Die Android 15-Plattform umfasst Verhaltensänderungen, die sich auf Ihre App auswirken können.
Die folgenden Verhaltensänderungen gelten für alle Apps, wenn sie unter Android 15 ausgeführt werden, unabhängig von targetSdkVersion. Sie sollten Ihre App testen und sie bei Bedarf so anpassen, dass sie diese Funktionen unterstützt.
Sehen Sie sich auch die Liste der Verhaltensänderungen an, die sich nur auf Apps auswirken, die auf Android 15 ausgerichtet sind.
Hauptfunktion
In Android 15 werden verschiedene Kernfunktionen des Android-Systems geändert oder erweitert.
Änderungen am Status „Angehalten“ von Paketen
软件包 FLAG_STOPPED 状态(用户可以通过在 AOSP build 中长按应用图标并选择“强制停止”来启用此状态)的用途一直是让应用保持在此状态,直到用户通过直接启动应用或间接与应用互动(通过 Sharesheet 或 widget、将应用选择为动态壁纸等)来明确将应用从此状态移除。在 Android 15 中,我们更新了系统行为,使其与此预期行为保持一致。应用应仅通过直接或间接的用户操作从停止状态移除。
为了支持预期行为,除了现有限制之外,当应用在搭载 Android 15 的设备上进入停止状态时,系统还会取消所有待处理 intent。当用户的操作将应用从停止状态移除时,系统会将 ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED 广播传送到应用,以便应用有机会重新注册所有待处理 intent。
您可以调用新的 ApplicationStartInfo.wasForceStopped() 方法来确认应用是否已进入停止状态。
Unterstützung für Seitengrößen von 16 KB
Bisher wurden in Android nur Arbeitsspeicherseiten mit 4 KB unterstützt. Dadurch wurde die Leistung des Systemspeichers für die durchschnittliche Menge an Gesamtspeicher optimiert, die Android-Geräte in der Regel hatten. Ab Android 15 unterstützt AOSP Geräte, die für die Verwendung einer Seitengröße von 16 KB konfiguriert sind (16‑KB-Geräte). Wenn Ihre App NDK-Bibliotheken verwendet, entweder direkt oder indirekt über ein SDK, müssen Sie Ihre App neu erstellen, damit sie auf diesen 16‑KB-Geräten funktioniert.
Da Gerätehersteller weiterhin Geräte mit größeren Mengen an physischem Arbeitsspeicher (RAM) entwickeln, werden viele dieser Geräte 16‑KB-Seitengrößen (und schließlich noch größere) verwenden, um die Leistung des Geräts zu optimieren. Wenn Sie Unterstützung für Geräte mit einer Seitengröße von 16 KB hinzufügen, kann Ihre App auf diesen Geräten ausgeführt werden und von den damit verbundenen Leistungsverbesserungen profitieren. Ohne Neukompilierung funktionieren Apps in zukünftigen Android-Versionen nicht auf Geräten mit 16 KB.
Damit Sie Ihre App entsprechend anpassen können, haben wir Anleitungen dazu bereitgestellt, wie Sie prüfen, ob Ihre App betroffen ist, wie Sie Ihre App neu erstellen (falls zutreffend) und wie Sie Ihre App mit Emulatoren (einschließlich Android 15-Systemabbildern für den Android-Emulator) in einer 16‑KB-Umgebung testen.
Benefits and performance gains
配置为使用 16 KB 页面大小的设备平均会使用略多一些的内存,但系统和应用的性能也会得到各种提升:
- 缩短了系统内存压力时的应用启动时间:平均降低了 3.16%;对于我们测试的某些应用而言,改进幅度更大(最高可达 30%)
- 应用启动期间的功耗降低:平均降低了 4.56%
- 相机启动更快:热启动速度平均提高了 4.48%,冷启动速度平均提高了 6.60%
- 缩短了系统启动时间:平均缩短了 8%(约 950 毫秒)
这些改进基于我们的初始测试,实际设备上的结果可能会有所不同。随着测试的继续进行,我们将进一步分析应用的潜在收益。
Check if your app is impacted
Wenn Ihre App nativen Code verwendet, sollten Sie Ihre App neu erstellen, um Geräte mit 16‑KB-Speicherseiten zu unterstützen. Wenn Sie sich nicht sicher sind, ob Ihre App nativen Code verwendet, können Sie mit dem APK Analyzer prüfen, ob nativer Code vorhanden ist, und dann die Ausrichtung von ELF-Segmenten für alle gefundenen gemeinsam genutzten Bibliotheken prüfen. Android Studio bietet auch Funktionen, mit denen Sie Ausrichtungsprobleme automatisch erkennen können.
Wenn Ihre App nur Code verwendet, der in der Programmiersprache Java oder in Kotlin geschrieben wurde, einschließlich aller Bibliotheken oder SDKs, unterstützt Ihre App bereits Geräte mit 16 KB. Wir empfehlen Ihnen jedoch, Ihre App in einer 16‑KB-Umgebung zu testen, um zu prüfen, ob es unerwartete Regressionen im App-Verhalten gibt.
Erforderliche Änderungen für einige Apps zur Unterstützung des vertraulichen Profils
Private space is a new feature in Android 15 that lets users create a separate space on their device where they can keep sensitive apps away from prying eyes, under an additional layer of authentication. Because apps in the private space have restricted visibility, some types of apps need to take additional steps to be able to see and interact with apps in a user's private space.
All apps
Because apps in the private space are kept in a separate user profile, similar to work profiles, apps shouldn't assume that any installed copies of their app that aren't in the main profile are in the work profile. If your app has logic related to work profile apps that make this assumption, you'll need to adjust this logic.
Medical apps
When a user locks the private space, all apps in the private space are stopped, and those apps can't perform foreground or background activities, including showing notifications. This behavior might critically impact the use and function of medical apps installed in the private space.
The private space setup experience warns users that the private space is not suitable for apps that need to perform critical foreground or background activities, such as showing notifications from medical apps. However, apps can't determine whether or not they're being used in the private space, so they can't show a warning to the user for this case.
For these reasons, if you develop a medical app, review how this feature might impact your app and take appropriate actions—such as informing your users not to install your app in the private space—to avoid disrupting critical app capabilities.
Launcher apps
If you develop a launcher app, you must do the following before apps in the private space will be visible:
- Your app must be assigned as the default launcher app for the device—that
is, possessing the
ROLE_HOMErole. - Your app must declare the
ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILESnormal permission in your app's manifest file.
Launcher apps that declare the ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILES permission must handle
the following private space use cases:
- Your app must have a separate launcher container for apps installed in the
private space. Use the
getLauncherUserInfo()method to determine which type of user profile is being handled. - The user must be able to hide and show the private space container.
- The user must be able to lock and unlock the private space container. Use
the
requestQuietModeEnabled()method to lock (by passingtrue) or unlock (by passingfalse) the private space. While locked, no apps in the private space container should be visible or discoverable through mechanisms such as search. Your app should register a receiver for the
ACTION_PROFILE_AVAILABLEandACTION_PROFILE_UNAVAILABLEbroadcasts and update the UI in your app when the locked or unlocked state of the private space container changes. Both of these broadcasts includeEXTRA_USER, which your app can use to refer to the private profile user.You can also use the
isQuietModeEnabled()method to check whether the private space profile is locked or not.
App store apps
The private space includes an "Install Apps" button that launches an implicit
intent to install apps into the user's private space. In order for your app to
receive this implicit intent, declare an <intent-filter>
in your app's manifest file with a <category> of
CATEGORY_APP_MARKET.
PNG-basierte Emoji-Schriftart entfernt
The legacy, PNG-based emoji font file (NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf) has been
removed, leaving just the vector-based file. Beginning with Android 13 (API
level 33), the emoji font file used by the system emoji renderer changed from a
PNG-based file to a vector based file. The system retained
the legacy font file in Android 13 and 14 for compatibility reasons, so that
apps with their own font renderers could continue to use the legacy font file
until they were able to upgrade.
To check if your app is affected, search your app's code for references to the
NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf file.
You can choose to adapt your app in a number of ways:
- Use platform APIs for text rendering. You can render text to a bitmap-backed
Canvasand use that to get a raw image if necessary. - Add COLRv1 font support to your app. The FreeType open source library supports COLRv1 in version 2.13.0 and higher.
- As a last resort, you can bundle the legacy emoji font file
(
NotoColorEmoji.ttf) into your APK, although in that case your app will be missing the latest emoji updates. For more information, see the Noto Emoji GitHub project page.
Die Mindest-SDK-Zielversion wurde von 23 auf 24 erhöht.
Android 15 builds on the
the changes that were made in Android 14 and extends this
security further. In Android 15, apps with a
targetSdkVersion lower than 24 can't be installed.
Requiring apps to meet modern API levels helps to ensure better security and
privacy.
Malware often targets lower API levels in order to bypass security and privacy
protections that have been introduced in higher Android versions. For example,
some malware apps use a targetSdkVersion of 22 to avoid being subjected to the
runtime permission model introduced in 2015 by Android 6.0 Marshmallow (API
level 23). This Android 15 change makes it harder for malware to avoid security
and privacy improvements. Attempting to install an app targeting a lower API
level results in an installation failure, with a message like the following one
appearing in Logcat:
INSTALL_FAILED_DEPRECATED_SDK_VERSION: App package must target at least SDK version 24, but found 7
On devices upgrading to Android 15, any apps with a targetSdkVersion lower
than 24 remain installed.
If you need to test an app targeting an older API level, use the following ADB command:
adb install --bypass-low-target-sdk-block FILENAME.apk
Sicherheit und Datenschutz
Android 15 引入了强大的措施来防范动态密码 (OTP) 欺诈并保护用户的敏感内容,重点是增强通知监听器服务和屏幕共享保护措施。主要增强功能包括从可供不可信应用访问的通知中隐去 OTP、在屏幕共享期间隐藏通知,以及在发布 OTP 时保护应用 activity。这些变更旨在保护用户的敏感内容,使其免受未经授权的操作者的侵害。
开发者需要注意以下事项,以确保其应用与 Android 15 中的变更兼容:
动态密码隐去
Android 会阻止实现 NotificationListenerService 的不受信任应用读取已检测到 OTP 的通知中的未隐去的内容。配套设备管理器关联等受信任应用不受这些限制。
屏幕共享保护
- 在屏幕共享会话期间,系统会隐藏通知内容,以保护用户的隐私。如果应用实现了
setPublicVersion(),Android 会显示通知的公开版本,该版本在不安全情境中用作替换通知。否则,系统会隐去通知内容,不提供任何其他背景信息。 - 系统会向远程观看者隐藏密码输入等敏感内容,以防止泄露用户的敏感信息。
- 如果在屏幕共享期间检测到动态密码,系统会隐藏在该时间段内发布通知的应用的活动。应用内容在启动时会向远程查看器隐藏。
- 除了 Android 自动识别敏感字段之外,开发者还可以使用
setContentSensitivity手动将应用的部分标记为敏感,在屏幕共享期间,这些敏感字段会对远程观看者隐藏。 - 开发者可以选择切换开发者选项下的停用屏幕共享防护选项,以便出于演示或测试目的豁免屏幕共享防护。默认的系统屏幕录制工具不受这些更改的影响,因为录制内容会保留在设备上。
Kamera und Medien
In Android 15 werden die folgenden Änderungen am Kamera- und Medienverhalten für alle Apps vorgenommen.
Durch die direkte und ausgelagerte Audiowiedergabe werden zuvor geöffnete direkte oder ausgelagerte Audiotracks ungültig, wenn Ressourcenlimits erreicht werden.
Before Android 15, if an app requested direct or offload audio playback while
another app was playing audio and the resource limits were reached, the app
would fail to open a new AudioTrack.
Beginning with Android 15, when an app requests direct or offload
playback and the resource
limits are reached, the system invalidates any currently open
AudioTrack objects which prevent fulfilling the new track request.
(Direct and offload audio tracks are typically opened for playback of compressed audio formats. Common use-cases for playing direct audio include streaming encoded audio over HDMI to a TV. Offload tracks are typically used to play compressed audio on a mobile device with hardware DSP acceleration.)
Nutzererfahrung und System-UI
Android 15 enthält einige Änderungen, die für eine einheitlichere und intuitivere User Experience sorgen sollen.
Animationen für intelligente „Zurück“-Touchgeste für Apps aktiviert, die sich dafür registriert haben
Beginning in Android 15, the developer option for predictive back animations has been removed. System animations such as back-to-home, cross-task, and cross-activity now appear for apps that have opted in to the predictive back gesture either entirely or at an activity level. If your app is affected, take the following actions:
- Ensure that your app has been properly migrated to use the predictive back gesture.
- Ensure that your fragment transitions work with predictive back navigation.
- Migrate away from animation and framework transitions and use animator and androidx transitions instead.
- Migrate away from back stacks that
FragmentManagerdoesn't know about. Use back stacks managed byFragmentManageror by the Navigation component instead.
Widgets werden deaktiviert, wenn ein Nutzer eine App erzwingt, dass sie beendet wird
If a user force-stops an app on a device running Android 15, the system temporarily disables all the app's widgets. The widgets are grayed out, and the user cannot interact with them. This is because beginning with Android 15, the system cancels all an app's pending intents when the app is force-stopped.
The system re-enables those widgets the next time the user launches the app.
For more information, see Changes to package stopped state.
Chip in der Statusleiste für die Medienprojektion informiert Nutzer über Bildschirmfreigabe, Streaming und Aufzeichnung
屏幕投影漏洞会泄露用户的私密数据(例如财务信息),因为用户不知道自己的设备屏幕正在共享。
对于搭载 Android 15 QPR1 或更高版本的设备上运行的应用,系统会在状态栏中显示一个醒目的大条状标签,以提醒用户正在进行的任何屏幕投影。用户可以点按该条状标签,停止共享、投放或录制其屏幕。此外,当设备屏幕锁定时,屏幕投影会自动停止。
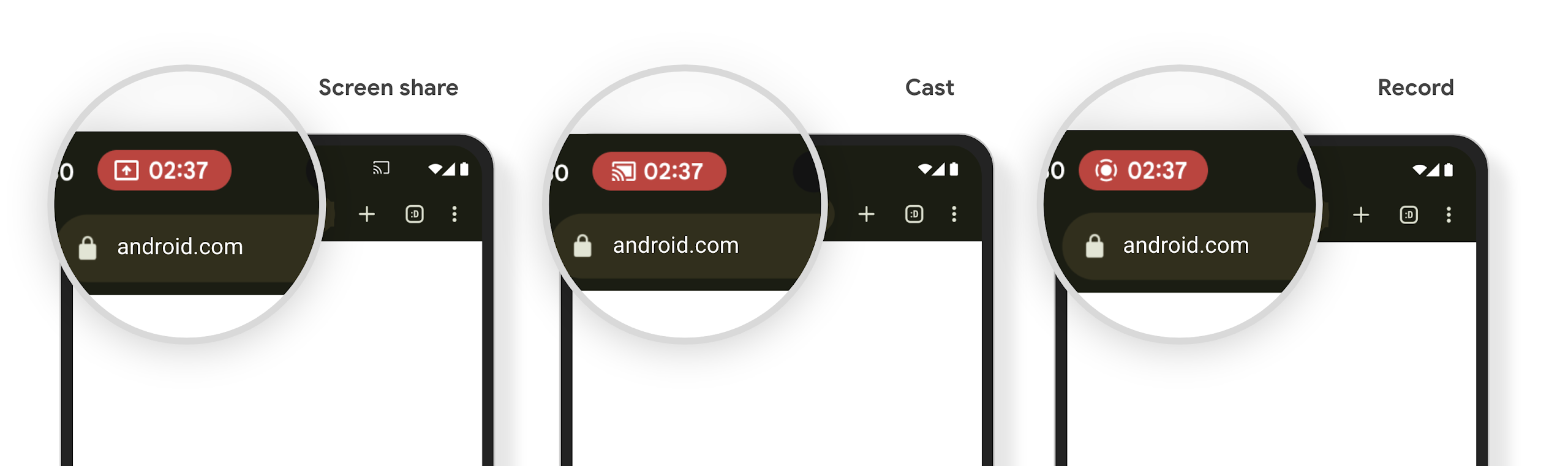
Check if your app is impacted
By default, your app includes the status bar chip and automatically suspends screen projection when the lock screen activates.
To learn more about how to test your app for these use cases, see Status bar chip and auto stop.
Einschränkungen für den Netzwerkzugriff im Hintergrund
在 Android 15 中,如果应用在有效的进程生命周期之外启动网络请求,则会收到异常。通常是 UnknownHostException 或其他与套接字相关的 IOException。在有效生命周期之外发生的网络请求通常是因为应用在不再活跃后,不知不觉地继续发出网络请求。
为缓解此异常,请使用生命周期感知型组件,确保您的网络请求具有生命周期感知功能,并在离开有效的进程生命周期时取消。如果您非常重视即使用户离开应用也要发出网络请求,请考虑使用 WorkManager 调度网络请求,或使用前台服务继续执行对用户可见的任务。
Einstellung
Mit jeder Veröffentlichung können bestimmte Android-APIs veraltet sein oder müssen refaktoriert werden, um ein besseres Entwicklererlebnis zu bieten oder neue Plattformfunktionen zu unterstützen. In diesen Fällen werden die veralteten APIs offiziell eingestellt und Entwickler werden auf alternative APIs verwiesen.
Das bedeutet, dass wir den offiziellen Support für die APIs eingestellt haben, sie aber weiterhin für Entwickler verfügbar sind. Weitere Informationen zu wichtigen Einstellungen in dieser Version von Android finden Sie auf der Seite zu Einstellungen.

