点击 Finish。
添加依赖项
与 Android Auto 一样,您需要声明对 :common:car-app-service 模块的依赖。这样一来,您可以在两个平台上共享您的实现。
此外,您需要添加对 androidx.car.app:app-automotive 工件的依赖项。与 Android Auto 上可选的 androidx.car.app:app-projected 工件不同,此依赖项在 Android Automotive OS 上是必需的,因为其中包含用于运行应用的 CarAppActivity。
- 首先,在
libs.versions.toml中为androidx.car.app:app-automotive制品添加一个条目。
libs.version.toml
[libraries]
...
androidx-car-app-automotive = { group = "androidx.car.app", name = "app-automotive", version.ref = "carApp"}
- 若要添加依赖项,请打开
build.gradle.kts文件,然后插入以下代码:
build.gradle.kts(模块 :automotive)
dependencies {
...
implementation(project(":common:car-app-service"))
implementation(libs.androidx.car.app.automotive)
...
}
通过此项更改,应用各模块的依赖关系图如下所示:
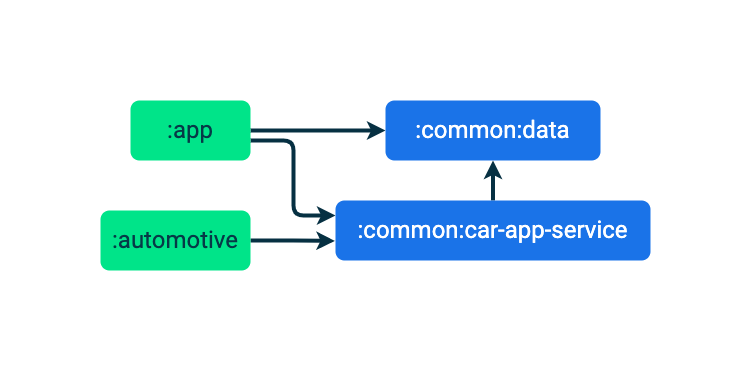
设置清单
- 首先,您需要声明两项功能,即
android.hardware.type.automotive和android.software.car.templates_host,如此处要求所述。
android.hardware.type.automotive 是一项系统功能,表示设备本身是一辆车(如需了解更多详细信息,请参阅 FEATURE_AUTOMOTIVE)。只有将此功能标记为必需的应用才能提交到 Play 管理中心上的 Automotive OS 轨道,而且提交到其他轨道的应用不得将此功能标记为必需。android.software.car.templates_host 是一项系统功能,仅存在于具有运行模板应用所需的模板主机的车辆中。对于此 Codelab,这些更改就足够了。在构建自己的应用时,请务必检查您的应用是否满足针对 Android Automotive OS 的所有 Google Play 功能要求。
AndroidManifest.xml (:automotive)
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<uses-feature
android:name="android.hardware.type.automotive"
android:required="true" />
<uses-feature
android:name="android.software.car.templates_host"
android:required="true" />
...
</manifest>
- 接下来,您需要添加对
automotive_app_desc.xml文件的引用,就像之前在 Android Auto 上的操作一样。
请注意,这次的 android:name 属性与之前不同,不再是 com.google.android.gms.car.application,而是 com.android.automotive。与之前一样,这引用了 :common:car-app-service 模块中的 automotive_app_desc.xml 文件,这意味着在 Android Auto 和 Android Automotive OS 中使用了相同的资源。此外,<meta-data> 元素位于 <application> 元素内(因此您必须更改 application 标签,以防自动闭合)。
AndroidManifest.xml (:automotive)
<application>
...
<meta-data android:name="com.android.automotive"
android:resource="@xml/automotive_app_desc"/>
...
</application>
- 最后,您需要为库中包含的
CarAppActivity添加一个<activity>元素。
AndroidManifest.xml (:automotive)
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
...
<application ...>
...
<activity
android:name="androidx.car.app.activity.CarAppActivity"
android:exported="true"
android:launchMode="singleTask"
android:theme="@android:style/Theme.DeviceDefault.NoActionBar">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
<meta-data
android:name="distractionOptimized"
android:value="true" />
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
此代码各元素的作用如下:
android:name列出app-automotive软件包中的CarAppActivity类的完全限定类名。android:exported设置为true,因为此Activity必须可由除自身之外的应用(启动器)启动。android:launchMode设置为singleTask,因此一次只能有一个CarAppActivity实例。android:theme设置为@android:style/Theme.DeviceDefault.NoActionBar,以便应用占用可用的全屏空间。- intent 过滤器指示这是应用的启动器
Activity。 <meta-data>元素向系统指示该应用可以在已设置用户体验限制的情况下使用,例如当车辆行驶时。
可选:从 :app 模块复制启动器图标
由于您刚刚创建了 :automotive 模块,因此该模块具有默认的绿色 Android 徽标图标。
- 如果需要,您可以将
:app模块的mipmap资源目录复制并粘贴到:automotive模块中,以使用与移动应用相同的启动器图标。
9. 使用 Android Automotive OS 模拟器进行测试
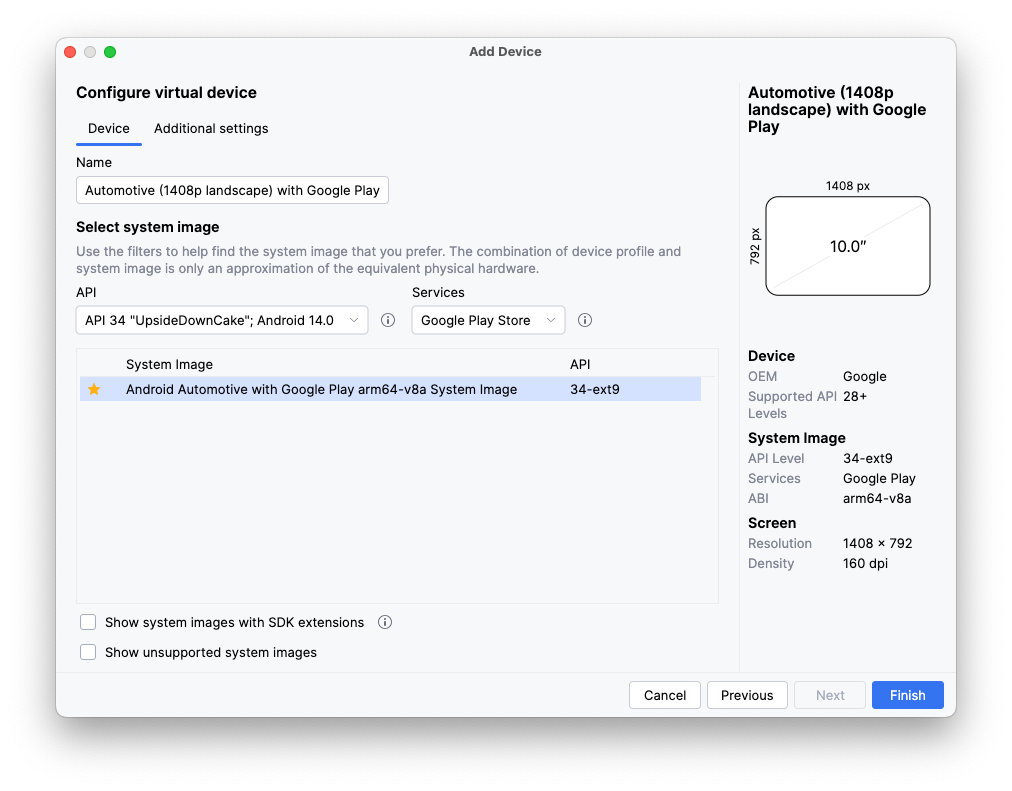
创建 Android Automotive OS Android 虚拟设备
- 打开设备管理器后,选择窗口左侧 Category 列下的 Automotive。然后,从列表中选择 Automotive (1408p landscape) with Google Play 设备定义,并点击 Next。
- 在下一页上,选择 API 34 系统映像(如果尚未下载,系统会下载该映像),然后点击 Finish 以创建 AVD。
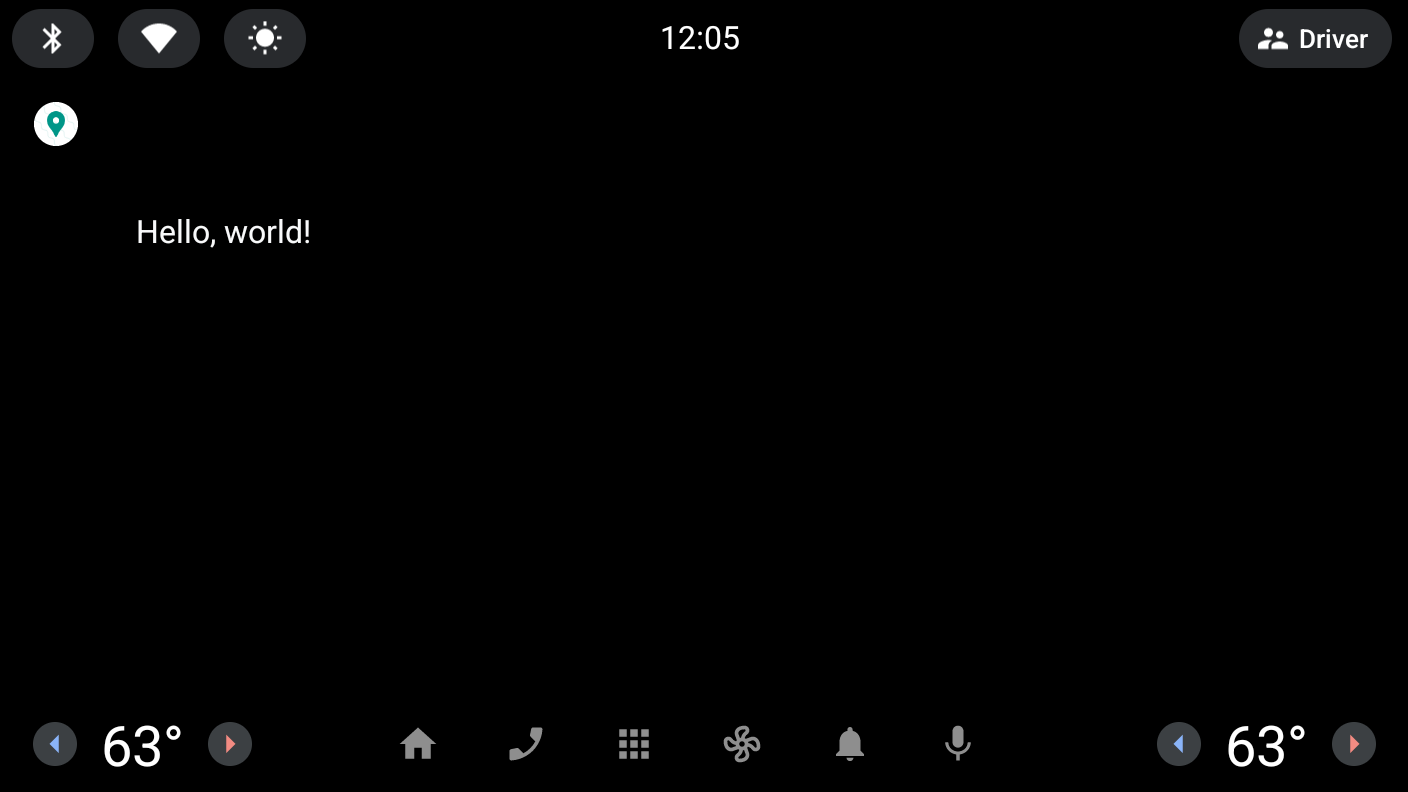
运行应用
在您刚刚使用 automotive 运行配置创建的模拟器上运行应用。

在下一步中,您将在 :common:car-app-service 模块中进行更改以显示地点列表,并允许用户开始导航到另一个应用中的选定地点。
10. 添加地图和详细信息屏幕
在主屏幕上添加地图
- 首先,将
MainScreen类的onGetTemplate方法中的代码替换为以下内容:
MainScreen.kt
import androidx.car.app.model.CarLocation
import androidx.car.app.model.Distance
import androidx.car.app.model.DistanceSpan
import androidx.car.app.model.ItemList
import androidx.car.app.model.Metadata
import androidx.car.app.model.Place
import androidx.car.app.model.PlaceListMapTemplate
import androidx.car.app.model.PlaceMarker
import com.example.places.data.PlacesRepository
...
override fun onGetTemplate(): Template {
val placesRepository = PlacesRepository()
val itemListBuilder = ItemList.Builder()
.setNoItemsMessage("No places to show")
placesRepository.getPlaces()
.forEach {
itemListBuilder.addItem(
Row.Builder()
.setTitle(it.name)
// Each item in the list *must* have a DistanceSpan applied to either the title
// or one of the its lines of text (to help drivers make decisions)
.addText(SpannableString(" ").apply {
setSpan(
DistanceSpan.create(
Distance.create(Math.random() * 100, Distance.UNIT_KILOMETERS)
), 0, 1, Spannable.SPAN_INCLUSIVE_INCLUSIVE
)
})
.setOnClickListener { TODO() }
// Setting Metadata is optional, but is required to automatically show the
// item's location on the provided map
.setMetadata(
Metadata.Builder()
.setPlace(Place.Builder(CarLocation.create(it.latitude, it.longitude))
// Using the default PlaceMarker indicates that the host should
// decide how to style the pins it shows on the map/in the list
.setMarker(PlaceMarker.Builder().build())
.build())
.build()
).build()
)
}
return PlaceListMapTemplate.Builder()
.setTitle("Places")
.setItemList(itemListBuilder.build())
.build()
}
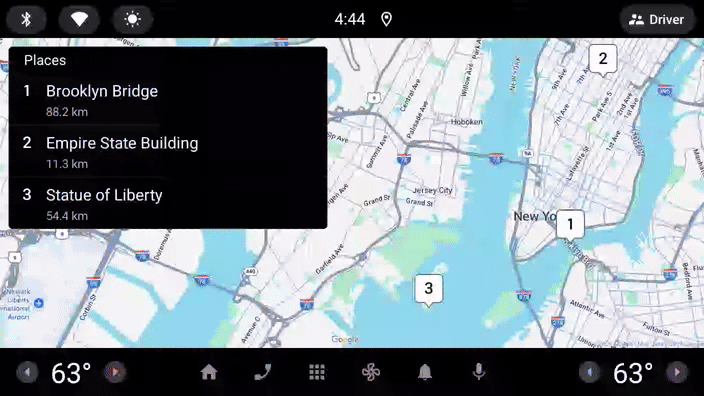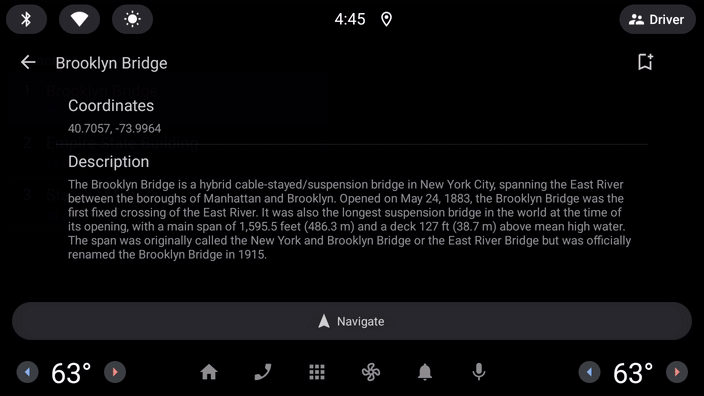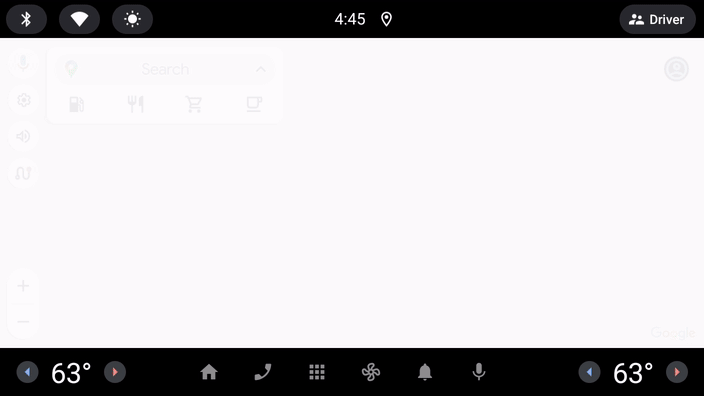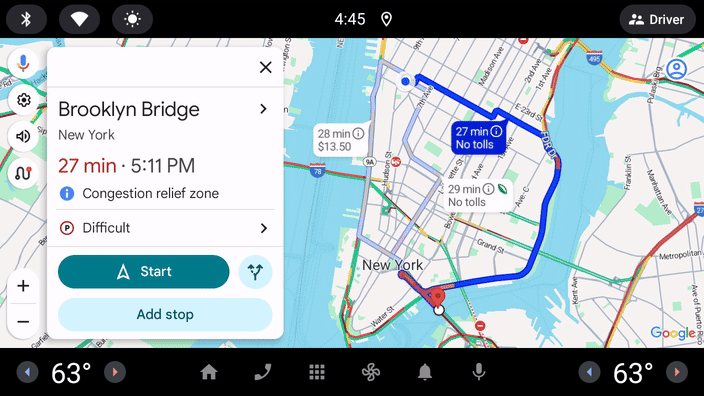
此代码从 PlacesRepository 读取 Place 实例列表,然后将每个实例转换为 Row,以添加到 PlaceListMapTemplate 显示的 ItemList。
- 再次运行应用(可以在其中一个或两个平台上运行),以查看结果:
Android Auto | Android Automotive OS |
|
|
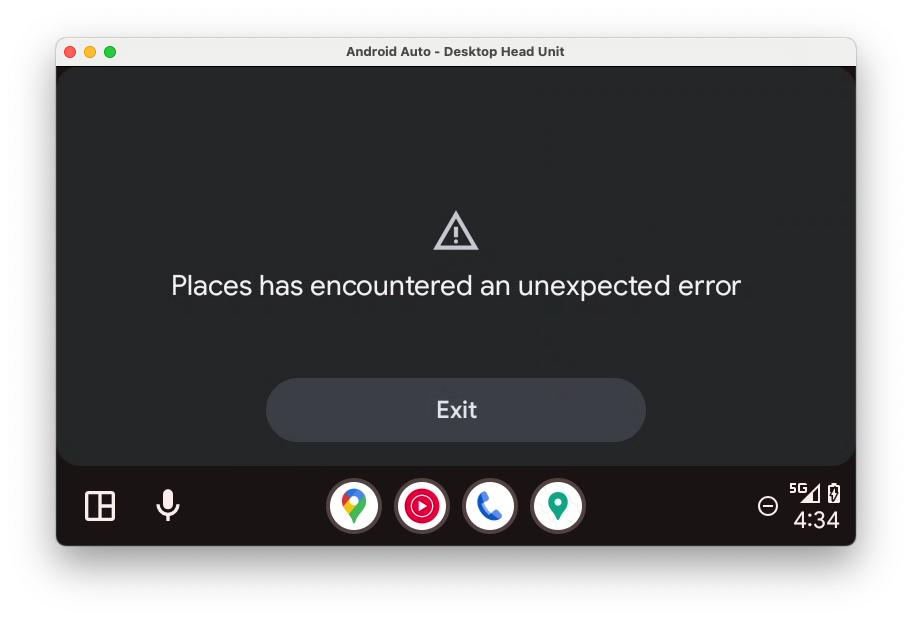
糟糕,又发生了一个错误 — 看起来是因为缺少权限。
java.lang.SecurityException: The car app does not have a required permission: androidx.car.app.MAP_TEMPLATES
at android.os.Parcel.createExceptionOrNull(Parcel.java:2373)
at android.os.Parcel.createException(Parcel.java:2357)
at android.os.Parcel.readException(Parcel.java:2340)
at android.os.Parcel.readException(Parcel.java:2282)
...
- 若要修复该错误,请在
:common:car-app-service模块的清单中添加以下<uses-permission>元素。
任何使用 PlaceListMapTemplate 的应用都必须声明此权限,否则应用将崩溃,就像刚才那样。请注意,只有将其类别声明为 androidx.car.app.category.POI 的应用才能使用此模板,进而使用此权限。
AndroidManifest.xml (:common:car-app-service)
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<uses-permission android:name="androidx.car.app.MAP_TEMPLATES" />
...
</manifest>
如果您在添加权限后运行应用,则应用在每个平台上的运行效果应如下所示:
Android Auto | Android Automotive OS |
|
|
当您提供所需的 Metadata 时,应用主机将为您完成地图渲染。
添加详细信息屏幕
接下来,可以添加一个详细信息屏幕,以便用户查看有关特定地点的更多信息,并且可以选择使用他们喜欢的导航应用导航到相应地点,或返回其他地点的列表。可以使用 PaneTemplate 来实现此目标,它允许您在可选操作按钮旁边显示最多四行信息。
- 首先,右键点击
:common:car-app-service模块中的res目录,依次点击 New > Vector Asset,然后使用以下配置创建导航图标:
- 资源类型:
Clip art - 剪贴画:
navigation - 名称:
baseline_navigation_24 - 大小:
24dp x24dp - 颜色:
#000000 - 不透明度:
100%
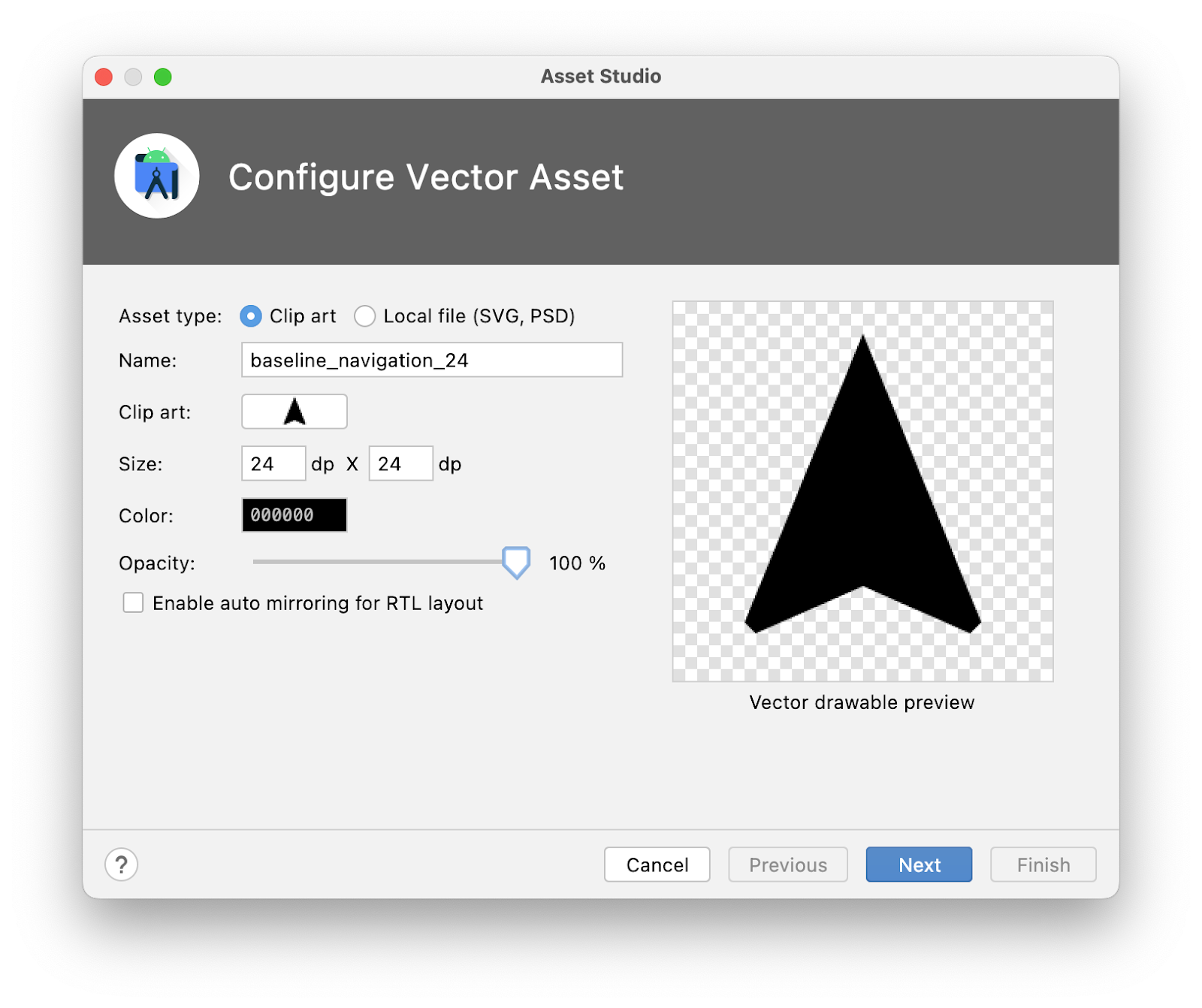
- 然后,在
screen软件包中创建一个名为DetailScreen.kt的文件(位于现有MainScreen.kt文件旁边)并添加以下代码:
DetailScreen.kt
import android.graphics.Color
import androidx.car.app.CarContext
import androidx.car.app.Screen
import androidx.car.app.model.Action
import androidx.car.app.model.CarColor
import androidx.car.app.model.CarIcon
import androidx.car.app.model.Header
import androidx.car.app.model.MessageTemplate
import androidx.car.app.model.Pane
import androidx.car.app.model.PaneTemplate
import androidx.car.app.model.Row
import androidx.car.app.model.Template
import androidx.core.graphics.drawable.IconCompat
import com.example.android.cars.carappservice.R
import com.example.places.data.PlacesRepository
import com.example.places.data.model.toIntent
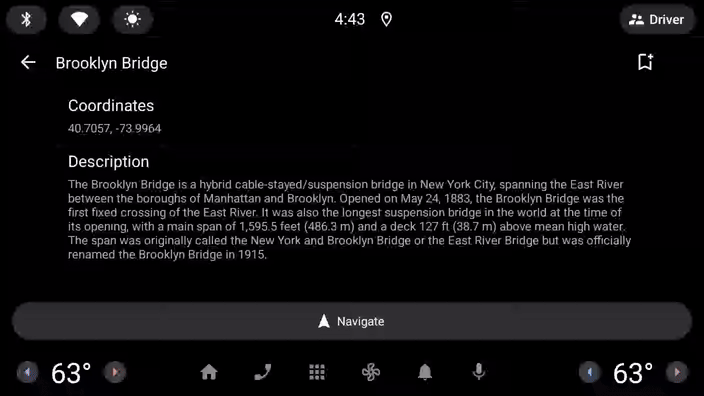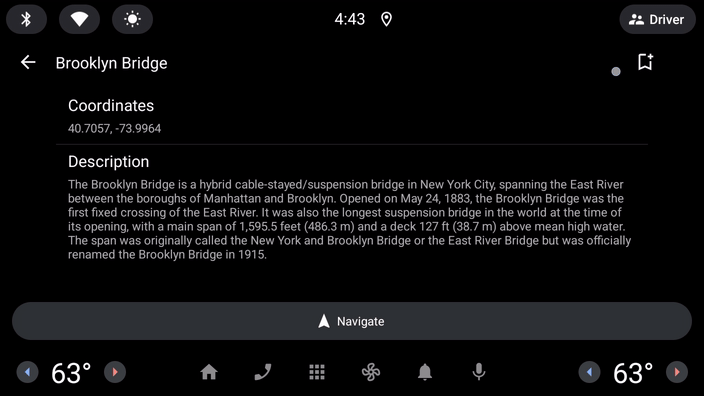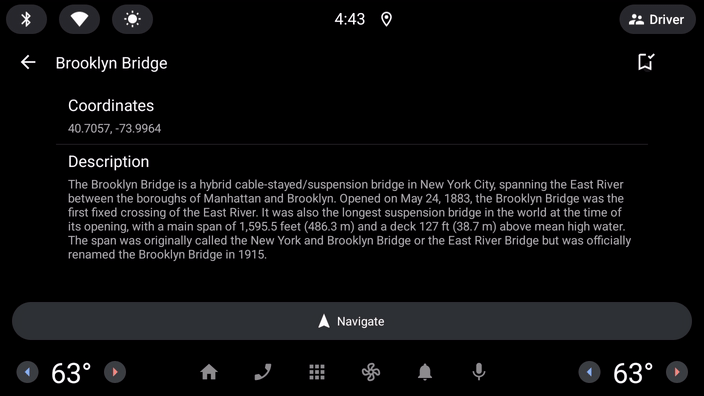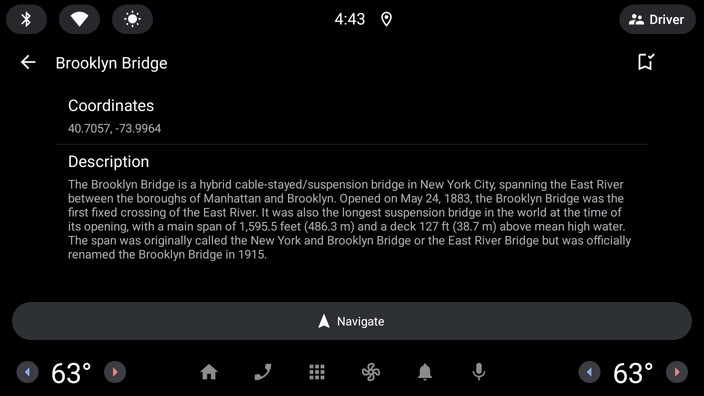
class DetailScreen(carContext: CarContext, private val placeId: Int) : Screen(carContext) {
private var isBookmarked = false
override fun onGetTemplate(): Template {
val place = PlacesRepository().getPlace(placeId)
?: return MessageTemplate.Builder("Place not found")
.setHeader(
Header.Builder()
.setStartHeaderAction(Action.BACK)
.build()
)
.build()
val navigateAction = Action.Builder()
.setTitle("Navigate")
.setIcon(
CarIcon.Builder(
IconCompat.createWithResource(
carContext,
R.drawable.baseline_navigation_24
)
).build()
)
// Only certain Intent actions are supported by `startCarApp`. Check its documentation
// for all of the details. To open another app that can handle navigating to a location
// you must use the CarContext.ACTION_NAVIGATE action and not Intent.ACTION_VIEW like
// you might on a phone.
.setOnClickListener { carContext.startCarApp(place.toIntent(CarContext.ACTION_NAVIGATE)) }
.build()
return PaneTemplate.Builder(
Pane.Builder()
.addAction(navigateAction)
.addRow(
Row.Builder()
.setTitle("Coordinates")
.addText("${place.latitude}, ${place.longitude}")
.build()
).addRow(
Row.Builder()
.setTitle("Description")
.addText(place.description)
.build()
).build()
).setHeader(
Header.Builder()
.setStartHeaderAction(Action.BACK)
.setTitle(place.name)
.build()
).build()
}
}
请重点注意 navigateAction 的构建方式 - OnClickListener 中对 startCarApp 的调用是与 Android Auto 和 Android Automotive OS 上的其他应用进行交互的关键。
在屏幕之间导航
现在已经有两种类型的屏幕,接下来可以在这些屏幕之间添加导航了。汽车应用库中的导航使用推送和弹出的堆栈模型,非常适合在驾驶过程中完成的简单任务流。
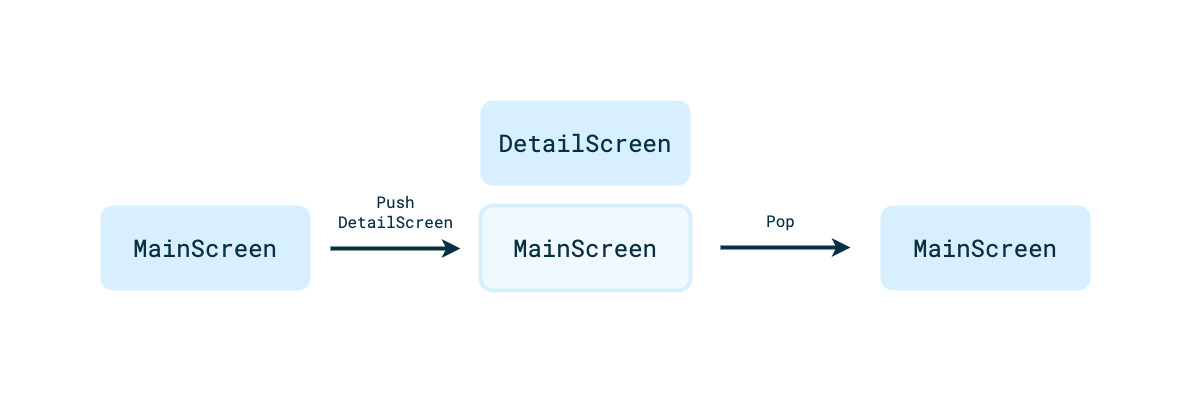
- 如要从
MainScreen上的列表项之一导航到该项目的DetailScreen,请添加以下代码:
MainScreen.kt
Row.Builder()
...
.setOnClickListener { screenManager.push(DetailScreen(carContext, it.id)) }
...
从 DetailScreen 导航回 MainScreen 的操作已得到妥善处理,因为在构建 DetailScreen 上显示的 PaneTemplate 时调用了 setHeaderAction(Action.BACK)。当用户点击标题操作时,主机会为您将当前屏幕从堆栈中弹出,但如果需要,您的应用可以覆盖此行为。
- 立即运行应用以查看
DetailScreen和应用内导航的实际效果。
11. 更新屏幕上的内容
通常,您会希望让用户与屏幕交互,并更改该屏幕上元素的状态。为了演示如何实现这一点,您要构建一项功能,允许用户在 DetailScreen 中添加或移除地点的书签。
- 首先,添加一个局部变量
isBookmarked来保存状态。在实际应用中,这应该作为数据层的一部分进行存储,但对于演示而言,一个局部变量就已经足够了。
DetailScreen.kt
class DetailScreen(carContext: CarContext, private val placeId: Int) : Screen(carContext) {
private var isBookmarked = false
...
}
- 接下来,右键点击
:common:car-app-service模块中的res目录,并依次点击 New > Vector Asset,然后使用以下配置创建两个书签图标:
- 资源类型:
Clip art - 名称:
outline_bookmark_add_24、outline_bookmark_added_24 - 剪贴画:
bookmark、bookmark_added(来自 Material Symbols Outlined 源代码集) - 大小:
24dp x24dp - 颜色:
#000000 - 不透明度:
100%
- 然后,在
DetailsScreen.kt中,为书签功能创建一个Action。
DetailScreen.kt
val navigateAction = ...
val bookmarkAction = Action.Builder()
.setIcon(
CarIcon.Builder(
IconCompat.createWithResource(
carContext,
if (isBookmarked) R.drawable.outline_bookmark_added_24 else R.drawable.outline_bookmark_add_24
)
).build()
)
.setOnClickListener {
isBookmarked = !isBookmarked
}.build()
...
这里有两个值得注意的地方:
CarIcon根据项目的状态进行着色。setOnClickListener用于对用户的输入做出反应并切换书签状态。
- 不要忘记对
PaneTemplate.Builder调用addEndHeaderAction,以便实际使用bookmarkAction。
DetailScreen.kt
Header.Builder()
...
.addEndHeaderAction(bookmarkAction)
.build()
- 现在运行应用,看看会发生什么情况:
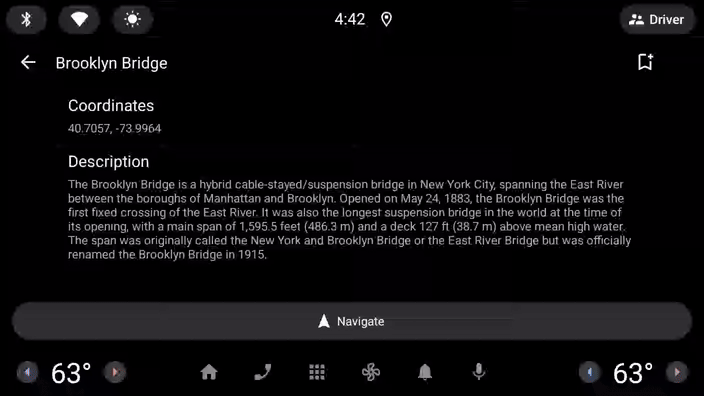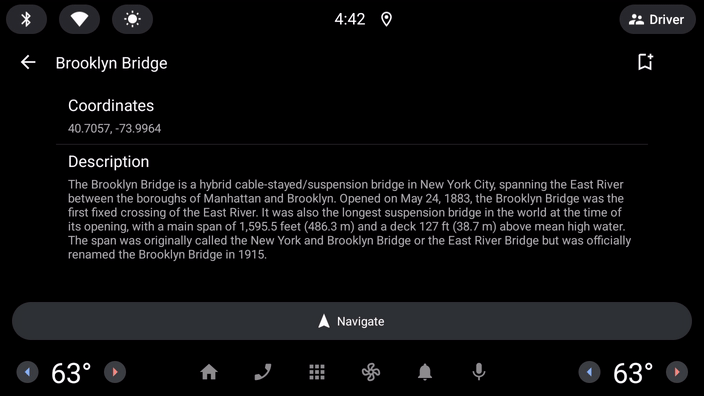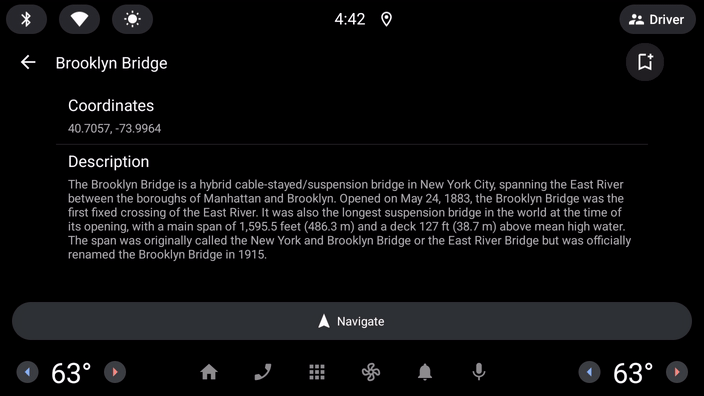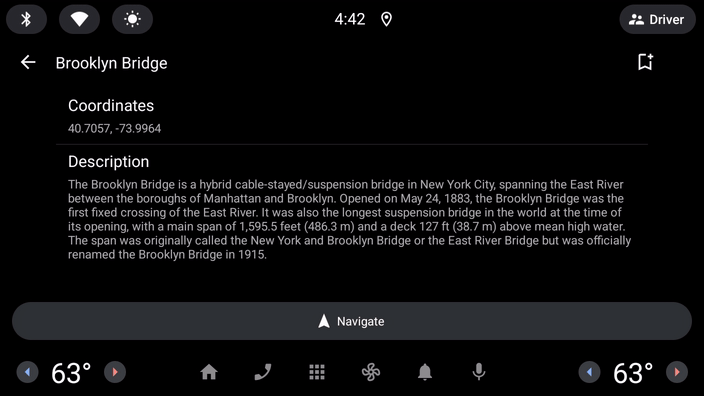
用户已执行点击操作,但图标没有发生变化。
这是因为汽车应用库有一个刷新的概念。为了避免驾驶员分心,刷新屏幕上的内容有一定的限制(具体取决于所显示的模板),并且在每次进行刷新时都必须由您自己的代码通过调用 Screen 类的 invalidate 方法来发起显式请求。仅更新在 onGetTemplate 中引用的某个状态不足以更新界面。
- 如需解决此问题,请按如下方式更新
bookmarkAction的OnClickListener:
DetailScreen.kt
.setOnClickListener {
isBookmarked = !isBookmarked
// Request that `onGetTemplate` be called again so that updates to the
// screen's state can be picked up
invalidate()
}
- 再次运行应用,您会发现,现在点击图标时图标会更新。
大功告成,您现在已经创建了一个与 Android Auto 和 Android Automotive OS 充分集成的基本应用!
12. 恭喜
您已经成功构建了您的第一个汽车应用库应用。现在是时候将您学到的知识应用到您自己的应用中了!
如前所述,目前只有使用汽车应用库构建的特定类别的应用可以提交到 Play 商店。如果您的应用属于受支持的类别,您今天就可以开始构建!
我们每年都会添加新的应用类别,因此即使您无法立即运用所学到的知识,也请不时回来看看,说不定正好就可以将您的应用扩展到汽车平台!
尝试以下任务
- 安装 OEM 模拟器并了解 OEM 自定义会如何改变 Android Automotive OS 上汽车应用库应用的外观。请注意,并非所有 OEM 模拟器都支持汽车应用库应用。
- 使用不同的 DHU 配置和 Android Automotive OS 模拟器硬件配置文件,了解宿主应用如何处理将应用调整为契合不同显示屏尺寸的情况。
- 查看 Showcase 示例应用,其中演示了汽车应用库的完整功能。
深入阅读
- 使用 Android for Cars 应用库涵盖了此 Codelab 中的内容以及更多其他信息。
- Android for Cars 应用库设计指南提供了所有不同模板的详细说明以及在构建应用时应当遵循的最佳实践。
- Android 汽车应用质量页面描述了您的应用必须满足什么标准,才能打造出色的用户体验并通过 Play 商店审核。