Android 14 wprowadza wiele przydatnych funkcji i interfejsów API dla deweloperów. Poniższe materiały pomogą Ci poznać funkcje aplikacji i zacząć korzystać z powiązanych interfejsów API.
Szczegółową listę dodanych, zmodyfikowanych i usuniętych interfejsów API znajdziesz w raporcie o różnicach w interfejsach API. Szczegółowe informacje o dodanych interfejsach API znajdziesz w dokumentacji interfejsu Android API. W przypadku Androida 14 poszukaj interfejsów API dodanych na poziomie 34. Aby dowiedzieć się więcej o obszarach, w których zmiany na platformie mogą mieć wpływ na Twoje aplikacje, zapoznaj się ze zmianami w działaniu Androida 14 w przypadku aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 14 i w przypadku wszystkich aplikacji.
Internacjonalizacja
Wybór języka według aplikacji
Android 14 rozszerza funkcje języka na poziomie aplikacji, które zostały wprowadzone w Androidzie 13 (poziom API 33), o te dodatkowe możliwości:
Automatyczne generowanie
localeConfigw aplikacji: od wersji Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 i AGP 8.1.0-alpha07 możesz skonfigurować aplikację tak, aby automatycznie obsługiwała ustawienia języka na poziomie aplikacji. Na podstawie zasobów projektu wtyczka Androida do obsługi Gradle generuje plikLocaleConfigi dodaje do niego odwołanie w pliku manifestu końcowego. Dzięki temu nie musisz już tworzyć ani aktualizować tego pliku ręcznie. AGP korzysta z zasobów w folderachresw modułach aplikacji oraz z zależnych modułów bibliotek, aby określić lokalizacje, które mają być uwzględnione w plikuLocaleConfig.Dynamiczne aktualizacje
localeConfigaplikacji: użyj metodsetOverrideLocaleConfig()igetOverrideLocaleConfig()wLocaleManager, aby dynamicznie aktualizować listę obsługiwanych języków aplikacji w ustawieniach systemu urządzenia. Dzięki tej elastyczności możesz dostosować listę obsługiwanych języków w danym regionie, przeprowadzać eksperymenty A/B lub przesyłać zaktualizowaną listę lokalizacji, jeśli Twoja aplikacja korzysta z push na serwerze do celów lokalizacji.Widoczność języka aplikacji w edytorach metody wprowadzania: edytorzy metody wprowadzania mogą korzystać z metody
getApplicationLocales(), aby sprawdzić język bieżącej aplikacji i dostosować do niego język edytora metody wprowadzania.
Grammatical Inflection API
3 miliardy ludzi mówi językami z płcią: językami, w których kategorie gramatyczne (np. rzeczowniki, czasowniki, przymiotniki i przyimki) odmieniają się w zależności od płci osób i rzeczy, do których się zwracamy lub o których mówimy. Tradycyjnie wiele języków z płcią gramatyczną używa męskiej formy gramatycznej jako domyślnej lub uniwersalnej.
Zwracanie się do użytkowników w niewłaściwym rodzaju gramatycznym, np. do kobiet w męskim rodzaju gramatycznym, może negatywne wpłynąć na ich wyniki i postawę. Z kolei interfejs z językiem, który poprawnie odzwierciedla płeć gramatyczną użytkownika, może zwiększyć zaangażowanie użytkowników i zapewnić bardziej spersonalizowane i naturalne wrażenia.
Aby ułatwić Ci tworzenie interfejsu przyjaznego dla użytkownika w językach z rodzajami gramatycznymi, Android 14 wprowadza interfejs Inflection API, który umożliwia dodanie obsługi rodzaju gramatycznego bez konieczności refaktoryzacji aplikacji.
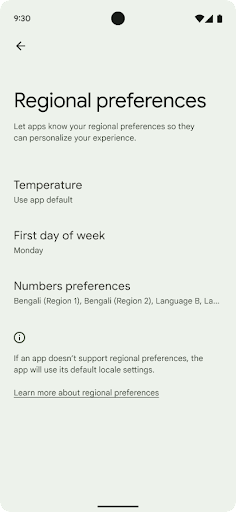
Preferencje regionalne
Preferencje regionalne pozwalają użytkownikom personalizować jednostki temperatury. dnia tygodnia i systemy numeracji. Europejczyk mieszkający w Stanach Zjednoczonych może preferować jednostki temperatury w stopniach Celsjusza zamiast w stopniach Fahrenheita, a aplikacje powinny traktować poniedziałek jako początek tygodnia zamiast niedzieli, która jest domyślną jednostką w Stanach Zjednoczonych.
Nowe menu ustawień Androida dla tych ustawień da użytkownikom
wykrywalną i scentralizowaną lokalizację na potrzeby zmiany ustawień aplikacji. Te ustawienia są również zachowywane podczas tworzenia kopii zapasowej i przywracania. Kilka interfejsów API i intencji, takich jak getTemperatureUnit i getFirstDayOfWeek, przyznaje aplikacji uprawnienia do odczytu ustawień użytkownika, dzięki czemu aplikacja może dostosowywać sposób wyświetlania informacji. Możesz też zarejestrować
BroadcastReceiver włączona
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED.
obsługi zmian konfiguracji języka w przypadku zmiany preferencji regionalnych.
Aby znaleźć te ustawienia, otwórz aplikację Ustawienia i kliknij System > Języki wejście > Ustawienia regionalne.
Ułatwienia dostępu
Nieliniowe skalowanie czcionki do 200%
Od Androida 14 system obsługuje skalowanie czcionek do 200%, co zapewnia użytkownikom dodatkowe opcje ułatwień dostępu.
Aby zapobiec nadmiernemu powiększaniu dużych elementów tekstowych na ekranie, system stosuje nieliniową krzywą skalowania. Ta strategia skalowania oznacza, że duży tekst nie jest skalowany w tym samym tempie co mniejszy. Nieliniowe skalowanie czcionki pomaga zachować proporcjonalną hierarchię między elementami o różnych rozmiarach, a jednocześnie zmniejsza problemy związane z liniowym skalowaniem tekstu przy dużych wartościach (np. ucinanie tekstu lub utrudnianie czytania tekstu z powodu bardzo dużych rozmiarów wyświetlacza).
Testowanie aplikacji z nieliniowym skalowaniem czcionki
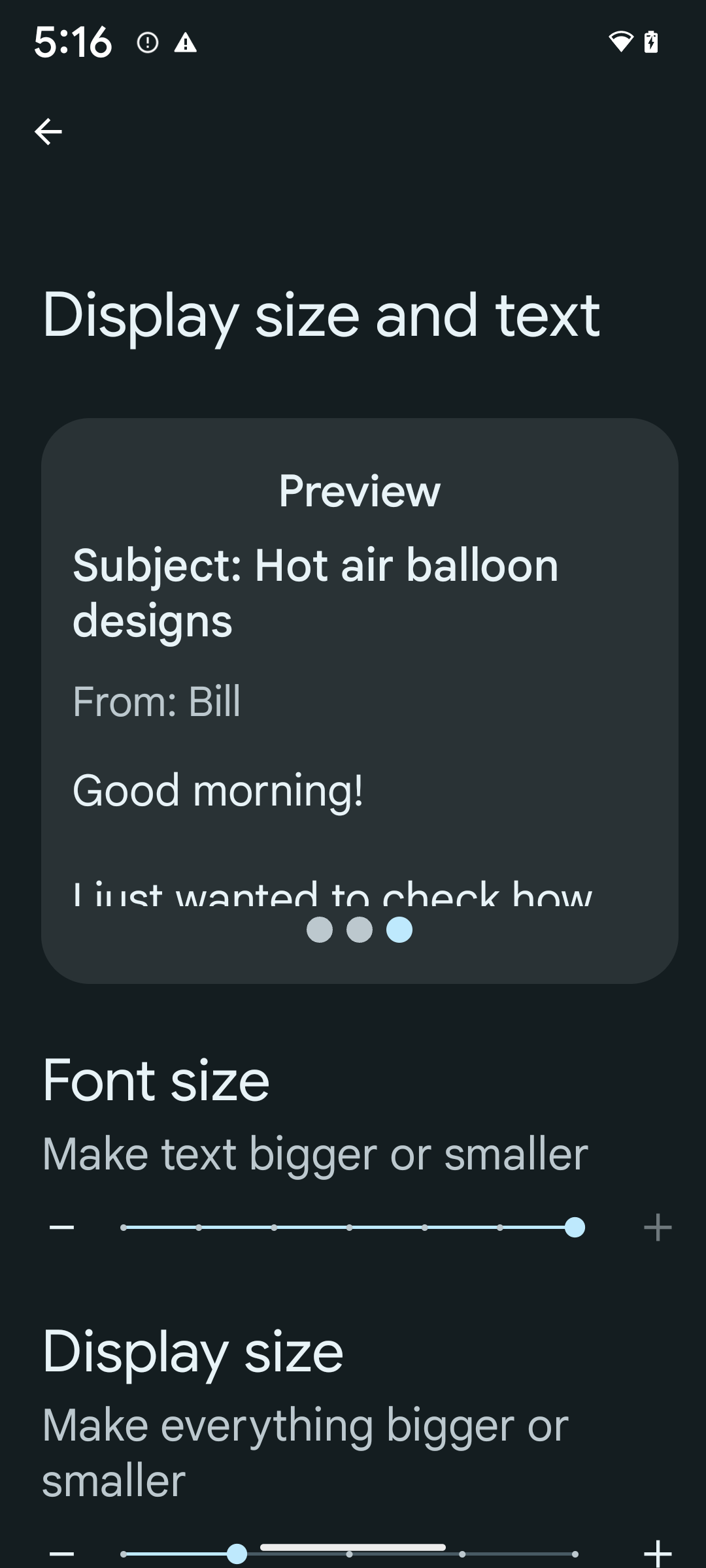
Jeśli do określania rozmiaru tekstu używasz już skalowalnych pikseli (sp), te dodatkowe opcje i ulepszenia skalowania są automatycznie stosowane do tekstu w aplikacji. Mimo to warto przeprowadzić testy interfejsu z włączonym maksymalnym rozmiarem czcionki (200%), aby upewnić się, że aplikacja prawidłowo stosuje rozmiary czcionek i może obsługiwać większe rozmiary bez wpływu na użyteczność.
Aby włączyć rozmiar czcionki 200%, wykonaj te czynności:
- Otwórz aplikację Ustawienia i kliknij Ułatwienia dostępu > Rozmiar wyświetlacza i tekst.
- W przypadku opcji Rozmiar czcionki klikaj ikonę plusa (+), aż włączone zostanie ustawienie maksymalnego rozmiaru czcionki, jak pokazano na ilustracji w tej sekcji.
Używaj skalowanych pikseli (sp) jako jednostek rozmiaru tekstu
Pamiętaj, aby zawsze określać rozmiary tekstu w jednostkach sp. Gdy aplikacja używa jednostek sp, Android może zastosować preferowany przez użytkownika rozmiar tekstu i odpowiednio go przeskalować.
Nie używaj jednostek sp w przypadku dopełnienia ani nie określaj wysokości widoku przy założeniu domyślnego dopełnienia: w przypadku nieliniowego skalowania czcionek wymiary sp mogą nie być proporcjonalne, więc 4 sp + 20 sp może nie być równe 24 sp.
Przeliczanie jednostek skalowalnych pikseli (sp)
Użyj funkcji TypedValue.applyDimension(), aby przekonwertować jednostki sp na piksele, a funkcji TypedValue.deriveDimension(), aby przekonwertować piksele na jednostki sp. Te metody automatycznie stosują odpowiednią nieliniową krzywą skalowania.
Unikaj kodowania na stałe równań za pomocą
Configuration.fontScale lub
DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity. Skalowanie czcionki jest nieliniowe, więc pole scaledDensity nie jest już dokładne. Pola fontScale należy używać wyłącznie do celów informacyjnych, ponieważ czcionki nie są już skalowane za pomocą pojedynczej wartości skalarnej.
Używaj jednostek sp w przypadku lineHeight
Zawsze definiuj android:lineHeight za pomocą jednostek sp zamiast dp, aby wysokość wiersza skalowała się wraz z tekstem. W przeciwnym razie, jeśli tekst jest w jednostkach sp, a lineHeight jest w jednostkach dp lub px, nie będzie skalowany i będzie wyglądać na ściśnięty.
TextView automatycznie koryguje lineHeight, aby zachować zamierzone proporcje, ale tylko wtedy, gdy zarówno textSize, jak i lineHeight są zdefiniowane w jednostkach sp.
Aparat i multimedia
Ultra HDR w przypadku zdjęć

Android 14 obsługuje obrazy High Dynamic Range (HDR), które zachowują więcej informacji z czujnika podczas robienia zdjęcia, co umożliwia uzyskanie żywszych kolorów i większego kontrastu. Android używa formatu ultra HDR, który jest w pełni zgodny z wstecz z obrazami JPEG. Dzięki temu aplikacje mogą płynnie współpracować z obrazami HDR, wyświetlając je w standardowym zakresie dynamiki (SDR), gdy zajdzie taka potrzeba.
Przetwarzanie tych obrazów w interfejsie w HDR jest wykonywane automatycznie przez platformę, gdy aplikacja zechce używać interfejsu HDR w oknie aktywności, albo za pomocą elementu manifestu, albo w czasie działania przez wywołanieWindow.setColorMode(). Na obsługiwanych urządzeniach możesz też robić skompresowane zdjęcia Ultra
HDR. Dzięki większej liczbie kolorów odzyskanych z czujnika edytowanie w postprodukcji może być bardziej elastyczne. Pliki Gainmap powiązane z obrazami Ultra HDR mogą służyć do ich renderowania za pomocą OpenGL lub Vulkan.
Powiększanie, ustawianie ostrości, podgląd po zrobieniu zdjęcia i inne funkcje w rozszerzeniach aparatu
Android 14 ulepsza rozszerzenia aparatu, co pozwala aplikacjom na dłuższe przetwarzanie, co z kolei umożliwia uzyskiwanie lepszych zdjęć przy użyciu algorytmów wymagających dużej mocy obliczeniowej, takich jak fotografowanie przy słabym oświetleniu na obsługiwanych urządzeniach. Te funkcje zapewniają użytkownikom jeszcze większą wygodę podczas korzystania z możliwości rozszerzenia aparatu. Przykłady takich ulepszeń:
- Dynamiczna szacowana latencja przetwarzania zdjęć zapewnia znacznie dokładniejsze szacunki czasu przetwarzania zdjęć na podstawie bieżących warunków sceny i otoczenia. Wywołaj metodę
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency(), aby uzyskać obiektStillCaptureLatency, który zawiera 2 metody oszacowania opóźnienia. MetodagetCaptureLatency()zwraca szacowane opóźnienie międzyonCaptureStartedaonCaptureProcessStarted(), a metodagetProcessingLatency()zwraca szacowane opóźnienie międzyonCaptureProcessStarted()a dostępnym ostatnim przetworzonym obrazem. - Obsługa wywołań zwrotnych postępu przechwytywania, dzięki którym aplikacje mogą wyświetlać bieżący postęp długotrwałych operacji przetwarzania zdjęć. Możesz sprawdzić, czy ta funkcja jest dostępna w
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailable, a jeśli tak, zaimplementować funkcję wywołania zwrotnegoonCaptureProcessProgressed(), która ma jako parametr postęp (od 0 do 100). metadane dotyczące rozszerzenia, takie jak
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTHdo powiększania obrazu, natężenie efektu rozszerzenia, np. rozmycie tła, za pomocąEXTENSION_BOKEH.Funkcja podglądu zdjęć w rozszerzeniach aparatu, która umożliwia wyświetlenie nieprzetworzonego obrazu szybciej niż w przypadku obrazu końcowego. Jeśli rozszerzenie wydłuża czas przetwarzania, obraz po wyświetleniu może być udostępniony jako element zastępczy, aby poprawić UX, a później zastąpiony przez ostateczny obraz. Aby sprawdzić, czy ta funkcja jest dostępna, przejdź do
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable. Następnie możesz przekazać parametrOutputConfigurationdo funkcjiExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration.Obsługa
SurfaceView, która umożliwia bardziej zoptymalizowaną i energooszczędną ścieżkę renderowania podglądu.Obsługa funkcji kliknięcia, aby ustawić ostrość i powiększyć widok podczas korzystania z rozszerzenia.
Zoom na matrycy
Gdy REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE w CameraCharacteristics zawiera SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW, aplikacja może korzystać z zaawansowanych możliwości czujnika, aby zapewnić przycięty strumień RAW z tymi samymi pikselami co pełne pole widzenia, używając CaptureRequest z docelowym strumieniem RAW, dla którego ustawiono CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW.
Dzięki wdrożeniu ustawień zastąpienia żądania zaktualizowana kamera umożliwia użytkownikom sterowanie zoomem jeszcze przed przygotowaniem innych ustawień.
Bezstratny dźwięk przez USB
Android 14 obsługuje bezstratne formaty dźwięku, dzięki czemu można uzyskać dźwięk w jakości studyjnej w przypadku przewodowych słuchawek USB. Możesz wysyłać zapytania do urządzenia USB w celu uzyskania preferowanych atrybutów miksera, rejestrować słuchacza zmian w preferowanych atrybutach miksera i konfigurować atrybuty miksera za pomocą klasy AudioMixerAttributes. Ta klasa reprezentuje format, np. maskę kanału, częstotliwość próbkowania i zachowanie miksera audio. Ta klasa umożliwia przesyłanie dźwięku bezpośrednio bez miksowania, regulowania głośności ani przetwarzania efektów.
Wydajność i narzędzia dla programistów
Credential Manager
Android 14 dodaje Credential Manager jako interfejs API platformy, z dodatkowym wsparciem dla urządzeń z Androidem 4.4 (poziom interfejsu API 19) za pomocą biblioteki Jetpack korzystającej z Usług Google Play. Credential Manager ułatwia użytkownikom logowanie się dzięki interfejsom API, które pobierają i przechowują dane logowania za pomocą dostawców danych logowania skonfigurowanych przez użytkownika. Credential Manager obsługuje wiele metod logowania, w tym logowanie przy użyciu nazwy użytkownika i hasła, kluczy dostępu i rozwiązań logowania sfederowanego (np. logowania przez Google) w jednym interfejsie API.
Klucze dostępu mają wiele zalet. Na przykład klucze dostępu oparte są na standardach branżowych, mogą działać w różnych systemach operacyjnych i ekosystemach przeglądarek oraz mogą być używane zarówno w witrynach, jak i w aplikacjach.
Więcej informacji znajdziesz w dokumentacji Menedżera danych uwierzytelniających i kluczy dostępu oraz w poście na blogu na temat Menedżera danych uwierzytelniających i kluczy dostępu.
Health Connect
Health Connect to repozytorium danych o zdrowiu i kondycji fizycznej użytkownika na urządzeniu. Umożliwia ona użytkownikom udostępnianie danych między ulubionymi aplikacjami i zarządzanie w jednym miejscu danymi, które chcą udostępniać tym aplikacjom.
Na urządzeniach z Androidem w wersjach starszych niż 14 aplikację Health Connect można pobrać ze Sklepu Google Play. Od Androida 14 Zarządzanie danymi o zdrowiu jest częścią platformy i otrzymuje aktualizacje w ramach aktualizacji systemowych Google Play bez konieczności osobnego pobierania. Dzięki temu Health Connect może być często aktualizowany, a Twoje aplikacje mogą korzystać z Health Connect na urządzeniach z Androidem w wersji 14 lub nowszej. Użytkownicy mogą korzystać z Health Connect w ustawieniach urządzenia, a ustawienia prywatności są zintegrowane z ustawieniami systemu.
Health Connect zawiera kilka nowych funkcji w Androidzie 14, takich jak trasy treningów, które umożliwiają użytkownikom udostępnianie trasy treningu, którą można wyświetlić na mapie. Trasa to lista lokalizacji zapisanych w określonym przedziale czasu. Aplikacja może wstawiać trasy do sesji ćwiczeń, łącząc je ze sobą. Aby mieć pełną kontrolę nad tymi poufnymi danymi, użytkownicy muszą zezwolić na udostępnianie poszczególnych tras innym aplikacjom.
Więcej informacji znajdziesz w dokumentacji dotyczącej funkcji Health Connection oraz w poście na blogu Co nowego w Androidzie Health.
Aktualizacje OpenJDK 17
Android 14 kontynuuje proces odświeżania podstawowych bibliotek Androida, aby dostosować je do funkcji najnowszych wersji OpenJDK LTS, w tym do aktualizacji bibliotek i obsługi języka Java 17 dla deweloperów aplikacji i platform.
Dostępne są następujące funkcje i ulepszenia:
- Zaktualizowano około 300 klas
java.base, aby obsługiwały Java 17. - Blokami tekstowymi, które wprowadzają do języka programowania Java wielowierszowe ciągi znaków.
- dopasowywanie wzoru do instanceof, które umożliwia traktowanie obiektu jako mającego określony typ w
instanceofbez żadnych dodatkowych zmiennych; - Zamknięte klasy, które umożliwiają ograniczenie zakresu klas i interfejsów, które mogą je rozszerzać lub implementować.
Dzięki aktualizacjom systemowym Google Play (projekt Mainline) ponad 600 milionów urządzeń może otrzymywać najnowsze aktualizacje środowiska wykonawczego Androida (ART), które zawierają te zmiany. Jest to część naszego zobowiązania do zapewnienia aplikacjom bardziej spójnego i bezpiecznego środowiska na różnych urządzeniach oraz udostępniania użytkownikom nowych funkcji i możliwości niezależnie od wersji platformy.
Java i OpenJDK są znakami towarowymi lub zastrzeżonymi znakami towarowymi firmy Oracle lub jej podmiotów stowarzyszonych.
Ulepszenia w sklepach z aplikacjami
Android 14 wprowadza kilka interfejsów API PackageInstaller, które umożliwiają sklepom z aplikacjami poprawę wrażeń użytkowników.
Prośba o zatwierdzenie instalacji przed pobraniem
Instalacja lub aktualizacja aplikacji może wymagać zaakceptowania przez użytkownika.
Na przykład gdy instalator korzystający z uprawnienia REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES próbuje zainstalować nową aplikację. W poprzednich wersjach Androida sklepy z aplikacjami mogą prosić o pozwolenie użytkownika dopiero po zapisaniu plików APK w sesji instalacji i zaakceptowaniu sesji.
Od Androida 14 metoda requestUserPreapproval() pozwala instalatorom poprosić o pozwolenie użytkownika przed rozpoczęciem sesji instalacji. Ta funkcja umożliwia opóźnienie pobierania plików APK do momentu zatwierdzenia instalacji przez użytkownika. Ponadto po zatwierdzeniu instalacji przez użytkownika aplikacja może pobrać i zainstalować aplikację w tle bez przerywania pracy użytkownika.
Przejmowanie odpowiedzialności za przyszłe aktualizacje
Metoda setRequestUpdateOwnership() pozwala instalatorowi wskazać systemowi, że będzie odpowiedzialny za przyszłe aktualizacje instalowanej aplikacji. Ta funkcja umożliwia egzekwowanie własności aktualizacji, co oznacza, że tylko właściciel aktualizacji może instalować automatyczne aktualizacje aplikacji. Egzekwowanie własności aktualizacji pomaga zapewnić, aby użytkownicy otrzymywali aktualizacje tylko z oczekiwanego sklepu z aplikacjami.
Aby zainstalować aktualizację, każdy inny instalator, w tym korzystający z uprawnienia INSTALL_PACKAGES, musi uzyskać wyraźną zgodę użytkownika. Jeśli użytkownik zdecyduje się na przeprowadzenie aktualizacji z innego źródła, utraci prawo własności do aktualizacji.
Aktualizuj aplikacje w godzinach, w których nie zakłócasz pracy.
Sklepy z aplikacjami zwykle nie chcą aktualizować aplikacji, która jest aktywnie używana, ponieważ powoduje to przerwanie jej procesów, co może zakłócić działanie użytkownika.
Od Androida 14 interfejs API InstallConstraints daje instalatorom możliwość zapewnienia, że aktualizacje aplikacji będą się odbywać w odpowiednim momencie. Sklep z aplikacjami może na przykład wywołać metodę commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet(), aby upewnić się, że aktualizacja zostanie zaakceptowana tylko wtedy, gdy użytkownik nie będzie już korzystać z aplikacji.
Bezproblemowe instalowanie opcjonalnych podziałów
W przypadku podzielonych plików APK funkcje aplikacji mogą być dostarczane w osobnych plikach APK, a nie jako monolityczny plik APK. Dzielone pliki APK umożliwiają sklepom z aplikacjami optymalizację dostarczania różnych komponentów aplikacji. Sklepy z aplikacjami mogą na przykład optymalizować na podstawie właściwości urządzenia docelowego. Interfejs API PackageInstaller obsługuje dzielenie na części od czasu wprowadzenia na poziomie 22 interfejsu API.
W Androidzie 14 metoda setDontKillApp() umożliwia instalatorowi wskazanie, że działające procesy aplikacji nie powinny zostać zakończone podczas instalowania nowych części. Sklepy z aplikacjami mogą używać tej funkcji do płynnego instalowania nowych funkcji aplikacji, gdy użytkownik z niej korzysta.
Pakiety metadanych aplikacji
Od Androida 14 instalator pakietów Androida umożliwia określanie metadanych aplikacji, takich jak zasady bezpieczeństwa danych, które mają być wyświetlane na stronach sklepów z aplikacjami, np. w Google Play.
Wykrywanie, kiedy użytkownicy robią zrzuty ekranu urządzenia
Aby zapewnić bardziej standardowe wykrywanie zrzutów ekranu, Android 14 wprowadza interfejs API do wykrywania zrzutów ekranu, który chroni prywatność. Ten interfejs API umożliwia aplikacjom rejestrowanie wywołań zwrotnych dla poszczególnych aktywności. Te wywołania zwrotne są wywoływane, a użytkownik jest powiadamiany, gdy zrobi zrzut ekranu podczas wyświetlania danego działania.
Interfejs użytkownika
Działania niestandardowe na arkuszu udostępniania i ulepszone rankingowanie
Android 14 aktualizuje systemowy panel udostępniania, aby obsługiwać niestandardowe działania aplikacji i bardziej szczegółowe podglądowe wyniki dla użytkowników.
Dodawanie działań niestandardowych
W Androidzie 14 aplikacja może dodawać niestandardowe działania do wywoływanego przez nią panelu udostępniania.
Ulepszanie rankingu celów udostępniania bezpośredniego
Android 14 używa większej liczby sygnałów z aplikacji, aby określać ranking celów udostępniania bezpośredniego i w ten sposób wyświetlać bardziej przydatne wyniki użytkownikom. Aby zapewnić najbardziej przydatny sygnał dotyczący rankingu, postępuj zgodnie ze wskazówkami dotyczącymi ulepszania pozycji docelowych w ramach funkcji Direct Share. Aplikacje do komunikacji mogą też zgłaszać użycie skrótu w przypadku wychodzących i przyjmowanych wiadomości.
Obsługa wbudowanych i niestandardowych animacji przewidywanego przejścia wstecz
Android 13 wprowadził przewidywaną animację powrotu do ekranu głównego, która jest dostępna dla deweloperów. Gdy ta opcja jest włączona w obsługiwanej aplikacji, przesunięcie w dół powoduje wyświetlenie animacji wskazującej, że gest cofania powoduje wyjście z aplikacji i powrót do ekranu głównego.
Android 14 zawiera wiele ulepszeń i nowe wskazówki dotyczące funkcji Wsteczne cofanie:
- Możesz ustawić
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=true, aby włączyć przewidywane animacje powrotu w poszczególnych aktywnościach zamiast w całej aplikacji. - Dodaliśmy nowe animacje systemu, które towarzyszą animacji powrotu do ekranu głównego w Androidzie 13. Nowe animacje systemowe są wspólne dla różnych działań i zadań. Otrzymasz je automatycznie po migracji na przewidywane przejście wstecz.
- Dodaliśmy nowe animacje komponentów w stylu Material Design dla arkuszy dolnych, arkuszy bocznych i wyszukiwarki.
- Przygotowaliśmy wskazówki dotyczące projektowania niestandardowych animacji i przejść w aplikacji.
- Dodaliśmy nowe interfejsy API, aby obsługiwać niestandardowe animacje przejść w aplikacji:
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- Użyj
overrideActivityTransitionzamiastoverridePendingTransitionw przypadku przejść, które reagują na gest przesunięcia palcem w lewo.
W tej wersji wstępnej Androida 14 wszystkie funkcje przewidywania powrotów pozostają dostępne tylko dla deweloperów. Zapoznaj się z przewodnikiem dla deweloperów dotyczącym migracji aplikacji na przewidywane cofnięcie oraz z przewodnikiem dla deweloperów dotyczącym tworzenia niestandardowych przejść w aplikacji.
Zastąpienia ustawień producenta urządzenia z dużym ekranem dla poszczególnych aplikacji
Zastąpienia dotyczące aplikacji umożliwiają producentom urządzeń zmianę działania aplikacji na urządzeniach z dużym ekranem. Na przykład zastąpienie FORCE_RESIZE_APP instruuje system, aby zmienił rozmiar aplikacji, aby pasowała do wyświetlanych wymiarów (unikając trybu zgodności rozmiaru), nawet jeśli w manifeście aplikacji ustawiono resizeableActivity="false".
Zastąpienia mają na celu poprawę wrażeń użytkowników na dużych ekranach.
Nowe właściwości pliku manifestu umożliwiają wyłączenie w przypadku aplikacji niektórych zastąpień producenta urządzenia.
Zastąpienia ustawień aplikacji dla użytkowników dużych ekranów
Zastąpienia dla poszczególnych aplikacji zmieniają zachowanie aplikacji na urządzeniach z dużym ekranem. Na przykład OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE zastąpienie producenta urządzenia ustawia format obrazu aplikacji na 16:9 niezależnie od konfiguracji aplikacji.
Android 14 QPR1 umożliwia użytkownikom stosowanie zastąpienia dla poszczególnych aplikacji za pomocą nowego menu ustawień na urządzeniach z dużym ekranem.
Udostępnianie ekranu aplikacji
Udostępnianie ekranu aplikacji umożliwia użytkownikom udostępnianie okna aplikacji zamiast całego ekranu urządzenia podczas nagrywania treści na ekranie.
Podczas udostępniania ekranu aplikacji pasek stanu, pasek nawigacji, powiadomienia i inne elementy interfejsu systemu nie są uwzględniane na wyświetlaczu. Udostępniona jest tylko zawartość wybranej aplikacji.
Udostępnianie ekranu aplikacji zwiększa produktywność i prywatność, ponieważ pozwala użytkownikom uruchamiać wiele aplikacji, ale ogranicza udostępnianie treści do jednej aplikacji.
Inteligentna odpowiedź na klawiaturze Gboard na Pixelu 8 Pro oparta na LLM
Na urządzeniach Pixel 8 Pro z aktualizacją z listopada deweloperzy mogą wypróbować inteligentne odpowiedzi lepszej jakości w klawiaturze Gboard, które są obsługiwane przez duże modele językowe (LLM) działające na procesorze Google Tensor.
Ta funkcja jest dostępna w wersji testowej w języku angielskim (USA) w aplikacji WhatsApp, Line i KakaoTalk. Wymaga użycia urządzenia Pixel 8 Pro z klawiaturą Gboard.
Aby wypróbować tę funkcję, najpierw włącz ją w sekcji Ustawienia > Opcje programisty > Ustawienia AICore > Włącz trwałe AICore.
Następnie otwórz rozmowę w obsługiwanej aplikacji, aby zobaczyć inteligentną odpowiedź w pasku sugestii Gboard, która jest obsługiwana przez LLM.
Grafika
Ścieżki można wyszukiwać i interpolować
Interfejs API Path na Androida to zaawansowany i elastyczny mechanizm tworzenia i renderowania grafiki wektorowej, który umożliwia kreślenie lub wypełnianie ścieżki, tworzenie ścieżki z segmentów linii albo krzywych kwadratowych i krzywych sześciennych, wykonywanie operacji logicznych w celu uzyskania jeszcze bardziej złożonych kształtów lub wszystkich tych elementów jednocześnie. Ograniczeniem jest możliwość sprawdzenia, co tak naprawdę znajduje się w obiekcie ścieżki. Elementy wewnętrzne obiektu są nieprzezroczyste po jego utworzeniu.
Aby utworzyć Path, użyj metod wywoływania takich jak moveTo(), lineTo() i cubicTo(), aby dodać segmenty ścieżki. Nie ma jednak możliwości określenia, jakie segmenty mają się znaleźć na tej ścieżce, więc musisz zachować te informacje w momencie tworzenia.
Począwszy od Androida 14 możesz wysyłać zapytania dotyczące ścieżek, aby dowiedzieć się, co się na nich znajduje.
Najpierw musisz uzyskać obiekt PathIterator, korzystając z interfejsu API Path.getPathIterator:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
Następnie możesz wywołać metodę PathIterator, by iterować po kolei segmenty i pobrać wszystkie niezbędne dane dla każdego z nich. W tym przykładzie użyto obiektów PathIterator.Segment, które gromadzą dane w formie pakietów:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
Funkcja PathIterator ma też wersję next(), która nie przydziela pamięci, i możesz jej użyć do przekazania bufora, aby przechowywać dane punktowe.
Jednym z ważnych zastosowań zapytań o dane Path jest interpolacja. Możesz na przykład chcieć animować (czyli przekształcać) 2 różne ścieżki. Aby jeszcze bardziej uprościć ten przypadek użycia, Android 14 zawiera też metodę interpolate() w Path. Zakładając, że 2 ścieżki mają taką samą strukturę wewnętrzną, metoda interpolate() tworzy nowy Path z tym interpolowanym wynikiem. Ten przykład zwraca ścieżkę, która jest połową (interpolacja liniowa 0,5) ścieżki path i otherPath:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
Biblioteka Jetpack graphics-path umożliwia korzystanie z podobnych interfejsów API również w starszych wersjach Androida.
Niestandardowe siatki z shaderami wierzchołków i fragmentów
Android od dawna obsługuje rysowanie trójkątnych siatek z niestandardowym cieniowaniem, ale format siatki wejściowej był ograniczony do kilku wstępnie zdefiniowanych kombinacji atrybutów. Android 14 obsługuje niestandardowe siatki, które można zdefiniować jako trójkąty lub trójkątne paski, a także opcjonalnie posortować. Te siatki są określane za pomocą niestandardowych atrybutów, kroków wierzchołków, zmiennych oraz shaderów wierzchołków i fragmentów napisanych w AGSL.
Shader wierzchołka definiuje zmienne, takie jak pozycja i kolor, a shader fragmentu może opcjonalnie zdefiniować kolor piksela, zwykle za pomocą zmiennych utworzonych przez shader wierzchołka. Jeśli kolor jest dostarczany przez fragment shadera, jest on mieszany z bieżącym kolorem Paint za pomocą trybu mieszania wybranego podczas rysowania siatki. Tablice jednolite można przekazywać do shaderów wierzchołkowych i fragmentów, aby zwiększyć elastyczność.
Renderowanie bufora sprzętowego w Canvas
Aby ułatwić korzystanie z interfejsu API Canvas w Androidzie do rysowania z przyspieszeniem sprzętowym w HardwareBuffer, Android 14 wprowadza HardwareBufferRenderer. Ten interfejs API jest
szczególnie przydatne, gdy Twój przypadek użycia obejmuje komunikację z systemem
kompozytor do SurfaceControl, by zapewnić małe opóźnienie
rysunek.
