पिछली रिलीज़ की तरह, Android 15 में भी कुछ बदलाव किए गए हैं. इनसे आपके ऐप्लिकेशन पर असर पड़ सकता है. यहां दिए गए बदलाव, सिर्फ़ उन ऐप्लिकेशन पर लागू होते हैं जो Android 15 या इसके बाद के वर्शन को टारगेट कर रहे हैं. अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन, Android 15 या इसके बाद के वर्शन को टारगेट कर रहा है, तो आपको अपने ऐप्लिकेशन में बदलाव करना चाहिए, ताकि इन व्यवहारों को सही तरीके से सपोर्ट किया जा सके. हालांकि, ऐसा सिर्फ़ उन मामलों में करना होगा जहां यह लागू होता है.
Android 15 पर चलने वाले सभी ऐप्लिकेशन पर असर डालने वाले बदलावों की सूची भी ज़रूर देखें. इससे कोई फ़र्क़ नहीं पड़ता कि आपके ऐप्लिकेशन का targetSdkVersion क्या है.
मुख्य फ़ंक्शन
Android 15, Android सिस्टम की कई मुख्य सुविधाओं में बदलाव करता है या उन्हें बेहतर बनाता है.
फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवाओं में बदलाव
हम Android 15 में फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवाओं में ये बदलाव कर रहे हैं.
- डेटा सिंक करने वाली फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा के टाइम आउट का व्यवहार
- मीडिया प्रोसेस करने वाली नई फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा का टाइप
- फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवाएं लॉन्च करने वाले
BOOT_COMPLETEDब्रॉडकास्ट रिसीवर पर पाबंदियां - ऐप्लिकेशन के पास
SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOWअनुमति होने पर, फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवाएं शुरू करने से जुड़ी पाबंदियां
डेटा सिंक करने वाली फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा के टाइम आउट का व्यवहार
Android 15 में, dataSync के लिए टाइम आउट का नया तरीका जोड़ा गया है. यह तरीका, Android 15 (एपीआई लेवल 35) या उसके बाद के वर्शन को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए है. यह व्यवहार, mediaProcessing फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा के नए टाइप पर भी लागू होता है.
सिस्टम, किसी ऐप्लिकेशन की dataSync सेवाओं को 24 घंटे में कुल छह घंटे तक चलने की अनुमति देता है. इसके बाद, सिस्टम चल रही सेवा के Service.onTimeout(int, int) तरीके को कॉल करता है. इसे Android 15 में लॉन्च किया गया था. इस दौरान, सेवा के पास Service.stopSelf() को कॉल करने के लिए कुछ सेकंड होते हैं. Service.onTimeout() को कॉल करने के बाद, सेवा को फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा नहीं माना जाता. अगर सेवा Service.stopSelf() को कॉल नहीं करती है, तो सिस्टम में कोई इंटरनल अपवाद दिखता है. अपवाद को Logcat में इस मैसेज के साथ लॉग किया जाता है:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type dataSync did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
इस बदलाव की वजह से होने वाली समस्याओं से बचने के लिए, इनमें से एक या एक से ज़्यादा काम किए जा सकते हैं:
- अपनी सेवा में
Service.onTimeout(int, int)का नया तरीका लागू करें. जब आपके ऐप्लिकेशन को कॉलबैक मिल जाए, तोstopSelf()को कुछ सेकंड के अंदर कॉल करना न भूलें. (अगर ऐप्लिकेशन को तुरंत नहीं रोका जाता, तो सिस्टम गड़बड़ी जनरेट करता है.) - पक्का करें कि आपके ऐप्लिकेशन की
dataSyncसेवाएं किसी भी 24 घंटे में कुल छह घंटे से ज़्यादा न चलें (जब तक कि उपयोगकर्ता टाइमर को रीसेट करके ऐप्लिकेशन से इंटरैक्ट न करे). dataSyncफ़ोरग्राउंड सेवाओं को सिर्फ़ उपयोगकर्ता के सीधे इंटरैक्शन के ज़रिए शुरू करें. सेवा शुरू होने पर, आपका ऐप्लिकेशन फ़ोरग्राउंड में होता है. इसलिए, ऐप्लिकेशन के बैकग्राउंड में जाने के बाद भी, आपकी सेवा के पास पूरे छह घंटे होते हैं.dataSyncफ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा का इस्तेमाल करने के बजाय, किसी अन्य एपीआई का इस्तेमाल करें.
अगर आपके ऐप्लिकेशन की dataSync फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवाएं पिछले 24 में छह घंटे तक चली हैं, तो आपके पास dataSync की दूसरी फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा शुरू करने का विकल्प नहीं है. जब तक उपयोगकर्ता आपके ऐप्लिकेशन को फ़ोरग्राउंड में न ले जाए (इससे टाइमर रीसेट हो जाता है). किसी दूसरी dataSync फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा को शुरू करने की कोशिश करने पर, सिस्टम ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException का गड़बड़ी का मैसेज दिखाता है. जैसे, "फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा के लिए समयसीमा खत्म हो चुकी है" डेटा सिंक करें.
टेस्ट करना
अपने ऐप्लिकेशन के व्यवहार की जांच करने के लिए, डेटा सिंक टाइम आउट की सुविधा चालू की जा सकती है. भले ही, आपका ऐप्लिकेशन Android 15 को टारगेट न करता हो. हालांकि, यह ज़रूरी है कि ऐप्लिकेशन Android 15 वाले डिवाइस पर चल रहा हो. टाइम आउट की सुविधा चालू करने के लिए, यहां दिया गया adb निर्देश चलाएं:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
टाइम आउट की अवधि में भी बदलाव किया जा सकता है, ताकि यह आसानी से जांचा जा सके कि तय सीमा पूरी होने पर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन कैसा व्यवहार करता है. टाइम आउट की नई अवधि सेट करने के लिए, यह adb कमांड चलाएं:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager data_sync_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
मीडिया प्रोसेस करने वाली नई फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा का टाइप
Android 15 में, फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा का एक नया टाइप mediaProcessing जोड़ा गया है. यह सेवा टाइप, मीडिया फ़ाइलों को ट्रांसकोड करने जैसे कामों के लिए सही है. उदाहरण के लिए, कोई मीडिया ऐप्लिकेशन किसी ऑडियो फ़ाइल को डाउनलोड कर सकता है और उसे चलाने से पहले, किसी दूसरे फ़ॉर्मैट में बदल सकता है. mediaProcessing फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा का इस्तेमाल करके, यह पक्का किया जा सकता है कि ऐप्लिकेशन बैकग्राउंड में होने पर भी कन्वर्ज़न जारी रहे.
सिस्टम किसी ऐप्लिकेशन की mediaProcessing सेवाओं को 24 घंटों में कुल छह घंटे चलाने की अनुमति देता है. इसके बाद, सिस्टम, मौजूदा सेवा के Service.onTimeout(int, int) तरीके को कॉल करता है (Android 15 में शुरू किया गया). फ़िलहाल, Service.stopSelf() को कॉल करने के लिए सेवा को कुछ सेकंड मिलेंगे. अगर सेवा Service.stopSelf() को कॉल नहीं करती है, तो सिस्टम में कोई इंटरनल अपवाद दिखता है. अपवाद को Logcat में लॉग इन किया जाता है जिसमें यह मैसेज शामिल है:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type mediaProcessing did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
अपवाद से बचने के लिए, इनमें से कोई एक काम किया जा सकता है:
- अपनी सेवा में
Service.onTimeout(int, int)का नया तरीका लागू करें. जब आपके ऐप्लिकेशन को कॉलबैक मिलता है, तो कुछ सेकंड के अंदरstopSelf()को कॉल करना न भूलें. (अगर ऐप्लिकेशन को तुरंत नहीं रोका जाता, तो सिस्टम गड़बड़ी जनरेट करता है.) - पक्का करें कि आपके ऐप्लिकेशन की
mediaProcessingसेवाएं, 24 घंटे में कुल छह घंटे से ज़्यादा न चलें. ऐसा तब तक नहीं होगा, जब तक उपयोगकर्ता ऐप्लिकेशन के साथ इंटरैक्ट करके, टाइमर को रीसेट नहीं करता. - सीधे उपयोगकर्ता के साथ इंटरैक्शन होने पर ही,
mediaProcessingफ़ोरग्राउंड सेवाएं शुरू करें. सेवा शुरू होने के समय, आपका ऐप्लिकेशन फ़ोरग्राउंड में होता है. इसलिए, ऐप्लिकेशन के बैकग्राउंड में चलने के बाद, आपकी सेवा को पूरे छह घंटे तक चालू रखा जाता है. mediaProcessingफ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा का इस्तेमाल करने के बजाय, WorkManager जैसे अन्य एपीआई का इस्तेमाल करें.
अगर आपके ऐप्लिकेशन की mediaProcessing फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवाएं पिछले 24 में छह घंटों तक चली हैं, तो mediaProcessing फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा को तब तक शुरू नहीं किया जा सकता, जब तक
उपयोगकर्ता आपके ऐप्लिकेशन को फ़ोरग्राउंड में न ले जाए (इससे टाइमर रीसेट हो जाता है). अगर कोई दूसरी mediaProcessing फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा शुरू करने की कोशिश की जाती है, तो सिस्टम ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException को गड़बड़ी का मैसेज दिखाता है. जैसे, "mediaProcessing टाइप की फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा के लिए, समयसीमा पहले ही खत्म हो चुकी है".
mediaProcessing सेवा टाइप के बारे में ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, Android 15 के लिए फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा टाइप में हुए बदलाव: मीडिया प्रोसेसिंग देखें.
टेस्ट करना
अपने ऐप्लिकेशन के काम करने के तरीके की जांच करने के लिए, मीडिया प्रोसेसिंग के टाइम आउट को चालू किया जा सकता है. भले ही, आपका ऐप्लिकेशन Android 15 को टारगेट न करता हो (जब तक कि ऐप्लिकेशन, Android 15 डिवाइस पर चल रहा हो). टाइम आउट की सुविधा चालू करने के लिए, यह adb कमांड चलाएं:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
टाइम आउट की अवधि में बदलाव भी किया जा सकता है. इससे यह जांचना आसान हो जाता है कि
तय सीमा पूरी होने पर, आपका ऐप्लिकेशन कैसे काम करता है. टाइम आउट की नई अवधि सेट करने के लिए, यह adb कमांड चलाएं:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager media_processing_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवाएं लॉन्च करने वाले BOOT_COMPLETED ब्रॉडकास्ट रिसीवर पर पाबंदियां
BOOT_COMPLETED ब्रॉडकास्ट रिसीवर के लिए, फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवाएं लॉन्च करने से जुड़ी नई पाबंदियां हैं. BOOT_COMPLETED रिसीवर को
फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवाओं के ये टाइप हैं:
dataSynccameramediaPlaybackphoneCallmediaProjectionmicrophone(यह पाबंदीmicrophoneके लिए तब से लागू है Android 14)
अगर BOOT_COMPLETED रिसीवर इनमें से किसी भी तरह के फ़ोरग्राउंड को लॉन्च करने की कोशिश करता है
सिस्टम, ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException की जानकारी देता है.
टेस्ट करना
अपने ऐप्लिकेशन के व्यवहार की जांच करने के लिए, ये नई पाबंदियां चालू की जा सकती हैं. भले ही, आपका ऐप्लिकेशन Android 15 को टारगेट न करता हो. हालांकि, यह ज़रूरी है कि ऐप्लिकेशन Android 15 वाले डिवाइस पर चल रहा हो. यहां दिया गया adb निर्देश चलाएं:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_BOOT_COMPLETED_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
डिवाइस को रीस्टार्ट किए बिना BOOT_COMPLETED ब्रॉडकास्ट भेजने के लिए,
नीचे दिया गया adb निर्देश चलाएं:
adb shell am broadcast -a android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED your-package-name
जब कोई ऐप्लिकेशन SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW अनुमति का इस्तेमाल कर रहा हो, तब फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवाएं शुरू करने से जुड़ी पाबंदियां
पहले, अगर किसी ऐप्लिकेशन के पास SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW अनुमति होती थी, तो वह फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा को लॉन्च कर सकता था. भले ही, वह ऐप्लिकेशन फ़िलहाल बैकग्राउंड में हो. इस बारे में बैकग्राउंड में शुरू करने से जुड़ी पाबंदियों से छूट में बताया गया है.
अगर कोई ऐप्लिकेशन Android 15 को टारगेट करता है, तो अब यह छूट कम हो गई है. ऐप्लिकेशन को अब SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW की अनुमति की ज़रूरत होगी. साथ ही, उसमें भी एक दिखने वाला ओवरले विंडो भी होनी चाहिए. इसका मतलब है कि ऐप्लिकेशन को सबसे पहले TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY विंडो लॉन्च करनी होगी और फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा शुरू करने से पहले, विंडो दिखनी चाहिए.
अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन इन नई ज़रूरी शर्तों को पूरा किए बिना, बैकग्राउंड से फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा शुरू करने की कोशिश करता है और उसे कोई छूट नहीं मिली है, तो सिस्टम ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException दिखाता है.
अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW अनुमति का एलान करता है और बैकग्राउंड से फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवाएं लॉन्च करता है, तो इस बदलाव का उस पर असर पड़ सकता है. अगर आपके ऐप्लिकेशन को ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException मिलता है, तो अपने ऐप्लिकेशन के काम करने का क्रम देखें और पक्का करें कि बैकग्राउंड से फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा शुरू करने से पहले, आपके ऐप्लिकेशन में एक ऐक्टिव ओवरले विंडो हो. View.getWindowVisibility() को कॉल करके, यह देखा जा सकता है कि ओवरले विंडो फ़िलहाल दिख रही है या नहीं. इसके अलावा, View.onWindowVisibilityChanged() को बदलकर, यह भी सेट किया जा सकता है कि ओवरले विंडो दिखने या न दिखने पर सूचना मिलती रहे.
टेस्ट करना
अपने ऐप्लिकेशन के व्यवहार की जांच करने के लिए, ये नई पाबंदियां चालू की जा सकती हैं. भले ही, आपका ऐप्लिकेशन Android 15 को टारगेट न करता हो. हालांकि, यह ज़रूरी है कि ऐप्लिकेशन Android 15 वाले डिवाइस पर चल रहा हो. बैकग्राउंड से फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवाएं शुरू करने से जुड़ी इन नई पाबंदियों को चालू करने के लिए, यहां दिया गया adb निर्देश चलाएं:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_SAW_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
'परेशान न करें' मोड की ग्लोबल स्थिति में बदलाव करने की सुविधा को ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए उपलब्ध कराने से जुड़े बदलाव
Android 15 (एपीआई लेवल 35) और उसके बाद के वर्शन को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन, अब किसी डिवाइस पर 'परेशान न करें' (डीएनडी) मोड की ग्लोबल स्थिति या नीति को नहीं बदल सकते. ऐसा, उपयोगकर्ता की सेटिंग में बदलाव करके या डीएनडी मोड को बंद करके नहीं किया जा सकता. इसके बजाय, ऐप्लिकेशन को AutomaticZenRule का योगदान देना होगा. सिस्टम, इस योगदान को सबसे ज़्यादा पाबंदी वाली मौजूदा नीति के साथ मिलाकर, ग्लोबल नीति बनाता है. पहले जिन मौजूदा एपीआई कॉल से ग्लोबल स्टेटस (setInterruptionFilter,
setNotificationPolicy) पर असर पड़ा था उनसे, एक 'असहमति' वाला AutomaticZenRule पैरामीटर बनता है या अपडेट होता है. यह पैरामीटर, उन एपीआई कॉल के कॉल-साइकल के हिसाब से टॉगल किया जाता है.
ध्यान दें कि इस बदलाव का असर सिर्फ़ तब पड़ता है, जब ऐप्लिकेशन setInterruptionFilter(INTERRUPTION_FILTER_ALL) को कॉल कर रहा हो और उसे उम्मीद हो कि उस कॉल से, AutomaticZenRule को बंद किया जा सकेगा. AutomaticZenRule को पहले उसके मालिकों ने चालू किया था.
OpenJDK API में हुए बदलाव
Android 15, Android की कोर लाइब्रेरी को रीफ़्रेश करने का काम जारी रखता है, ताकि उन्हें OpenJDK LTS की नई रिलीज़ में मौजूद सुविधाओं के साथ अलाइन किया जा सके.
इनमें से कुछ बदलावों का असर, Android 15 (एपीआई लेवल 35) को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के साथ काम करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन पर पड़ सकता है:
स्ट्रिंग फ़ॉर्मैट करने वाले एपीआई में बदलाव: अब
String.format()औरFormatter.format()एपीआई का इस्तेमाल करते समय, आर्ग्युमेंट इंडेक्स, फ़्लैग, चौड़ाई, और सटीक वैल्यू की पुष्टि करने के लिए ज़्यादा सख्त नियम लागू होंगे:String.format(String, Object[])String.format(Locale, String, Object[])Formatter.format(String, Object[])Formatter.format(Locale, String, Object[])
उदाहरण के लिए, जब फ़ॉर्मैट स्ट्रिंग में 0 (
%0) के आर्ग्युमेंट इंडेक्स का इस्तेमाल किया जाता है, तो यह अपवाद दिखता है:IllegalFormatArgumentIndexException: Illegal format argument index = 0इस मामले में, फ़ॉर्मैट स्ट्रिंग में 1 (
%1) का आर्ग्युमेंट इंडेक्स इस्तेमाल करके समस्या को ठीक किया जा सकता है.Arrays.asList(...).toArray()के कॉम्पोनेंट टाइप में बदलाव:Arrays.asList(...).toArray()का इस्तेमाल करने पर, नतीजे के तौर पर मिलने वाले ऐरे का कॉम्पोनेंट टाइप अबObjectहै. यह, अंडरलाइंग ऐरे के एलिमेंट का टाइप नहीं है. इसलिए, नीचे दिया गया कोडClassCastExceptionदिखाता है:String[] elements = (String[]) Arrays.asList("one", "two").toArray();इस मामले में, नतीजे के तौर पर मिले ऐरे में
Stringको कॉम्पोनेंट टाइप के तौर पर बनाए रखने के लिए,Collection.toArray(Object[])का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है:String[] elements = Arrays.asList("two", "one").toArray(new String[0]);भाषा कोड हैंडल करने के तरीके में बदलाव:
LocaleAPI का इस्तेमाल करते समय, हिब्रू, येडिश, और इंडोनेशियाई भाषा के कोड अब पुराने फ़ॉर्मैट में नहीं बदले जाते (हिब्रू:iw, येडिश:ji, और इंडोनेशियाई:in). इनमें से किसी एक भाषा के लिए भाषा कोड तय करते समय, ISO 639-1 से कोड इस्तेमाल करें (हिब्रू:he, येडिश:yi, और इंडोनेशियाई:id).रैंडम इंट सीक्वेंस में बदलाव: https://bugs.openjdk.org/browse/JDK-8301574 में किए गए बदलावों के बाद, अब ये
Random.ints()तरीके,Random.nextInt()तरीकों से अलग संख्या वाला सीक्वेंस दिखाते हैं:आम तौर पर, इस बदलाव से ऐप्लिकेशन के काम करने के तरीके पर कोई असर नहीं पड़ता. हालांकि, आपके कोड को
Random.ints()तरीकों से जनरेट किए गए क्रम केRandom.nextInt()से मेल खाने की उम्मीद नहीं करनी चाहिए.
SequencedCollection एपीआई का इस्तेमाल करने के लिए, अपने ऐप्लिकेशन की बिल्ड कॉन्फ़िगरेशन फ़ाइल में compileSdk को अपडेट करने के बाद, आपके ऐप्लिकेशन की कंपैटिबिलिटी पर असर पड़ सकता है. इसके लिए, आपको Android 15 (एपीआई लेवल 35) का इस्तेमाल करना होगा:
kotlin-stdlibमेंMutableList.removeFirst()औरMutableList.removeLast()एक्सटेंशन फ़ंक्शन के साथ टकरावJava में
Listटाइप को Kotlin मेंMutableListटाइप पर मैप किया जाता है.List.removeFirst()औरList.removeLast()एपीआई, Android 15 (एपीआई लेवल 35) में पेश किए गए हैं. इसलिए, Kotlin कंपाइलर, फ़ंक्शन कॉल को हल करता है. उदाहरण के लिए,list.removeFirst()कोkotlin-stdlibमें एक्सटेंशन फ़ंक्शन के बजाय, नएListएपीआई के लिए स्टैटिक तौर पर हल करता है.अगर किसी ऐप्लिकेशन को
compileSdkको35पर सेट करके औरminSdkको34या इससे कम पर सेट करके फिर से कंपाइल किया जाता है और फिर ऐप्लिकेशन को Android 14 और इससे पहले के वर्शन पर चलाया जाता है, तो रनटाइम में गड़बड़ी होती है:java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: No virtual method removeFirst()Ljava/lang/Object; in class Ljava/util/ArrayList;Android Gradle प्लग इन में मौजूद
NewApiलिंट विकल्प, एपीआई के इन नए इस्तेमाल का पता लगा सकता है../gradlew lintMainActivity.kt:41: Error: Call requires API level 35 (current min is 34): java.util.List#removeFirst [NewApi] list.removeFirst()रनटाइम एक्सेप्शन और लिंट की गड़बड़ियों को ठीक करने के लिए, Kotlin में
removeFirst()औरremoveLast()फ़ंक्शन कॉल को क्रमशःremoveAt(0)औरremoveAt(list.lastIndex)से बदला जा सकता है. अगर Android Studio Ladybug | 2024.1.3 या इसके बाद के वर्शन का इस्तेमाल किया जा रहा है, तो यह गड़बड़ियों को तुरंत ठीक करने का विकल्प भी देता है.अगर लिंट का विकल्प बंद कर दिया गया है, तो
@SuppressLint("NewApi")औरlintOptions { disable 'NewApi' }को हटाएं.Java में अन्य तरीकों के साथ टकराव
मौजूदा टाइप में नए तरीके जोड़े गए हैं. उदाहरण के लिए,
ListऔरDeque. ऐसा हो सकता है कि ये नई विधियां, अन्य इंटरफ़ेस और क्लास में एक ही नाम और आर्ग्युमेंट टाइप वाली विधियों के साथ काम न करें. अगर किसी तरीके के सिग्नेचर में टकराव होता है और वह काम नहीं करता है, तोjavacकंपाइलर, बिल्ड-टाइम की गड़बड़ी दिखाता है. उदाहरण के लिए:गड़बड़ी का पहला उदाहरण:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:135: error: removeLast() in MyList cannot implement removeLast() in List public void removeLast() { ^ return type void is not compatible with Object where E is a type-variable: E extends Object declared in interface Listगड़बड़ी का दूसरा उदाहरण:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:7: error: types Deque<Object> and List<Object> are incompatible; public class MyList implements List<Object>, Deque<Object> { both define reversed(), but with unrelated return types 1 errorगड़बड़ी का तीसरा उदाहरण:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:43: error: types List<E#1> and MyInterface<E#2> are incompatible; public static class MyList implements List<Object>, MyInterface<Object> { class MyList inherits unrelated defaults for getFirst() from types List and MyInterface where E#1,E#2 are type-variables: E#1 extends Object declared in interface List E#2 extends Object declared in interface MyInterface 1 errorबिल्ड से जुड़ी इन गड़बड़ियों को ठीक करने के लिए, इन इंटरफ़ेस को लागू करने वाली क्लास को, मिलते-जुलते रिटर्न टाइप के साथ इस तरीके को बदलना चाहिए. उदाहरण के लिए:
@Override public Object getFirst() { return List.super.getFirst(); }
सुरक्षा
Android 15 में ऐसे बदलाव किए गए हैं जिनसे सिस्टम की सुरक्षा को बढ़ावा मिलता है. इससे ऐप्लिकेशन और लोगों को नुकसान पहुंचाने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन से बचाने में मदद मिलती है.
पाबंदी वाले टीएलएस वर्शन
Android 15, TLS के 1.0 और 1.1 वर्शन के इस्तेमाल पर पाबंदी लगाता है. इन वर्शन को पहले Android में बंद कर दिया गया था. हालांकि, अब Android 15 को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, इनका इस्तेमाल करने की अनुमति नहीं है.
बैकग्राउंड में सुरक्षित तरीके से गतिविधि शुरू करना
Android 15, उपयोगकर्ताओं को नुकसान पहुंचाने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन से बचाता है और उन्हें इन चीज़ों पर ज़्यादा कंट्रोल देता है नुकसान पहुंचाने वाले बैकग्राउंड ऐप्लिकेशन को अन्य ऐप्लिकेशन को फ़ोरग्राउंड में लाना, उनकी खास सुविधाओं को बेहतर बनाना, और गलत इस्तेमाल करना उपयोगकर्ता इंटरैक्शन. Android 10 (एपीआई लेवल 29) से, बैकग्राउंड में गतिविधि शुरू करने पर पाबंदी लगा दी गई है.
अन्य बदलाव
यूआईडी मैचिंग पर पाबंदी के अलावा, ये अन्य बदलाव भी शामिल हैं:
PendingIntentक्रिएटर्स को बदलें, ताकि बैकग्राउंड में होने वाली गतिविधियों की लॉन्च को ब्लॉक किया जा सके डिफ़ॉल्ट बनाएं. इससे ऐप्लिकेशन को ग़लती सेPendingIntent, जिसका इस्तेमाल नुकसान पहुंचाने वाले लोग या ग्रुप गलत इस्तेमाल कर सकते हैं.- किसी ऐप्लिकेशन को तब तक फ़ोरग्राउंड में न लाएं, जब तक उसे भेजने वाला
PendingIntentव्यक्ति न हो इसकी अनुमति देता है. इस बदलाव का मकसद, नुकसान पहुंचाने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन को बैकग्राउंड में गतिविधियां शुरू करने की सुविधा का गलत इस्तेमाल करने से रोकना है. डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से, ऐप्लिकेशन को टास्क स्टैक को फ़ोरग्राउंड में लाने की अनुमति नहीं होती. ऐसा तब तक नहीं होता, जब तक कि क्रिएटर ने बैकग्राउंड गतिविधि को लॉन्च करने की अनुमतियां नहीं दी हैं या मैसेज भेजने वाले के पास बैकग्राउंड गतिविधि को लॉन्च करने की अनुमतियां नहीं हैं. - कंट्रोल करें कि किसी टास्क स्टैक की सबसे लोकप्रिय गतिविधि से टास्क पूरा कैसे हो सकता है. अगर सबसे ऊपर मौजूद टास्क पूरा हो जाता है, तो Android उस टास्क पर वापस चला जाएगा जो आखिरी बार चालू था. इसके अलावा, अगर कोई ऐसी गतिविधि पूरी हो जाती है जो टॉप पर नहीं है, तो Android फिर से होम स्क्रीन पर चला जाएगा. हालांकि, यह गतिविधि पूरी होने से नहीं रोकेगा.
- दूसरे ऐप्लिकेशन से अपने टास्क में कोई भी ऐक्टिविटी लॉन्च होने से रोकना. इस बदलाव से, नुकसान पहुंचाने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन, उपयोगकर्ताओं को फ़िशिंग से बचाते हैं. इसके लिए, वे ऐसी गतिविधियां करते हैं जो दूसरे ऐप्लिकेशन से की गई लगती हैं.
- ऐसी विंडो को बैकग्राउंड में गतिविधि शुरू करने के लिए ब्लॉक करें जो दिख नहीं रही हैं. इससे, नुकसान पहुंचाने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन को बैकग्राउंड में होने वाली गतिविधि का गलत इस्तेमाल करने से रोका जा सकता है. ऐसा इसलिए किया जाता है, ताकि उपयोगकर्ताओं को अनचाहा या नुकसान पहुंचाने वाला कॉन्टेंट न दिखाया जा सके.
ज़्यादा सुरक्षित इंटेंट
Android 15 में, इंटेंट को ज़्यादा सुरक्षित बनाने के लिए नए वैकल्पिक सुरक्षा उपाय पेश किए गए हैं और ज़्यादा मज़बूत. इन बदलावों का मकसद, किसी भी जोखिम की आशंका को रोकना है ऐसे इरादों का गलत तरीके से इस्तेमाल किया जा सके जिनका फ़ायदा नुकसान पहुंचाने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन उठा सकते हैं. Android 15 में, इंटेंट की सुरक्षा को बेहतर बनाने के लिए दो मुख्य बदलाव किए गए हैं:
- टारगेट इंटेंट फ़िल्टर का मैच करें: ऐसे इंटेंट जो खास कॉम्पोनेंट को टारगेट करते हैं टारगेट के इंटेंट-फ़िल्टर की जानकारी से सटीक रूप से मैच होता हो. अगर आपने किसी का इस्तेमाल करने के लिए, टारगेट इंटेंट कॉम्पोनेंट को पाने वाली गतिविधि के तय इंटेंट-फ़िल्टर के साथ अलाइन करें.
- इंटेंट में कार्रवाइयां होनी चाहिए: बिना कार्रवाई वाले इंटेंट, अब किसी भी इंटेंट-फ़िल्टर से मैच नहीं करेंगे. इसका मतलब है कि गतिविधियों या सेवाओं को शुरू करने के लिए इस्तेमाल किए गए इंटेंट में, साफ़ तौर पर बताई गई कार्रवाई होनी चाहिए.
आपका ऐप्लिकेशन इन बदलावों के हिसाब से कैसी प्रतिक्रिया देता है, यह देखने के लिए इसका इस्तेमाल करें
आपके ऐप्लिकेशन में StrictMode. पूरी जानकारी देखने के लिए
Intent के इस्तेमाल से जुड़े उल्लंघनों के लॉग में, नीचे दिया गया तरीका जोड़ें:
Kotlin
fun onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build() ) }
Java
public void onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(new VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build()); }
उपयोगकर्ता अनुभव और सिस्टम यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई)
Android 15 में कुछ ऐसे बदलाव किए गए हैं जिनसे उपयोगकर्ताओं को बेहतर और आसान अनुभव मिलेगा.
विंडो इंसर्ट में बदलाव
Android 15 में, विंडो इनसेट से जुड़े दो बदलाव किए गए हैं: डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से, स्क्रीन के किनारों तक विंडो दिखती है. साथ ही, कॉन्फ़िगरेशन में भी बदलाव किए गए हैं. जैसे, सिस्टम बार का डिफ़ॉल्ट कॉन्फ़िगरेशन.
एज-टू-एज एनफ़ोर्समेंट
अगर कोई ऐप्लिकेशन Android 15 (एपीआई लेवल 35) को टारगेट कर रहा है, तो Android 15 पर चलने वाले डिवाइसों पर वह डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से एज-टू-एज डिसप्ले दिखाएगा.
यह एक बड़ा बदलाव है. इससे आपके ऐप्लिकेशन के यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई) पर बुरा असर पड़ सकता है. बदलावों से यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई) के इन हिस्सों पर असर पड़ता है:
- जेस्चर हैंडल वाला नेविगेशन बार
- डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से पारदर्शी होता है.
- बॉटम ऑफ़सेट बंद है. इसलिए, कॉन्टेंट सिस्टम नेविगेशन बार के पीछे दिखता है. हालांकि, अगर इंसर्ट लागू किए जाते हैं, तो ऐसा नहीं होता.
setNavigationBarColorऔरR.attr#navigationBarColorको बंद कर दिया गया है. इनका इस्तेमाल करने से, हाथ के जेस्चर (स्पर्श) वाले नेविगेशन पर कोई असर नहीं पड़ता.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedऔरR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedका जेस्चर नेविगेशन पर कोई असर नहीं पड़ता.
- तीन बटन वाला नेविगेशन
- ओपैसिटी डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से 80% पर सेट होती है. इसका रंग, विंडो के बैकग्राउंड से मेल खा सकता है.
- बॉटम ऑफ़सेट बंद है, इसलिए कॉन्टेंट सिस्टम नेविगेशन बार के पीछे दिखता है. हालांकि, अगर इंसर्ट लागू किए जाते हैं, तो ऐसा नहीं होगा.
setNavigationBarColorऔरR.attr#navigationBarColorको डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से, विंडो के बैकग्राउंड से मैच करने के लिए सेट किया जाता है. डिफ़ॉल्ट सेटिंग लागू करने के लिए, विंडो का बैकग्राउंड, ड्रॉ करने लायक रंग होना चाहिए. इस एपीआई का इस्तेमाल अब नहीं किया जा सकता. हालांकि, इससे तीन बटन वाले नेविगेशन पर अब भी असर पड़ता है.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedऔरR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedकी वैल्यू डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से सही पर सेट होती है. इससे तीन बटन वाले नेविगेशन में, 80% अपारदर्शी बैकग्राउंड जुड़ जाता है.
- स्टेटस बार
- डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से पारदर्शी होता है.
- टॉप ऑफ़सेट बंद है. इसलिए, स्टेटस बार के पीछे कॉन्टेंट तब तक नहीं दिखता, जब तक कि इंसर्ट लागू नहीं किए जाते.
setStatusBarColorऔरR.attr#statusBarColorअब काम नहीं करते. इनका Android 15 पर कोई असर नहीं पड़ता.setStatusBarContrastEnforcedऔरR.attr#statusBarContrastEnforcedअब काम नहीं करते, लेकिन इनका असर अब भी Android 15 पर पड़ता है.
- डिसप्ले कटआउट
- नॉन-फ़्लोटिंग विंडो का
layoutInDisplayCutoutModeLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYSहोना चाहिए.SHORT_EDGES,NEVER, औरDEFAULTकोALWAYSके तौर पर दिखाया जाता है, ताकि उपयोगकर्ताओं को डिसप्ले कटआउट की वजह से काली पट्टी न दिखे और वे किनारे से किनारे तक दिखें.
- नॉन-फ़्लोटिंग विंडो का
यहां दिए गए उदाहरण में, Android 15 (एपीआई लेवल 35) को टारगेट करने से पहले और बाद में ऐप्लिकेशन को दिखाया गया है. साथ ही, इनसेट लागू करने से पहले और बाद में ऐप्लिकेशन को दिखाया गया है. यह उदाहरण पूरी जानकारी नहीं देता. यह Android Auto पर अलग तरह से दिख सकता है.
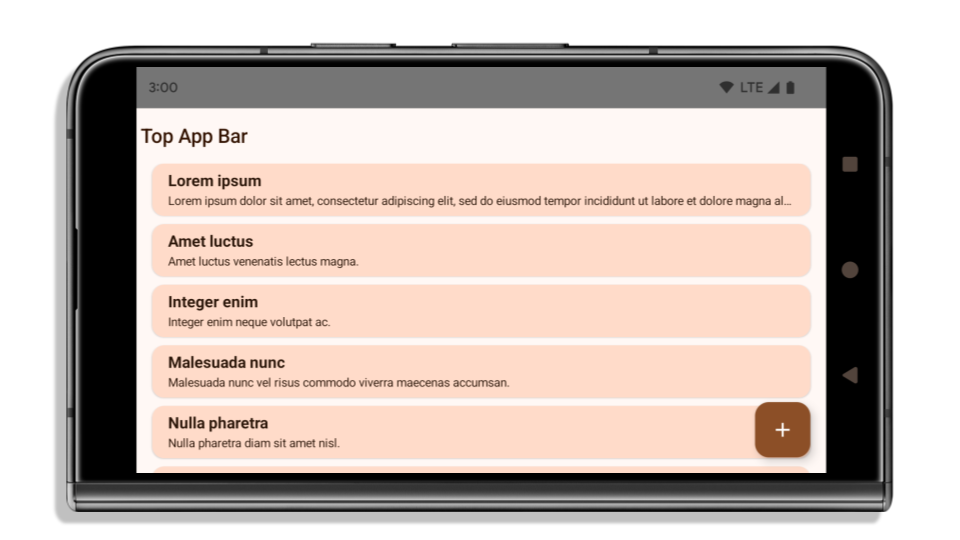

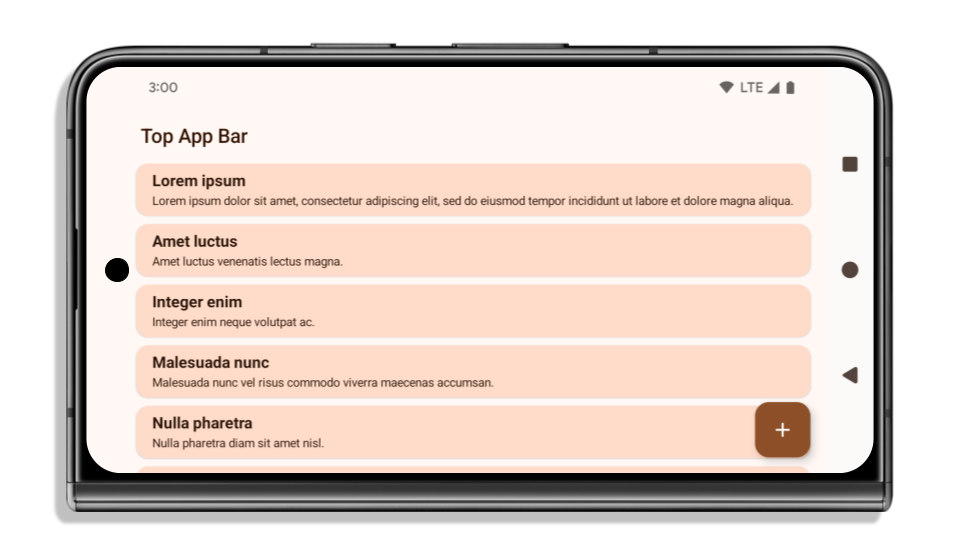
अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन पहले से ही एज-टू-एज है, तो क्या जांच करें
अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन पहले से ही एज-टू-एज है और उसमें इनसेट लागू हैं, तो आपको ज़्यादा असर नहीं पड़ेगा. हालांकि, इन स्थितियों में असर पड़ सकता है. हालांकि, अगर आपको लगता है कि आपके ऐप्लिकेशन पर इसका असर नहीं पड़ा है, तो भी हमारा सुझाव है कि आप अपने ऐप्लिकेशन की जांच करें.
- आपके पास ऐसी विंडो है जो फ़्लोटिंग नहीं है. जैसे,
ActivityजोLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYSके बजायSHORT_EDGES,NEVERयाDEFAULTका इस्तेमाल करती है. अगर लॉन्च होने पर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन क्रैश हो जाता है, तो ऐसा स्प्लैशस्क्रीन की वजह से हो सकता है. core splashscreen डिपेंडेंसी को 1.2.0-alpha01 या उसके बाद के वर्शन पर अपग्रेड किया जा सकता है. इसके अलावा,window.attributes.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = WindowManager.LayoutInDisplayCutoutMode.alwaysसेट किया जा सकता है. - ऐसा हो सकता है कि यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई) के कुछ हिस्से ढके होने की वजह से, स्क्रीन पर कम ट्रैफ़िक हो. पुष्टि करें कि कम विज़िट की जाने वाली इन स्क्रीन पर, यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई) का कोई हिस्सा छिपा हुआ न हो. कम ट्रैफ़िक वाली स्क्रीन में ये शामिल हैं:
- ऑनबोर्डिंग या साइन-इन स्क्रीन
- सेटिंग पेज
अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन पहले से ही एज-टू-एज नहीं है, तो क्या देखना चाहिए
अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन पहले से ही एज-टू-एज नहीं है, तो हो सकता है कि आप पर इसका असर पड़े. पहले से ही एज-टू-एज डिसप्ले वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के अलावा, आपको इन बातों का भी ध्यान रखना चाहिए:
- अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन, Compose में Material 3 कॉम्पोनेंट (
androidx.compose.material3) का इस्तेमाल करता है, जैसे किTopAppBar,BottomAppBar, औरNavigationBar, तो इन कॉम्पोनेंट पर असर नहीं पड़ेगा, क्योंकि ये इनसेट को अपने-आप मैनेज करते हैं. - अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन Compose में Material 2 कॉम्पोनेंट (
androidx.compose.material) का इस्तेमाल कर रहा है, तो ये कॉम्पोनेंट इंसर्ट को अपने-आप मैनेज नहीं करते. हालांकि, आपको इनसेट का ऐक्सेस मिल सकता है और उन्हें मैन्युअल तरीके से लागू किया जा सकता है. androidx.compose.material 1.6.0 और इसके बाद के वर्शन में,windowInsetsपैरामीटर का इस्तेमाल करके,BottomAppBar,TopAppBar,BottomNavigation, औरNavigationRailके लिए इंसर्ट मैन्युअल तरीके से लागू करें. इसी तरह,Scaffoldके लिएcontentWindowInsetsपैरामीटर का इस्तेमाल करें. - अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन व्यू और Material Components (
com.google.android.material) का इस्तेमाल करता है, तो व्यू पर आधारित ज़्यादातर Material Components, जैसे किBottomNavigationView,BottomAppBar,NavigationRailViewयाNavigationView, इनसेट को मैनेज करते हैं. इसके लिए, आपको कुछ और करने की ज़रूरत नहीं होती. हालांकि,AppBarLayoutका इस्तेमाल करने पर,android:fitsSystemWindows="true"को जोड़ना ज़रूरी है. - कस्टम कंपोज़ेबल के लिए, पैडिंग के तौर पर इंसर्ट को मैन्युअल तरीके से लागू करें. अगर आपका कॉन्टेंट
Scaffoldमें है, तोScaffoldपैडिंग वैल्यू का इस्तेमाल करके, इनसेट का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है. इसके अलावा,WindowInsetsमें से किसी एक का इस्तेमाल करके पैडिंग लागू करें. - अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन व्यू और
BottomSheet,SideSheetया कस्टम कंटेनर का इस्तेमाल कर रहा है, तोViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListenerका इस्तेमाल करके पैडिंग लागू करें.RecyclerViewके लिए, इस लिसनर का इस्तेमाल करके पैडिंग लागू करें. साथ ही,clipToPadding="false"जोड़ें.
अगर आपके ऐप्लिकेशन में बैकग्राउंड में काम करने वाली सुविधा के लिए, कस्टम सुरक्षा की सुविधा उपलब्ध कराना ज़रूरी है, तो आपको किन बातों का ध्यान रखना चाहिए
अगर आपके ऐप्लिकेशन को तीन बटन वाले नेविगेशन या स्टेटस बार के लिए, कस्टम बैकग्राउंड सुरक्षा की सुविधा देनी है, तो आपके ऐप्लिकेशन को सिस्टम बार के पीछे कंपोज़ेबल या व्यू रखना चाहिए. इसके लिए, WindowInsets.Type#tappableElement() का इस्तेमाल करके तीन बटन वाले नेविगेशन बार की ऊंचाई या WindowInsets.Type#statusBars का इस्तेमाल करना चाहिए.
पूरी स्क्रीन पर दिखने वाले अन्य संसाधन
इनसेट लागू करने के बारे में ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, Edge to Edge Views और Edge to Edge Compose गाइड देखें.
पुराने एपीआई
ये एपीआई बंद कर दिए गए हैं, लेकिन इन्हें अब भी इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है:
R.attr#enforceStatusBarContrastR.attr#navigationBarColor(तीन बटन वाले नेविगेशन के लिए, 80% ऐल्फ़ा के साथ)Window#isStatusBarContrastEnforcedWindow#setNavigationBarColor(तीन बटन वाले नेविगेशन के लिए, 80% ऐल्फ़ा के साथ)Window#setStatusBarContrastEnforced
इन एपीआई को बंद कर दिया गया है और ये काम नहीं करेंगे:
R.attr#navigationBarColor(जेस्चर वाले नेविगेशन के लिए)R.attr#navigationBarDividerColorR.attr#statusBarColorWindow#setDecorFitsSystemWindowsWindow#getNavigationBarColorWindow#getNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#getStatusBarColorWindow#setNavigationBarColor(जेस्चर वाले नेविगेशन के लिए)Window#setNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#setStatusBarColor
स्टेबल कॉन्फ़िगरेशन
अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन, Android 15 (एपीआई लेवल 35) या इसके बाद के वर्शन को टारगेट करता है, तो Configuration अब सिस्टम बार को शामिल नहीं करता है. अगर लेआउट का हिसाब लगाने के लिए, Configuration क्लास में स्क्रीन साइज़ का इस्तेमाल किया जाता है, तो आपको इसे बेहतर विकल्पों से बदलना चाहिए. जैसे, अपनी ज़रूरत के हिसाब से सही ViewGroup, WindowInsets या WindowMetricsCalculator.
Configuration, एपीआई 1 से उपलब्ध है. आम तौर पर, इसे Activity.onConfigurationChanged से लिया जाता है. इससे विंडो डेंसिटी, ओरिएंटेशन, और साइज़ जैसी जानकारी मिलती है. Configuration से मिले विंडो साइज़ की एक अहम खासियत यह है कि इसमें पहले सिस्टम बार शामिल नहीं होते थे.
कॉन्फ़िगरेशन साइज़ का इस्तेमाल आम तौर पर संसाधन चुनने के लिए किया जाता है. जैसे, /res/layout-h500dp. यह अब भी इस्तेमाल का मान्य उदाहरण है. हालांकि, लेआउट का हिसाब लगाने के लिए इसका इस्तेमाल करने से हमेशा मना किया जाता है. अगर आपने ऐसा किया है, तो आपको अब इससे दूर हो जाना चाहिए. आपको Configuration की जगह, अपनी ज़रूरत के हिसाब से कोई और बेहतर विकल्प इस्तेमाल करना चाहिए.
अगर आपको लेआउट का हिसाब लगाने के लिए इसका इस्तेमाल करना है, तो सही ViewGroup का इस्तेमाल करें. जैसे, CoordinatorLayout या ConstraintLayout. अगर इसका इस्तेमाल सिस्टम के नेविगेशन बार की ऊंचाई का पता लगाने के लिए किया जाता है, तो WindowInsets का इस्तेमाल करें. अगर आपको अपने ऐप्लिकेशन की विंडो का मौजूदा साइज़ जानना है, तो computeCurrentWindowMetrics का इस्तेमाल करें.
यहां दी गई सूची में, उन फ़ील्ड के बारे में बताया गया है जिन पर इस बदलाव का असर पड़ा है:
Configuration.screenWidthDpऔरscreenHeightDpसाइज़ में अब सिस्टम बार शामिल होते हैं.Configuration.smallestScreenWidthDpपरscreenWidthDpऔरscreenHeightDpमें हुए बदलावों का असर पड़ता है.Configuration.orientationपर, स्क्वेयर जैसे डिवाइसों परscreenWidthDpऔरscreenHeightDpमें किए गए बदलावों का असर पड़ता है.Display.getSize(Point)पर,Configurationमें हुए बदलावों का असर सीधे तौर पर नहीं पड़ता. इसे एपीआई लेवल 30 से बंद कर दिया गया है.Display.getMetrics(), एपीआई लेवल 33 से ही इस तरह काम कर रहा है.
elegantTextHeight एट्रिब्यूट डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से सही पर सेट होता है
Android 15 (एपीआई लेवल 35) को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, elegantTextHeight TextView एट्रिब्यूट डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से true हो जाता है. इससे, डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से इस्तेमाल किए जाने वाले कॉम्पैक्ट फ़ॉन्ट की जगह, कुछ ऐसी स्क्रिप्ट का इस्तेमाल किया जाता है जिनमें बड़ी वर्टिकल मेट्रिक होती हैं. इन मेट्रिक को पढ़ना ज़्यादा आसान होता है.
कॉम्पैक्ट फ़ॉन्ट को लेआउट के बीच में रुकावट आने से रोकने के लिए लॉन्च किया गया था. Android 13 (एपीआई लेवल 33), fallbackLineSpacing एट्रिब्यूट का इस्तेमाल करके, टेक्स्ट लेआउट की वर्टिकल ऊंचाई को बढ़ाकर, इनमें से कई रुकावटों को रोकता है.
Android 15 में, कॉम्पैक्ट फ़ॉन्ट अब भी सिस्टम में मौजूद है. इसलिए, आपका ऐप्लिकेशन पहले जैसा व्यवहार पाने के लिए, elegantTextHeight को false पर सेट कर सकता है. हालांकि, आने वाले समय में रिलीज़ होने वाले वर्शन में, इसकी सुविधा काम नहीं करेगी. इसलिए, अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन इन स्क्रिप्ट के साथ काम करता है: ऐरेबिक, लाओ, म्यांमार, तमिल, गुजराती, कन्नड़, मलयालम, उड़ीया, तेलुगु या थाई, तो elegantTextHeight को true पर सेट करके अपने ऐप्लिकेशन की जांच करें.
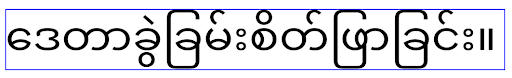
elegantTextHeight Android 14 (एपीआई लेवल 34) और उससे पहले के वर्शन को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए व्यवहार.
elegantTextHeight Android 15 को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए व्यवहार.जटिल अक्षर के आकार के लिए, TextView की चौड़ाई में बदलाव होता है
Android के पिछले वर्शन में, पेचीदा आकार वाले कुछ कर्सिव फ़ॉन्ट या भाषाएं, पिछले या अगले वर्ण के एरिया में अक्षर खींच सकती हैं.
कुछ मामलों में, ऐसे अक्षरों को शुरुआत या आखिर में काटकर छोटा किया गया था.
Android 15 से, TextView ऐसे अक्षरों के लिए ज़रूरी जगह बनाने के लिए
चौड़ाई तय करता है. साथ ही, क्लिप बनाने से रोकने के लिए,
ऐप्लिकेशन बाईं ओर ज़्यादा पैडिंग (जगह) का अनुरोध कर सकते हैं.
इस बदलाव का असर इस बात पर पड़ता है कि TextView, चौड़ाई का फ़ैसला कैसे लेता है. इसलिए, अगर ऐप्लिकेशन Android 15 (एपीआई लेवल 35) या उसके बाद के वर्शन को टारगेट करता है, तो TextView डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से ज़्यादा चौड़ाई तय करता है. setUseBoundsForWidth पर एपीआई को कॉल करके, इस सुविधा को चालू या बंद किया जा सकता है.TextView
बाईं ओर की पैडिंग जोड़ने से, हो सकता है कि मौजूदा लेआउट गलत तरीके से अलाइन हो जाएं. ऐसा होने पर, Android 15 या इसके बाद के वर्शन को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए भी पैडिंग (जगह) डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से नहीं जोड़ी जाती.
हालांकि, setShiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang को कॉल करके, क्लिपिंग को रोकने के लिए अतिरिक्त पैडिंग जोड़ी जा सकती है.
नीचे दिए गए उदाहरणों से पता चलता है कि इन बदलावों से कुछ फ़ॉन्ट और भाषाओं के लिए टेक्स्ट लेआउट को बेहतर कैसे बनाया जा सकता है.

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" />

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />
EditText के लिए, स्थान-भाषा के हिसाब से लाइन की डिफ़ॉल्ट ऊंचाई
Android के पिछले वर्शन में, टेक्स्ट लेआउट, टेक्स्ट की ऊंचाई को बढ़ा देता था, ताकि मौजूदा स्थानीय भाषा से मैच करने वाले फ़ॉन्ट की लाइन की ऊंचाई पूरी की जा सके. उदाहरण के लिए, अगर कॉन्टेंट जैपनीज़ में था, तो टेक्स्ट की ऊंचाई थोड़ी ज़्यादा हो गई, क्योंकि जैपनीज़ फ़ॉन्ट की लाइन की ऊंचाई, लैटिन फ़ॉन्ट की लाइन की ऊंचाई से थोड़ी ज़्यादा होती है. हालांकि, लाइन हाइट में इन अंतरों के बावजूद, इस्तेमाल किए जा रहे स्थानीय भाषा के बावजूद, EditText एलिमेंट का साइज़ एक जैसा था, जैसा कि इस इमेज में दिखाया गया है:

EditText एलिमेंट दिखाने वाले तीन बॉक्स, जिनमें इंग्लिश (en), जैपनीज़ (ja), और बर्मीज़ (my) भाषा का टेक्स्ट हो सकता है. EditText की ऊंचाई एक जैसी है, भले ही इन भाषाओं की लाइन की ऊंचाई एक-दूसरे से अलग हो.Android 15 (एपीआई लेवल 35) को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, EditText के लिए कम से कम लाइन हाइट तय की गई है. इससे, तय की गई लोकेल के रेफ़रंस फ़ॉन्ट से मैच करने में मदद मिलती है. इसकी जानकारी इस इमेज में दी गई है:

EditText एलिमेंट दिखाने वाले तीन बॉक्स, जिनमें इंग्लिश (en), जैपनीज़ (ja), और बर्मीज़ (my) भाषा का टेक्स्ट हो सकता है. EditText की ऊंचाई में अब इन भाषाओं के फ़ॉन्ट के लिए, डिफ़ॉल्ट लाइन की ऊंचाई को शामिल करने के लिए स्पेस शामिल है.ज़रूरत पड़ने पर, आपका ऐप्लिकेशन useLocalePreferredLineHeightForMinimum एट्रिब्यूट को false पर सेट करके, पहले जैसा व्यवहार वापस ला सकता है. साथ ही, आपका ऐप्लिकेशन Kotlin और Java में setMinimumFontMetrics एपीआई का इस्तेमाल करके, कस्टम मिनिमम वर्टिकल मेट्रिक सेट कर सकता है.
कैमरा और मीडिया
Android 15 या इसके बाद के वर्शन को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, Android 15 में कैमरा और मीडिया के काम करने के तरीके में ये बदलाव किए गए हैं.
ऑडियो फ़ोकस का अनुरोध करने पर लगी पाबंदियां
Android 15 (एपीआई लेवल 35) को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन को ऑडियो फ़ोकस का अनुरोध करने के लिए, टॉप ऐप्लिकेशन या फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा के तौर पर चलना होगा. अगर कोई ऐप्लिकेशन इनमें से किसी एक ज़रूरी शर्त को पूरा न करने पर फ़ोकस का अनुरोध करता है, तो कॉल AUDIOFOCUS_REQUEST_FAILED दिखाता है.
ऑडियो फ़ोकस के बारे में ज़्यादा जानने के लिए, ऑडियो फ़ोकस मैनेज करें पर जाएं.
एसडीके इंटिग्रेट किए बगैर इस्तेमाल की जाने वाली सुविधाओं पर लगी पाबंदियां अपडेट की गईं
Android 15 में, पाबंदी वाले नॉन-एसडीके इंटरफ़ेस की अपडेट की गई सूचियां शामिल हैं. ये सूचियां, Android डेवलपर के साथ मिलकर काम करने और हाल ही में हुई इंटरनल टेस्टिंग के आधार पर बनाई गई हैं. हम यह पक्का करते हैं कि गैर-एसडीके इंटरफ़ेस को प्रतिबंधित करने से पहले, सार्वजनिक विकल्प उपलब्ध हों.
अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन Android 15 को टारगेट नहीं करता है, तो हो सकता है कि इनमें से कुछ बदलावों का असर आप पर तुरंत न पड़े. हालांकि, आपके ऐप्लिकेशन के टारगेट एपीआई लेवल के हिसाब से, आपका ऐप्लिकेशन कुछ नॉन-एसडीके इंटरफ़ेस ऐक्सेस कर सकता है. हालांकि, किसी भी नॉन-एसडीके तरीके या फ़ील्ड का इस्तेमाल करने से, आपके ऐप्लिकेशन के काम न करने का खतरा हमेशा बना रहता है.
अगर आपको पक्का नहीं है कि आपका ऐप्लिकेशन, गैर-एसडीके इंटरफ़ेस का इस्तेमाल करता है, तो यह पता लगाने के लिए अपने ऐप्लिकेशन की जांच करें. अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन, नॉन-एसडीके इंटरफ़ेस पर निर्भर करता है, तो आपको एसडीके के विकल्पों पर माइग्रेट करने की योजना बनानी चाहिए. हालांकि, हम समझते हैं कि कुछ ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, गैर-एसडीके इंटरफ़ेस का इस्तेमाल करना ज़रूरी होता है. अगर आपको अपने ऐप्लिकेशन में किसी सुविधा के लिए, एसडीके के अलावा किसी अन्य इंटरफ़ेस का इस्तेमाल करने का विकल्प नहीं मिल रहा है, तो आपको नए सार्वजनिक एपीआई का अनुरोध करना चाहिए.
Android के इस वर्शन में हुए बदलावों के बारे में ज़्यादा जानने के लिए, Android 15 में, SDK टूल के अलावा अन्य इंटरफ़ेस से जुड़ी पाबंदियों में हुए अपडेट देखें. आम तौर पर, SDK टूल के बाहर के इंटरफ़ेस के बारे में ज़्यादा जानने के लिए, SDK टूल के बाहर के इंटरफ़ेस पर लगी पाबंदियां देखें.

