在 Chromebook 上运行 Android 应用可让用户使用庞大的 Android 生态系统,还能让 Android 开发者有机会吸引 ChromeOS 用户。
ChromeOS 为 Android 开发者提供了各种工具,供他们在 Chromebook 上部署和测试应用。为了改善用户体验,请在不同类型的设备上验证您的应用。
无论是直接从 ChromeOS 部署 Android 应用(在 Chromebook 中使用 Android Studio),还是从其他设备部署 Android 应用,您都可以使用 Android 调试桥部署应用,并调试与 Chromebook 的不同交互。
启用 ADB 调试
以前,开发者只能在开发者模式下在 Chromebook 上使用 ADB。自 Chrome 81 推出以来,开发者可让其设备脱离开发者模式,同时仍可直接在 ChromeOS 中部署他们开发的应用。具体方法如下:
前往设置,然后开启 Linux(如果尚未开启)。
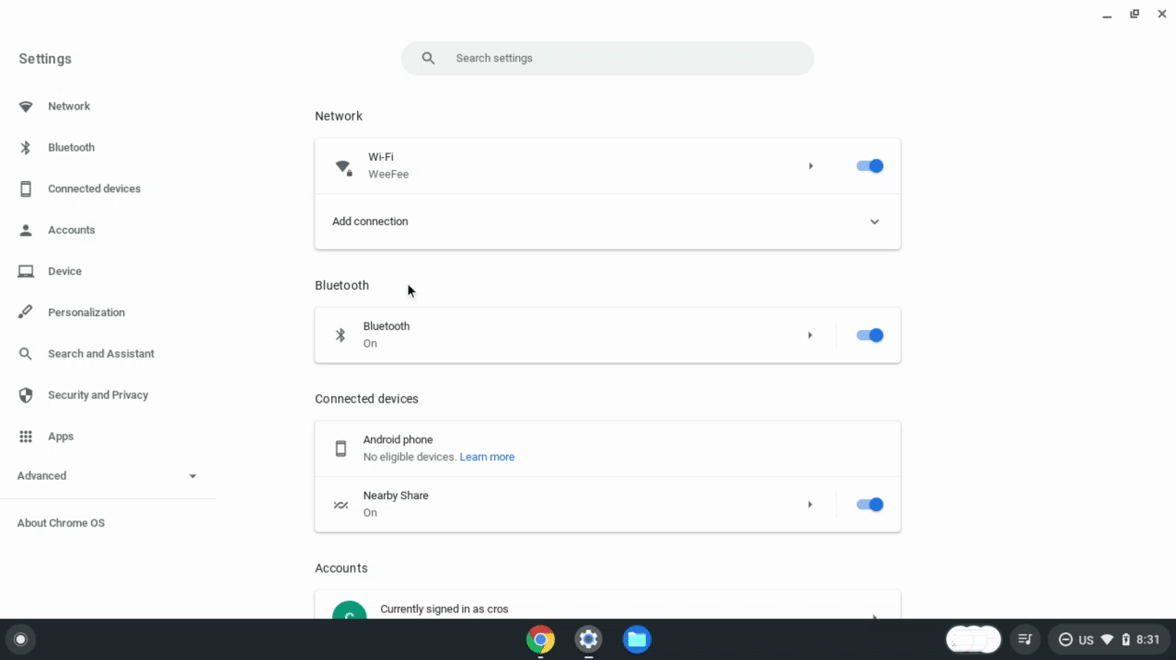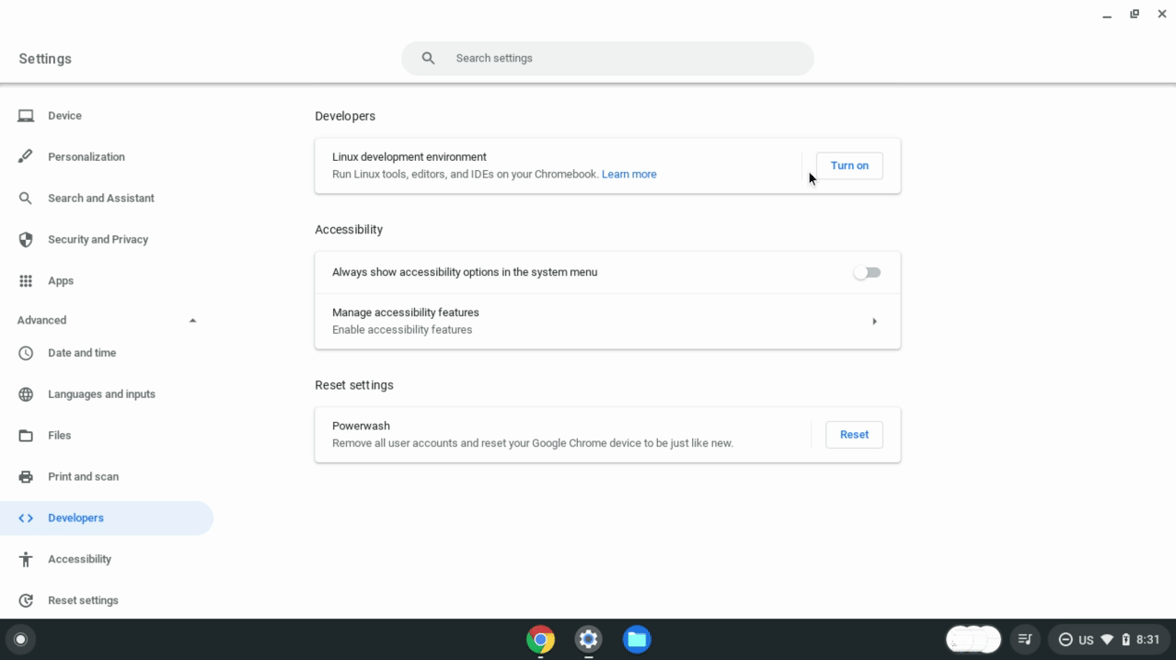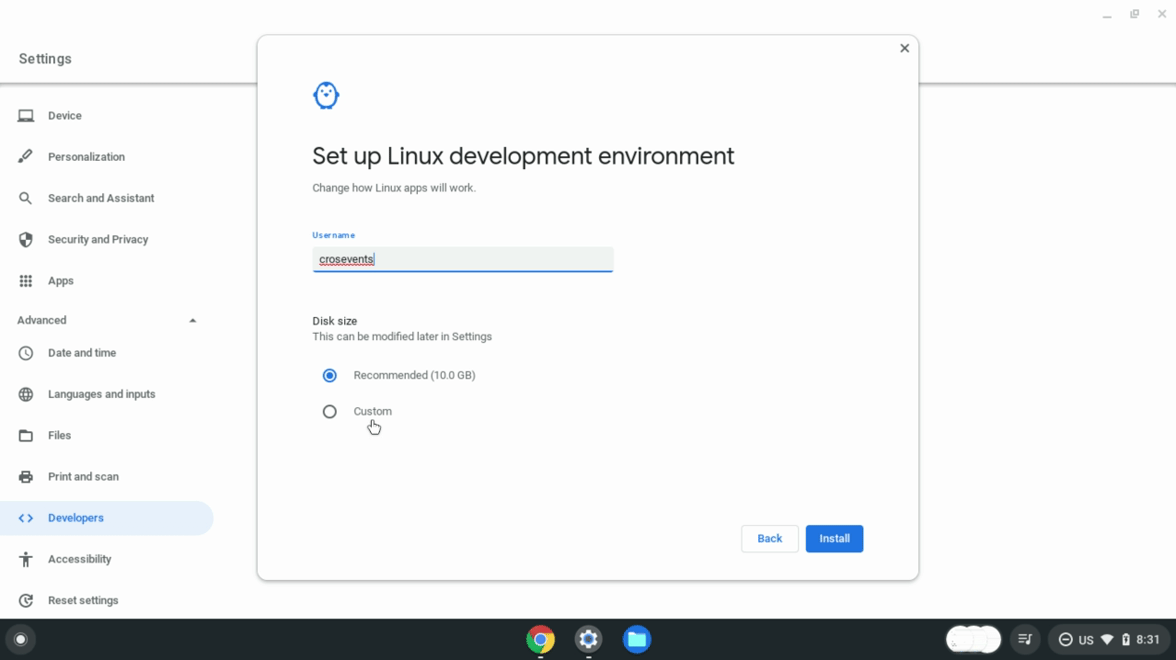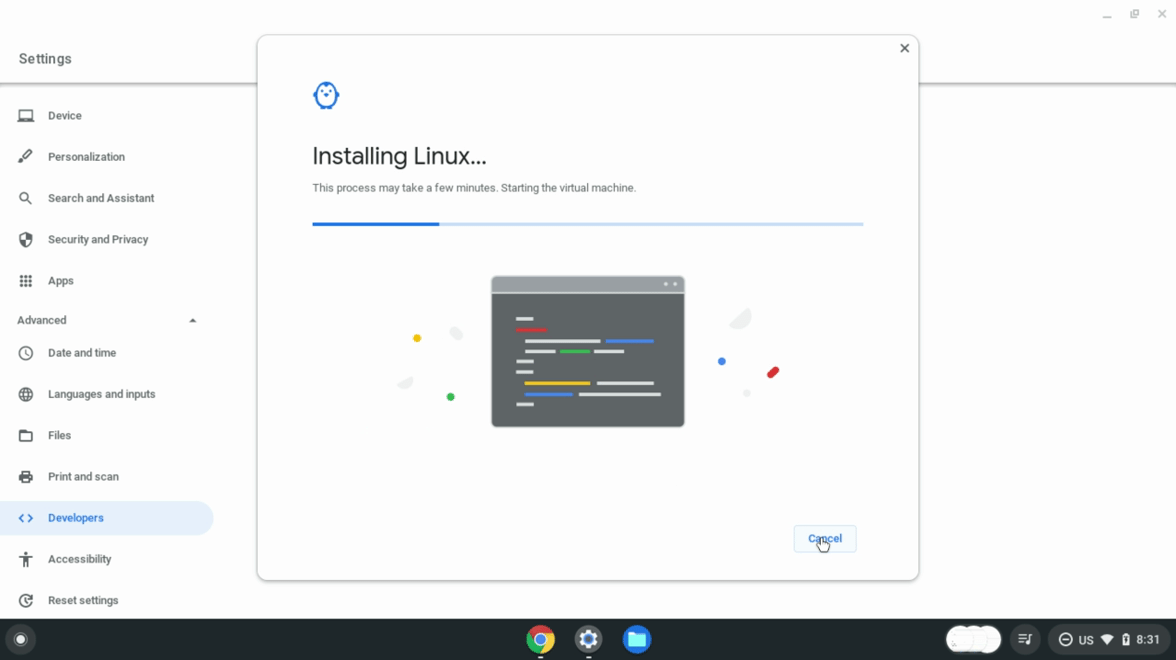
图 1. 在 ChromeOS 设置中启用 Linux。 Linux 可用后,打开 Linux 设置。
打开开发 Android 应用 选项。
切换启用 ADB 调试。Chromebook 会重启。
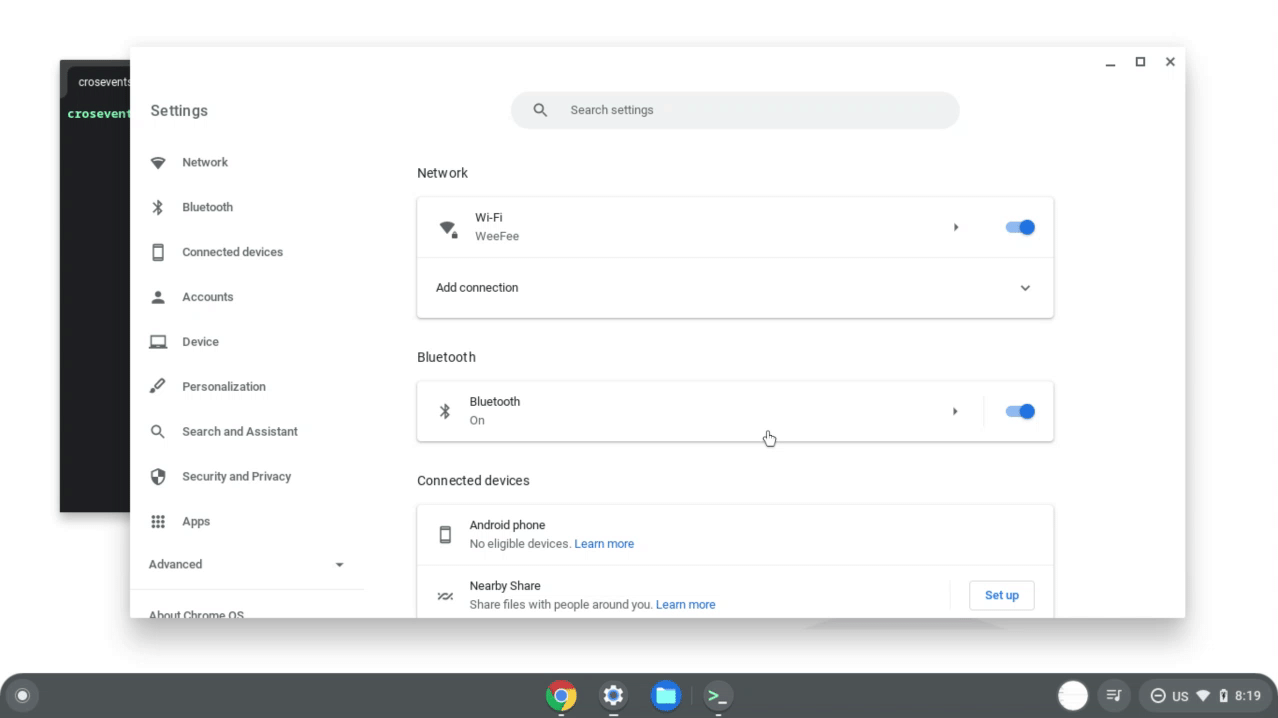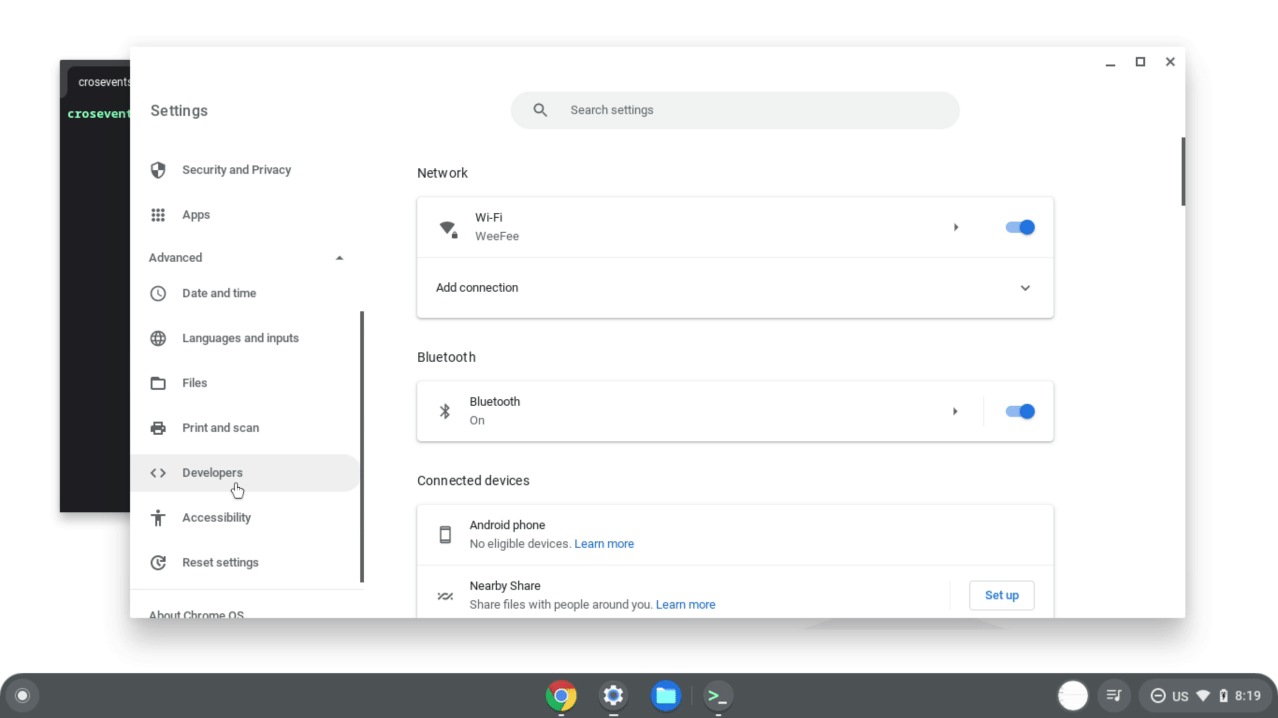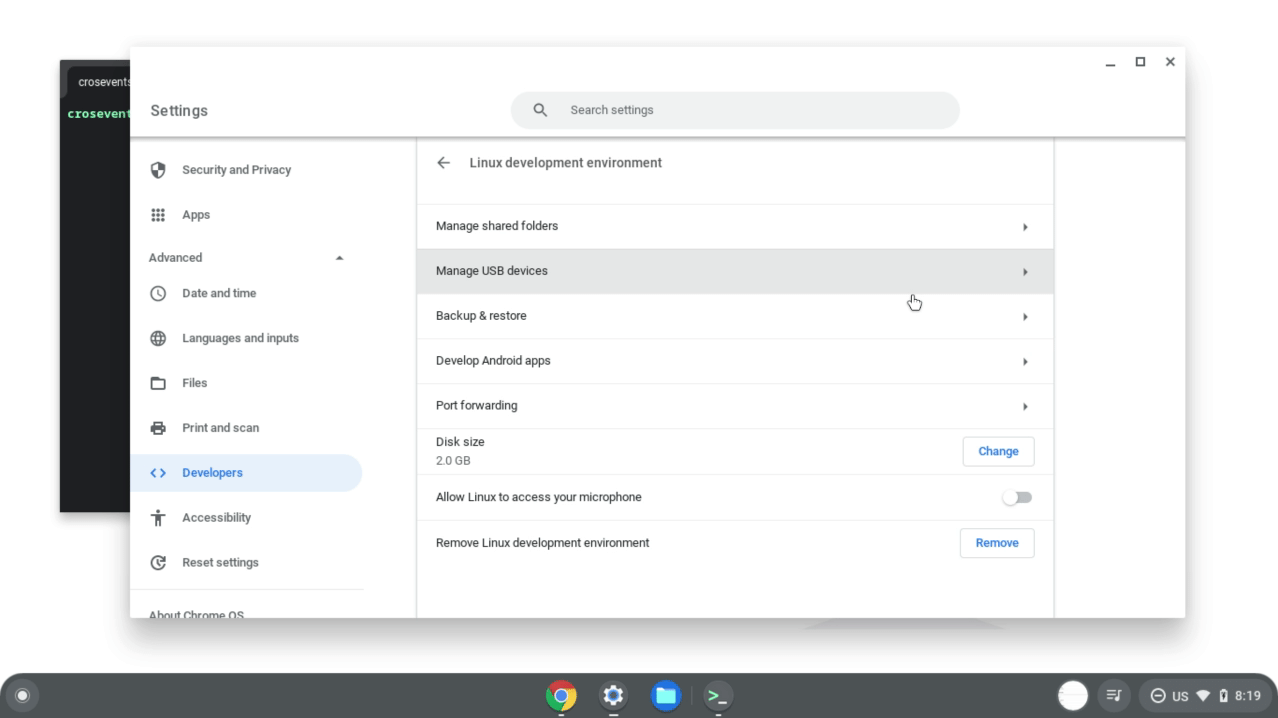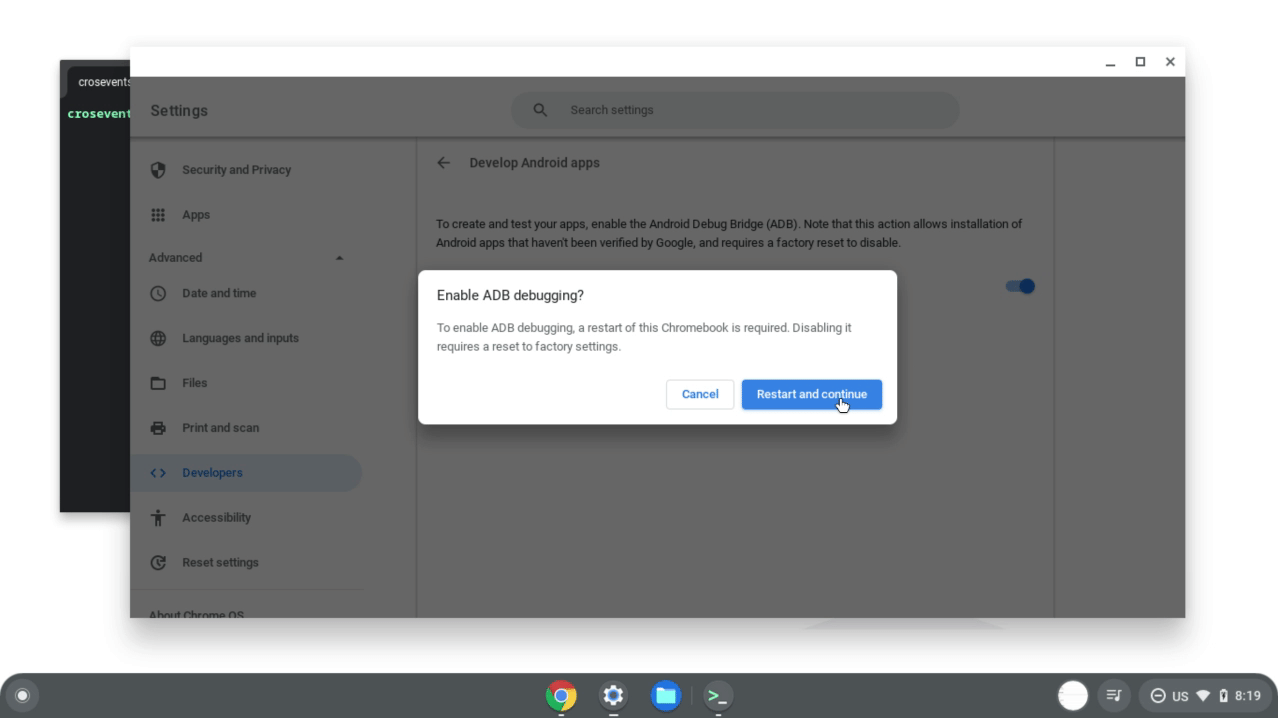
图 2. 在 Linux 设置中启用 ADB 调试。 Chromebook 重启后,系统会显示一条消息,告知您可能有一些应用不是从设备上的应用商店下载的。

图 3. 启用 ADB 后,有关非 Play 商店应用的通知。 ADB 现在可以将应用部署到 Chromebook、运行调试命令并直接与设备进行交互了。
为了验证您的 Android 应用可以在各种 Chromebook 设备和可用设备类型上正常运行,Google 建议您在以下设备上对您的应用进行测试:
- 基于 ARM 的 Chromebook
- 基于 x86 的 Chromebook
- 带触摸屏的设备和不带触摸屏的设备
- 可在笔记本电脑和平板电脑之间切换的可转换设备
- 带触控笔的设备
从 ChromeOS 部署
启用 ADB 调试后,您可以使用 Android Studio 直接将 Android 应用加载到 ChromeOS 设备上。如果您有 Android 软件包套件 (APK),可以使用终端加载它。
使用 Android Studio 部署
设置 Android Studio 和 ADB 后,您可以直接从 Android Studio 将应用推送到 Chromebook 的 Android 容器。Chromebook 会在设备菜单中显示为一个选项:

当您将应用推送到 Chromebook 时,系统会显示 ADB 授权对话框。授权后,您的应用会在新窗口中启动。
现在,您可以将应用部署到 Chromebook 并对其进行测试和调试。
使用终端进行部署
如需使用终端将应用部署到 Chromebook,请按以下步骤操作:
如有必要,使用以下命令安装 ADB:
sudo apt install adb使用以下命令连接到设备:
adb connect arc系统会显示 USB 调试的授权对话框。授予授权:

图 6. USB 调试授权对话框。 使用以下命令从终端安装应用:
adb install [path to your APK]

从其他设备部署
如果您无法使用上述方法而需要从其他设备推送您的应用,您可以使用 USB 连接或网络地址将设备连接到 ADB。
通过网络连接到 ADB
如需通过网络连接到 ADB,请按以下步骤操作:
确保您已启用 ADB 调试。
按照以下步骤获取 Chromebook 的 IP 地址:
- 点击屏幕右下角区域的时钟。
- 点击齿轮图标。
- 点击您连接到的网络类型(例如 WLAN 或移动数据网络),然后点击相应网络的名称。
- 记下 IP 地址。
连接到 Chromebook:
返回开发机器,并使用 ADB 连接到 Chromebook(通过其 IP 地址):
adb connect <ip_address>在 Chromebook 上,当系统提示您是否允许使用调试程序时,点击允许。您的 ADB 会话即已建立。
排查通过网络进行 ADB 调试的问题
有时,当一切连接正常时,ADB 设备却显示为离线状态。在这种情况下,请完成以下步骤来排查问题:
- 在“开发者选项”中停用 ADB 调试。
- 在终端窗口中,运行
adb kill-server。 - 重新激活 ADB 调试选项。
- 在终端窗口中,尝试运行
adb connect。 - 当系统提示您是否允许进行调试时,点击允许。您的 ADB 会话即已建立。
通过 USB 连接到 ADB
为了从其他设备将 APK 推送到 Chromebook,您必须在开发者模式下启动 ChromeOS,以便配置 Chromebook 并从主机推送应用。
请按照以下步骤进入开发者模式:
- 启用 ADB 调试。
- 确定您的设备是否支持 USB 调试。
- 按
Control+Alt+T启动 ChromeOS 终端。 输入
shell以进入 bash 命令 shell:crosh> shell chronos@localhost / $输入以下命令以设置您的设备:
$ sudo crossystem dev_enable_udc=1 $ sudo reboot重新启动后,再次打开终端并运行以下命令,以在 Chromebook 的 USB 端口上启用 ADB:
$ sudo ectool usbpd <port number> dr_swap
每次拔下 USB 线再重新插上时,都应使用此命令。如需确保 Chromebook 处于上游面向端口 (UFP) 模式,您可以运行 ectool usbpd <port number>。
如需建立 ADB 会话,请按照以下步骤操作:
- 将 USB 线插入设备上支持的端口。
- 通过主机上的 Android SDK 平台工具运行
adb devices,可以看到您的 Chromebook 列为 ADB 支持的设备。 - 在 Chromebook 上,当系统提示您是否允许使用调试程序时,点击允许。您的 ADB 会话即已建立。
