เช่นเดียวกับรุ่นก่อนๆ Android 16 มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานที่อาจส่งผลต่อแอปของคุณ การเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานต่อไปนี้มีผลเฉพาะกับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 ขึ้นไป หากแอปกำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 ขึ้นไป คุณควรแก้ไขแอปให้รองรับลักษณะการทำงานเหล่านี้ในกรณีที่เกี่ยวข้อง
นอกจากนี้ โปรดตรวจสอบรายการการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานที่มีผลต่อแอปทั้งหมด
ที่ทำงานบน Android 16 ไม่ว่า targetSdkVersion ของแอปจะเป็นอย่างไร
ประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้และ UI ของระบบ
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ซึ่งมีจุดประสงค์ เพื่อสร้างประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้ที่สอดคล้องกันและใช้งานง่ายยิ่งขึ้น
การเลือกไม่ใช้แบบไร้ขอบจะสิ้นสุดลง
Android 15 强制执行全屏显示,但您的应用可以通过将 R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement 设置为 true 来选择停用此功能。对于以 Android 16(API 级别 36)为目标平台的应用,R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement 已被废弃并停用,并且您的应用无法选择不采用从边缘到边缘的布局。
- 如果您的应用以 Android 16(API 级别 36)为目标平台,并且在 Android 15 设备上运行,则
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement会继续正常运行。 - 如果您的应用以 Android 16(API 级别 36)为目标平台,并且在 Android 16 设备上运行,则
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement会被停用。
如需在 Android 16 中进行测试,请确保您的应用支持无边框设计,并移除所有 R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement 用法,以便您的应用在 Android 15 设备上也能支持无边框设计。如需支持从边缘到边缘的显示,请参阅 Compose 和 Views 指南。
ต้องย้ายข้อมูลหรือเลือกไม่ใช้เพื่อใช้การคาดการณ์การย้อนกลับ
对于以 Android 16(API 级别 36)或更高版本为目标平台且在搭载 Android 16 或更高版本的设备上运行的应用,预测性返回系统动画(返回主屏幕、跨任务和跨 activity)默认处于启用状态。此外,系统不再调用 onBackPressed,也不再调度 KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK。
如果您的应用会拦截返回事件,但您尚未迁移到预测性返回,请更新应用以使用受支持的返回导航 API,或者通过在应用的 AndroidManifest.xml 文件的 <application> 或 <activity> 标记中将 android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback 属性设置为 false 来暂时选择停用。
เลิกใช้งานและปิดใช้ Elegant Font API
以 Android 15(API 级别 35)为目标平台的应用默认将 elegantTextHeight
TextView 属性设置为 true,从而将紧凑型字体替换为可读性更高的字体。您可以通过将 elegantTextHeight 属性设置为 false 来替换此设置。
Android 16 弃用了 elegantTextHeight 属性,当您的应用以 Android 16 为目标平台后,系统会忽略该属性。由这些 API 控制的“界面字体”即将停用,因此您应调整所有布局,以确保阿拉伯语、老挝语、缅甸语、泰米尔语、古吉拉特语、卡纳达语、马拉雅拉姆语、奥里亚语、泰卢固语或泰语文本的呈现效果一致且不受未来变化的影响。
elegantTextHeight 属性设置为 false 替换默认值的应用,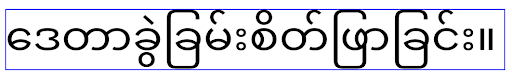
elegantTextHeight 行为。elegantTextHeight 属性设置为 false 来替换默认值的应用,其 elegantTextHeight 行为。
ฟังก์ชันหลัก
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ซึ่งจะแก้ไขหรือ ขยายความสามารถหลักต่างๆ ของระบบ Android
การเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการจัดกำหนดเวลางานแบบอัตราคงที่
在以 Android 16 为目标平台之前,如果 scheduleAtFixedRate 因不在有效的进程生命周期内而错过了任务执行,则当应用返回到有效的生命周期时,所有错过的执行会立即执行。
以 Android 16 为目标平台时,当应用返回到有效的生命周期时,系统会立即执行最多 1 次未执行的 scheduleAtFixedRate 执行。此行为变更预计会提升应用性能。在您的应用中测试此行为,检查您的应用是否受到影响。您还可以使用应用兼容性框架并启用 STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS 兼容性标志进行测试。
รูปแบบของอุปกรณ์
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้สำหรับแอปเมื่อ แสดงบนอุปกรณ์หน้าจอขนาดใหญ่
เลย์เอาต์แบบปรับขนาดได้
เนื่องจากตอนนี้แอป Android ทำงานบนอุปกรณ์หลากหลายประเภท (เช่น โทรศัพท์ แท็บเล็ต อุปกรณ์พับได้ เดสก์ท็อป รถยนต์ และทีวี) และโหมดการจัดหน้าต่างบนหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ (เช่น การแยกหน้าจอและการจัดหน้าต่างบนเดสก์ท็อป) นักพัฒนาแอปจึงควรสร้างแอป Android ที่ปรับให้เข้ากับขนาดหน้าจอและหน้าต่างได้ทุกขนาด ไม่ว่าอุปกรณ์จะวางแนวใดก็ตาม กระบวนทัศน์ต่างๆ เช่น การจำกัดการวางแนวและความสามารถในการปรับขนาด มีข้อจำกัดมากเกินไปในโลกที่มีอุปกรณ์หลายเครื่องในปัจจุบัน
ไม่สนใจข้อจำกัดด้านการวางแนว ความสามารถในการปรับขนาด และสัดส่วนภาพ
สำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) ข้อจำกัดด้านการวางแนว ความสามารถในการปรับขนาด และอัตราส่วนภาพจะไม่มีผลกับการแสดงผลที่มีความกว้างน้อยที่สุด >= 600dp อีกต่อไป แอปจะแสดงเต็มหน้าต่างแสดงผล ไม่ว่าสัดส่วนภาพหรือการวางแนวที่ผู้ใช้ต้องการจะเป็นอย่างไร และจะไม่มีการใช้แถบดำด้านข้าง
การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้จะทำให้แพลตฟอร์มมีลักษณะการทำงานที่เป็นมาตรฐานใหม่ Android กำลังเปลี่ยนไปใช้โมเดลที่คาดหวังให้แอปปรับให้เข้ากับการวางแนว ขนาดการแสดงผล และสัดส่วนภาพต่างๆ ข้อจำกัดต่างๆ เช่น การวางแนวคงที่ หรือการปรับขนาดที่จำกัด จะขัดขวางความสามารถในการปรับตัวของแอป ทำให้แอปของคุณ ปรับเปลี่ยนตามอุปกรณ์เพื่อมอบประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้ที่ดีที่สุด
นอกจากนี้ คุณยังทดสอบลักษณะการทำงานนี้ได้โดยใช้
เฟรมเวิร์กความเข้ากันได้ของแอปและเปิดใช้
UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT compat flag
การเปลี่ยนแปลงที่ส่งผลกับส่วนอื่นในระบบที่พบบ่อย
การไม่สนใจข้อจำกัดด้านการวางแนว ความสามารถในการปรับขนาด และสัดส่วนภาพอาจส่งผลต่อ UI ของแอปในอุปกรณ์บางเครื่อง โดยเฉพาะองค์ประกอบที่ออกแบบมาสำหรับเลย์เอาต์ขนาดเล็ก ที่ล็อกในการวางแนวตั้ง เช่น ปัญหาต่างๆ เช่น เลย์เอาต์ที่ยืด และภาพเคลื่อนไหวและคอมโพเนนต์ที่อยู่นอกหน้าจอ การคาดเดาเกี่ยวกับสัดส่วนภาพหรือการวางแนวอาจทำให้เกิดปัญหาด้านภาพกับแอป ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับวิธีหลีกเลี่ยงปัญหาดังกล่าวและปรับปรุงลักษณะการทำงานแบบปรับเปลี่ยนได้ของแอป
การอนุญาตให้หมุนอุปกรณ์จะทำให้เกิดการสร้างกิจกรรมใหม่มากขึ้น ซึ่งอาจส่งผล ให้สถานะของผู้ใช้สูญหายหากไม่ได้เก็บรักษาไว้อย่างถูกต้อง ดูวิธีบันทึกสถานะ UI อย่างถูกต้องในบันทึกสถานะ UI
รายละเอียดการติดตั้งใช้งาน
ระบบจะละเว้นแอตทริบิวต์ของไฟล์ Manifest และ API รันไทม์ต่อไปนี้ในอุปกรณ์หน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ในโหมดเต็มหน้าจอและโหมดหลายหน้าต่าง
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
ระบบจะละเว้นค่าต่อไปนี้สำหรับ screenOrientation, setRequestedOrientation() และ getRequestedOrientation()
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
ในส่วนของการปรับขนาดจอแสดงผล android:resizeableActivity="false",
android:minAspectRatio และ android:maxAspectRatio จะไม่มีผล
สำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) ระบบจะละเว้นข้อจำกัดด้านการวางแนว ความสามารถในการปรับขนาด และสัดส่วนภาพของแอปบนหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่โดยค่าเริ่มต้น แต่แอปทุกแอปที่ยังไม่พร้อมอย่างเต็มที่สามารถลบล้างลักษณะการทำงานนี้ชั่วคราวได้โดยการเลือกไม่ใช้ (ซึ่งจะส่งผลให้แอปมีลักษณะการทำงานก่อนหน้าคืออยู่ในโหมดความเข้ากันได้)
ข้อยกเว้น
ข้อจำกัดด้านการวางแนว ความสามารถในการปรับขนาด และสัดส่วนภาพของ Android 16 จะไม่ มีผลในกรณีต่อไปนี้
- เกม (อิงตามธง
android:appCategory) - ผู้ใช้เลือกใช้ลักษณะการทำงานเริ่มต้นของแอปอย่างชัดแจ้งในการตั้งค่าสัดส่วนภาพของอุปกรณ์
- หน้าจอที่มีขนาดเล็กกว่า
sw600dp
เลือกไม่ใช้ชั่วคราว
หากต้องการเลือกไม่ใช้กิจกรรมที่เฉพาะเจาะจง ให้ประกาศPROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITYพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ของไฟล์ Manifest ดังนี้
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
หากส่วนต่างๆ ของแอปยังไม่พร้อมสำหรับ Android 16 คุณสามารถเลือกไม่ใช้ ทั้งหมดได้โดยใช้พร็อพเพอร์ตี้เดียวกันที่ระดับแอปพลิเคชัน
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
สุขภาพและการออกกำลังกาย
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับข้อมูลสุขภาพ และการออกกำลังกาย
สิทธิ์ด้านสุขภาพและการออกกำลังกาย
对于以 Android 16(API 级别 36)或更高版本为目标平台的应用,BODY_SENSORS 权限使用 android.permissions.health 下更精细的权限,健康数据共享也使用这些权限。自 Android 16 起,凡是以前需要具有 BODY_SENSORS 或 BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND 权限的 API,现在都需要获取相应的 android.permissions.health 权限。这会影响以下数据类型、API 和前台服务类型:
- 从 Wear OS 上的健康服务中获取
HEART_RATE_BPM - 来自 Android Sensor Manager 的
Sensor.TYPE_HEART_RATE - 在 Wear OS 上,
ProtoLayout中的heartRateAccuracy和heartRateBpm FOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTH,其中需要使用相应的android.permission.health权限来代替BODY_SENSORS
如果您的应用使用这些 API,则应请求相应的精细权限:
- 对于使用期间的心率、血氧饱和度或体表温度监测:请求
android.permissions.health下的精细权限,例如READ_HEART_RATE,而不是BODY_SENSORS。 - 对于后台传感器访问权限:请求
READ_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUND而不是BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND。
这些权限与用于保护对 Health Connect(Android 健康、健身和身心状态数据存储区)中读取数据的访问权限相同。
移动应用
迁移到使用 READ_HEART_RATE 和其他精细权限的移动应用还必须声明 activity 以显示应用的隐私权政策。此要求与健康数据共享的要求相同。
การเชื่อมต่อ
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ในสแต็กบลูทูธ เพื่อปรับปรุงการเชื่อมต่อกับอุปกรณ์ต่อพ่วง
เจตนาใหม่ในการจัดการการสูญเสียพันธะและการเปลี่ยนแปลงการเข้ารหัส
การจัดการการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงที่ดีขึ้นทำให้ Android 16 เปิดตัว Intent ใหม่ 2 รายการเพื่อให้แอปรับรู้ถึงการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงและการเปลี่ยนแปลงการเข้ารหัสได้ดียิ่งขึ้น
ตอนนี้แอปที่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 ทําสิ่งต่อไปนี้ได้
- รับ Intent
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGเมื่อตรวจพบการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงระยะไกล ซึ่งช่วยให้สามารถแสดงความคิดเห็นที่เป็นประโยชน์ต่อผู้ใช้มากขึ้นและดำเนินการที่เหมาะสม - รับ Intent
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEเมื่อใดก็ตามที่สถานะการเข้ารหัสของลิงก์มีการเปลี่ยนแปลง ซึ่งรวมถึงการเปลี่ยนแปลงสถานะการเข้ารหัส การเปลี่ยนแปลงอัลกอริทึมการเข้ารหัส และการเปลี่ยนแปลงขนาดคีย์การเข้ารหัส แอปต้องถือว่าการเชื่อมโยงได้รับการคืนค่าหากลิงก์ได้รับการเข้ารหัสเรียบร้อยแล้วเมื่อได้รับ IntentACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEในภายหลัง
การปรับให้เข้ากับการใช้งาน OEM ที่หลากหลาย
แม้ว่า Android 16 จะเปิดตัว Intent ใหม่เหล่านี้ แต่การใช้งานและการออกอากาศอาจแตกต่างกันไปตามผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์ (OEM) แต่ละราย นักพัฒนาแอปควรออกแบบการจัดการการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงให้ปรับให้เข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงที่อาจเกิดขึ้นเหล่านี้ได้อย่างราบรื่น เพื่อให้แอปมอบประสบการณ์การใช้งานที่สอดคล้องกันและเชื่อถือได้ในอุปกรณ์ทุกเครื่อง
เราขอแนะนําลักษณะการทํางานของแอปดังต่อไปนี้
หากมีการออกอากาศ Intent
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGให้ทำดังนี้ระบบจะตัดการเชื่อมต่อลิงก์ ACL (การเชื่อมต่อแบบไม่ใช้การเชื่อมต่อแบบแอซิงโครนัส) แต่ระบบจะเก็บข้อมูลการเชื่อมโยงสำหรับอุปกรณ์ไว้ (ตามที่อธิบายไว้ที่นี่)
แอปของคุณควรใช้ Intent นี้เป็นสัญญาณหลักในการจับสัญญาณการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงและแนะนำผู้ใช้ให้ยืนยันว่าอุปกรณ์ระยะไกลอยู่ในระยะสัญญาณก่อนที่จะเริ่มการลืมอุปกรณ์หรือการจับคู่อีกครั้ง
หากอุปกรณ์ตัดการเชื่อมต่อหลังจากได้รับ
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGแอปของคุณควรระมัดระวังเกี่ยวกับการเชื่อมต่ออีกครั้ง เนื่องจากอุปกรณ์อาจไม่ได้จับคู่กับระบบแล้วหากไม่ได้ออกอากาศ Intent
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGลิงก์ ACL จะยังคงเชื่อมต่ออยู่ และระบบจะนำข้อมูลการเชื่อมโยงของอุปกรณ์ออก เช่นเดียวกับลักษณะการทำงานใน Android 15
ในกรณีนี้ แอปของคุณควรใช้กลไกการจัดการการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงที่มีอยู่ต่อไปเช่นเดียวกับใน Android รุ่นก่อนหน้า เพื่อตรวจหาและจัดการเหตุการณ์การสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยง
วิธีใหม่ในการนำการจับคู่บลูทูธออก
ตอนนี้แอปทั้งหมดที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 สามารถยกเลิกการจับคู่อุปกรณ์บลูทูธได้โดยใช้ API สาธารณะใน CompanionDeviceManager หากอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ร่วมกันได้รับการจัดการเป็นการเชื่อมโยง CDM แอปจะทริกเกอร์การนำการเชื่อมโยงบลูทูธออกได้โดยใช้ removeBond(int) API ใหม่ในอุปกรณ์ที่เชื่อมโยง แอปสามารถตรวจสอบการเปลี่ยนแปลงสถานะการเชื่อมโยงได้โดยฟังเหตุการณ์การแพร่กระจายข้อมูลของอุปกรณ์บลูทูธ
ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED
ความปลอดภัย
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงด้านความปลอดภัยต่อไปนี้
การล็อกดาวน์เวอร์ชัน MediaStore
对于以 Android 16 或更高版本为目标平台的应用,MediaStore#getVersion() 现在将是每个应用的唯一标识。这会从版本字符串中移除标识属性,以防止滥用和用于指纹识别技术。应用不应对此版本的格式做出任何假设。在使用此 API 时,应用应已处理版本变更,并且在大多数情况下无需更改其当前行为,除非开发者尝试推断超出此 API 预期范围的其他信息。
เจตนาที่ปลอดภัยกว่า
ฟีเจอร์ Intent ที่ปลอดภัยยิ่งขึ้นเป็นโครงการริเริ่มด้านความปลอดภัยแบบหลายเฟสที่ออกแบบมาเพื่อ ปรับปรุงความปลอดภัยของกลไกการแก้ไข Intent ของ Android เป้าหมายคือการปกป้องแอปจากการกระทำที่เป็นอันตรายโดยการเพิ่มการตรวจสอบระหว่าง การประมวลผล Intent และการกรอง Intent ที่ไม่เป็นไปตามเกณฑ์ที่เฉพาะเจาะจง
ใน Android 15 ฟีเจอร์นี้มุ่งเน้นที่แอปที่ส่ง แต่ใน Android 16 จะเปลี่ยนการควบคุมไปที่แอปที่รับ ซึ่งช่วยให้นักพัฒนาแอปเลือกใช้ความละเอียดของ Intent ที่เข้มงวดได้โดยใช้ไฟล์ Manifest ของแอป
เราจะดำเนินการเปลี่ยนแปลงที่สำคัญ 2 อย่างต่อไปนี้
Intent แบบเจาะจงปลายทางต้องตรงกับตัวกรอง Intent ของคอมโพเนนต์เป้าหมาย หาก Intent กำหนดเป้าหมายคอมโพเนนต์อย่างชัดแจ้ง Intent นั้นควรตรงกับ ตัวกรอง Intent ของคอมโพเนนต์นั้น
Intent ที่ไม่มีการดำเนินการจะจับคู่กับตัวกรอง Intent ไม่ได้: Intent ที่ไม่ได้ระบุการดำเนินการไม่ควรได้รับการแก้ไขเป็นตัวกรอง Intent ใดๆ
การเปลี่ยนแปลงเหล่านี้จะมีผลเมื่อเกี่ยวข้องกับแอปหลายแอปเท่านั้น และจะไม่มีผลต่อ การจัดการ Intent ภายในแอปเดียว
ผลกระทบ
ลักษณะการเลือกใช้หมายความว่านักพัฒนาแอปต้องเปิดใช้ฟีเจอร์นี้อย่างชัดแจ้งใน ไฟล์ Manifest ของแอปเพื่อให้มีผล ด้วยเหตุนี้ ผลกระทบของฟีเจอร์นี้จึงจำกัดอยู่เฉพาะแอปที่นักพัฒนาแอป
- ทราบถึงฟีเจอร์เจตนาที่ปลอดภัยยิ่งขึ้นและประโยชน์ของฟีเจอร์นี้
- เลือกที่จะนำแนวทางปฏิบัติในการจัดการ Intent ที่เข้มงวดมากขึ้นมาใช้ในแอปของตน
แนวทางในการเลือกใช้นี้ช่วยลดความเสี่ยงที่จะทำให้แอปที่มีอยู่ซึ่งอาจต้องอาศัย ลักษณะการทำงานของการแก้ปัญหา Intent ที่มีความปลอดภัยน้อยในปัจจุบันใช้งานไม่ได้
แม้ว่าผลกระทบเริ่มต้นใน Android 16 อาจมีจำกัด แต่โครงการ Safer Intents มีแผนงานที่จะสร้างผลกระทบในวงกว้างขึ้นใน Android รุ่นต่อๆ ไป แผนของเราคือการทำให้การแก้เจตนาอย่างเข้มงวดเป็นลักษณะการทำงานเริ่มต้นในที่สุด
ฟีเจอร์ Intent ที่ปลอดภัยยิ่งขึ้นมีศักยภาพในการปรับปรุง ความปลอดภัยของระบบนิเวศ Android ได้อย่างมากด้วยการทำให้แอปที่เป็นอันตราย ใช้ประโยชน์จากช่องโหว่ในกลไกการแก้ไข Intent ได้ยากขึ้น
อย่างไรก็ตาม การเปลี่ยนไปใช้การเลือกไม่ใช้และการบังคับใช้ที่จำเป็นต้องได้รับการจัดการอย่างรอบคอบเพื่อแก้ไขปัญหาความเข้ากันได้ที่อาจเกิดขึ้นกับแอปที่มีอยู่
การใช้งาน
นักพัฒนาแอปต้องเปิดใช้การจับคู่ Intent ที่เข้มงวดขึ้นอย่างชัดแจ้งโดยใช้แอตทริบิวต์
intentMatchingFlags ในไฟล์ Manifest ของแอป
ต่อไปนี้คือตัวอย่างกรณีที่ฟีเจอร์นี้เป็นแบบเลือกใช้สำหรับทั้งแอป
แต่ปิดใช้/เลือกไม่ใช้ในตัวรับ
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับฟีเจอร์ที่รองรับ
| ชื่อแฟล็ก | คำอธิบาย |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | บังคับใช้การจับคู่ที่เข้มงวดขึ้นสำหรับ Intent ขาเข้า |
| ไม่มี | ปิดใช้กฎการจับคู่พิเศษทั้งหมดสำหรับ Intent ขาเข้า เมื่อระบุหลายแฟล็ก ค่าที่ขัดแย้งกันจะได้รับการแก้ไขโดยให้ความสำคัญกับแฟล็ก "none" |
| allowNullAction | ผ่อนปรนกฎการจับคู่เพื่อให้ Intent ที่ไม่มีการดำเนินการจับคู่ได้ Flag นี้ใช้ร่วมกับ "enforceIntentFilter" เพื่อให้ได้ลักษณะการทำงานที่เฉพาะเจาะจง |
การทดสอบและการแก้ไขข้อบกพร่อง
เมื่อการบังคับใช้มีผล แอปควรทํางานได้อย่างถูกต้องหากผู้เรียกใช้ Intent ป้อนข้อมูล Intent อย่างถูกต้อง
อย่างไรก็ตาม Intent ที่ถูกบล็อกจะทริกเกอร์ข้อความบันทึกคำเตือน เช่น
"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" และ "Access blocked:"
พร้อมแท็ก "PackageManager."
ซึ่งบ่งบอกถึงปัญหาที่อาจส่งผลต่อแอปและต้อง
ได้รับความสนใจ
ตัวกรอง Logcat:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
การกรอง Syscall ของ GPU
เพื่อเพิ่มความปลอดภัยของพื้นผิว Mali GPU เราจึงบล็อก IOCTL ของ Mali GPU ที่เลิกใช้งานแล้วหรือมีไว้สำหรับการพัฒนา GPU เท่านั้นในบิลด์เวอร์ชันที่ใช้งานจริง นอกจากนี้ IOCTL ที่ใช้สำหรับการสร้างโปรไฟล์ GPU ยังถูกจำกัดไว้สำหรับกระบวนการเชลล์หรือแอปพลิเคชันที่แก้ไขข้อบกพร่องได้ ดูรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับนโยบายระดับแพลตฟอร์มได้ที่การปรับปรุง SAC
การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้จะมีผลในอุปกรณ์ Pixel ที่ใช้ GPU ของ Mali (Pixel 6-9) Arm
ได้จัดหมวดหมู่ IOCTL อย่างเป็นทางการใน
Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst ของรุ่น r54p2 เราจะดูแลรายการนี้ต่อไปในการเผยแพร่ไดรเวอร์ในอนาคต
การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้ไม่ส่งผลต่อ API กราฟิกที่รองรับ (รวมถึง Vulkan และ OpenGL) และคาดว่าจะไม่ส่งผลต่อนักพัฒนาแอปหรือแอปพลิเคชันที่มีอยู่ เครื่องมือสร้างโปรไฟล์ GPU เช่น Streamline Performance Analyzer และ Android GPU Inspector จะไม่ได้รับผลกระทบ
การทดสอบ
หากเห็นการปฏิเสธ SELinux ที่คล้ายกับข้อความต่อไปนี้ แสดงว่าแอปพลิเคชันของคุณอาจได้รับผลกระทบจากการเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
หากแอปพลิเคชันของคุณต้องใช้ IOCTL ที่ถูกบล็อก โปรดรายงานข้อบกพร่องและมอบหมายให้ android-partner-security@google.com
คำถามที่พบบ่อย
การเปลี่ยนแปลงนโยบายนี้มีผลกับ OEM ทุกรายไหม การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้จะเป็นแบบเลือกใช้ แต่พร้อมให้บริการแก่ OEM ทุกรายที่ต้องการใช้วิธีการเสริมความแข็งแกร่งนี้ ดูวิธีการใช้การเปลี่ยนแปลงได้ใน เอกสารประกอบการใช้งาน
จำเป็นต้องทำการเปลี่ยนแปลงในฐานของโค้ด OEM เพื่อใช้ฟีเจอร์นี้ไหม หรือฟีเจอร์นี้จะมาพร้อมกับ AOSP รุ่นใหม่โดยค่าเริ่มต้น การเปลี่ยนแปลงระดับแพลตฟอร์มจะมาพร้อมกับการเปิดตัว AOSP ใหม่โดยค่าเริ่มต้น ผู้ให้บริการ อาจเลือกใช้การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้ในโค้ดเบสหากต้องการใช้
SoC มีหน้าที่รับผิดชอบในการอัปเดตรายการ IOCTL ให้เป็นปัจจุบันใช่ไหม เช่น หากอุปกรณ์ของฉันใช้ GPU ของ ARM Mali ฉันจะต้องติดต่อ ARM เพื่อขอรับการเปลี่ยนแปลงไหม SoC แต่ละรายการต้องอัปเดตรายการ IOCTL ต่ออุปกรณ์เมื่อมีการเผยแพร่ไดรเวอร์ เช่น ARM จะอัปเดตรายการ IOCTL ที่เผยแพร่เมื่อมีการอัปเดตไดรเวอร์ อย่างไรก็ตาม OEM ควรตรวจสอบว่าได้รวมการอัปเดตไว้ใน SEPolicy และเพิ่ม IOCTL ที่กำหนดเองที่เลือกไว้ลงในรายการตามที่จำเป็น
การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้จะมีผลกับอุปกรณ์ Pixel ทุกรุ่นที่วางจำหน่ายโดยอัตโนมัติ หรือผู้ใช้ต้องดำเนินการบางอย่างเพื่อเปิด/ปิดการตั้งค่าเพื่อใช้การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้ การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้จะมีผลกับอุปกรณ์ Pixel ทุกเครื่องที่วางจำหน่ายซึ่งใช้ GPU Mali (Pixel 6-9) ผู้ใช้ไม่จำเป็นต้องดำเนินการใดๆ เพื่อใช้การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้
การใช้นโยบายนี้จะส่งผลต่อประสิทธิภาพของไดรเวอร์เคอร์เนลไหม เราได้ทดสอบนโยบายนี้ใน GPU ของ Mali โดยใช้ GFXBench และไม่พบการเปลี่ยนแปลงที่วัดได้ ในประสิทธิภาพของ GPU
จำเป็นไหมที่รายการ IOCTL จะต้องสอดคล้องกับเวอร์ชันปัจจุบันของไดรเวอร์ในเคอร์เนลและพื้นที่ผู้ใช้ ได้ รายการ IOCTL ที่อนุญาตต้องซิงค์กับ IOCTL ที่ไดรเวอร์ทั้งใน Userspace และเคอร์เนลรองรับ หากมีการอัปเดต IOCTL ในพื้นที่ผู้ใช้หรือ ไดรเวอร์เคอร์เนล จะต้องอัปเดตรายการ IOCTL ของ SEPolicy ให้ตรงกัน
ARM ได้จัดหมวดหมู่ IOCTL เป็น "จำกัด" / "การวัด" แต่เราต้องการใช้ IOCTL บางรายการในกรณีการใช้งานจริง และ/หรือปฏิเสธรายการอื่นๆ OEM/SoC แต่ละรายมีหน้าที่รับผิดชอบในการตัดสินใจว่าจะจัดหมวดหมู่ IOCTL ที่ใช้ตามการกำหนดค่าของไลบรารี Mali ในพื้นที่ผู้ใช้ของตนอย่างไร คุณใช้รายการของ ARM เพื่อช่วยในการตัดสินใจได้ แต่กรณีการใช้งานของ OEM/SoC แต่ละรายอาจแตกต่างกัน
ความเป็นส่วนตัว
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงด้านความเป็นส่วนตัวต่อไปนี้
สิทธิ์เข้าถึงเครือข่ายภายใน
แอปที่มีINTERNETจะเข้าถึงอุปกรณ์ใน LAN ได้
ซึ่งช่วยให้แอปเชื่อมต่อกับอุปกรณ์ในพื้นที่ได้ง่าย แต่ก็มีผลกระทบด้านความเป็นส่วนตัวด้วย เช่น การสร้างลายนิ้วมือของผู้ใช้ และการเป็นพร็อกซีสำหรับตำแหน่ง
โปรเจ็กต์การปกป้องเครือข่าย LAN มีเป้าหมายเพื่อปกป้องความเป็นส่วนตัวของผู้ใช้โดย จำกัดการเข้าถึงเครือข่าย LAN ไว้เบื้องหลังสิทธิ์รันไทม์ใหม่
แผนการเปิดตัว
การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้จะเปิดตัวระหว่าง 2 รุ่น ได้แก่ 25Q2 และ 26Q2 ตามลำดับ นักพัฒนาแอปต้องปฏิบัติตามคำแนะนำนี้สำหรับ 25Q2 และแชร์ความคิดเห็น เนื่องจากระบบจะบังคับใช้การป้องกันเหล่านี้ใน Android รุ่นต่อๆ ไป นอกจากนี้ นักพัฒนาแอปจะต้องอัปเดตสถานการณ์ที่ขึ้นอยู่กับการเข้าถึงเครือข่ายภายในโดยนัยโดยใช้คำแนะนำต่อไปนี้ และเตรียมพร้อมสำหรับการปฏิเสธของผู้ใช้ และการเพิกถอนสิทธิ์ใหม่
ผลกระทบ
ในระยะปัจจุบัน LNP เป็นฟีเจอร์ที่ต้องเลือกใช้ ซึ่งหมายความว่าจะมีผลกับแอปที่เลือกใช้เท่านั้น เป้าหมายของระยะการเลือกใช้คือการช่วยให้นักพัฒนาแอป เข้าใจว่าส่วนใดของแอปที่ต้องอาศัยการเข้าถึงเครือข่าย LAN โดยนัย เพื่อเตรียมพร้อมที่จะใช้การป้องกันสิทธิ์สำหรับส่วนดังกล่าวในการเปิดตัวครั้งถัดไป
แอปจะได้รับผลกระทบหากเข้าถึงเครือข่ายท้องถิ่นของผู้ใช้โดยใช้สิ่งต่อไปนี้
- การใช้ซ็อกเก็ตดิบโดยตรงหรือผ่านไลบรารีในที่อยู่เครือข่ายภายใน (เช่น โปรโตคอลการค้นพบบริการ mDNS หรือ SSDP)
- การใช้คลาสระดับเฟรมเวิร์กที่เข้าถึงเครือข่ายในเครื่อง (เช่น NsdManager)
การรับส่งข้อมูลไปยังและจากที่อยู่เครือข่ายภายในต้องมีสิทธิ์เข้าถึงเครือข่ายภายใน ตารางต่อไปนี้แสดงกรณีที่พบบ่อย
| การดำเนินการเครือข่ายระดับต่ำของแอป | ต้องมีสิทธิ์เข้าถึงเครือข่ายภายใน |
|---|---|
| สร้างการเชื่อมต่อ TCP ขาออก | ใช่ |
| ยอมรับการเชื่อมต่อ TCP ขาเข้า | ใช่ |
| การส่ง Unicast, Multicast, Broadcast แบบ UDP | ใช่ |
| การรับ Unicast, Multicast, Broadcast UDP ขาเข้า | ใช่ |
ข้อจำกัดเหล่านี้จะใช้ในส่วนลึกของสแต็กเครือข่าย จึงมีผลกับAPI เครือข่ายทั้งหมด ซึ่งรวมถึงซ็อกเก็ตที่สร้างขึ้นในโค้ดเนทีฟหรือโค้ดที่มีการจัดการ ไลบรารีเครือข่าย เช่น Cronet และ OkHttp รวมถึง API ใดๆ ที่ใช้งานอยู่บนไลบรารีเหล่านั้น การพยายามแก้ไขบริการใน เครือข่ายภายใน (เช่น บริการที่มีคำต่อท้าย .local) จะต้องมีสิทธิ์เข้าถึงเครือข่ายภายใน
ข้อยกเว้นสำหรับกฎข้างต้น
- หากเซิร์ฟเวอร์ DNS ของอุปกรณ์อยู่ในเครือข่ายภายใน การรับส่งข้อมูลไปยังหรือจากเซิร์ฟเวอร์ดังกล่าว (ที่พอร์ต 53) ไม่จำเป็นต้องมีสิทธิ์เข้าถึงเครือข่ายภายใน
- แอปพลิเคชันที่ใช้ตัวสลับเอาต์พุตเป็นเครื่องมือเลือกในแอปจะไม่ต้องมีสิทธิ์เข้าถึงเครือข่ายในพื้นที่ (จะมีคำแนะนำเพิ่มเติมในไตรมาสที่ 4 ปี 2025)
คำแนะนำสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอป (เลือกใช้)
หากต้องการเลือกใช้ข้อจำกัดเครือข่ายในเครื่อง ให้ทำดังนี้
- แฟลชอุปกรณ์เป็นบิลด์ที่มี 25Q2 เบต้า 3 ขึ้นไป
- ติดตั้งแอปที่จะทดสอบ
สลับสถานะ Appcompat ใน adb โดยทำดังนี้
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>รีบูตอุปกรณ์
ตอนนี้สิทธิ์เข้าถึงเครือข่าย LAN ของแอปถูกจำกัดแล้ว และการพยายามเข้าถึงเครือข่าย LAN จะทำให้เกิดข้อผิดพลาดของซ็อกเก็ต หากคุณใช้ API ที่ ดำเนินการในเครือข่ายภายในนอกกระบวนการของแอป (เช่น NsdManager) API เหล่านี้จะไม่ได้รับผลกระทบในระหว่างระยะการเลือกใช้
หากต้องการกู้คืนสิทธิ์เข้าถึง คุณต้องให้สิทธิ์แอปในการเข้าถึง NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES
- ตรวจสอบว่าแอปประกาศสิทธิ์
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESในไฟล์ Manifest - ไปที่การตั้งค่า > แอป > [ชื่อแอปพลิเคชัน] > สิทธิ์ > อุปกรณ์ที่อยู่ใกล้เคียง > อนุญาต
ตอนนี้สิทธิ์เข้าถึงเครือข่าย LAN ของแอปควรได้รับการกู้คืนแล้ว และสถานการณ์ทั้งหมดควรทํางานได้เหมือนก่อนที่จะเลือกใช้แอป
เมื่อการบังคับใช้เพื่อการปกป้องเครือข่าย LAN เริ่มขึ้น การเข้าชมเครือข่ายของแอป จะได้รับผลกระทบดังนี้
| สิทธิ์ | คำขอ LAN ขาออก | คำขออินเทอร์เน็ตขาออก/ขาเข้า | คำขอ LAN ขาเข้า |
|---|---|---|---|
| ให้สิทธิ์ | Works | Works | Works |
| ไม่ให้สิทธิ์ | เรื่องหน้าแตก | Works | เรื่องหน้าแตก |
ใช้คำสั่งต่อไปนี้เพื่อเปิด/ปิด Flag App-Compat
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
ข้อผิดพลาด
ระบบจะส่งข้อผิดพลาดที่เกิดจากข้อจำกัดเหล่านี้กลับไปยังซ็อกเก็ตที่เรียกใช้ เมื่อใดก็ตามที่เรียกใช้ send หรือตัวแปร send ไปยังที่อยู่เครือข่ายภายใน
ตัวอย่างข้อผิดพลาด
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
คำจำกัดความของเครือข่ายภายใน
เครือข่ายภายในในโปรเจ็กต์นี้หมายถึงเครือข่าย IP ที่ใช้อินเทอร์เฟซเครือข่ายที่รองรับการออกอากาศ เช่น Wi-Fi หรืออีเทอร์เน็ต แต่ไม่รวมการเชื่อมต่อเซลลูลาร์ (WWAN) หรือ VPN
เครือข่ายต่อไปนี้ถือเป็นเครือข่ายท้องถิ่น
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // ลิงก์ภายใน
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- ลิงก์ภายใน
- เส้นทางที่เชื่อมต่อโดยตรง
- เครือข่าย Stub เช่น Thread
- หลายซับเน็ต (จะแจ้งภายหลัง)
นอกจากนี้ ทั้งที่อยู่แบบมัลติแคสต์ (224.0.0.0/4, ff00::/8) และที่อยู่ IPv4 แบบบรอดแคสต์ (255.255.255.255) จะจัดเป็นที่อยู่เครือข่ายภายใน
รูปภาพที่เป็นของแอป
当面向 SDK 36 或更高版本的应用在搭载 Android 16 或更高版本的设备上提示用户授予照片和视频权限时,如果用户选择限制对所选媒体的访问权限,则会在照片选择器中看到该应用拥有的所有照片。用户可以取消选择任何这些预选项,这会撤消该应用对这些照片和视频的访问权限。
