Trong Material Design, một giàn giáo là một cấu trúc cơ bản cung cấp một nền tảng chuẩn hoá cho các giao diện người dùng phức tạp. Cấu phần này kết hợp nhiều phần khác nhau của giao diện người dùng, chẳng hạn như thanh ứng dụng và nút hành động nổi, mang đến cho ứng dụng giao diện nhất quán.
Khả năng tương thích của phiên bản
Phương thức triển khai này yêu cầu bạn đặt minSDK của dự án thành API cấp 21 trở lên.
Phần phụ thuộc
Tạo một giàn giáo
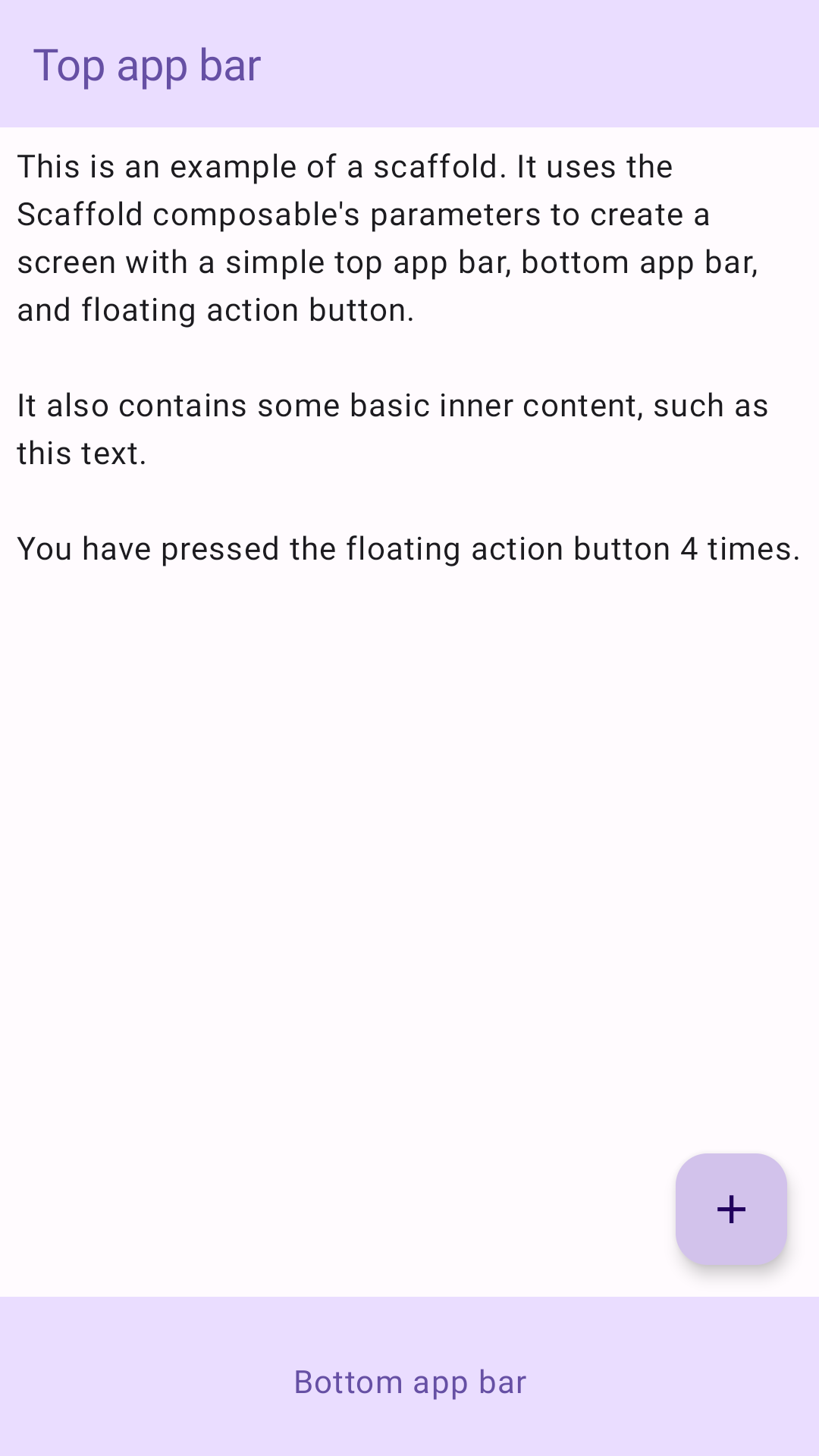
Ví dụ sau đây cung cấp ví dụ đầy đủ về cách bạn có thể triển khai Scaffold. Cấu phần này chứa thanh ứng dụng trên cùng, thanh ứng dụng dưới cùng và nút hành động nổi tương tác với trạng thái nội bộ của Scaffold.
Kết quả
Điểm chính
Thành phần kết hợp Scaffold cung cấp một API đơn giản mà bạn có thể sử dụng để nhanh chóng tập hợp cấu trúc của ứng dụng theo nguyên tắc Material Design.
Scaffold chấp nhận một số thành phần kết hợp làm tham số. Trong số đó có:
topBar: Thanh ứng dụng ở đầu màn hình.bottomBar: Thanh ứng dụng ở cuối màn hình.floatingActionButton: Một nút di chuột qua góc dưới cùng bên phải của màn hình mà bạn có thể sử dụng để hiển thị các thao tác chính.
Để biết thêm ví dụ chi tiết về cách triển khai cả thanh ứng dụng trên cùng và dưới cùng, hãy xem trang về thanh ứng dụng.
Bạn cũng có thể truyền nội dung Scaffold như cách bạn truyền nội dung đến các vùng chứa khác. Hàm này truyền giá trị innerPadding đến hàm lambda content mà bạn có thể sử dụng trong các thành phần kết hợp con.
Các bộ sưu tập chứa hướng dẫn này
Hướng dẫn này là một phần của các bộ sưu tập Hướng dẫn nhanh được tuyển chọn này, bao gồm các mục tiêu phát triển Android rộng hơn:
Tạo một giàn đỡ màn hình chính




