Android 15에는 개발자를 위한 훌륭한 기능과 API가 도입되었습니다. 다음 섹션에서는 관련 API를 시작하는 데 도움이 되도록 이러한 기능을 요약합니다.
추가된 API, 수정된 API, 삭제된 API에 관한 자세한 목록은 API 차이점 보고서를 참고하세요. 추가된 API에 관한 자세한 내용은 Android API 참조를 참고하세요. Android 15의 경우 API 수준 35에 추가된 API를 찾아보세요. 플랫폼 변경이 앱에 영향을 줄 수 있는 분야에 관해 알아보려면 Android 15를 타겟팅하는 앱 및 모든 앱의 Android 15 동작 변경사항을 확인해야 합니다.
카메라 및 미디어
Android 15에는 카메라 및 미디어 환경을 개선하고 크리에이터가 Android에서 자신의 비전을 실현할 수 있도록 지원하는 도구와 하드웨어에 액세스할 수 있는 다양한 기능이 포함되어 있습니다.
Android 미디어 및 카메라의 최신 기능과 개발자 솔루션에 관한 자세한 내용은 Google I/O의 최신 Android 미디어 및 카메라 환경 빌드 강연을 참고하세요.
어두운 조명 모드
Android 15에서는 Camera 2와 야간 모드 카메라 확장 프로그램에서 모두 사용할 수 있는 자동 노출 모드인 어두운 조명 모드를 도입합니다. 어두운 조명 모드는 저조도 환경에서 미리보기 스트림의 노출을 조정합니다. 야간 모드는 연속 촬영한 사진을 결합하여 하나의 향상된 이미지를 만들기 때문에 야간 모드 카메라 확장 프로그램이 정지 이미지를 만드는 방식과는 다릅니다. 야간 모드는 정지 이미지를 만드는 데 매우 효과적이지만 연속 프레임 스트림을 만들 수는 없습니다. 하지만 저조도 부스트는 가능합니다. 따라서 저조도 부스트를 사용하면 다음과 같은 카메라 기능을 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 사용자가 저조도 사진을 더 잘 찍을 수 있도록 향상된 이미지 미리보기를 제공합니다.
- 저조도에서 QR 코드 스캔
어두운 조명 모드를 사용 설정하면 조명이 어두울 때 자동으로 켜지고 밝을 때는 꺼집니다.
앱은 저조도 환경에서 미리보기 스트림을 녹화하여 밝기가 향상된 동영상을 저장할 수 있습니다.
자세한 내용은 저조도 부스트를 참고하세요.
인앱 카메라 컨트롤
Android 15에서는 지원되는 기기에서 카메라 하드웨어와 알고리즘을 더 세부적으로 제어할 수 있는 확장 프로그램을 추가합니다.
HDR 헤드룸 제어
Android 15는 기본 기기 기능과 패널의 비트 심도에 적합한 HDR 헤드룸을 선택합니다. 단일 HDR 썸네일을 표시하는 메시지 앱과 같이 SDR 콘텐츠가 많은 페이지의 경우 이 동작으로 인해 SDR 콘텐츠의 인식된 밝기에 부정적인 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다. Android 15에서는 setDesiredHdrHeadroom를 사용하여 HDR 헤드룸을 제어하여 SDR 콘텐츠와 HDR 콘텐츠 간의 균형을 맞출 수 있습니다.
라우드니스 제어

Android 15에서는 CTA-2075 음량 표준을 오디오 음량 불일치를 피하고 사용자가 콘텐츠 전환 시 볼륨 조정 이 시스템은 AAC 오디오 콘텐츠에서 사용할 수 있는 소리 크기 메타데이터와 함께 출력 장치(헤드폰 및 스피커)의 알려진 특성을 활용하여 오디오 소리 크기와 다이내믹 레인지 압축 수준을 지능적으로 조정합니다.
이 기능을 사용 설정하려면 AAC 콘텐츠에서 음량 메타데이터를 사용할 수 있는지 확인하고 앱에서 플랫폼 기능을 사용 설정해야 합니다. 이렇게 하려면 연결된 AudioTrack의 오디오 세션 ID를 사용하여 create 팩토리 메서드를 호출하여 LoudnessCodecController 객체를 인스턴스화합니다. 그러면 오디오 업데이트가 자동으로 적용됩니다. OnLoudnessCodecUpdateListener를 전달하여 볼륨 매개변수가 MediaCodec에 적용되기 전에 수정하거나 필터링할 수 있습니다.
// Media contains metadata of type MPEG_4 OR MPEG_D
val mediaCodec = …
val audioTrack = AudioTrack.Builder()
.setSessionId(sessionId)
.build()
...
// Create new loudness controller that applies the parameters to the MediaCodec
try {
val lcController = LoudnessCodecController.create(mSessionId)
// Starts applying audio updates for each added MediaCodec
}
AndroidX media3 ExoPlayer도
원활한 앱 통합을 위한 LoudnessCodecController API
가상 MIDI 2.0 기기
Android 13에서는 범용 MIDI 패킷 (UMP)을 사용하여 통신하는 USB를 사용하는 MIDI 2.0 기기에 연결하는 지원을 추가했습니다. Android 15에서는 UMP 지원을 가상 MIDI 앱으로 확장하여 작곡 앱이 USB MIDI 2.0 기기에서와 마찬가지로 가상 MIDI 2.0 기기로 신디사이저 앱을 제어할 수 있도록 합니다.
더 효율적인 AV1 소프트웨어 디코딩

VideoLAN의 인기 AV1 소프트웨어 디코더인 dav1d는 하드웨어에서 AV1 디코딩을 지원하지 않는 Android 기기에서 사용할 수 있습니다. dav1d는 기존 AV1 소프트웨어 디코더보다 최대 3배 더 우수한 성능을 제공하므로 일부 하위 및 중급 기기를 포함한 더 많은 사용자에게 HD AV1 재생을 제공할 수 있습니다.
앱은 dav1d를 "c2.android.av1-dav1d.decoder" 이름으로 호출하여 dav1d 사용을 선택해야 합니다. dav1d는 후속 업데이트에서 기본 AV1 소프트웨어 디코더가 됩니다. 이 지원은 표준화되어 Google Play 시스템 업데이트를 수신하는 Android 11 기기로 백포팅됩니다.
개발자 생산성 및 도구
생산성 향상을 위한 대부분의 작업은 Android 스튜디오, Jetpack Compose, Android Jetpack 라이브러리와 같은 도구를 중심으로 이루어지지만, Google에서는 플랫폼에서 비전을 더 쉽게 실현할 수 있는 방법을 항상 모색하고 있습니다.
OpenJDK 17 업데이트
Android 15에서는 최신 OpenJDK LTS 출시의 기능과 일치하도록 Android의 핵심 라이브러리를 새로고침하는 작업을 계속하고 있습니다.
다음과 같은 주요 기능과 개선사항이 포함됩니다.
- NIO 버퍼 관련 편의성 개선
- 스트림
- 추가
math및strictmath메서드 - 순서가 지정된
collection,map,set를 포함한util패키지 업데이트 Deflater의ByteBuffer지원X500PrivateCredential및 보안 키 업데이트와 같은 보안 업데이트
이러한 API는 Google Play 시스템 업데이트를 통해 Android 12 (API 수준 31) 및 이후 버전을 실행하는 10억 대 이상의 기기에서 업데이트되므로 최신 프로그래밍 기능을 타겟팅할 수 있습니다.
PDF 개선사항
Android 15에서는 PdfRenderer API가 크게 개선되었습니다. 앱에는 렌더링과 같은 고급 기능을
비밀번호로 보호된 파일, 주석, 양식 수정,
검색, 선택(사본 포함) 선형화된 PDF
로컬 PDF 보기의 속도를 높이고 리소스 사용을 줄이기 위해 최적화가 지원됩니다.
Jetpack PDF 라이브러리는 이러한 API를 사용하여 PDF 추가를 간소화합니다.
앱에 추가할 수 있습니다.
PdfRenderer를 Google을 사용하여 업데이트할 수 있는 모듈로 이동했습니다.
플랫폼 출시와는 별개인 Play 시스템 업데이트(Google에서는
Android 11 (API 수준 30)으로 다시 돌아가
API 노출 영역 Android 15 이전 버전
PdfRendererPreV
자동 언어 전환 개선사항
Android 14에서는 언어 간에 자동으로 전환되는 오디오의 기기 내 다중 언어 인식을 추가했지만, 이로 인해 단어가 누락될 수 있습니다. 특히 두 발화 간에 언어가 전환되는 시점에 휴식 시간이 거의 없을 때 그렇습니다. Android 15에서는 앱이 이 전환을 사용 사례에 맞게 조정하는 데 도움이 되는 추가 제어 기능을 제공합니다.
EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_INITIAL_ACTIVE_DURATION_TIME_MILLIS는 자동 전환을 오디오 세션 시작으로 제한하고 EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_MATCH_SWITCHES는 지정된 전환 횟수 후에 언어 전환을 비활성화합니다. 이러한 옵션은 세션 중에 자동 감지되어야 하는 단일 언어가 사용될 것으로 예상되는 경우에 특히 유용합니다.
개선된 OpenType 가변 글꼴 API
Android 15에서는 OpenType 가변 글꼴의 사용성을 개선합니다. buildVariableFamily API로 두께 축을 지정하지 않고도 가변 글꼴에서 FontFamily 인스턴스를 만들 수 있습니다. 텍스트 렌더기는
wght 축의 값을 변경하여 표시 텍스트와 일치시킵니다.
API를 사용하면 Typeface를 만드는 코드가 상당히 간소화됩니다.
Kotlin
val newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build()
자바
Typeface newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build();
이전에는 동일한 Typeface를 만들려면 훨씬 더 많은 코드가 필요했습니다.
Kotlin
val oldTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build()) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ).build() ).build()
자바
Typeface oldTypeface = new Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ) .build() ).build();
다음은 Typeface가 이전 API와 새 API를 모두 사용하여 생성된 방법의 예입니다.
렌더링:

이 예에서 이전 API로 만든 Typeface에는 350, 450, 550, 650 Font 인스턴스의 정확한 글꼴 두께를 만들 수 있는 기능이 없으므로 렌더러는 가장 가까운 두께로 대체합니다. 따라서 이 경우 350 대신 300이 렌더링되고 450 대신 400이 렌더링됩니다. 반면 새 API로 만든 Typeface는 지정된 무게에 대해 Font 인스턴스를 동적으로 만들므로 350, 450, 550, 650에도 정확한 무게가 렌더링됩니다.
세부적인 줄바꿈 제어
Android 15부터 TextView 및 기본 줄 바꿈은 가독성을 개선하기 위해 텍스트의 지정된 부분을 동일한 줄에 유지할 수 있습니다. 문자열 리소스 또는 createNoBreakSpan에서 <nobreak> 태그를 사용하여 이 줄바꿈 맞춤설정을 활용할 수 있습니다. 마찬가지로 <nohyphen> 태그 또는 createNoHyphenationSpan를 사용하여 단어를 구두점을 사용하지 않고 유지할 수 있습니다.
예를 들어 다음 문자열 리소스에는 줄바꿈이 포함되어 있지 않으며 'Pixel 8 Pro'라는 텍스트로 렌더링되며 원치 않는 위치에서 줄바꿈이 발생합니다.
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind Pixel 8 Pro.</string>
</resources>
반대로 이 문자열 리소스에는 'Pixel 8 Pro'라는 문구를 래핑하고 줄바꿈을 방지하는 <nobreak> 태그가 포함되어 있습니다.
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind <nobreak>Pixel 8 Pro.</nobreak></string>
</resources>
이러한 문자열이 렌더링되는 방식의 차이는 다음 이미지에 나와 있습니다.

<nobreak> 태그를 사용하여 'Pixel 8 Pro'라는 문구가 줄바꿈되지 않은 텍스트 줄의 레이아웃
<nobreak> 태그를 사용하여 래핑된 동일한 텍스트 줄의 레이아웃앱 보관처리
Android 및 Google Play는 작년에 앱 보관 지원을 발표하여 사용자가 Google Play에서 Android App Bundle을 사용하여 게시된 기기에서 자주 사용하지 않는 앱을 부분적으로 삭제하여 공간을 확보할 수 있도록 했습니다. Android 15에는 앱 보관처리를 위한 OS 수준 지원이 포함되어 있습니다. 모든 앱 스토어에서 이를 더 쉽게 구현할 수 있습니다.
REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES 권한이 있는 앱은 PackageInstaller requestArchive 메서드를 호출하여 설치된 앱 패키지 보관처리를 요청할 수 있습니다. 이 경우 APK와 캐시된 파일이 삭제되지만 사용자 데이터는 유지됩니다. 보관처리된 앱은 LauncherApps API를 통해 표시 가능한 앱으로 반환됩니다. 사용자에게는 이러한 앱이 보관처리되었음을 강조하는 UI 처리가 표시됩니다. 사용자가 보관처리된 앱을 탭하면 해당 설치 프로그램은
보관 취소 요청을 받게 되며, 복원 프로세스는
ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED 브로드캐스트에서 모니터링됩니다.
개발자 옵션을 사용하여 기기에서 16KB 모드 사용 설정
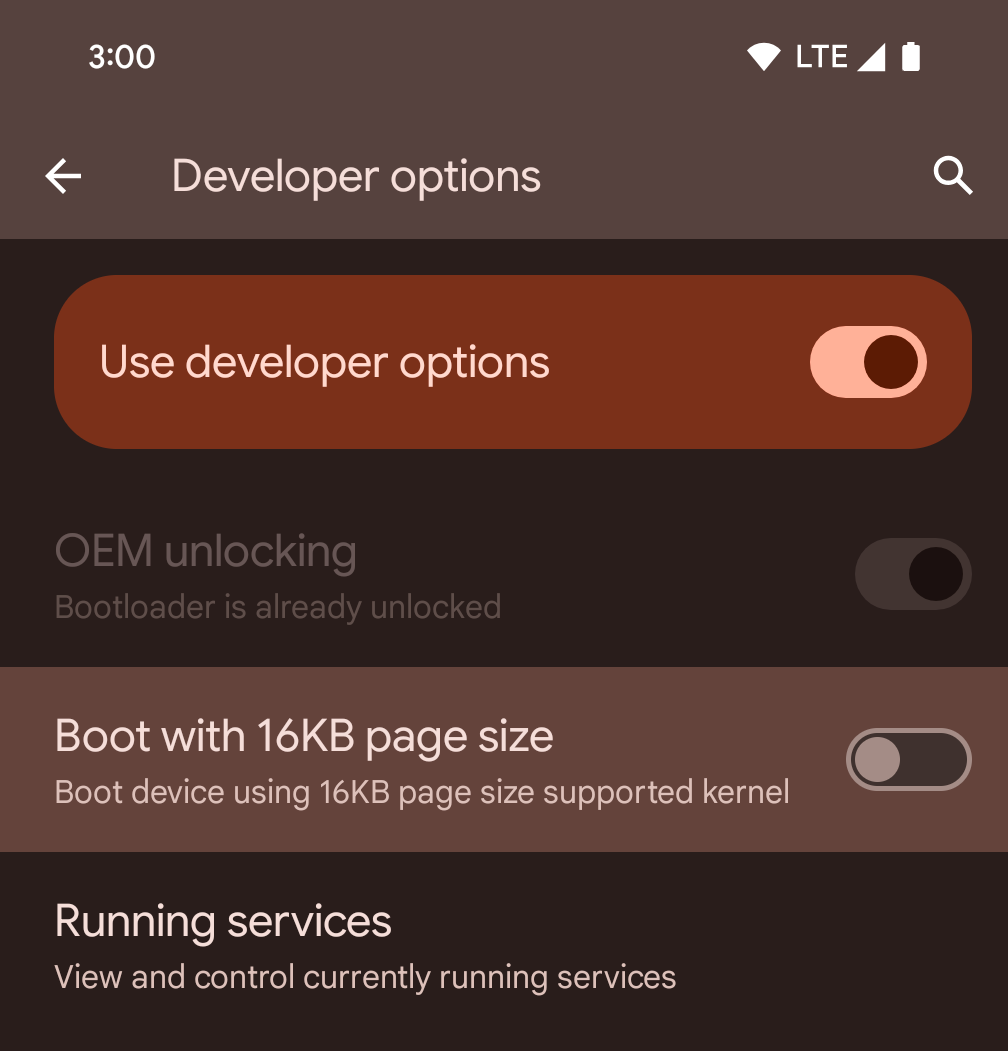
16KB 페이지 크기로 부팅 개발자 옵션을 전환하여 16KB 모드로 기기를 부팅합니다.
Android 15의 QPR 버전에서는 특정 기기에서 사용할 수 있는 개발자 옵션을 사용하여 기기를 16KB 모드로 부팅하고 온디바이스 테스트를 실행할 수 있습니다. 개발자 옵션을 사용하기 전에 설정 > 시스템 > 소프트웨어 업데이트로 이동하여 사용 가능한 업데이트를 적용합니다.
이 개발자 옵션은 다음 기기에서 사용할 수 있습니다.
Pixel 8 및 8 Pro (Android 15 QPR1 이상)
Pixel 8a (Android 15 QPR1 이상)
Pixel 9, 9 Pro, 9 Pro XL (Android 15 QPR2 베타 2 이상)
그래픽
Android 15에는 ANGLE 및 Canvas 그래픽 시스템 추가 등 최신 그래픽 개선사항이 적용되었습니다.
Android의 GPU 액세스 현대화

Android 하드웨어는 핵심 OS가 단일 CPU에서 실행되고 GPU에 고정 기능 파이프라인을 기반으로 하는 API를 사용하여 액세스하던 초기부터 상당히 발전했습니다. Vulkan® 그래픽 API는 Android 7.0 (API 수준 24)부터 NDK에서 최신 GPU 하드웨어를 더 잘 반영하고, 여러 CPU 코어를 지원하도록 더 효과적으로 확장하며, CPU 드라이버 오버헤드를 줄여 앱 성능을 개선하는 하위 수준 추상화를 통해 사용할 수 있습니다. Vulkan은 모든 최신 게임 엔진에서 지원됩니다.
Vulkan은 Android에서 GPU에 사용하는 기본 인터페이스입니다. 따라서 Android 15에는 Vulkan 위에 OpenGL® ES를 실행하기 위한 선택적 레이어로 ANGLE가 포함되어 있습니다. ANGLE로 전환하면 Android OpenGL 구현이 표준화되어 호환성이 개선되고 경우에 따라 성능이 개선됩니다. Android 15에서 설정 -> 시스템 -> 개발자 옵션 -> 실험용: ANGLE 사용 설정에서 개발자 옵션을 사용 설정하여 ANGLE로 OpenGL ES 앱 안정성과 성능을 테스트할 수 있습니다.
Vulkan 기반 Android ANGLE 로드맵
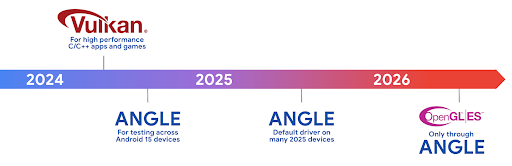
GPU 스택을 간소화하기 위한 일환으로 앞으로 더 많은 새 기기에서 ANGLE을 GL 시스템 드라이버로 제공할 예정이며, 향후 OpenGL/ES는 ANGLE을 통해서만 제공될 것으로 예상됩니다. 하지만 모든 기기에서 OpenGL ES를 계속 지원할 계획입니다.
권장되는 다음 단계
개발자 옵션을 사용하여 OpenGL ES용 ANGLE 드라이버를 선택하고 앱을 테스트합니다. 새 프로젝트의 경우 C/C++에 Vulkan을 사용하는 것이 좋습니다.
Canvas 개선사항
Android 15에서는 다음과 같은 추가 기능을 통해 Android의 Canvas 그래픽 시스템을 계속 현대화합니다.
Matrix44는 3D로 캔버스를 조작할 때 사용해야 하는 좌표 변환을 위한 4x4 행렬을 제공합니다.clipShader는 현재 클립을 지정된 셰이더와 교차시키고clipOutShader는 클립을 현재 클립과 셰이더의 차이로 설정하며, 각각 셰이더를 알파 마스크로 취급합니다. 이렇게 하면 복잡한 도형을 효율적으로 그릴 수 있습니다.
성능 및 배터리
Android는 앱의 성능과 품질을 개선하는 데 계속 집중하고 있습니다. Android 15에서는 앱에서 작업을 더 효율적으로 실행하고, 앱 성능을 최적화하고, 앱에 관한 유용한 정보를 수집하는 데 도움이 되는 API를 도입합니다.
배터리 효율적인 권장사항, 네트워크 및 전력 사용량 디버깅, Android 15 및 최신 버전의 Android에서 백그라운드 작업의 배터리 효율성을 개선하는 방법에 관한 자세한 내용은 Google I/O의 Android에서 백그라운드 작업의 배터리 효율성 개선 강연을 참고하세요.
ApplicationStartInfo API
이전 버전의 Android에서는 앱 시작이 다소 미스터리였습니다. 앱 내에서 콜드, 웜, 핫 상태 중에서 시작되었는지 확인하기 어려웠습니다. 프로세스 포크, onCreate 호출, 첫 번째 프레임 그리기 등 다양한 시작 단계에서 앱이 소비한 시간을 알기도 어려웠습니다. Application 클래스가 인스턴스화될 때 앱이 broadcast, 콘텐츠 제공자, 작업, 백업, 부팅 완료, 알람 또는 Activity에서 시작되었는지 알 수 있는 방법이 없었습니다.
Android 15의 ApplicationStartInfo API는 이 모든 기능을 제공합니다. 한곳에서 타이밍 데이터를 수집하는 데 도움이 되도록 흐름에 자체 타임스탬프를 추가할 수도 있습니다. 측정항목을 수집하는 것 외에도 ApplicationStartInfo를 사용하여 앱 시작을 직접 최적화할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 브로드캐스트로 인해 앱이 시작될 때 Application 클래스 내에서 UI 관련 라이브러리를 인스턴스화하는 데 드는 비용을 없앨 수 있습니다.
자세한 앱 크기 정보
Android 8.0 (API 수준 26)부터 Android에는 앱의 설치된 크기를 APK 크기, APK에서 추출된 파일의 크기, 기기에서 생성된 파일 (예: AOT 컴파일 코드)의 합계인 단일 바이트 숫자로 요약하는 StorageStats.getAppBytes API가 포함되어 있습니다. 이 숫자는 앱에서 스토리지를 사용하는 방식에 관해 유용한 정보를 제공하지 않습니다.
Android 15에서는 APK 파일 분할, AOT 및 속도 향상 관련 코드, dex 메타데이터, 라이브러리, 안내 프로필을 비롯하여 앱이 모든 공간을 사용하는 방식을 파악할 수 있는 StorageStats.getAppBytesByDataType([type]) API를 추가합니다.
앱 관리 프로파일링
Android 15에는 힙 덤프, 힙 프로필, 스택 샘플링과 같은 프로파일링 정보를 앱 내에서 수집할 수 있는 ProfilingManager 클래스가 포함되어 있습니다. 앱의 파일 디렉터리에 전송되는 출력 파일을 식별하는 제공된 태그와 함께 앱에 콜백을 제공합니다. API는 성능 영향을 최소화하기 위해 비율 제한을 사용합니다.
앱에서 프로파일링 요청 구성을 간소화하려면 Core 1.15.0-rc01 이상에서 사용할 수 있는 상응하는 Profiling AndroidX API를 사용하는 것이 좋습니다.
SQLite 데이터베이스 개선사항
Android 15에서는 특정 성능 문제를 대상으로 하는 기본 SQLite 엔진의 매니페스트 파일에 있습니다 이러한 API는 SQLite를 버전으로 업데이트하면서 3.44.3.
특히 대규모 데이터베이스를 사용하거나 지연 시간에 민감한 쿼리를 실행할 때는 SQLite 성능 권장사항을 참고하여 SQLite 데이터베이스를 최대한 활용해야 합니다.
- 읽기 전용 지연된 트랜잭션:
읽기 전용 (쓰기 문은 포함하지 않음), 사용
beginTransactionReadOnly()및beginTransactionWithListenerReadOnly(SQLiteTransactionListener)읽기 전용DEFERRED거래를 발행할 수 있습니다. 이러한 트랜잭션은 서로 동시에 실행될 수 있으며, 데이터베이스가 WAL 모드인 경우IMMEDIATE또는EXCLUSIVE트랜잭션과 동시에 실행될 수 있습니다. - 행 수 및 ID: 변경된 행 수를 검색하기 위해 API가 추가되었습니다.
행 또는 마지막으로 삽입된 행 ID를 반환할 수 있습니다.
getLastChangedRowCount()는 현재 트랜잭션 내에서 가장 최근 SQL 문에 의해 삽입, 업데이트 또는 삭제된 행 수를 반환하고getTotalChangedRowCount()는 현재 연결의 개수를 반환합니다.getLastInsertRowId()는 마지막 행의rowid를 반환합니다. 현재 연결에 삽입됩니다. - 원시 문: 편의를 우회하여 원시 SQlite 문을 실행합니다. 발생할 수 있는 추가 처리 오버헤드에 대해 걱정할 필요가 없습니다.
Android 동적 성능 프레임워크 업데이트
Android 15에서는 게임 및 성능 집약적인 앱이 Android 기기의 전원 시스템 및 열 관련 시스템과 더 직접적으로 상호작용할 수 있는 API 집합인 Android 동적 성능 프레임워크 (ADPF)에 대한 투자를 계속하고 있습니다. 지원되는 기기에서 Android 15는 다음과 같은 ADPF 기능을 추가합니다.
- 힌트 세션의 전원 효율 모드는 연결된 스레드가 성능보다 절전 모드를 우선해야 함을 나타냅니다. 장기 실행 백그라운드 워크로드에 적합합니다.
- GPU 및 CPU 작업 기간을 모두 힌트 세션에서 보고할 수 있으므로 시스템은 워크로드 수요를 가장 잘 충족하도록 CPU 및 GPU 주파수를 함께 조정할 수 있습니다.
- 헤드룸 예측을 기반으로 가능한 열 제한 상태를 해석하는 열 헤드룸 기준점
앱과 게임에서 ADPF를 사용하는 방법을 자세히 알아보려면 문서를 참고하세요.
개인정보처리방침
Android 15에는 앱 개발자가 사용자 개인 정보를 보호하는 데 도움이 되는 다양한 기능이 포함되어 있습니다.
화면 녹화 감지
Android 15에서는 녹화 중임을 감지하는 앱 지원을 추가합니다. 콜백은 앱이 화면 녹화 내에서 표시 또는 숨김 상태 간에 전환될 때마다 호출됩니다. 앱은 등록 프로세스의 UID가 소유한 활동이 표시되는 경우 표시되는 것으로 간주됩니다. 있습니다. 이렇게 하면 앱에서 민감한 작업을 실행하는 경우 녹화 중임을 사용자에게 알릴 수 있습니다.
val mCallback = Consumer<Int> { state ->
if (state == SCREEN_RECORDING_STATE_VISIBLE) {
// We're being recorded
} else {
// We're not being recorded
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val initialState =
windowManager.addScreenRecordingCallback(mainExecutor, mCallback)
mCallback.accept(initialState)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
windowManager.removeScreenRecordingCallback(mCallback)
}
확장된 IntentFilter 기능
Android 15는 UriRelativeFilterGroup를 통해 더 정확한 Intent 해상도를 지원합니다. 여기에는 URL 쿼리 매개변수, URL 프래그먼트, 차단 또는 제외 규칙 등 각각 충족해야 하는 Intent 매칭 규칙 집합을 형성하는 UriRelativeFilter 객체의 집합이 포함됩니다.
이러한 규칙은 android:allow 태그를 선택적으로 포함할 수 있는 <uri-relative-filter-group> 태그를 사용하여 AndroidManifest XML 파일에서 정의할 수 있습니다. 이러한 태그에는 기존 데이터 태그 속성과 android:query 및 android:fragment 속성을 사용하는 <data> 태그가 포함될 수 있습니다.
다음은 AndroidManifest 문법의 예입니다.
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="astore.com" />
<uri-relative-filter-group>
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="region=na" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="mobileoptout=true" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:fragmentPrefix="faq" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
</intent-filter>
비공개 스페이스
비공개 스페이스를 사용하면 사용자는 기기에 별도의 공간을 만들어 민감한 앱을 다른 사람이 보지 못하도록 추가 인증 레이어로 보관할 수 있습니다. 비공개 스페이스는 별도의 사용자 프로필을 사용합니다. 사용자는 비공개 스페이스에 기기 잠금을 사용할지, 또는 별도의 잠금 수단을 사용할지 선택할 수 있습니다.
비공개 스페이스의 앱은 런처의 별도의 컨테이너에 표시되며, 비공개 스페이스가 잠겨 있으면 최근 항목 보기, 알림, 설정, 그 밖의 앱에서 숨겨집니다. 사용자가 생성했거나 다운로드한 콘텐츠 (예: 미디어 또는 파일)와 계정은 비공개 스페이스와 기본 스페이스 간에 구분되어 보관됩니다. 시스템 Sharesheet 및 사진 선택 도구를 사용하면 비공개 스페이스가 잠금 해제된 경우 앱이 여러 스페이스의 콘텐츠에 액세스하도록 허용할 수 있습니다.
사용자는 기존 앱과 데이터를 비공개 스페이스로 이동할 수 없습니다. 대신 사용자는 비공개 스페이스에서 설치 옵션을 선택하여 원하는 앱 스토어를 사용하여 앱을 설치합니다. 비공개 스페이스의 앱은 기본 스페이스의 앱과 별도의 사본으로 설치됩니다 (동일한 앱의 새 사본).
사용자가 비공개 스페이스를 잠그면 프로필이 중지됩니다. 프로필이 중지된 동안 비공개 스페이스의 앱은 더 이상 활성 상태가 아니며 알림 표시와 같은 포그라운드 또는 백그라운드 활동을 실행할 수 없습니다.
특히 앱이 다음 카테고리 중 하나에 해당하는 경우 비공개 공간으로 앱을 테스트하여 앱이 예상대로 작동하는지 확인하는 것이 좋습니다.
- 기본 프로필에 없는 설치된 앱 사본이 직장 프로필에 있다고 가정하는 직장 프로필 로직이 있는 앱
- 의료 앱
- 런처 앱
- 앱 스토어 앱
선택한 사진 액세스에 대한 가장 최근 사용자 선택 쿼리
이제 앱은 미디어 권한에 대한 부분 액세스가 부여된 경우 가장 최근에 선택한 사진과 동영상만 강조 표시할 수 있습니다. 이 기능은
사진과 동영상 액세스를 자주 요청하는 앱의 사용자 환경을
동영상 앱에서 이 기능을 사용하려면
MediaStore를 쿼리할 때 QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY 인수
ContentResolver까지
Kotlin
val externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external") val mediaColumns = arrayOf( FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE, ) val queryArgs = bundleOf( // Return only items from the last selection (selected photos access) QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY to true, // Sort returned items chronologically based on when they were added to the device's storage QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER to "${FileColumns.DATE_ADDED} DESC", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION to "${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ? OR ${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ?", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS to arrayOf( FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE.toString(), FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.toString() ) )
Java
Uri externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external"); String[] mediaColumns = { FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE }; Bundle queryArgs = new Bundle(); queryArgs.putBoolean(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, true); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER, FileColumns.DATE_ADDED + " DESC"); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION, FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ? OR " + FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ?"); queryArgs.putStringArray(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS, new String[] { String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE), String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) });
Android의 개인 정보 보호 샌드박스
Android 15에는 최신 버전의 Android의 개인 정보 보호 샌드박스를 통합한 최신 Android 광고 서비스 확장 프로그램이 포함되어 있습니다. 이번 추가는 사용자 개인 정보 보호를 개선하고 모바일 앱에 효과적인 개인 맞춤 광고 경험을 제공하는 기술을 개발하기 위한 Google의 노력의 일환입니다. 개인 정보 보호 샌드박스 페이지에서 Android의 개인 정보 보호 샌드박스 개발자 프리뷰 및 베타 프로그램에 관한 자세한 내용을 확인하고 시작해 보세요.
헬스 커넥트
Android 15는 앱에서 수집한 건강/피트니스 데이터를 관리하고 공유하는 안전하고 중앙 집중식 플랫폼인 Android용 헬스 커넥트를 중심으로 최신 확장 프로그램을 통합합니다. 이번 업데이트에서는 피트니스, 영양, 피부 온도, 훈련 계획 등에서 추가 데이터 유형을 지원합니다.
피부 온도 측정으로 보다 정확하게 저장하고 공유할 수 있음 웨어러블 또는 기타 추적 장치의 온도 데이터.
트레이닝 계획은 사용자가 피트니스 목표를 달성할 수 있도록 도와주는 구조화된 운동 계획입니다. 트레이닝 계획 지원에는 다양한 완료 및 실적 목표가 포함됩니다.
- 칼로리 소모량과 같은 달성 목표 distance, duration 반복, 단계입니다.
- 다음과 같은 실적 목표 최대한 많이 반복하기 (AMRAP), 케이던스, 심박수, 파워, 운동 인지 속도 및 속도.
Android에서 헬스 커넥트의 최신 업데이트에 관해 자세히 알아보려면 Android로 적응형 환경 구축 Health 강연을 확인해 보세요.
앱 화면 공유
Android 15에서는 앱 화면 공유를 지원하므로 사용자가 전체 기기 화면이 아닌 앱 창만 공유하거나 녹화할 수 있습니다. Android 14 QPR2에서 처음 사용 설정된 이 기능에는 앱에서 앱 화면 공유 환경을 맞춤설정할 수 있는 MediaProjection 콜백이 포함되어 있습니다. Android 14 (API 수준 34) 이상을 타겟팅하는 앱의 경우 각 MediaProjection 캡처 세션에 사용자 동의가 필요합니다.
사용자 환경 및 시스템 UI
Android 15에서는 앱 개발자와 사용자가 필요에 맞게 기기를 구성할 수 있는 더 많은 제어 기능과 유연성을 제공합니다.
Android 15의 최신 개선사항을 사용하여 앱의 사용자 환경을 개선하는 방법을 자세히 알아보려면 Google I/O의 Android 앱의 사용자 환경 개선 강연을 참고하세요.
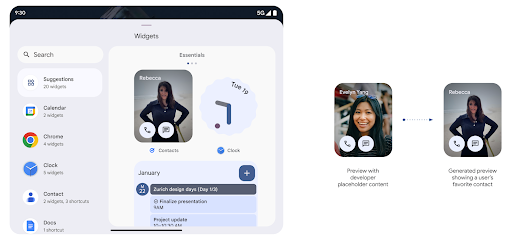
생성된 미리보기 API를 사용한 풍부한 위젯 미리보기
Android 15 이전에는 위젯 선택 도구 미리보기를 제공하는 유일한 방법은 정적 이미지 또는 레이아웃 리소스. 이러한 미리보기는 홈 화면에 배치된 실제 위젯의 모양과 크게 다를 수 있습니다. 또한 Jetpack Glance로는 정적 리소스를 만들 수 없으므로 Glance 개발자는 위젯 미리보기를 보려면 위젯의 스크린샷을 찍거나 XML 레이아웃을 만들어야 했습니다.
Android 15에는 생성된 미리보기 지원이 추가되었습니다. 즉, 앱 위젯이
제공자는 선택 도구 미리보기로 사용할 RemoteViews를 대신 생성할 수 있습니다.
정의할 수 있습니다
Push API
앱은 Push API를 통해 생성된 미리보기를 제공할 수 있습니다. 앱은 수명 주기의 어느 시점에서나 미리보기를 제공할 수 있으며 호스트로부터 미리보기를 제공하라는 명시적인 요청을 받지 않습니다. 미리보기는 AppWidgetService에 유지되며 호스트는 필요에 따라 미리보기를 요청할 수 있습니다. 다음 예는 XML 위젯을 로드합니다.
레이아웃 리소스를 추가하고 이를 미리보기로 설정합니다.
AppWidgetManager.getInstance(appContext).setWidgetPreview(
ComponentName(
appContext,
SociaLiteAppWidgetReceiver::class.java
),
AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN,
RemoteViews("com.example", R.layout.widget_preview)
)
예상되는 흐름은 다음과 같습니다.
- 위젯 제공업체는 언제든지
setWidgetPreview를 호출합니다. 제공된 미리보기는 다른 제공업체 정보와 함께AppWidgetService에 유지됩니다. setWidgetPreview는AppWidgetHost.onProvidersChanged콜백을 통해 호스트에게 업데이트된 미리보기를 알립니다. 이에 따라 위젯 호스트는 모든 제공업체 정보를 새로고침합니다.- 위젯 미리보기를 표시할 때 호스트는 다음을 확인합니다.
AppWidgetProviderInfo.generatedPreviewCategories및 선택한 사용 가능한 경우,AppWidgetManager.getWidgetPreview를 호출하여 다음을 수행합니다. 이 공급자에 대해 저장된 미리보기를 반환합니다.
setWidgetPreview 호출 시점
미리보기를 제공하는 콜백이 없으므로 앱은 실행 중인 시점 중 언제든지 미리보기를 전송하도록 선택할 수 있습니다. 미리보기를 업데이트하는 빈도는 위젯의 사용 사례에 따라 다릅니다.
다음 목록에서는 미리보기 사용 사례의 두 가지 주요 카테고리를 설명합니다.
- 위젯 미리보기에 실제 데이터(예: 맞춤설정된 데이터)를 표시하는 제공업체 최신 정보를 얻을 수 있습니다. 이러한 제공업체는 사용자가 로그인했거나 앱에서 초기 구성을 완료한 사용자 그런 다음 주기적인 작업을 설정하여 선택한 주기로 미리보기를 업데이트할 수 있습니다. 이러한 위젯 유형의 예로는 사진, 캘린더, 날씨, 뉴스 등이 있습니다. 위젯에 추가합니다.
- 미리보기 또는 빠른 작업 위젯에 정적 정보를 표시하는 제공자 데이터를 표시할 수 있습니다. 이러한 제공자는 있습니다. 이러한 위젯 유형의 예로는 작업 위젯이나 Chrome 바로가기 위젯을 사용할 수 있습니다.
일부 제공업체는 허브 모드 선택 도구에는 정적 미리보기를 표시하지만 홈 화면 선택 도구에는 실제 정보를 표시할 수 있습니다. 이러한 제공업체는 미리보기를 설정하기 위해 두 가지 사용 사례에 관한 안내를 모두 따라야 합니다.
PIP 모드
Android 15에서는 PIP 모드의 변경사항을 도입하여 더 매끄럽게 전환됩니다. 이렇게 하면 기본 UI 위에 UI 요소가 오버레이된 앱은 PIP 모드로 전환됩니다.
개발자는 onPictureInPictureModeChanged 콜백을 사용하여 오버레이된 UI 요소의 공개 상태를 전환하는 로직을 정의합니다. 이 콜백은
PIP 시작 또는 종료 애니메이션이 완료되면 트리거됩니다. 시작까지
Android 15에서는 PictureInPictureUiState 클래스에 다른 상태가 포함되어 있습니다.
이 UI 상태에서 Android 15 (API 수준 35)를 타겟팅하는 앱은
다음으로 호출되는 Activity#onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged 콜백
isTransitioningToPip() PIP 애니메이션이 시작되는 즉시 작동합니다. 현재
앱이 PIP 모드일 때 앱과 관련이 없는 많은 UI 요소가
예시 뷰 또는 레이아웃에서
동영상, 평점, 제목 등이 있습니다. 앱이 PIP 모드로 전환되면
onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged 콜백으로 UI 요소를 숨깁니다. 이
PIP 창에서 앱이 전체 화면 모드로 전환되면
다음과 같이 이러한 요소를 숨기기 해제하는 onPictureInPictureModeChanged 콜백
다음 예를 참고하세요.
override fun onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged(pipState: PictureInPictureUiState) {
if (pipState.isTransitioningToPip()) {
// Hide UI elements
}
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean) {
if (isInPictureInPictureMode) {
// Unhide UI elements
}
}
관련 없는 UI 요소 (PIP 창)를 빠르게 볼 수 있도록 전환하면 도움이 됩니다. 더 매끄럽고 깜박임이 없는 PIP 입력 애니메이션을 제공합니다.
방해 금지 모드 규칙 개선
AutomaticZenRule를 사용하면 앱에서 Attention(관심 유도)을 맞춤설정할 수 있습니다.
관리 (방해 금지 모드) 규칙 및 활성화 또는 비활성화 시점 결정
있습니다. Android 15에서는 사용자 환경을 개선하기 위해 이러한 규칙을 대폭 개선했습니다. 다음과 같은 개선사항이 포함됩니다.
AutomaticZenRule에 유형 추가(시스템에서 특수 항목 적용 가능) 일부 규칙이 적용되지 않습니다AutomaticZenRule에 아이콘을 추가하여 모드를 더 쉽게 인식할 수 있도록 했습니다.AutomaticZenRule에 다음을 설명하는triggerDescription문자열 추가 사용자에게 규칙이 활성화되기 위한 조건입니다.- 추가됨
ZenDeviceEffects드림 규칙을 통해 그레이 스케일 등의 작업을 트리거할 수 있으므로AutomaticZenRule로 변경 디스플레이, 야간 모드, 또는 배경화면을 어둡게 할 수 있습니다.
알림 채널의 VibrationEffect 설정
Android 15는 NotificationChannel.setVibrationEffect를 사용하여 채널별로 수신 알림에 리치 진동을 설정할 수 있도록 지원하므로 사용자가 기기를 보지 않고도 다양한 유형의 알림을 구분할 수 있습니다.
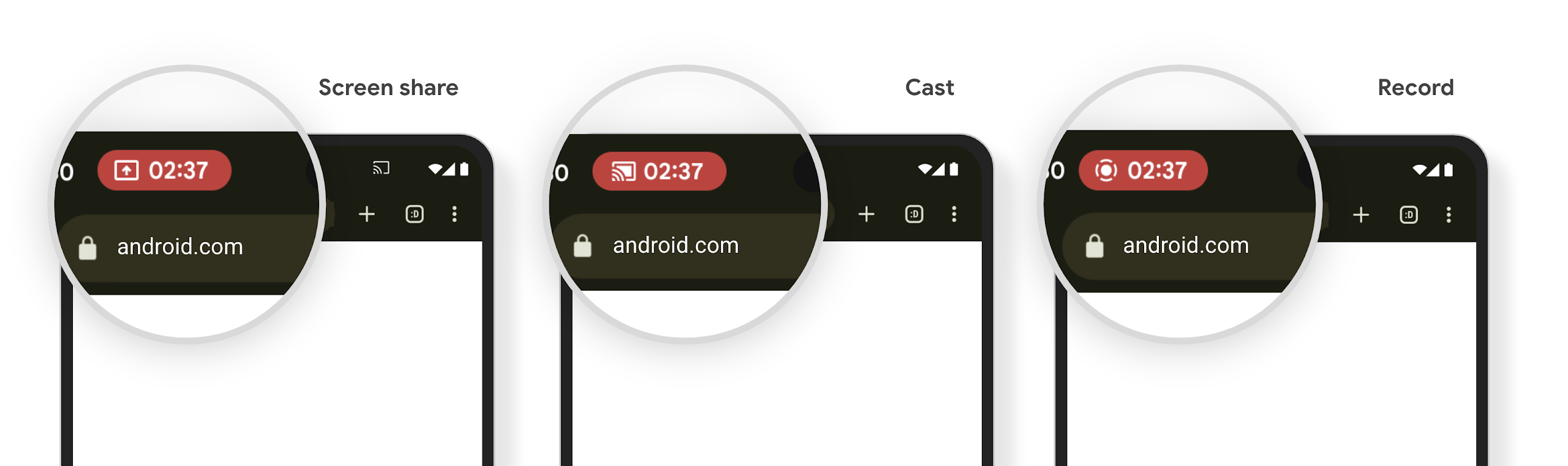
미디어 프로젝션 상태 표시줄 칩 및 자동 중지
미디어 프로젝션은 비공개 사용자 정보를 노출할 수 있습니다. 눈에 띄는 새로운 상태 표시줄 칩을 통해 진행 중인 화면 프로젝션을 사용자에게 알립니다. 사용자는 칩을 탭하여 화면 전송, 공유 또는 녹화를 중지할 수 있습니다. 또한 더 직관적인 사용자 환경을 위해 이제 기기 화면이 잠기면 진행 중인 화면 프로젝션이 자동으로 중지됩니다.
대형 화면 및 폼 팩터
Android 15에서는 대형 화면, 플립형, 폴더블을 비롯한 Android의 폼 팩터를 최대한 활용할 수 있도록 앱을 지원합니다.
향상된 대형 화면 멀티태스킹
Android 15는 사용자가 대형 화면 기기에서 멀티태스킹하는 더 나은 방법을 제공합니다. 대상 예를 들어 사용자는 자주 사용하는 화면 분할 앱 조합을 저장하여 빠르게 화면의 태스크 바에 액세스하고 고정하여 앱 간에 빠르게 전환할 수 있습니다. 다시 말해 하는 것이 그 어느 때보다 중요하다고 생각합니다.
Google I/O의 적응형 Android 빌드 빌드 앱 및 Material 3으로 UI 빌드 적응형 라이브러리 이 문서에는 대규모 캠페인을 위한 디자인 화면을 선택합니다.
커버 화면 지원
앱은 Android 15에서 사용하는 속성을 선언하여 지원되는 폴더블 기기의 작은 커버 화면에 Application 또는 Activity가 표시되도록 허용할 수 있습니다. 이러한 화면은 너무 작아서 Android 앱이 실행될 수 있는 호환 타겟으로 간주되지는 않지만 앱에서 이를 지원하도록 선택하면 더 많은 위치에서 앱을 사용할 수 있습니다.
연결
Android 15는 앱이 최신 통신 및 무선 기술을 이용할 수 있도록 플랫폼을 업데이트합니다.
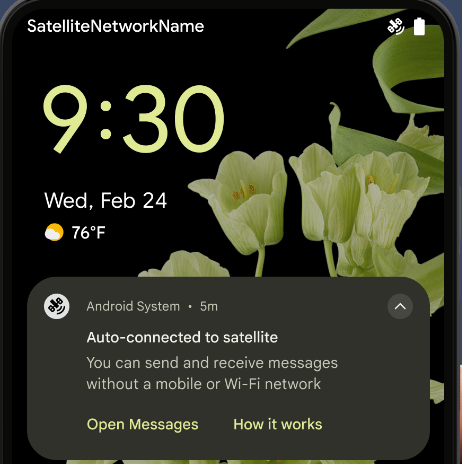
위성 지원
Android 15는 위성 연결에 대한 플랫폼 지원을 계속 확장하고 위성 연결 환경 전반에서 일관된 사용자 환경을 보장하기 위한 몇 가지 UI 요소를 포함합니다.
앱은 ServiceState.isUsingNonTerrestrialNetwork()를 사용하여 기기가 위성에 연결된 시점을 감지하여 전체 네트워크 서비스를 사용할 수 없는 이유를 더 잘 파악할 수 있습니다. 또한 Android 15는 메시지 전송 및 수신에 위성 연결을 사용하도록 사전 로드된 RCS 앱뿐만 아니라 SMS 및 MMS 앱을 지원합니다.
더 원활한 NFC 환경
Android 15에서는 Android의 강력한 NFC 앱 생태계를 계속 지원하는 동시에 탭 투 페이라고 하는 결제 환경을 더욱 원활하고 안정적으로 만들기 위해 노력하고 있습니다. 지원되는 기기에서 앱은 NfcAdapter에 관찰 모드로 전환하도록 요청할 수 있습니다. 이 모드에서는 기기가 리슨하지만 NFC 리더에 응답하지 않으며 앱의 NFC 서비스 PollingFrame
객체를 전송하여 처리합니다. PollingFrame 객체는 NFC 리더와의 첫 번째 통신 전에 인증하는 데 사용할 수 있으므로 대부분의 경우 원탭 거래가 가능합니다.
또한 앱은 지원되는 기기에서 필터를 등록하여 폴링 루프 활동에 관한 알림을 받을 수 있으므로 여러 NFC 지원 애플리케이션을 원활하게 사용할 수 있습니다.
월렛 역할
Android 15에서는 사용자의 기본 월렛 앱과 더 긴밀하게 통합할 수 있는 월렛 역할을 도입합니다. 이 역할은 NFC 기본 미접촉 결제 설정을 대체합니다. 사용자는 설정 > 앱 > 기본 앱으로 이동하여 월렛 역할 소유자를 관리할 수 있습니다.
지갑 역할은 결제 카테고리에 등록된 AID의 NFC 탭을 라우팅할 때 사용됩니다. 동일한 AID에 등록된 다른 앱이 포그라운드에서 실행 중이 아닌 한 탭은 항상 월렛 역할 소유자에게 전달됩니다.
이 역할은 활성화 시 월렛 빠른 액세스 타일이 표시될 위치를 결정하는 데도 사용됩니다. 역할이 '없음'으로 설정된 경우 빠른 액세스 타일을 사용할 수 없으며 결제 카테고리 NFC 탭이 포그라운드 앱에만 전송됩니다.
보안
Android 15를 사용하면 앱의 보안을 강화하고 앱의 데이터를 보호할 수 있으며 사용자에게 데이터에 대한 투명성과 제어 기능을 더 많이 제공할 수 있습니다. Google I/O의 Android에서 사용자 보안 보호 강연에서 사용자 보호 조치를 개선하고 새로운 위협으로부터 앱을 보호하기 위해 Google이 어떤 노력을 기울이고 있는지 자세히 알아보세요.
자동 완성과 인증 관리자 통합
Android 15부터 개발자는 사용자 이름 또는 비밀번호 필드와 같은 특정 뷰를 인증 관리자 요청에 연결하여 로그인 프로세스 중에 맞춤설정된 사용자 환경을 더 쉽게 제공할 수 있습니다. 사용자가 이러한 뷰 중 하나에 포커스를 맞추면 해당 요청이 인증 관리자로 전송됩니다. 결과 사용자 인증 정보는 여러 제공업체에서 집계되어 인라인 추천 또는 드롭다운 추천과 같은 자동 완성 대체 UI에 표시됩니다. Jetpack androidx.credentials 라이브러리는 개발자가 사용하는 것이 좋으며 곧 Android 15 이상에서 이 기능을 더욱 개선하는 데 사용할 수 있게 됩니다.
원탭 가입 및 로그인을 생체 인식 메시지와 통합
인증 관리자는 생체 인식 메시지를 사용자 인증 정보 생성에 통합 및 로그인 프로세스로 이루어져 있으므로 제공업체가 생체 인식 프롬프트 따라서 사용자 인증 정보 제공업체는 생성 및 가져오기 흐름의 결과를 제공하며, 생체 인식 흐름 결과로 보강됩니다. 이 간소화된 프로세스로 더 효율적이고 간소화된 사용자 인증 정보를 만들 수 있습니다. 생성 및 검색 프로세스가 포함됩니다.
엔드 투 엔드 암호화 키 관리
Android 15에서는 암호화 공개 키 저장을 위한 OS 수준 API를 제공하여 Android 앱에서 엔드 투 엔드 암호화 (E2EE)를 지원하는 E2eeContactKeysManager를 도입합니다.
E2eeContactKeysManager는 플랫폼 연락처 앱과 통합되어 사용자에게 연락처의 공개 키를 중앙 집중식으로 관리하고 확인할 수 있는 방법을 제공하도록 설계되었습니다.
콘텐츠 URI에 대한 권한 확인
Android 15에서는 콘텐츠 URI에 대한 권한 확인을 실행하는 API 세트를 도입합니다.
Context.checkContentUriPermissionFull: 콘텐츠 URI에 대한 전체 권한 검사를 실행합니다.Activity매니페스트 속성requireContentUriPermissionFromCaller: 활동 시작 시 제공된 콘텐츠 URI에 지정된 권한을 적용합니다.Activity호출자를 위한ComponentCaller클래스: 활동을 실행한 앱을 나타냅니다.
접근성
Android 15에는 사용자의 접근성을 개선하는 기능이 추가되었습니다.
점자 개선
Android 15에서는 TalkBack이 USB와 보안 블루투스 모두를 통해 HID 표준을 사용하는 점자 디스플레이를 지원할 수 있도록 했습니다.
이 표준은 마우스와 키보드에서 사용하는 표준과 마찬가지로 시간이 지남에 따라 Android가 더 다양한 점자 디스플레이를 지원하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
다국어 지원
Android 15에서는 기기가 여러 언어로 사용될 때 사용자 환경을 보완하는 기능이 추가되었습니다.
CJK 가변 글꼴
Android 15부터 중국어, 일본어, 한국어 (CJK) 언어의 글꼴 파일인 NotoSansCJK가 이제 가변 글꼴이 되었습니다. 가변 글꼴을 사용하면 CJK 언어로 창의적인 서체를 만들 수 있습니다. 디자이너는 더 다양한 스타일을 살펴보고 이전에는 어렵거나 불가능했던 시각적으로 눈에 띄는 레이아웃을 만들 수 있습니다.

문자 간 정렬
Android 15부터
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER 사용 이전 단어 간 사유(이전):
Android 8.0 (API 수준 26)에서 처음 도입되었으며
근거는 특정 API를 사용하는 언어에 유사한 기능을
중국어, 일본어 등 분할을 위한 공백 문자

JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE를 사용한 일본어 텍스트 레이아웃
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE를 사용한 영어 텍스트 레이아웃
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD를 사용한 일본어 텍스트 레이아웃
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD를 사용한 영어 텍스트 레이아웃
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER를 사용한 일본어 텍스트 레이아웃
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER를 사용한 영어 텍스트 레이아웃자동 줄바꿈 구성
Android는 일본어와 한국어의 구문 기반 줄바꿈을
Android 13 (API 수준 33) 그러나 구문 기반 줄바꿈은 짧은 텍스트 줄의 가독성을 개선하지만 긴 텍스트 줄에는 적합하지 않습니다.
Android 15에서는 앱이 짧은 줄에만 구문 기반 줄바꿈을 적용할 수 있습니다.
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO를 사용하여 텍스트 생성
옵션을 선택합니다. 이 옵션을 선택하면 텍스트에 가장 적합한 단어 스타일 옵션이 선택됩니다.
짧은 텍스트 줄의 경우 동일하게 작동하는 구문 기반 줄바꿈이 사용됨
다음과 같이 LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE로 설정합니다.
다음 이미지:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO은 짧은 텍스트 줄의 경우 구문 기반 줄바꿈을 적용하여 텍스트의 가독성을 개선합니다.
이 방법은
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE텍스트가 더 긴 경우 LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO는 no를 사용합니다.
줄바꿈 단어 스타일로,
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE
다음 이미지:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
줄바꿈 단어 스타일을 적용하지 않으므로 텍스트의 가독성이 향상됩니다.
이 방법은
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE추가 일본어 변체 가나 글꼴
Android 15의 오래된 일본어 히라가나 (헨타이가나) 글꼴 파일 기본적으로 번들로 묶여 있습니다. 독특한 모양의 헨타이가나 캐릭터는 예술 작품이나 디자인에 독특한 감각을 더하는 동시에 전송 및 이해에 대해 살펴봤습니다.

VideoLAN 원뿔 저작권 (c) 1996-2010 VideoLAN. 이 로고 또는 수정된 버전은 누구나 VideoLAN 프로젝트 또는 VideoLAN팀에서 개발한 제품을 언급하기 위해 사용하거나 수정할 수 있지만, 프로젝트의 추천을 나타내지는 않습니다.
Vulkan 및 Vulkan 로고는 Khronos Group Inc.의 등록 상표입니다.
OpenGL은 등록된 상표이며 OpenGL ES 로고는 Khronos의 허가를 받아 Hewlett Packard Enterprise의 상표입니다.

