Android 14 面向开发者引入了一些出色的功能和 API。以下内容可帮助您了解适用于您的应用的功能并开始使用相关 API。
如需查看新增、修改和移除的 API 的详细列表,请参阅 API 差异报告。如需详细了解添加的 API,请访问 Android API 参考文档。对于 Android 14,请查找在 API 级别 34 中添加的 API。如需了解平台变更可能会在哪些方面影响您的应用,请务必查看会影响以 Android 14 为目标平台的应用和所有应用的 Android 14 行为变更。
国际化
单个应用语言设置
Android 14 expands on the per-app language features that were introduced in Android 13 (API level 33) with these additional capabilities:
Automatically generate an app's
localeConfig: Starting with Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 and AGP 8.1.0-alpha07, you can configure your app to support per-app language preferences automatically. Based on your project resources, the Android Gradle plugin generates theLocaleConfigfile and adds a reference to it in the final manifest file, so you no longer have to create or update the file manually. AGP uses the resources in theresfolders of your app modules and any library module dependencies to determine the locales to include in theLocaleConfigfile.Dynamic updates for an app's
localeConfig: Use thesetOverrideLocaleConfig()andgetOverrideLocaleConfig()methods inLocaleManagerto dynamically update your app's list of supported languages in the device's system settings. Use this flexibility to customize the list of supported languages per region, run A/B experiments, or provide an updated list of locales if your app utilizes server-side pushes for localization.App language visibility for input method editors (IMEs): IMEs can utilize the
getApplicationLocales()method to check the language of the current app and match the IME language to that language.
Grammatical Inflection API
有 30 亿人在使用区分性别的语言,此类语言的语法类别(例如名词、动词、形容词和介词)会根据您交谈所涉及的人或物的性别而变化。传统上,许多区分性别的语言使用阳性语法性别作为默认或通用性别。
以错误的语法性别来称呼用户,例如以阳性语法性别来称呼女性,可能会对她们的表现和态度产生负面影响。相比之下,界面语言如果能正确反映用户的语法性别,就可以提高用户互动度,并提供更个性化、更自然的用户体验。
To help you build a user-centric UI for gendered languages, Android 14 introduces the Grammatical Inflection API, which lets you add support for grammatical gender without refactoring your app.
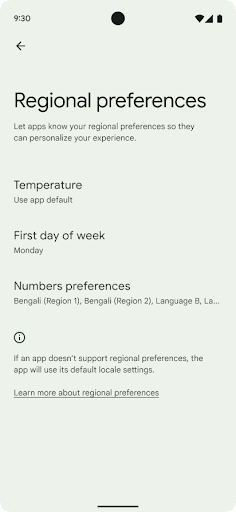
地区偏好设置
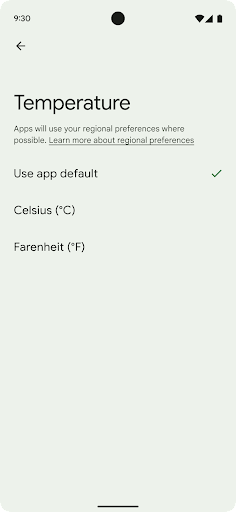
Regional preferences enable users to personalize temperature units, the first day of the week, and numbering systems. A European living in the United States might prefer temperature units to be in Celsius rather than Fahrenheit and for apps to treat Monday as the beginning of the week instead of the US default of Sunday.
New Android Settings menus for these preferences provide users with a
discoverable and centralized location to change app preferences. These
preferences also persist through backup and restore. Several APIs and
intents—such as
getTemperatureUnit
and
getFirstDayOfWeek—
grant your app read access to user preferences, so your app can adjust how it
displays information. You can also register a
BroadcastReceiver on
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED
to handle locale configuration changes when regional preferences change.
To find these settings, open the Settings app and navigate to System > Languages & input > Regional preferences.
无障碍
非线性字体放大至 200%
从 Android 14 开始,系统支持字体放大高达 200%,为弱视用户提供了符合网络内容无障碍指南 (WCAG) 的其他无障碍功能选项。
为防止屏幕上的大文本元素放大放大, 应用非线性缩放曲线。这种放大策略意味着大号文本的放大比例不会与较小的文本相同。非线性字体放大有助于保持不同大小元素之间的比例层次结构,同时缓解高级别线性文本放大存在的问题(例如文本被截断或文本因非常大的显示大小而难以阅读)。
使用非线性字体放大测试应用
如果您已使用放大像素 (sp) 单位来定义文字大小,那么这些 其他选项和扩缩方面的改进会自动应用到 。不过,您仍应使用 启用字体大小 (200%),以确保应用采用 且可以适应较大字号,并且不会影响易用性。
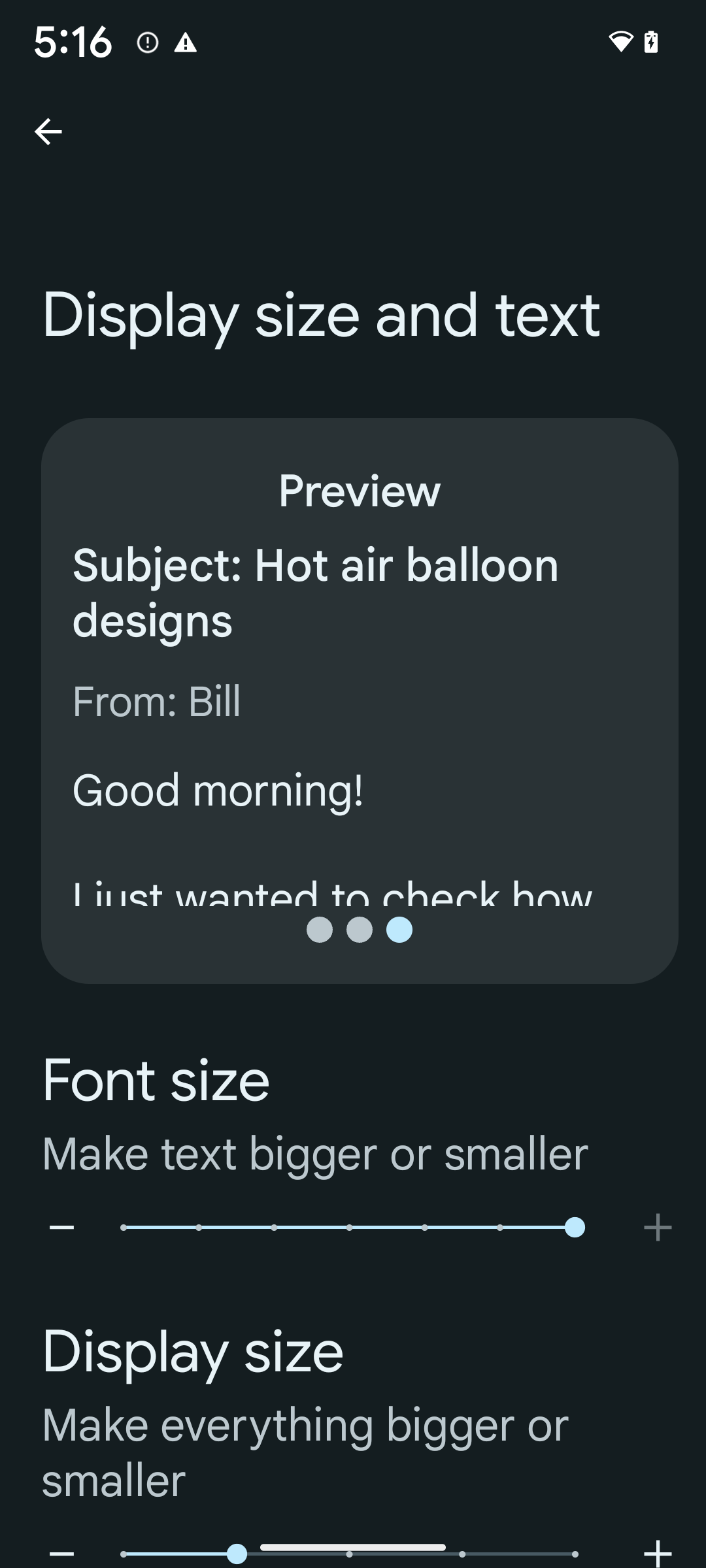
要启用 200% 字号,请按以下步骤操作:
- 打开“设置”应用,然后依次前往无障碍 > 显示大小和文字。
- 在字号选项中,点按加号 (+) 图标,直到启用最大字号设置,如本部分随附的图片所示。
针对文本大小使用放大像素 (sp) 单位
请务必始终以 sp 为单位指定文字大小。当应用使用 sp 单位时,Android 可以应用用户的首选文本大小,并相应地进行缩放。
请勿为内边距使用 sp 单位,也不要假定内边距来定义视图高度:使用非线性字体放大 sp 尺寸可能并不成比例,因此 4sp + 20sp 可能并不等于 24sp。
转换放大像素 (sp) 单位
使用 TypedValue.applyDimension() 从 sp 单位转换为像素,并使用 TypedValue.deriveDimension() 将像素转换为 sp。这些方法会自动应用适当的非线性放大曲线。
避免对公式进行硬编码,使用以下代码
Configuration.fontScale 或
DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity。因为字体缩放
非线性的,则 scaledDensity 字段不再准确。fontScale
字段应仅用于提供信息,
使用单个标量值进行扩缩。
为 lineHeight 使用 sp 单位
始终使用 sp 单位定义 android:lineHeight
dp 为 dp,因此行高会随文本一起缩放。否则,如果文本使用 sp,但 lineHeight 使用 dp 或 px,则文本不会缩放,并且看起来很拥挤。TextView 会自动更正 lineHeight,以便实现您的目标
比例会得到保留,但前提是 textSize 和 lineHeight
以 sp 为单位进行定义。
摄像头和媒体
图片 Ultra HDR

Android 14 新增了对高动态范围 (HDR) 图片的支持,可在拍摄照片时保留更多来自传感器的信息,从而实现鲜艳的色彩和更高的对比度。Android 使用 Ultra HDR 格式,该格式与 JPEG 图片完全向后兼容,可让应用与 HDR 图片无缝互操作,并根据需要以标准动态范围 (SDR) 显示这些图片。
当您的应用选择为其 activity 窗口使用 HDR 界面(通过清单条目或通过在运行时调用 Window.setColorMode())时,框架会自动在界面中以 HDR 格式渲染这些图片。您还可以在受支持的设备上拍摄压缩的 Ultra HDR 静态图片。从传感器中恢复的颜色越多,后期编辑的灵活性就越高。与 Ultra HDR 图片关联的 Gainmap 可用于使用 OpenGL 或 Vulkan 渲染这些图片。
相机扩展中的缩放、聚焦、postview 等功能
Android 14 升级并改进了相机扩展程序,让应用能够处理更长的处理时间,从而支持在受支持的设备上使用计算密集型算法(例如弱光摄影)来改善图片。这些功能可让用户在使用相机扩展功能时获得更出色的体验。这些改进的示例包括:
- 动态静态拍摄处理延迟时间估算功能可根据当前场景和环境条件提供更准确的静态拍摄延迟时间估算值。调用
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()可获取具有两种延迟时间估算方法的StillCaptureLatency对象。getCaptureLatency()方法会返回onCaptureStarted和onCaptureProcessStarted()之间的估算延迟时间,而getProcessingLatency()方法会返回onCaptureProcessStarted()和可用的最终处理帧之间的估算延迟时间。 - 支持拍摄进度回调,以便应用可以显示长时间运行的静态拍摄处理操作的当前进度。您可以检查
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailable是否支持此功能,如果支持,则实现onCaptureProcessProgressed()回调,并将进度(从 0 到 100)作为参数传入。 扩展程序专用元数据,例如用于调节扩展程序效果(例如背景虚化程度)的
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTH和EXTENSION_BOKEH。相机扩展程序中的静态图片拍摄预览功能,该功能比最终图片更快地提供经过较少处理的图片。如果扩展程序的处理延迟时间增加,可以提供 postview 图片作为占位符以提升用户体验,并在稍后改用最终图片。您可以使用
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable检查此功能是否可用。然后,您可以将OutputConfiguration传递给ExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration。支持
SurfaceView,可实现更优化且能效更高的预览渲染路径。支持在使用扩展程序时点按对焦和缩放。
传感器内变焦
When REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE in
CameraCharacteristics contains
SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW, your app
can use advanced sensor capabilities to give a cropped RAW stream the same
pixels as the full field of view by using a CaptureRequest
with a RAW target that has stream use case set to
CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW.
By implementing the request override controls, the updated camera gives users
zoom control even before other camera controls are ready.
无损 USB 音频
Android 14 支持无损音频格式,可通过 USB 有线耳机提供发烧友级体验。您可以查询 USB 设备的首选混音器属性,注册监听器以监听首选混音器属性的更改,以及使用 AudioMixerAttributes 类配置混音器属性。此类表示音频混音器的格式,例如声道掩码、采样率和行为。该类允许直接发送音频,而无需混音、调节音量或处理效果。
开发者工作效率和工具
Credential Manager
Android 14 将 Credential Manager 添加为平台 API,并通过使用 Google Play 服务的 Jetpack 库,向后额外支持 Android 4.4(API 级别 19)设备。Credential Manager 旨在通过 API 使用用户配置的凭据提供程序检索和存储凭据,让用户更轻松地登录。Credential Manager 在单个 API 中支持多种登录方法,包括用户名和密码、通行密钥和联合登录解决方案(如“使用 Google 账号登录”)。
通行密钥具有许多优势。例如,通行密钥是基于业界标准构建的,可在各种不同的操作系统和浏览器生态系统中使用,并且可用于网站和应用。
如需了解详情,请参阅 Credential Manager 和通行密钥文档以及介绍 Credential Manager 和通行密钥的博文。
健康数据共享
Health Connect is an on-device repository for user health and fitness data. It allows users to share data between their favorite apps, with a single place to control what data they want to share with these apps.
On devices running Android versions prior to Android 14, Health Connect is available to download as an app on the Google Play store. Starting with Android 14, Health Connect is part of the platform and receives updates through Google Play system updates without requiring a separate download. With this, Health Connect can be updated frequently, and your apps can rely on Health Connect being available on devices running Android 14 or higher. Users can access Health Connect from the Settings in their device, with privacy controls integrated into the system settings.
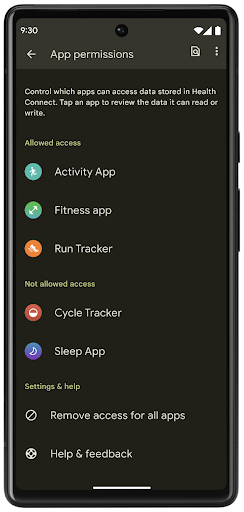
Health Connect includes several new features in Android 14, such as exercise routes, allowing users to share a route of their workout which can be visualized on a map. A route is defined as a list of locations saved within a window of time, and your app can insert routes into exercise sessions, tying them together. To ensure that users have complete control over this sensitive data, users must allow sharing individual routes with other apps.
For more information, see the Health Connection documentation and the blogpost on What's new in Android Health.
OpenJDK 17 更新
Android 14 continues the work of refreshing Android's core libraries to align with the features in the latest OpenJDK LTS releases, including both library updates and Java 17 language support for app and platform developers.
The following features and improvements are included:
- Updated approximately 300
java.baseclasses to Java 17 support. - Text Blocks, which introduce multi-line string literals to the Java programming language.
- Pattern Matching for instanceof, which allows an object to
be treated as having a specific type in an
instanceofwithout any additional variables. - Sealed classes, which allow you restrict which classes and interfaces can extend or implement them.
Thanks to Google Play system updates (Project Mainline), over 600 million devices are enabled to receive the latest Android Runtime (ART) updates that include these changes. This is part of our commitment to give apps a more consistent, secure environment across devices, and to deliver new features and capabilities to users independent of platform releases.
Java and OpenJDK are trademarks or registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
针对应用商店的改进
Android 14 引入了多个 PackageInstaller API,可帮助应用商店改善其用户体验。
下载之前请求批准安装
安装或更新应用可能需要用户批准。例如,当使用 REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES 权限的安装程序尝试安装新应用时。在之前的 Android 版本中,只有在将 APK 写入安装会话并且提交会话后,应用商店才能请求用户批准。
从 Android 14 开始,requestUserPreapproval() 方法可让安装程序在提交安装会话之前请求用户批准。此项改进可让应用商店将任何 APK 的下载操作推迟到用户批准安装之后。此外,用户批准安装后,应用商店可以在后台下载并安装应用,而不会干扰用户。
承担未来更新的责任
借助 setRequestUpdateOwnership() 方法,安装程序可以向系统表明它打算负责将被安装的应用未来的更新。此 capability 可实现更新所有权强制执行,即仅允许更新所有者为应用安装自动更新。更新所有权强制执行有助于确保用户仅收到来自预期应用商店的更新。
任何其他安装程序(包括使用 INSTALL_PACKAGES 权限的安装程序)都必须获得用户的明确批准,才能安装更新。如果用户决定继续从其他来源安装更新,则会失去更新所有权。
在干扰较少的时段更新应用
应用商店通常希望避免更新正在使用的应用,因为这会导致应用正在运行的进程被终止,而这可能会中断用户正在执行的操作。
从 Android 14 开始,InstallConstraints API 让安装程序可以确保其应用更新在适当的时机进行。例如,应用商店可以调用 commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() 方法来确保仅在用户不再与相应应用互动时才进行更新。
无缝安装可选拆分
借助拆分 APK,应用的功能可以通过单独的 APK 文件提供,而不是以单体式 APK 的形式提供。借助拆分 APK,应用商店可以优化不同应用组件的提供。例如,应用商店可能会根据目标设备的属性进行优化。自在 API 级别 22 中引入以来,PackageInstaller API 一直支持拆分。
在 Android 14 中,setDontKillApp() 方法可让安装程序指明在安装新的拆分项时应用的运行进程不应终止。应用商店可以使用此功能,在用户使用应用时无缝安装应用的新功能。
应用元数据软件包
从 Android 14 开始,Android 软件包安装程序可让您指定应用元数据(例如数据安全做法),以在 Google Play 等应用商店页面上架。
检测用户何时截取设备屏幕截图
为了打造更加标准化的屏幕截图检测体验,Android 14 引入了可保护隐私的屏幕截图检测 API。借助此 API,应用可以按 activity 注册回调。如果用户在该 activity 可见时截取屏幕截图,系统会调用这些回调并通知用户。
用户体验
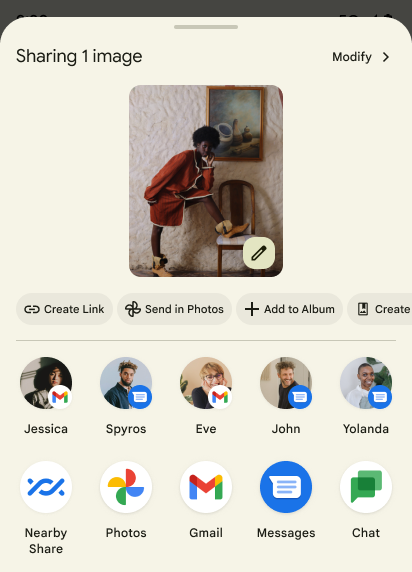
Sharesheet 自定义操作和经过改进的排名系统
Android 14 updates the system sharesheet to support custom app actions and more informative preview results for users.
Add custom actions
With Android 14, your app can add custom actions to the system sharesheet it invokes.
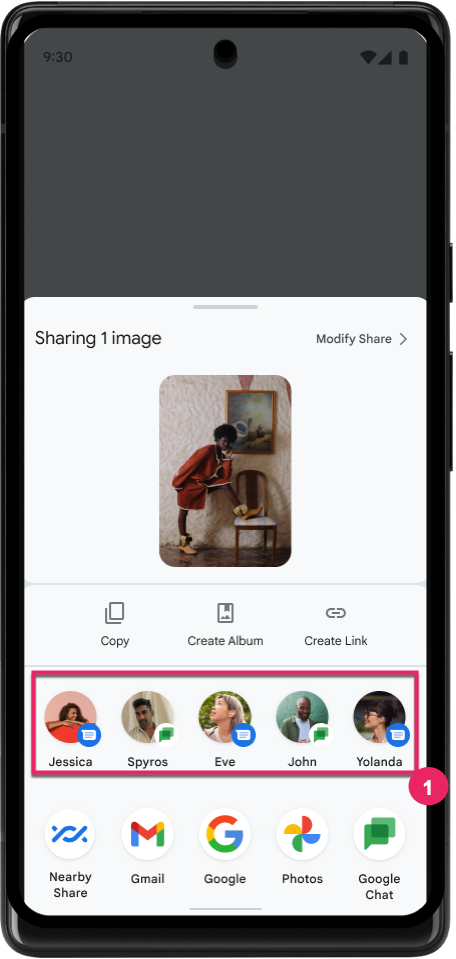
Improve ranking of Direct Share targets
Android 14 uses more signals from apps to determine the ranking of the direct share targets to provide more helpful results for the user. To provide the most useful signal for ranking, follow the guidance for improving rankings of your Direct Share targets. Communication apps can also report shortcut usage for outgoing and incoming messages.
支持内置和自定义预测性返回动画
Android 13 introduced the predictive back-to-home animation behind a developer option. When used in a supported app with the developer option enabled, swiping back shows an animation indicating that the back gesture exits the app back to the home screen.
Android 14 includes multiple improvements and new guidance for Predictive Back:
- You can set
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueto opt in to predictive back system animations per-Activity instead of for the entire app. - We've added new system animations to accompany the back-to-home animation from Android 13. The new system animations are cross-activity and cross-task, which you get automatically after migrating to Predictive Back.
- We've added new Material Component animations for Bottom sheets, Side sheets, and Search.
- We've created design guidance for creating custom in-app animations and transitions.
- We've added new APIs to support custom in-app transition animations:
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- Use
overrideActivityTransitioninstead ofoverridePendingTransitionfor transitions that respond as the user swipes back.
With this Android 14 preview release, all features of Predictive Back remain behind a developer option. See the developer guide to migrate your app to predictive back, as well as the developer guide to creating custom in-app transitions.
大屏设备制造商按应用替换项
Per-app overrides enable device manufacturers to change the behavior of apps on large screen devices. For example, the FORCE_RESIZE_APP override instructs the system to resize the app to fit display dimensions (avoiding size compatibility mode) even if resizeableActivity="false" is set in the app manifest.
Overrides are intended to improve the user experience on large screens.
New manifest properties enable you to disable some device manufacturer overrides for your app.
大屏设备用户按应用替换项
Per-app overrides change the behavior of apps on large screen devices. For example, the OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE device manufacturer override sets the app aspect ratio to 16:9 regardless of the app's configuration.
Android 14 QPR1 enables users to apply per‑app overrides by means of a new settings menu on large screen devices.
应用屏幕共享
借助应用界面共享功能,用户可以在录制屏幕内容时共享应用窗口,而不是整个设备屏幕。
在应用屏幕共享模式下,状态栏、导航栏、通知和其他系统界面元素会从共享显示屏中排除。系统只会分享所选应用的内容。
应用屏幕共享功能可让用户运行多个应用,但将内容共享限制为单个应用,从而提高工作效率并保护隐私。
Pixel 8 Pro 上由 LLM 提供支持的 Gboard 智能回复功能
On Pixel 8 Pro devices with the December Feature Drop, developers can try out higher-quality smart replies in Gboard powered by on-device Large Language Models (LLMs) running on Google Tensor.
This feature is available as a limited preview for US English in WhatsApp, Line, and KakaoTalk. It requires using a Pixel 8 Pro device with Gboard as your keyboard.
To try it out, first enable the feature in Settings > Developer Options > AiCore Settings > Enable Aicore Persistent.
Next, open a conversation in a supported app to see LLM-powered Smart Reply in Gboard's suggestion strip in response to incoming messages.
图形
路径可查询和插值
Android 的 Path API 是一种强大且灵活的机制,可用于创建和渲染矢量图形,能够描边或填充路径、根据线段或二次曲线或立方曲线构建路径、执行布尔运算以获取更复杂的形状,或同时执行所有这些操作。但有一个限制是,您无法了解 Path 对象中实际包含的内容;该对象的内部信息在创建后对调用方是不透明的。
如需创建 Path,您可以调用 moveTo()、lineTo() 和 cubicTo() 等方法来添加路径段。但是,无法询问该路径有哪些片段,因此您必须在创建时保留该信息。
从 Android 14 开始,您可以查询路径以了解其内部内容。首先,您需要使用 Path.getPathIterator API 获取 PathIterator 对象:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
接下来,您可以调用 PathIterator 逐个遍历片段,并检索每个片段的所有必要数据。以下示例使用了 PathIterator.Segment 对象,它会为您打包数据:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator 还有一个非分配版 next(),您可以在其中传入缓冲区来保存点数据。
查询 Path 数据的一个重要用例是插值。例如,您可能想在两个不同的路径之间添加动画(或变形)。为了进一步简化该用例,Android 14 针对 Path 还包含 interpolate() 方法。假设两个路径具有相同的内部结构,interpolate() 方法会使用该插值结果创建一个新的 Path。以下示例返回了一个形状介于 path 和 otherPath 之间的一半(线性插值为 0.5)的路径:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
Jetpack graphics-path 库也为早期版本的 Android 启用了类似的 API。
使用顶点着色器和片段着色器的自定义网格
Android has long supported drawing triangle meshes with custom shading, but the input mesh format has been limited to a few predefined attribute combinations. Android 14 adds support for custom meshes, which can be defined as triangles or triangle strips, and can, optionally, be indexed. These meshes are specified with custom attributes, vertex strides, varying, and vertex and fragment shaders written in AGSL.
The vertex shader defines the varyings, such as position and color, while the
fragment shader can optionally define the color for the pixel, typically by
using the varyings created by the vertex shader. If color is provided by the
fragment shader, it is then blended with the current Paint
color using the blend mode selected when
drawing the mesh. Uniforms can be passed
into the fragment and vertex shaders for additional flexibility.
Canvas 的硬件缓冲区渲染器
协助使用 Android 的 Canvas API 通过
硬件加速至 HardwareBuffer、Android 14
引入了 HardwareBufferRenderer。如果您的用例涉及通过 SurfaceControl 与系统合成器通信以实现低延迟绘制,此 API 特别有用。

