Android 15 incluye excelentes funciones y APIs para desarrolladores. En las siguientes secciones, se resumen estas funciones para ayudarte a comenzar a usar las APIs relacionadas.
Para obtener una lista detallada de las APIs agregadas, modificadas y quitadas, consulta el informe de diferencias de la API. Para obtener detalles sobre las APIs agregadas, consulta la referencia de la API de Android. En Android 15, busca las APIs que se agregaron en el nivel de API 35. Para conocer las áreas en las que los cambios de la plataforma podrían afectar tus apps, asegúrate de revisar los cambios en el comportamiento de Android 15 para apps orientadas a Android 15 y para todas las apps.
Cámara y contenido multimedia
Android 15 incluye una variedad de funciones que mejoran la experiencia de la cámara y el contenido multimedia, y que te brindan acceso a herramientas y hardware para ayudar a los creadores a hacer realidad su visión en Android.
Para obtener más información sobre las funciones y soluciones para desarrolladores más recientes de la cámara y el contenido multimedia de Android, consulta la charla Building modern Android media and camera experiences de Google I/O.
Mejora con poca luz
Android 15 presenta Mejora de poca luz, un modo de exposición automática disponible para Camera 2 y la extensión de cámara del modo nocturno. La mejora con poca luz ajusta la exposición de la transmisión de vista previa en condiciones de poca luz. Esto es diferente de la forma en que la extensión de cámara del modo nocturno crea imágenes fijas, ya que el modo nocturno combina una ráfaga de fotos para crear una sola imagen mejorada. Si bien el modo nocturno funciona muy bien para crear una imagen fija, no puede crear una transmisión continua de fotogramas, pero el modo de mejora con poca luz sí puede hacerlo. Por lo tanto, el modo de poca luz habilita las siguientes funciones de la cámara:
- Proporciona una vista previa de imagen mejorada para que los usuarios puedan encuadrar mejor sus fotos con poca luz.
- Cómo escanear códigos QR con poca luz
Si habilitas la función de mejora de poca luz, esta se activa automáticamente cuando hay un nivel de luz bajo y se desactiva cuando hay más luz.
Las apps pueden grabar desde la transmisión de vista previa en condiciones de poca luz para guardar un video más brillante.
Para obtener más información, consulta Aumento de poca luz.
Controles de cámara en la app
Android 15 agrega una extensión para tener más control sobre el hardware de la cámara y sus algoritmos en dispositivos compatibles:
- Ajustes avanzados de la intensidad del flash que permiten un control preciso de la intensidad del flash en los modos
SINGLEyTORCHmientras se capturan imágenes.
Control de espacio libre de HDR
Android 15 elige el margen de HDR adecuado para las capacidades subyacentes del dispositivo y la profundidad de bits del panel. En el caso de las páginas que tienen mucho contenido SDR, como una app de mensajería que muestra una sola miniatura HDR, este comportamiento puede influir de manera negativa en el brillo percibido del contenido SDR. Android 15 te permite controlar el margen de HDR con setDesiredHdrHeadroom para lograr un equilibrio entre el contenido SDR y HDR.
Control de volumen

Android 15 admite el estándar de volumen CTA-2075 para ayudarte a evitar inconsistencias en el volumen de audio y garantizar que los usuarios no tengan que ajustar el volumen constantemente cuando cambien de contenido. El sistema aprovecha las características conocidas de los dispositivos de salida (auriculares y bocinas) junto con los metadatos de volumen disponibles en el contenido de audio AAC para ajustar de forma inteligente el volumen de audio y los niveles de compresión del rango dinámico.
Para habilitar esta función, debes asegurarte de que los metadatos de volumen estén disponibles en tu contenido AAC y habilitar la función de la plataforma en tu app. Para ello, debes crear una instancia de un objeto LoudnessCodecController llamando a su método de fábrica create con el ID de sesión de audio del AudioTrack asociado. Esto comenzará a aplicar actualizaciones de audio automáticamente. Puedes pasar un OnLoudnessCodecUpdateListener para modificar o filtrar los parámetros de volumen antes de que se apliquen en MediaCodec.
// Media contains metadata of type MPEG_4 OR MPEG_D
val mediaCodec = …
val audioTrack = AudioTrack.Builder()
.setSessionId(sessionId)
.build()
...
// Create new loudness controller that applies the parameters to the MediaCodec
try {
val lcController = LoudnessCodecController.create(mSessionId)
// Starts applying audio updates for each added MediaCodec
}
AndroidX media3 ExoPlayer también se actualizará para usar las APIs de LoudnessCodecController para una integración de apps sin problemas.
Dispositivos MIDI 2.0 virtuales
Android 13 agregó compatibilidad para conectarse a dispositivos MIDI 2.0 a través de USB, que se comunican con paquetes MIDI universales (UMP). Android 15 extiende la compatibilidad con UMP a las apps de MIDI virtual, lo que permite que las apps de composición controlen las apps de sintetizador como un dispositivo MIDI 2.0 virtual, al igual que lo harían con un dispositivo MIDI 2.0 USB.
Decodificación de software AV1 más eficiente

dav1d, el popular decodificador de software AV1 de VideoLAN, está disponible para dispositivos Android que no admiten la decodificación de AV1 en hardware. dav1d tiene hasta 3 veces más rendimiento que el decodificador de software AV1 heredado, lo que permite la reproducción de AV1 en HD para más usuarios, incluidos algunos dispositivos de nivel bajo y medio.
Tu app debe habilitar el uso de dav1d invocándolo por nombre "c2.android.av1-dav1d.decoder". dav1d se convertirá en el decodificador de software de AV1 predeterminado en una actualización posterior. Esta compatibilidad está estandarizada y se ofrece portabilidad a los dispositivos Android 11 que reciben actualizaciones del sistema de Google Play.
Productividad y herramientas para desarrolladores
Si bien la mayor parte de nuestro trabajo para mejorar tu productividad se centra en herramientas como Android Studio, Jetpack Compose y las bibliotecas de Android Jetpack, siempre buscamos formas en la plataforma para ayudarte a concretar tu visión con mayor facilidad.
Actualizaciones de OpenJDK 17
Android 15 continúa la tarea de actualizar las bibliotecas principales de Android para alinearlas con las funciones de las versiones más recientes de LTS de OpenJDK.
Se incluyen las siguientes funciones y mejoras clave:
- Se realizaron mejoras de calidad de vida en los buffers de NIO.
- Transmisiones
- Métodos adicionales
mathystrictmath - Actualizaciones de paquetes
util, incluidascollection,mapyseten secuencia - Compatibilidad con
ByteBufferenDeflater - Actualizaciones de seguridad, como
X500PrivateCredentialy actualizaciones de claves de seguridad
Estas APIs se actualizan en más de mil millones de dispositivos que ejecutan Android 12 (nivel de API 31) y versiones posteriores a través de las actualizaciones del sistema de Google Play, por lo que puedes segmentar tu contenido para las funciones de programación más recientes.
Mejoras en el PDF
Android 15 incluye mejoras sustanciales en las APIs de PdfRenderer. Las apps pueden incorporar funciones avanzadas, como la renderización de archivos protegidos por contraseña, las anotaciones, la edición de formularios, la búsqueda y la selección con copia. Se admiten optimizaciones de PDF linealizados para acelerar la visualización de PDF local y reducir el uso de recursos.
La biblioteca de PDF de Jetpack usa estas APIs para simplificar la adición de funciones de visualización de PDF a tu app.
Se trasladó PdfRenderer a un módulo que se puede actualizar con Google.
Las actualizaciones del sistema de Play son independientes
de la versión de la plataforma,
estos cambios a Android 11 (nivel de API 30) mediante la creación de una versión
versión de la plataforma de API anterior a Android 15, llamada
PdfRendererPreV
Mejoras en el cambio automático de idioma
Android 14 agregó el reconocimiento multilingüe integrado en el dispositivo en el audio con cambio automático entre idiomas, pero esto puede provocar que se omitan palabras, en especial cuando los idiomas cambian con menos pausa entre las dos oraciones. Android 15 agrega controles adicionales para ayudar a las apps a ajustar este cambio según su caso de uso.
EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_INITIAL_ACTIVE_DURATION_TIME_MILLIS limita el cambio automático al comienzo de la sesión de audio, mientras que EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_MATCH_SWITCHES desactiva el cambio de idioma después de una cantidad definida de cambios. Estas opciones son particularmente útiles si esperas que se hable un solo idioma durante la sesión que se debe detectar automáticamente.
Se mejoró la API de fuentes variables de OpenType
Android 15 mejora la usabilidad de la fuente variable OpenType. Puedes crear
una instancia de FontFamily a partir de una fuente variable sin especificar los ejes de grosor
con la API de buildVariableFamily. El renderizador de texto anula el valor del eje wght para que coincida con el texto que se muestra.
El uso de la API simplifica considerablemente el código para crear un Typeface:
Kotlin
val newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build()
Java
Typeface newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build();
Anteriormente, para crear el mismo Typeface, necesitabas mucho más código:
Kotlin
val oldTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build()) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ).build() ).build()
Java
Typeface oldTypeface = new Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ) .build() ).build();
Este es un ejemplo de cómo se creó un objeto Typeface con la API anterior y la nueva.
renderiza:
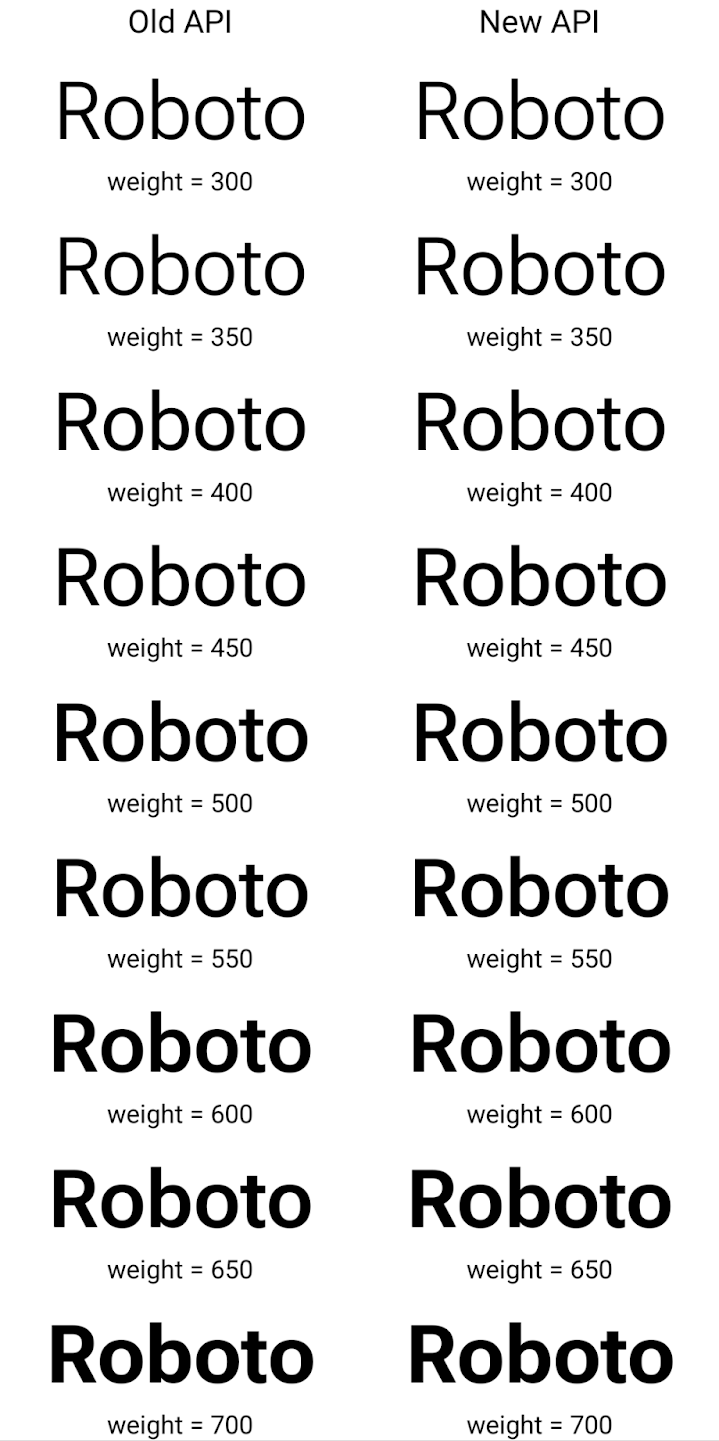
En este ejemplo, el Typeface creado con la API anterior no tiene la capacidad de crear grosores de fuente precisos para las instancias de Font de 350, 450, 550 y 650, por lo que el renderizador recurre al grosor más cercano. Por lo tanto, en este caso, se renderiza 300 en lugar de 350, 400 en lugar de 450, etcétera. Por el contrario, el Typeface creado con las APIs nuevas crea de forma dinámica
una instancia de Font para una ponderación determinada, por lo que se procesan las ponderaciones precisas de 350
450, 550 y 650.
Controles detallados de saltos de línea
A partir de Android 15, un TextView y el separador de líneas subyacente pueden preservar la parte determinada de texto en la misma línea para mejorar la legibilidad. Puedes aprovechar esta personalización de salto de línea con la etiqueta <nobreak> en los recursos de cadenas o con createNoBreakSpan. De manera similar, puedes evitar que las palabras se dividan en sílabas con la etiqueta <nohyphen> o createNoHyphenationSpan.
Por ejemplo, el siguiente recurso de cadenas no incluye un salto de línea y se renderiza con el texto "Pixel 8 Pro" que se interrumpe en un lugar no deseado:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind Pixel 8 Pro.</string>
</resources>
En cambio, este recurso de cadena incluye la etiqueta <nobreak>, que une la frase "Pixel 8 Pro" y evita los saltos de línea:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind <nobreak>Pixel 8 Pro.</nobreak></string>
</resources>
La diferencia en la forma en que se renderizan estas strings se muestra en las siguientes imágenes:

<nobreak>.
<nobreak>.Archivado de apps
Android y Google Play anunciaron la compatibilidad con el archivado de apps el año pasado, lo que permite a los usuarios liberar espacio quitando parcialmente del dispositivo las apps que se usan con poca frecuencia y que se publicaron con Android App Bundle en Google Play. Android 15 incluye compatibilidad a nivel del SO para el archivado y desarchivado de apps, lo que facilita su implementación en todas las tiendas de aplicaciones.
Las apps con el permiso REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES pueden llamar al método PackageInstaller requestArchive para solicitar el archivado de un paquete de app instalado, lo que quita el APK y los archivos almacenados en caché, pero conserva los datos del usuario. Las apps archivadas se muestran como apps que se pueden mostrar a través de la
APIs de LauncherApps; los usuarios verán un tratamiento de la IU para destacar que
apps se archivan. Si un usuario presiona una app archivada, el instalador responsable recibirá una solicitud para desarchivarla, y la transmisión ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED puede supervisar el proceso de restauración.
Habilita el modo de 16 KB en un dispositivo con las opciones para desarrolladores
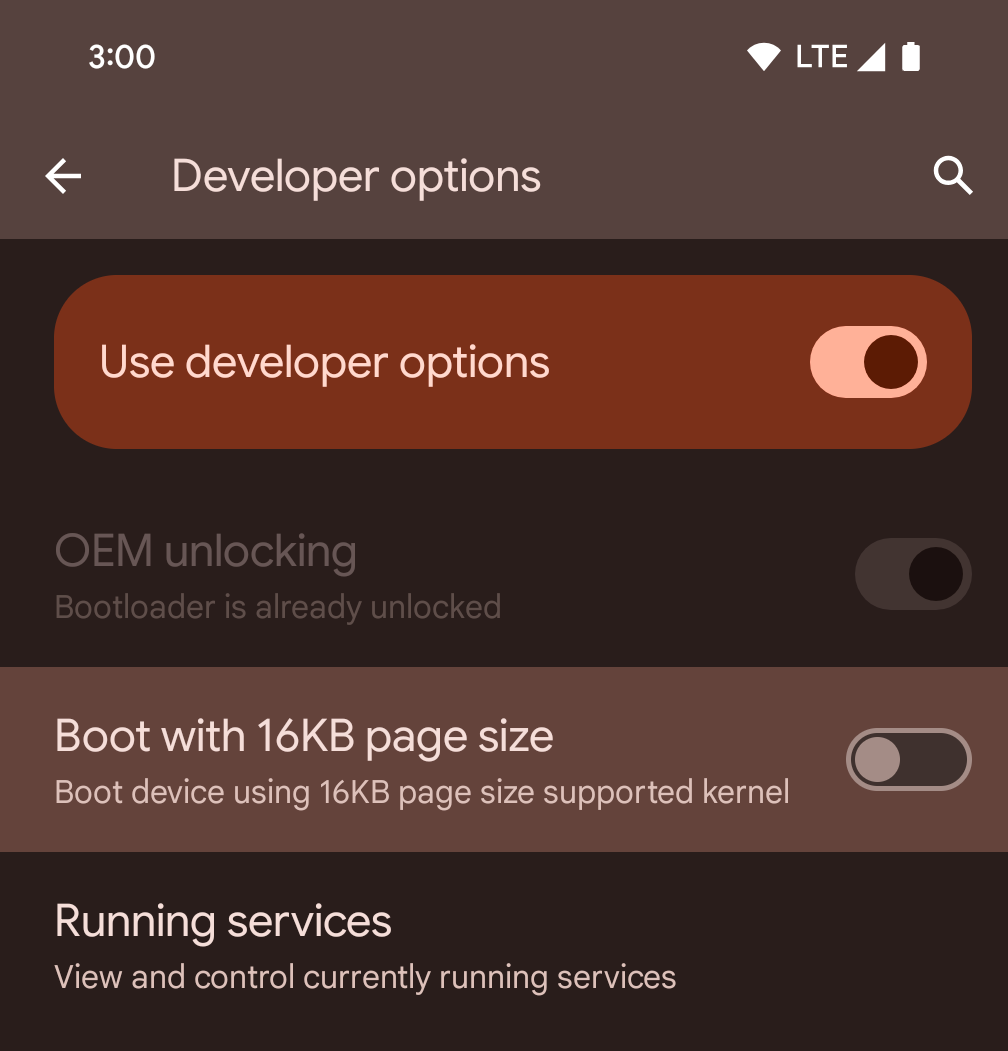
Activa la opción para desarrolladores Iniciar con tamaño de página de 16 KB para iniciar un dispositivo en el modo de 16 KB.
A partir de Android 15 QPR1, puedes usar la opción para desarrolladores disponible en ciertos dispositivos para iniciar el dispositivo en modo de 16 KB y realizar pruebas en el dispositivo. Antes de usar la opción para desarrolladores, ve a Configuración > Sistema > Actualizaciones de software y aplica las actualizaciones disponibles.
Esta opción para desarrolladores está disponible en los siguientes dispositivos:
Pixel 8 y 8 Pro (con Android 15 QPR1 o versiones posteriores)
Pixel 8a (con Android 15 QPR1 o versiones posteriores)
Pixel 9, 9 Pro y 9 Pro XL (con Android 15 QPR2 Beta 2 o versiones posteriores)
Gráficos
Android 15 incluye las mejoras gráficas más recientes, como ANGLE y adiciones al sistema de gráficos de Canvas.
Modernización del acceso a la GPU de Android

El hardware de Android evolucionó bastante desde los primeros días, en los que el SO principal se ejecutaba en una sola CPU y se accedía a las GPUs con APIs basadas en canalizaciones de funciones fijas. La API de gráficos de Vulkan® está disponible en el NDK desde Android 7.0 (nivel de API 24) con una abstracción de nivel inferior que refleja mejor el hardware de GPU moderno, se escala mejor para admitir varios núcleos de CPU y ofrece una sobrecarga reducida del controlador de CPU, lo que mejora el rendimiento de la app. Todos los motores de juego modernos son compatibles con Vulkan.
Vulkan es la interfaz preferida de Android para la GPU. Por lo tanto, Android 15 incluye ANGLE como una capa opcional para ejecutar OpenGL® ES sobre Vulkan. El cambio a ANGLE estandarizará la implementación de OpenGL de Android para mejorar la compatibilidad y, en algunos casos, el rendimiento. Para probar la estabilidad y el rendimiento de tu app de OpenGL ES con ANGLE, habilita la opción para desarrolladores en Configuración -> Sistema -> Opciones para desarrolladores -> Experimental: Habilita ANGLE en Android 15.
Plan de ruta de ANGLE para Android en Vulkan
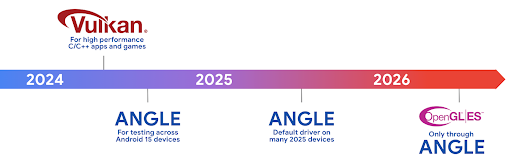
Como parte de la optimización de nuestra pila de GPU, en el futuro, enviaremos ANGLE como el controlador del sistema GL en más dispositivos nuevos, con la expectativa de que OpenGL/ES solo esté disponible a través de ANGLE. Dicho esto, planeamos seguir admitiendo OpenGL ES en todos los dispositivos.
Próximos pasos recomendados
Usa las opciones para desarrolladores para seleccionar el controlador ANGLE para OpenGL ES y probar tu app. Para proyectos nuevos, te recomendamos que uses Vulkan para C/C++.
Mejoras en Canvas
Android 15 continúa con la modernización del sistema de gráficos Canvas de Android con las siguientes capacidades adicionales:
Matrix44proporciona una matriz 4x4 para transformar las coordenadas que se deben usar cuando deseas manipular el lienzo en 3D.clipShaderinterseca el clip actual con el sombreador especificado, mientras queclipOutShaderestablece el clip en la diferencia entre el clip actual y el sombreador, cada uno de los cuales trata el sombreador como una máscara alfa. Esto admite el dibujo de formas complejas de manera eficiente.
Rendimiento y batería
Android sigue enfocándose en ayudarte a mejorar el rendimiento y la calidad de tus apps. Android 15 introduce APIs que ayudan a que las tareas de tu app se ejecuten de manera más eficiente, optimizan el rendimiento de la app y recopilan estadísticas sobre tus apps.
Para conocer las prácticas recomendadas que permiten ahorrar batería, depurar el uso de la red y la energía, y obtener detalles sobre cómo mejoramos la eficiencia de la batería del trabajo en segundo plano en Android 15 y versiones recientes de Android, consulta la charla Improving battery efficiency of background work on Android (Cómo mejorar la eficiencia de la batería del trabajo en segundo plano en Android) de Google I/O.
API de ApplicationStartInfo
En versiones anteriores de Android, el inicio de la app era un misterio. Era difícil determinar dentro de tu app si se inició desde un estado en frío, semicaliente o en caliente. También era difícil saber cuánto tiempo pasó tu app durante las diferentes fases del lanzamiento: bifurcar el proceso, llamar a onCreate, dibujar el primer fotograma y mucho más. Cuando se creó una instancia de tu clase Application, no tenías ninguna manera de saber si la app se inició desde una transmisión, un proveedor de contenido, un trabajo, una copia de seguridad, un inicio completo, una alarma o un Activity.
La API de ApplicationStartInfo en Android 15 proporciona todo esto y mucho más. Incluso puedes agregar tus propias marcas de tiempo al flujo para ayudar a recopilar datos de tiempo en un solo lugar. Además de recopilar métricas, puedes usar ApplicationStartInfo para ayudar a optimizar directamente el inicio de la app. Por ejemplo, puedes eliminar la creación de instancias costosa de bibliotecas relacionadas con la IU dentro de tu clase Application cuando se inicia la app debido a una transmisión.
Información detallada sobre el tamaño de la app
Desde Android 8.0 (nivel de API 26), Android incluye la API de StorageStats.getAppBytes que resume el tamaño instalado de una app como un solo número de bytes, que es la suma del tamaño del APK, el tamaño de los archivos extraídos del APK y los archivos que se generaron en el dispositivo, como el código compilado por adelantado (AOT). Este número no es muy útil en términos de cómo tu app usa el almacenamiento.
Android 15 agrega la API de StorageStats.getAppBytesByDataType([type]), que te permite obtener estadísticas sobre cómo tu app usa todo ese espacio, incluidas las divisiones de archivos APK, el código relacionado con AOT y la aceleración, los metadatos de DEX, las bibliotecas y los perfiles guiados.
Creación de perfiles administrada por la app
Android 15 incluye la clase ProfilingManager, que te permite recopilar información de perfil desde tu app, como volcados de montón, perfiles de montón, muestreo de pila y mucho más. Proporciona una devolución de llamada a tu app con una etiqueta proporcionada para identificar el archivo de salida, que se entrega al directorio de archivos de tu app. La API aplica un límite de frecuencia para minimizar el impacto en el rendimiento.
Para simplificar la construcción de solicitudes de generación de perfiles en tu app, te recomendamos que uses la API de AndroidX Profiling correspondiente, disponible en Core 1.15.0-rc01 o versiones posteriores.
Mejoras en la base de datos SQLite
Android 15 presenta las APIs de SQLite que exponen funciones avanzadas del un motor SQLite subyacente que se dirija a problemas de rendimiento específicos que pueden en las apps. Estas APIs se incluyen con la actualización de SQLite a la versión 3.44.3
Los desarrolladores deben consultar las prácticas recomendadas para el rendimiento de SQLite para aprovechar al máximo su base de datos, en especial cuando trabajan con bases de datos grandes o cuando ejecutan consultas sensibles a la latencia.
- Transacciones diferidas de solo lectura: Cuando emitas transacciones de solo lectura (no incluyas instrucciones de escritura), usa
beginTransactionReadOnly()ybeginTransactionWithListenerReadOnly(SQLiteTransactionListener)para emitir transaccionesDEFERREDde solo lectura. Estas transacciones se pueden ejecutar de forma simultánea entre sí y, si la base de datos está en modo WAL, se pueden ejecutar de forma simultánea con transaccionesIMMEDIATEoEXCLUSIVE. - Recuento y IDs de filas: Se agregaron APIs para recuperar el recuento de filas modificadas o el ID de la última fila insertada sin emitir una consulta adicional.
getLastChangedRowCount()muestra la cantidad de filas que se insertaron, actualizaron o borraron mediante la instrucción de SQL más reciente en la transacción actual, mientras quegetTotalChangedRowCount()devuelve el recuento de la conexión actual.getLastInsertRowId()muestra elrowidde la última fila que se insertará en la conexión actual. - Sentencias sin procesar: Emite una sentencia SQlite sin procesar, omitiendo los wrappers de conveniencia y cualquier sobrecarga de procesamiento adicional que puedan generar.
Actualizaciones del framework de rendimiento dinámico de Android
Android 15 continúa nuestra inversión en el framework de rendimiento dinámico de Android (ADPF), un conjunto de APIs que permiten que los juegos y las apps de alto rendimiento interactúen de forma más directa con los sistemas térmicos y de alimentación de los dispositivos Android. En dispositivos compatibles, Android 15 agrega las siguientes funciones de ADPF:
- Un modo de eficiencia energética para las sesiones de sugerencias que indique que sus subprocesos asociados deben preferir el ahorro de energía en lugar del rendimiento, lo que es ideal para cargas de trabajo en segundo plano de larga duración.
- Las duraciones de trabajo de la GPU y la CPU se pueden informar en sesiones de sugerencias, lo que permite que el sistema ajuste las frecuencias de la CPU y la GPU en conjunto para satisfacer mejor las demandas de la carga de trabajo.
- Umbrales de margen térmico para interpretar posibles estados de limitación térmica en función de la predicción del margen.
Para obtener más información sobre cómo usar ADPF en tus apps y juegos, consulta la documentación.
Privacidad
Android 15 incluye una variedad de funciones que ayudan a los desarrolladores de apps a proteger la privacidad del usuario.
Detección de grabación de pantalla
En Android 15, se agrega compatibilidad con apps para detectar estas fallas se están grabando. Se invoca una devolución de llamada cada vez que la app pasa de ser visible a invisible dentro de una grabación de pantalla. Una app se considera visible si se registran actividades que pertenecen al UID del proceso de registro. De esta manera, si tu app realiza una operación sensible, puede informar al usuario que se está grabando.
val mCallback = Consumer<Int> { state ->
if (state == SCREEN_RECORDING_STATE_VISIBLE) {
// We're being recorded
} else {
// We're not being recorded
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val initialState =
windowManager.addScreenRecordingCallback(mainExecutor, mCallback)
mCallback.accept(initialState)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
windowManager.removeScreenRecordingCallback(mCallback)
}
Capacidades expandidas de IntentFilter
Android 15 incluye compatibilidad con una resolución Intent más precisa a través de UriRelativeFilterGroup, que contiene un conjunto de objetos UriRelativeFilter que forman un conjunto de reglas de coincidencia Intent que deben cumplirse, incluidos los parámetros de consulta de URL, los fragmentos de URL y las reglas de bloqueo o exclusión.
Estas reglas se pueden definir en el archivo en formato XML AndroidManifest con la etiqueta <uri-relative-filter-group>, que puede incluir, de manera opcional, una etiqueta android:allow. Estas etiquetas pueden contener etiquetas <data> que usan atributos de etiqueta de datos existentes, así como los atributos android:query y android:fragment.
Este es un ejemplo de la sintaxis de AndroidManifest:
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="astore.com" />
<uri-relative-filter-group>
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="region=na" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="mobileoptout=true" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:fragmentPrefix="faq" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
</intent-filter>
Espacio privado
El espacio privado permite a los usuarios crear un espacio independiente en su dispositivo en el que pueden mantener las apps sensibles lejos de miradas indiscretas, con una capa adicional de autenticación. El espacio privado usa un perfil de usuario independiente. El usuario puede optar por usar el bloqueo del dispositivo o un factor de bloqueo independiente para el espacio privado.
Las apps del espacio privado aparecen en un contenedor independiente en el selector y se ocultan de la vista de apps recientes, las notificaciones, la configuración y otras apps cuando el espacio privado está bloqueado. El contenido generado y descargado por el usuario (como contenido multimedia o archivos) y las cuentas se separan entre el espacio privado y el espacio principal. La hoja compartida del sistema y el selector de fotos se pueden usar para permitir que las apps accedan al contenido de todos los espacios cuando el espacio privado está desbloqueado.
Los usuarios no pueden mover las apps existentes ni sus datos al espacio privado. En su lugar, los usuarios seleccionan una opción de instalación en el espacio privado para instalar una app con la tienda de aplicaciones que prefieran. Las apps del espacio privado se instalan como copias separadas de las apps del espacio principal (copias nuevas de la misma app).
Cuando un usuario bloquea el espacio privado, se detiene el perfil. Mientras el perfil está detenido, las apps del espacio privado dejan de estar activas y no pueden realizar actividades en primer o segundo plano, como mostrar notificaciones.
Te recomendamos que pruebes tu app con espacio privado para asegurarte de que funcione según lo previsto, en especial si pertenece a una de las siguientes categorías:
- Apps con lógica para perfiles de trabajo que suponen que las copias instaladas de su app que no están en el perfil principal están en el perfil de trabajo.
- Apps médicas
- Apps de selector
- Apps de tiendas de aplicaciones
Consultar la selección del usuario más reciente para el acceso a las fotos seleccionadas
Ahora las apps pueden destacar solo las fotos y los videos seleccionados más recientemente cuando se otorga acceso parcial a los permisos de contenido multimedia. Esta función puede mejorar la experiencia del usuario de las apps que solicitan acceso a fotos y videos con frecuencia. Para usar esta función en tu app, habilita el argumento QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY cuando consultes MediaStore a través de ContentResolver.
Kotlin
val externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external") val mediaColumns = arrayOf( FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE, ) val queryArgs = bundleOf( // Return only items from the last selection (selected photos access) QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY to true, // Sort returned items chronologically based on when they were added to the device's storage QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER to "${FileColumns.DATE_ADDED} DESC", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION to "${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ? OR ${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ?", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS to arrayOf( FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE.toString(), FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.toString() ) )
Java
Uri externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external"); String[] mediaColumns = { FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE }; Bundle queryArgs = new Bundle(); queryArgs.putBoolean(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, true); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER, FileColumns.DATE_ADDED + " DESC"); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION, FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ? OR " + FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ?"); queryArgs.putStringArray(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS, new String[] { String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE), String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) });
Privacy Sandbox en Android
Android 15 incluye las extensiones más recientes de los servicios de anuncios de Android, que incorporan la versión más reciente de Privacy Sandbox en Android. Esta incorporación forma parte de nuestro trabajo para desarrollar tecnologías que mejoren la privacidad del usuario y permitan brindar experiencias de publicidad personalizadas y efectivas en apps para dispositivos móviles. En nuestra página de Privacy Sandbox, encontrarás más información sobre los programas de versión beta y de vista previa para desarrolladores de Privacy Sandbox en Android para ayudarte a comenzar.
Health Connect
Android 15 integra las extensiones más recientes de Health Connect de Android, una plataforma segura y centralizada para administrar y compartir datos de salud y fitness recopilados por la app. Esta actualización agrega compatibilidad con tipos de datos adicionales en estado físico, nutrición, temperatura cutánea, planes de entrenamiento y mucho más.
El seguimiento de la temperatura de la piel permite a los usuarios almacenar y compartir datos de temperatura más precisos desde un dispositivo wearable o algún otro dispositivo de seguimiento.
Los planes de entrenamiento son planes de entrenamiento estructurados para ayudar a un usuario a alcanzar sus objetivos de fitness. La compatibilidad con los planes de entrenamiento incluye una variedad de objetivos de finalización y rendimiento:
- Objetivos de finalización relacionados con las calorías quemadas, la distancia, la duración, la repetición y los pasos.
- Los objetivos de rendimiento muchas repeticiones como sea posible (AMRAP), cadencia, frecuencia cardíaca, alimentación, tasa percibida del esfuerzo y Velocidad.
Obtén más información sobre las actualizaciones más recientes de Health Connect en Android en la charla Cómo crear experiencias adaptables con Android Health de Google I/O.
Compartir pantalla de una app
Android 15 admite el uso compartido de la pantalla de la app para que los usuarios puedan compartir o grabar solo una ventana de la app en lugar de toda la pantalla del dispositivo. Esta función, que se habilitó por primera vez en Android 14 QPR2, incluye callbacks de MediaProjection que permiten que tu app personalice la experiencia de uso compartido de pantalla de la app. Ten en cuenta que, para las apps orientadas a Android 14 (nivel de API 34) o versiones posteriores, se requiere el consentimiento del usuario para cada sesión de captura de MediaProjection.
Experiencia del usuario y la IU del sistema
Android 15 brinda a los desarrolladores de apps y a los usuarios más control y flexibilidad para configurar sus dispositivos según sus necesidades.
Para obtener más información sobre cómo usar las mejoras más recientes de Android 15 para mejorar la experiencia del usuario de tu app, consulta la charla Mejora la experiencia del usuario de tu app para Android de Google I/O.
Vistas previas de widgets más completas con la API de Generated Previews
Antes de Android 15, la única forma de proporcionar vistas previas del selector de widgets era especificar un recurso de imagen o diseño estático. Estas vistas previas suelen diferir significativamente del aspecto del widget real cuando se coloca en la pantalla principal. Además, no se pueden crear recursos estáticos con Jetpack Glance, por lo que un vistazo desarrollador tuvo que hacer una captura de pantalla de su widget o crear un diseño XML para tener una vista previa del widget.
Android 15 agrega compatibilidad con vistas previas generadas. Esto significa que el widget de la app
los proveedores pueden generar RemoteViews para usar como vista previa del selector, en lugar
de un recurso estático.
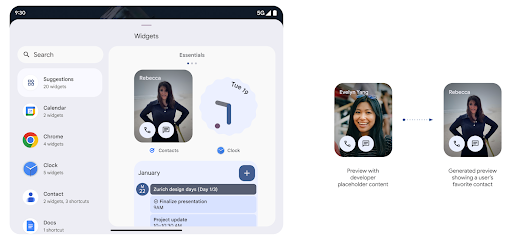
API de Push
Las apps pueden proporcionar vistas previas generadas a través de una API de push. Las apps pueden proporcionar vistas previas en cualquier momento de su ciclo de vida y no reciben una solicitud explícita del host para proporcionarlas. Las vistas previas se conservan en AppWidgetService,
y los hosts pueden solicitarlas a pedido. En el siguiente ejemplo, se carga un recurso de diseño de widget XML y se establece como la vista previa:
AppWidgetManager.getInstance(appContext).setWidgetPreview(
ComponentName(
appContext,
SociaLiteAppWidgetReceiver::class.java
),
AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN,
RemoteViews("com.example", R.layout.widget_preview)
)
El flujo esperado es el siguiente:
- En cualquier momento, el proveedor de widgets llama a
setWidgetPreview. El valor proporcionado las vistas previas se conservan enAppWidgetServicecon otra información del proveedor setWidgetPreviewnotifica a los hosts una vista previa actualizada a través de la devolución de llamadaAppWidgetHost.onProvidersChanged. En respuesta, el host del widget vuelve a cargar toda la información del proveedor.- Cuando se muestra una vista previa del widget, el host verifica
AppWidgetProviderInfo.generatedPreviewCategoriesy si el elemento elegido categoría está disponible, llama aAppWidgetManager.getWidgetPreviewpara mostrar la vista previa guardada para este proveedor.
Cuándo llamar a setWidgetPreview
Debido a que no hay devolución de llamada para proporcionar vistas previas, las apps pueden optar por enviar vistas previas en cualquier momento mientras se están ejecutando. La frecuencia con la que se actualiza la vista previa depende del caso de uso del widget.
En la siguiente lista, se describen las dos categorías principales de casos de uso de vista previa:
- Los proveedores que muestran datos reales en las vistas previas de sus widgets, como los o información reciente. Estos proveedores pueden configurar la vista previa una vez que el usuario accede o realiza la configuración inicial en su app. Después de esto, pueden configurar una tarea periódica para actualizar las vistas previas en la cadencia que elijan. Algunos ejemplos de este tipo de widget son los de fotos, calendario, clima o noticias.
- Proveedores que muestran información estática en vistas previas o widgets de acción rápida que no muestran ningún dato. Estos proveedores pueden establecer vistas previas una vez, cuando se inicia la app por primera vez. Algunos ejemplos de este tipo de widget son el widget de acciones rápidas de Drive o el widget de accesos directos de Chrome.
Algunos proveedores pueden mostrar vistas previas estáticas en el selector del modo Hub información del selector de la pantalla principal. Estos proveedores deben seguir las instrucciones para ambos casos de uso para configurar las vistas previas.
Pantalla en pantalla
Android 15 introduce cambios en la función pantalla en pantalla (PIP) que garantiza una transición más fluida cuando se ingresa al modo de PIP. Esto será beneficioso para apps con elementos de la IU superpuestos sobre su IU principal, que va en PIP.
Los desarrolladores usan la devolución de llamada onPictureInPictureModeChanged para definir la lógica
que activa o desactiva la visibilidad de los elementos superpuestos de la IU. Esta devolución de llamada se activa cuando se completa la animación de entrada o salida de PiP. A partir de Android 15, la clase PictureInPictureUiState incluye otro estado.
Con este estado de la IU, las apps orientadas a Android 15 (nivel de API 35) observarán la
Se invoca la devolución de llamada Activity#onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged con
isTransitioningToPip() en cuanto comienza la animación de PIP. Existen
muchos elementos de la IU que no son relevantes para la app cuando está en modo de PIP, por
vistas o diseños de ejemplo que incluyen información como sugerencias, próximos
videos, calificaciones y títulos. Cuando la app entre en modo de PIP, usa la
Es la devolución de llamada onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged para ocultar estos elementos de la IU. Cuando la app cambia al modo de pantalla completa desde la ventana de PiP, usa la devolución de llamada onPictureInPictureModeChanged para mostrar estos elementos, como se muestra en los siguientes ejemplos:
override fun onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged(pipState: PictureInPictureUiState) {
if (pipState.isTransitioningToPip()) {
// Hide UI elements
}
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean) {
if (isInPictureInPictureMode) {
// Unhide UI elements
}
}
Este botón de activación rápida de visibilidad de elementos irrelevantes de la IU (para una ventana de PIP) ayuda garantizar una animación de entrada de PIP más fluida y sin parpadeos.
Reglas de No interrumpir mejoradas
AutomaticZenRule permite que las apps personalicen las reglas de la Administración de atención (No interrumpir) y decidan cuándo activarlas o desactivarlas. Android 15 mejora considerablemente estas reglas con el objetivo de mejorar la
la experiencia del usuario. Se incluyen las siguientes mejoras:
- Se agregan tipos a
AutomaticZenRule, lo que permite que el sistema aplique tipos tratamiento a algunas reglas. - Se agregó un ícono a
AutomaticZenRulepara que los modos sean más atractivos reconocibles. - Agrega una cadena
triggerDescriptionaAutomaticZenRuleque describa las condiciones en las que la regla debe activarse para el usuario. - Agregado
ZenDeviceEffectsaAutomaticZenRule, lo que permite que las reglas activen, por ejemplo, la escala de grises la pantalla, el modo nocturno o la atenuación del fondo de pantalla.
Cómo establecer VibrationEffect para los canales de notificación
Android 15 admite la configuración de vibraciones enriquecidas para las notificaciones entrantes
canal con NotificationChannel.setVibrationEffect, por lo que
los usuarios pueden distinguir entre distintos tipos de notificaciones
tener que mirar su dispositivo.
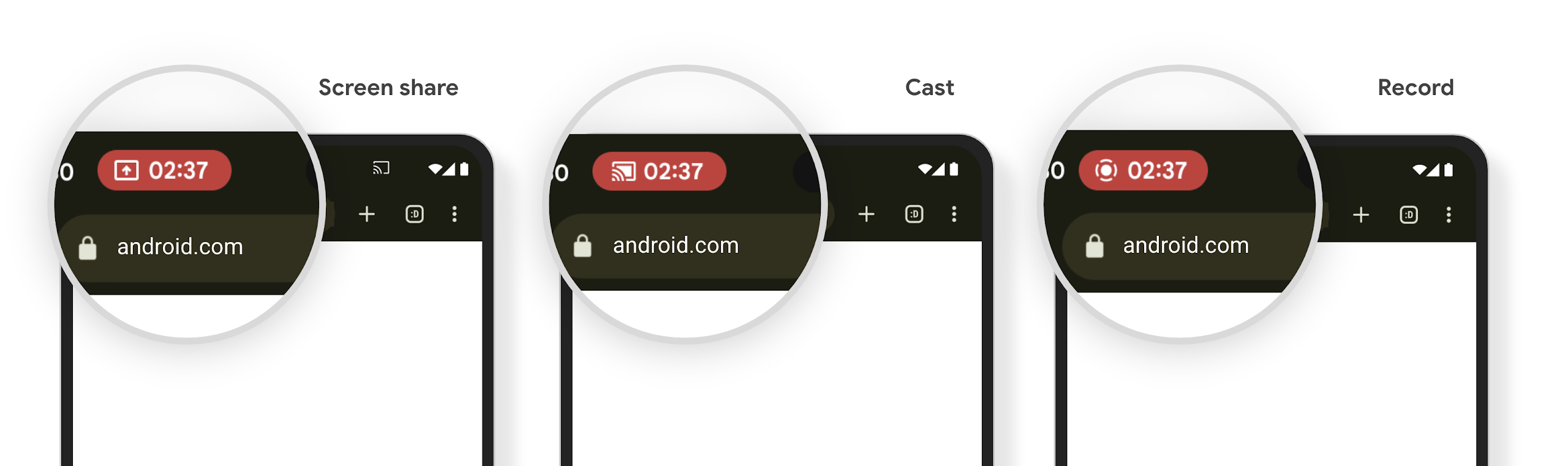
Chip de la barra de estado de proyección de contenido multimedia y detención automática
La proyección de contenido multimedia puede exponer información privada del usuario. Un nuevo chip de barra de estado prominente informa a los usuarios sobre cualquier proyección de pantalla en curso. Los usuarios pueden presionar el chip para detener la transmisión, el uso compartido o la grabación de la pantalla. Además, para brindar una experiencia del usuario más intuitiva, cualquier proyección de pantalla en curso ahora se detiene automáticamente cuando se bloquea la pantalla del dispositivo.
Pantallas grandes y factores de forma
Android 15 brinda a tus apps la compatibilidad necesaria para aprovechar al máximo los factores de forma de Android, incluidas las pantallas grandes, los dispositivos plegables y los que se pueden voltear.
Mejoras en la realización de tareas múltiples en pantallas grandes
Android 15 ofrece a los usuarios mejores formas de realizar varias tareas a la vez en dispositivos con pantalla grande. Para ejemplo, los usuarios pueden guardar sus combinaciones favoritas de apps con pantalla dividida para accede y fija la barra de tareas en la pantalla para cambiar de app rápidamente. Esto significa que asegurarse de que tu app sea adaptable es más importante que nunca.
Google I/O tiene sesiones sobre Cómo compilar apps para Android adaptativas y Cómo compilar una IU con la biblioteca de Material 3 adaptativa que pueden ayudarte. Además, nuestra documentación tiene más información para ayudarte a diseñar para pantallas grandes.
Compatibilidad con la pantalla de la cubierta
Tu app puede declarar una propiedad que Android 15 usa para permitir que tu Application o Activity se presente en las pantallas de portada pequeñas de los dispositivos plegables compatibles. Estas pantallas son demasiado pequeñas para considerarse objetivos compatibles en los que se ejecuten apps para Android, pero tu app puede admitirlas, lo que la hará disponible en más lugares.
Conectividad
Android 15 actualiza la plataforma para que tu app tenga acceso a los avances más recientes en tecnologías inalámbricas y de comunicación.
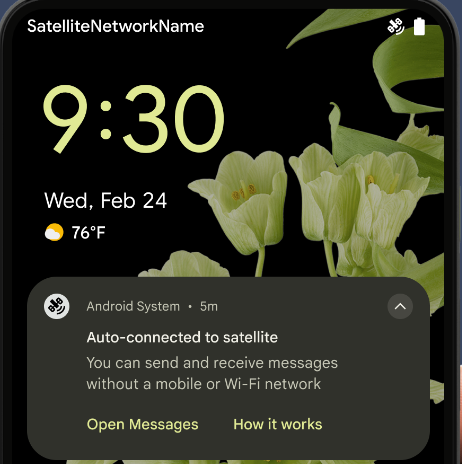
Compatibilidad con satélites
Android 15 continúa ampliando la compatibilidad de la plataforma con la conectividad satelital y, además, incluye algunos elementos de la IU para garantizar una experiencia del usuario coherente en todo el panorama de conectividad satelital.
Las apps pueden usar ServiceState.isUsingNonTerrestrialNetwork() para detectar cuándo un dispositivo está conectado a un satélite, lo que les permite saber por qué es posible que los servicios de red completos no estén disponibles. Además, Android 15 admite apps de SMS y MMS, así como apps de RCS precargadas para usar conectividad satelital para enviar y recibir mensajes.
Experiencias de NFC más fluidas
Android 15 está trabajando para que la experiencia de pago con un toque sea más fluida y confiable, a la vez que sigue admitiendo el sólido ecosistema de apps de NFC de Android. En los dispositivos compatibles, las apps pueden solicitar que NfcAdapter ingrese al modo de observación, en el que el dispositivo escucha, pero no responde a los lectores NFC, y envía los objetos PollingFrame del servicio de NFC de la app para que se procesen. Los objetos PollingFrame se pueden usar para autenticar antes de la primera comunicación con el lector de NFC, lo que permite una transacción con un solo toque en muchos casos.
Además, las apps pueden registrar un filtro en dispositivos compatibles para que se les notifique la actividad del bucle de sondeo, lo que permite un funcionamiento fluido con varias aplicaciones compatibles con NFC.
Rol de la billetera
Android 15 presenta un rol de billetera que permite una integración más estrecha con la app de billetera preferida del usuario. Este rol reemplaza la configuración predeterminada de pago sin contacto de NFC. Los usuarios pueden administrar el titular del rol de la Billetera navegando a Configuración > Apps > Apps predeterminadas.
El rol de billetera se usa cuando se enrutan los toques NFC para los AID registrados en la categoría de pago. Los toques siempre se dirigen al titular del rol de la Billetera, a menos que otra app que esté registrada para el mismo AID se esté ejecutando en primer plano.
Este rol también se usa para determinar dónde debe ir la tarjeta de acceso rápido a la Billetera cuando se activa. Cuando el rol se establece en "Ninguno", la tarjeta de acceso rápido no está disponible y las presiones de NFC de la categoría de pago solo se entregan a la app en primer plano.
Seguridad
Android 15 te ayuda a mejorar la seguridad de tu app, proteger sus datos y brindarles a los usuarios más transparencia y control sobre sus datos. Para obtener más información sobre lo que estamos haciendo para mejorar las medidas de protección del usuario y proteger tu app contra nuevas amenazas, mira la charla Safeguarding user security on Android de Google I/O.
Cómo integrar Credential Manager con el autocompletado
A partir de Android 15, los desarrolladores pueden vincular vistas específicas, como campos de nombre de usuario o contraseña, con solicitudes de Credential Manager, lo que facilita la prestación de una experiencia del usuario personalizada durante el proceso de acceso. Cuando el usuario se enfoca en una de estas vistas, se envía una solicitud correspondiente al Administrador de credenciales. Las credenciales resultantes se agregan en todos los proveedores y se muestran en las IU de resguardo de autocompletado, como las sugerencias intercaladas o desplegables. La biblioteca androidx.credentials de Jetpack es el extremo preferido que deben usar los desarrolladores y pronto estará disponible para mejorar aún más esta función en Android 15 y versiones posteriores.
Integra el acceso y el registro con un solo toque con solicitudes biométricas
El Administrador de credenciales integra mensajes biométricos en la creación de credenciales. y procesos de acceso, lo que elimina la necesidad de que los proveedores gestionen instrucciones biométricas. Como resultado, los proveedores de credenciales solo deben enfocarse en los resultados de los flujos de creación y obtención, junto con el resultado del flujo biométrico. Este proceso simplificado crea una credencial más eficiente y optimizada de creación y recuperación.
Administración de claves para la encriptación de extremo a extremo
Presentamos E2eeContactKeysManager en Android 15, que facilita la encriptación de extremo a extremo (E2EE) en tus apps para Android, ya que proporciona una API a nivel del SO para el almacenamiento de claves públicas criptográficas.
E2eeContactKeysManager está diseñado para integrarse a la app de contactos de la plataforma y brindarles a los usuarios una forma centralizada de administrar y verificar las claves públicas de sus contactos.
Verificaciones de permisos en URIs de contenido
Android 15 presenta un conjunto de APIs que realizan verificaciones de permisos en los URIs de contenido:
Context.checkContentUriPermissionFull: Realiza una verificación de permisos completa en los URIs de contenido.- Atributo del manifiesto
ActivityrequireContentUriPermissionFromCaller: Aplica permisos especificados en los URIs de contenido proporcionados al iniciar la actividad. - Clase
ComponentCallerpara los llamadores deActivity: Representa la app que inició la actividad.
Accesibilidad
Android 15 agrega funciones que mejoran la accesibilidad para los usuarios.
Mejoras en el braille
En Android 15, habilitamos que TalkBack admita pantallas braille que usan el estándar HID a través de USB y Bluetooth seguro.
Este estándar, al igual que el que usan los mouses y los teclados, ayudará a que Android admita una gama más amplia de pantallas braille con el tiempo.
Internacionalización
Android 15 agrega funciones y capacidades que complementan la experiencia del usuario cuando un dispositivo se usa en diferentes idiomas.
Fuente variable CJK
A partir de Android 15, el archivo de fuente para los idiomas chino, japonés y coreano (CJK), NotoSansCJK, ahora es una fuente variable. Las fuentes variables abren posibilidades para la tipografía creativa en los idiomas CJK. Los diseñadores pueden explorar una variedad más amplia de estilos y crear diseños visualmente llamativos que antes eran difíciles o imposibles de lograr.

Justificación entre caracteres
A partir de Android 15, el texto puede justificarse utilizando el espaciado entre letras de la siguiente manera:
con JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER. La justificación entre palabras era
se introducen por primera vez en Android 8.0 (nivel de API 26) y los caracteres
proporciona capacidades similares para los idiomas que usan
un carácter de espacio en blanco para la segmentación, como chino, japonés y otros.

JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.Configuración automática de saltos de línea
Android comenzó a admitir saltos de línea basados en frases para japonés y coreano en
Android 13 (nivel de API 33) Sin embargo, aunque los saltos de línea basados en frases mejoran la
la legibilidad de las líneas de texto cortas, no funcionan bien para las líneas de texto largas.
En Android 15, las apps pueden aplicar saltos de línea basados en frases solo para líneas breves de texto con la opción LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO. Esta opción selecciona la mejor opción de estilo de palabra para el texto.
Para las líneas cortas de texto, se utilizan saltos de línea basados en frases, que funcionan de la misma manera.
como LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE, como se muestra en el
siguiente imagen:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
Aplica saltos de línea basados en frases para mejorar la legibilidad del texto.
Esto es lo mismo que aplicar
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASEPara líneas de texto más largas, LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO usa el prefijo "no"
de salto de línea y que funcione igual que
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE, como se muestra en el
siguiente imagen:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
No aplica ningún estilo de palabra de salto de línea para mejorar la legibilidad del texto.
Esto es lo mismo que aplicar
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONEFuente adicional de Hentaigana japonés
En Android 15, se incluyó un archivo de fuente para el antiguo hiragana japonés (conocido como Hentaigana). se agrupa de forma predeterminada. Las formas únicas de los caracteres hentaigana pueden agregar un estilo distintivo al material gráfico o al diseño, a la vez que ayudan a preservar la transmisión y la comprensión precisas de los documentos japoneses antiguos.

VideoLAN cone Copyright (c) 1996-2010 VideoLAN. Cualquier persona puede usar o modificar este logotipo o una versión modificada para hacer referencia al proyecto VideoLAN o a cualquier producto desarrollado por el equipo de VideoLAN, pero no indica que el proyecto lo respalde.
Vulkan y el logotipo de Vulkan son marcas registradas de Khronos Group Inc.
OpenGL es una marca comercial registrada, y el logotipo de OpenGL ES es una marca comercial de Hewlett Packard Enterprise que se usa con permiso de Khronos.

