Wie bei früheren Versionen enthält Android 15 Verhaltensänderungen, die sich auf Ihre App auswirken können. Die folgenden Verhaltensänderungen gelten ausschließlich für Apps, die auf Android 15 oder höher ausgerichtet sind. Wenn Ihre App auf Android 15 oder höher ausgerichtet ist, sollten Sie sie gegebenenfalls so anpassen, dass sie diese Verhaltensweisen richtig unterstützt.
Sehen Sie sich auch die Liste der Verhaltensänderungen an, die sich auf alle Apps auswirken, die unter Android 15 ausgeführt werden, unabhängig vom targetSdkVersion Ihrer App.
Hauptfunktion
In Android 15 werden verschiedene Kernfunktionen des Android-Systems geändert oder erweitert.
Änderungen an Vordergrunddiensten
Mit Android 15 nehmen wir die folgenden Änderungen an Diensten im Vordergrund vor.
- Verhalten bei Zeitüberschreitung des Diensts „Datensynchronisierung im Vordergrund“
- Neuer Typ für Dienste im Vordergrund zur Medienverarbeitung
- Einschränkungen für
BOOT_COMPLETED-Übertragungsempfänger, die Dienste im Vordergrund starten - Einschränkungen beim Starten von Diensten im Vordergrund, während eine App die Berechtigung
SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOWhat
Zeitüberschreitung des Diensts „Datensynchronisierung im Vordergrund“
Unter Android 15 wird für dataSync ein neues Zeitlimit für Apps eingeführt, die auf Android 15 (API-Level 35) oder höher ausgerichtet sind. Dies gilt auch für den neuen Diensttyp mediaProcessing im Vordergrund.
Das System erlaubt es den dataSync-Diensten einer App, innerhalb eines Zeitraums von 24 Stunden insgesamt 6 Stunden lang ausgeführt zu werden. Danach ruft das System die Methode Service.onTimeout(int, int) des laufenden Dienstes auf (in Android 15 eingeführt). Derzeit hat der Dienst einige Sekunden Zeit, um Service.stopSelf() aufzurufen. Wenn Service.onTimeout() aufgerufen wird, gilt der Dienst nicht mehr als Dienst im Vordergrund. Wenn der Dienst Service.stopSelf() nicht aufruft, löst das System eine interne Ausnahme aus. Die Ausnahme wird mit der folgenden Meldung in Logcat protokolliert:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type dataSync did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
So vermeiden Sie Probleme mit dieser Verhaltensänderung:
- Lassen Sie Ihren Dienst die neue
Service.onTimeout(int, int)-Methode implementieren. Wenn Ihre App den Callback empfängt, müssen Sie innerhalb weniger SekundenstopSelf()anrufen. Wenn Sie die App nicht sofort beenden, generiert das System einen Fehler. - Die
dataSync-Dienste deiner App dürfen innerhalb von 24 Stunden nicht länger als sechs Stunden ausgeführt werden, es sei denn, der Nutzer interagiert mit der App und setzt den Timer zurück. - Starten Sie
dataSyncDienste im Vordergrund nur als Folge einer direkten Nutzerinteraktion. Da sich Ihre App beim Start des Dienstes im Vordergrund befindet, hat Ihr Dienst die vollen sechs Stunden Zeit, nachdem die App in den Hintergrund gewechselt ist. - Verwenden Sie stattdessen eine alternative API.
dataSync
Wenn die dataSync-Dienste im Vordergrund Ihrer App in den letzten 24 Stunden sechs Stunden lang ausgeführt wurden, können Sie keinen weiteren dataSync-Dienst im Vordergrund starten, es sei denn, der Nutzer hat Ihre App in den Vordergrund gebracht (wodurch der Timer zurückgesetzt wird). Wenn Sie versuchen, einen weiteren dataSync-Vordergrunddienst zu starten, gibt das System ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException mit einer Fehlermeldung zurück, z. B. „Zeitlimit für den Typ ‚dataSync‘ des Vordergrunddienstes bereits überschritten“.
Testen
Sie können Zeitüberschreitungen für die Datensynchronisierung aktivieren, um das Verhalten Ihrer App zu testen, auch wenn Ihre App nicht auf Android 15 ausgerichtet ist, solange die App auf einem Android 15-Gerät ausgeführt wird. Führen Sie den folgenden Befehl adb aus, um Zeitüberschreitungen zu aktivieren:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
Sie können auch die Zeitüberschreitung anpassen, um das Verhalten Ihrer App nach Erreichen des Limits leichter zu testen. Führen Sie den folgenden adb-Befehl aus, um ein neues Zeitlimit festzulegen:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager data_sync_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
Neuer Typ für Dienste im Vordergrund zur Medienverarbeitung
In Android 15 wird der neue Diensttyp mediaProcessing eingeführt. Dieser Diensttyp eignet sich für Vorgänge wie das Transcodieren von Mediendateien. Eine Medien-App könnte beispielsweise eine Audiodatei herunterladen und sie vor der Wiedergabe in ein anderes Format konvertieren. Sie können einen mediaProcessing-Dienst im Vordergrund verwenden, damit die Conversion auch dann fortgesetzt wird, wenn die App im Hintergrund ausgeführt wird.
Das System lässt zu, dass die mediaProcessing-Dienste einer App insgesamt 6 Stunden innerhalb von 24 Stunden ausgeführt werden. Anschließend ruft das System die Service.onTimeout(int, int)-Methode des laufenden Dienstes auf (in Android 15 eingeführt). Derzeit hat der Dienst einige Sekunden Zeit, um Service.stopSelf() aufzurufen. Wenn der Dienst Service.stopSelf() nicht aufruft, löst das System eine interne Ausnahme aus. Die Ausnahme wird in Logcat mit der folgenden Meldung protokolliert:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type mediaProcessing did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
Sie können eine Ausnahme vermeiden, indem Sie einen der folgenden Schritte ausführen:
- Implementieren Sie in Ihrem Dienst die neue
Service.onTimeout(int, int)-Methode. Wenn Ihre App den Callback empfängt, müssen Sie innerhalb weniger SekundenstopSelf()anrufen. Wenn Sie die App nicht sofort beenden, generiert das System einen Fehler. - Die
mediaProcessing-Dienste Ihrer App dürfen innerhalb eines 24-Stunden-Zeitraums insgesamt nicht länger als 6 Stunden ausgeführt werden, es sei denn, der Nutzer interagiert mit der App und setzt den Timer zurück. - Starten Sie
mediaProcessingDienste im Vordergrund nur als Folge einer direkten Nutzerinteraktion. Da sich Ihre App beim Start des Dienstes im Vordergrund befindet, hat Ihr Dienst die vollen sechs Stunden Zeit, nachdem die App in den Hintergrund gewechselt ist. - Verwende anstelle eines
mediaProcessing-Dienstes im Vordergrund eine alternative API wie WorkManager.
Wenn die mediaProcessing-Dienste im Vordergrund Ihrer App in den letzten 24 Stunden sechs Stunden lang ausgeführt wurden, können Sie keinen weiteren mediaProcessing-Dienst im Vordergrund starten, es sei denn, der Nutzer hat Ihre App in den Vordergrund gebracht (wodurch der Timer zurückgesetzt wird). Wenn Sie versuchen, einen weiteren mediaProcessing-Vordergrunddienst zu starten, löst das System ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException mit einer Fehlermeldung wie „Zeitlimit für den Typ „mediaProcessing“ des Dienstes im Vordergrund bereits überschritten“ aus.
Weitere Informationen zum Diensttyp mediaProcessing finden Sie unter Änderungen an Diensttypen im Vordergrund für Android 15: Medienverarbeitung.
Testen
Wenn du das Verhalten deiner App testen möchtest, kannst du Zeitüberschreitungen bei der Medienverarbeitung aktivieren, auch wenn deine App nicht auf Android 15 ausgerichtet ist, solange sie auf einem Android 15-Gerät ausgeführt wird. Führen Sie den folgenden Befehl adb aus, um Zeitüberschreitungen zu aktivieren:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
Sie können auch das Zeitlimit anpassen, um zu testen, wie sich Ihre Anwendung verhält, wenn das Limit erreicht ist. Führen Sie den folgenden adb-Befehl aus, um ein neues Zeitlimit festzulegen:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager media_processing_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
Einschränkungen für BOOT_COMPLETED-Übertragungsempfänger, die Dienste im Vordergrund starten
Es gelten neue Einschränkungen für die Einführung von BOOT_COMPLETED Übertragungsempfängern
Dienste im Vordergrund. BOOT_COMPLETED Empfänger dürfen nicht Folgendes starten:
folgende Arten von Diensten im Vordergrund:
dataSynccameramediaPlaybackphoneCallmediaProjectionmicrophone(Diese Einschränkung gilt seit demmicrophonefürmicrophoneAndroid 14)
Wenn ein BOOT_COMPLETED-Empfänger versucht, einen dieser Dienste im Vordergrund zu starten, löst das System ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException aus.
Testen
Um das Verhalten Ihrer App zu testen, können Sie diese neuen Einschränkungen auch dann aktivieren, wenn Ihre
Die App ist nicht auf Android 15 ausgerichtet (solange die App auf einem Android 15 ausgeführt wird)
Gerät). Führen Sie den folgenden adb-Befehl aus:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_BOOT_COMPLETED_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
Wenn Sie eine BOOT_COMPLETED-Broadcastnachricht senden möchten, ohne das Gerät neu zu starten, führen Sie den folgenden Befehl adb aus:
adb shell am broadcast -a android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED your-package-name
Einschränkungen beim Starten von Diensten im Vordergrund, während eine App die Berechtigung SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW hat
Bisher konnte eine App mit der Berechtigung SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW einen Dienst im Vordergrund starten, auch wenn sie sich gerade im Hintergrund befand (wie unter Ausnahmen von Einschränkungen beim Starten im Hintergrund beschrieben).
Wenn eine App auf Android 15 ausgerichtet ist, ist diese Ausnahme jetzt eingeschränkter. Die App benötigt jetzt die Berechtigung SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW und auch ein sichtbares Overlay-Fenster. Das bedeutet, dass die App zuerst ein TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY-Fenster öffnen und das Fenster sichtbar sein muss, bevor Sie einen Dienst im Vordergrund starten.
Wenn Ihre App versucht, einen Dienst im Vordergrund aus dem Hintergrund zu starten, ohne diese neuen Anforderungen zu erfüllen (und keine andere Ausnahme vorliegt), löst das System ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException aus.
Wenn Ihre App die Berechtigung SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW deklariert und Dienste im Vordergrund aus dem Hintergrund startet, kann sich diese Änderung auf Ihre App auswirken. Wenn deine App eine ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException erhält, prüfe die Reihenfolge der Vorgänge in deiner App und achte darauf, dass deine App bereits ein aktives Overlay-Fenster hat, bevor sie versucht, einen Dienst im Vordergrund im Hintergrund zu starten. Du kannst mit View.getWindowVisibility() prüfen, ob dein Overlay-Fenster gerade sichtbar ist. Du kannst auch View.onWindowVisibilityChanged() überschreiben, um benachrichtigt zu werden, wenn sich die Sichtbarkeit ändert.
Testen
Um das Verhalten deiner App zu testen, kannst du diese neuen Einschränkungen auch dann aktivieren, wenn deine App nicht auf Android 15 ausgerichtet ist, solange sie auf einem Android 15-Gerät ausgeführt wird. Wenn Sie diese neuen Einschränkungen für den Start von Diensten im Vordergrund aus dem Hintergrund aktivieren möchten, führen Sie den folgenden adb-Befehl aus:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_SAW_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
Änderungen daran, wann Apps den globalen Status des Modus „Bitte nicht stören“ ändern können
Bei Apps, die auf Android 15 (API-Level 35) und höher ausgerichtet sind, kann der globale Status oder die Richtlinie für „Bitte nicht stören“ (DND) auf einem Gerät nicht mehr geändert werden. Das gilt sowohl für die Änderung der Nutzereinstellungen als auch für das Deaktivieren des DND-Modus. Stattdessen müssen Apps eine AutomaticZenRule einreichen, die vom System in eine globale Richtlinie mit dem bestehenden Verfahren „Die restriktivste Richtlinie gilt“ kombiniert wird. Aufrufe vorhandener APIs, die sich zuvor auf den globalen Status ausgewirkt haben (setInterruptionFilter, setNotificationPolicy), führen zum Erstellen oder Aktualisieren einer impliziten AutomaticZenRule, die je nach Aufrufzyklus dieser API-Aufrufe aktiviert oder deaktiviert wird.
Diese Änderung wirkt sich nur auf das beobachtbare Verhalten aus, wenn die App setInterruptionFilter(INTERRUPTION_FILTER_ALL) aufruft und davon ausgeht, dass durch diesen Aufruf ein AutomaticZenRule deaktiviert wird, das zuvor von den Eigentümern aktiviert wurde.
OpenJDK-API-Änderungen
Mit Android 15 werden die Core-Bibliotheken von Android weiter aktualisiert, um sie an die Funktionen in den neuesten OpenJDK-LTS-Releases anzupassen.
Einige dieser Änderungen können sich auf die App-Kompatibilität von Apps auswirken, die auf Android 15 (API-Level 35) ausgerichtet sind:
Änderungen an APIs für die Stringformatierung: Die Validierung von Argumentindex, Flags, Breite und Genauigkeit ist jetzt strenger, wenn die folgenden
String.format()- undFormatter.format()-APIs verwendet werden:String.format(String, Object[])String.format(Locale, String, Object[])Formatter.format(String, Object[])Formatter.format(Locale, String, Object[])
Die folgende Ausnahme wird beispielsweise ausgelöst, wenn ein Argumentindex von 0 verwendet wird (
%0im Formatstring):IllegalFormatArgumentIndexException: Illegal format argument index = 0In diesem Fall kann das Problem behoben werden, indem Sie den Argumentindex 1 (
%1im Formatstring) verwenden.Änderungen am Komponententyp von
Arrays.asList(...).toArray(): Bei Verwendung vonArrays.asList(...).toArray()ist der Komponententyp des resultierenden Arrays jetztObjectund nicht der Typ der Elemente des zugrunde liegenden Arrays. Der folgende Code löst daher eineClassCastExceptionaus:String[] elements = (String[]) Arrays.asList("one", "two").toArray();Um in diesem Fall
Stringals Komponententyp im resultierenden Array beizubehalten, können Sie stattdessenCollection.toArray(Object[])verwenden:String[] elements = Arrays.asList("two", "one").toArray(new String[0]);Änderungen bei der Verarbeitung von Sprachcodes: Wenn Sie die
LocaleAPI verwenden, werden Sprachcodes für Hebräisch, Jiddisch und Indonesisch nicht mehr in ihre veralteten Formen konvertiert (Hebräisch:iw, Jiddisch:jiund Indonesisch:in). Wenn Sie den Sprachcode für eines dieser Gebietsschemas angeben, verwenden Sie stattdessen die Codes aus ISO 639-1 (Hebräisch:he, Jiddisch:yiund Indonesisch:id).Änderungen an zufälligen Ganzzahlfolgen: Nach den Änderungen in https://bugs.openjdk.org/browse/JDK-8301574 geben die folgenden
Random.ints()-Methoden jetzt eine andere Zahlenfolge als dieRandom.nextInt()-Methoden zurück:Im Allgemeinen sollte diese Änderung nicht zu einem fehlerhaften Verhalten der App führen. Ihr Code sollte jedoch nicht davon ausgehen, dass die Sequenz, die von
Random.ints()-Methoden generiert wird, mitRandom.nextInt()übereinstimmt.
Die neue SequencedCollection API kann sich auf die Kompatibilität Ihrer App auswirken, nachdem Sie compileSdk in der Build-Konfiguration Ihrer App aktualisiert haben, um Android 15 (API-Level 35) zu verwenden:
Konflikt mit den Erweiterungsfunktionen
MutableList.removeFirst()undMutableList.removeLast()inkotlin-stdlibDer Typ
Listin Java wird dem TypMutableListin Kotlin zugeordnet. Da die APIsList.removeFirst()undList.removeLast()in Android 15 (API-Level 35) eingeführt wurden, löst der Kotlin-Compiler Funktionsaufrufe wielist.removeFirst()statisch zu den neuenList-APIs auf, anstatt zu den Erweiterungsfunktionen inkotlin-stdlib.Wenn eine App mit
compileSdkauf35undminSdkauf34oder niedriger neu kompiliert und dann unter Android 14 oder niedriger ausgeführt wird, wird ein Laufzeitfehler ausgegeben:java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: No virtual method removeFirst()Ljava/lang/Object; in class Ljava/util/ArrayList;Die vorhandene
NewApi-Lint-Option im Android-Gradle-Plug-in kann diese neuen API-Verwendungen erkennen../gradlew lintMainActivity.kt:41: Error: Call requires API level 35 (current min is 34): java.util.List#removeFirst [NewApi] list.removeFirst()Um die Laufzeit-Ausnahme und die Lint-Fehler zu beheben, können die Funktionsaufrufe
removeFirst()undremoveLast()in Kotlin durchremoveAt(0)bzw.removeAt(list.lastIndex)ersetzt werden. Wenn Sie Android Studio Ladybug | 2024.1.3 oder höher verwenden, wird auch eine Option für eine schnelle Lösung für diese Fehler angeboten.Entfernen Sie
@SuppressLint("NewApi")undlintOptions { disable 'NewApi' }, wenn die Lint-Option deaktiviert wurde.Kollision mit anderen Methoden in Java
Den vorhandenen Typen wurden neue Methoden hinzugefügt, z. B.
ListundDeque. Diese neuen Methoden sind möglicherweise nicht mit den Methoden mit demselben Namen und denselben Argumenttypen in anderen Schnittstellen und Klassen kompatibel. Bei einer Kollision der Methodensignatur mit Inkompatibilität gibt derjavac-Compiler einen Build-Time-Fehler aus. Beispiel:Beispiel für Fehler 1:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:135: error: removeLast() in MyList cannot implement removeLast() in List public void removeLast() { ^ return type void is not compatible with Object where E is a type-variable: E extends Object declared in interface ListBeispiel für Fehler 2:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:7: error: types Deque<Object> and List<Object> are incompatible; public class MyList implements List<Object>, Deque<Object> { both define reversed(), but with unrelated return types 1 errorBeispiel für Fehler 3:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:43: error: types List<E#1> and MyInterface<E#2> are incompatible; public static class MyList implements List<Object>, MyInterface<Object> { class MyList inherits unrelated defaults for getFirst() from types List and MyInterface where E#1,E#2 are type-variables: E#1 extends Object declared in interface List E#2 extends Object declared in interface MyInterface 1 errorUm diese Build-Fehler zu beheben, sollte die Klasse, die diese Schnittstellen implementiert, die Methode mit einem kompatiblen Rückgabetyp überschreiben. Beispiel:
@Override public Object getFirst() { return List.super.getFirst(); }
Sicherheit
Android 15 enthält Änderungen, die die Systemsicherheit fördern und dazu beitragen, Apps und Nutzer vor schädlichen Apps zu schützen.
Eingeschränkte TLS-Versionen
Unter Android 15 ist die Verwendung der TLS-Versionen 1.0 und 1.1 eingeschränkt. Diese Versionen wurden bereits in Android eingestellt, sind aber jetzt für Apps, die auf Android 15 ausgerichtet sind, nicht mehr zulässig.
Sichere Starts von Hintergrundaktivitäten
Android 15 schützt Nutzer vor schädlichen Apps und gibt ihnen mehr Kontrolle über ihre Geräte. Dazu werden Änderungen eingeführt, die verhindern, dass schädliche Hintergrund-Apps andere Apps in den Vordergrund holen, ihre Berechtigungen erweitern und Nutzerinteraktionen missbrauchen. Das Starten von Hintergrundaktivitäten ist seit Android 10 (API-Level 29) eingeschränkt.
Sonstige Änderungen
PendingIntent-Ersteller standardmäßig so ändern, dass Starts von Hintergrundaktivitäten blockiert werden: So wird verhindert, dass Apps versehentlich einePendingIntenterstellen, die von böswilligen Akteuren missbraucht werden könnte.- Eine App darf nur dann in den Vordergrund gebracht werden, wenn der
PendingIntent-Absender dies zulässt. Mit dieser Änderung soll verhindert werden, dass schädliche Apps die Möglichkeit zum Starten von Aktivitäten im Hintergrund missbrauchen. Standardmäßig dürfen Apps den Task-Stack nicht in den Vordergrund holen, es sei denn, der Ersteller erlaubt das Starten von Hintergrundaktivitäten oder der Absender hat die Berechtigung zum Starten von Hintergrundaktivitäten. - Steuern, wie die oberste Aktivität eines Aufgabenstapels ihre Aufgabe beenden kann Wenn die oberste Aktivität eine Aufgabe beendet, kehrt Android zur zuletzt aktiven Aufgabe zurück. Wenn eine Aktivität, die nicht im Vordergrund ausgeführt wird, ihre Aufgabe beendet, kehrt Android zum Startbildschirm zurück. Das Beenden dieser Aktivität wird nicht blockiert.
- Verhindern, dass beliebige Aktivitäten aus anderen Apps in Ihrem eigenen Task gestartet werden. Diese Änderung verhindert, dass schädliche Apps Nutzer durch das Erstellen von Aktivitäten, die von anderen Apps zu stammen scheinen, zum Phishing verleiten.
- Blockieren, dass nicht sichtbare Fenster für Starts von Hintergrundaktivitäten berücksichtigt werden: So wird verhindert, dass schädliche Apps Hintergrundaktivitäten starten, um Nutzern unerwünschte oder schädliche Inhalte zu präsentieren.
Sicherere Intents
In Android 15 wird StrictMode für Intents eingeführt.
So rufen Sie detaillierte Logs zu Verstößen gegen die Nutzungsbedingungen von Intent auf:
Kotlin
fun onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build() ) }
Java
public void onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(new VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build()); }
Nutzererfahrung und System-UI
Android 15 enthält einige Änderungen, die für eine einheitlichere und intuitivere User Experience sorgen sollen.
Änderungen am Fenstereinsatz
In Android 15 gibt es zwei Änderungen im Zusammenhang mit Fenstereinblendungen: Vollbild wird standardmäßig erzwungen. Außerdem gibt es Konfigurationsänderungen, z. B. an der Standardkonfiguration der Systemleisten.
Edge-to-Edge-Erzwingung
Apps werden auf Geräten mit Android 15 standardmäßig randlos angezeigt, wenn die App auf Android 15 (API‑Level 35) ausgerichtet ist.
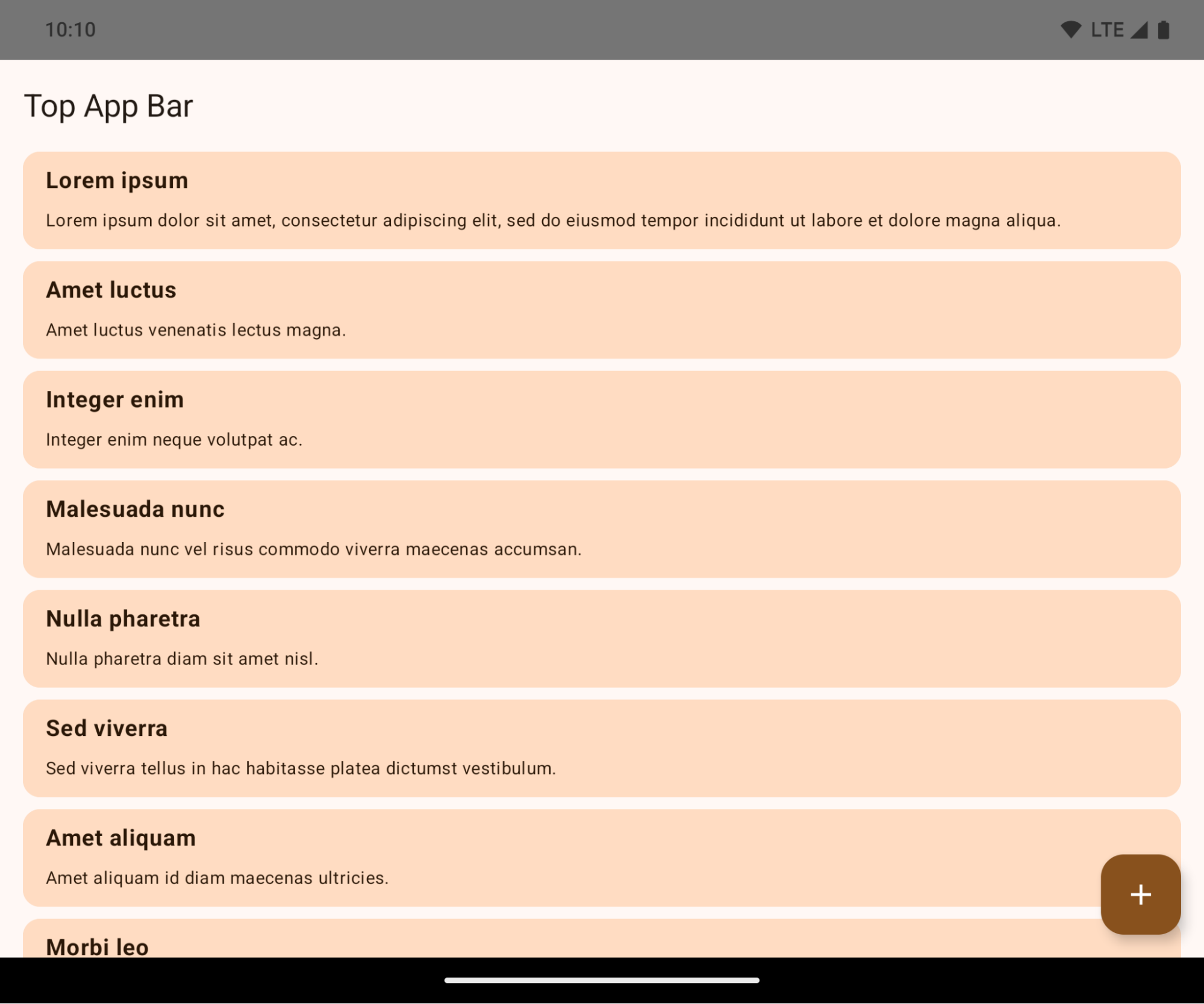
Dies ist eine schwerwiegende Änderung, die sich negativ auf die Benutzeroberfläche Ihrer App auswirken kann. Die Änderungen betreffen die folgenden Bereiche der Benutzeroberfläche:
- Navigationsleiste mit Geste
- Standardmäßig transparent.
- Der untere Offset ist deaktiviert. Inhalte werden also hinter der Systemnavigationsleiste gerendert, sofern keine Insets angewendet werden.
setNavigationBarColorundR.attr#navigationBarColorsind veraltet und wirken sich nicht auf die Bedienung über Gesten aus.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedundR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedhaben weiterhin keine Auswirkungen auf die Gestennavigation.
- Bedienung über 3 Schaltflächen
- Die Deckkraft ist standardmäßig auf 80% eingestellt. Die Farbe kann mit dem Fensterhintergrund übereinstimmen.
- Der untere Offset ist deaktiviert, sodass Inhalte hinter der Systemnavigationsleiste gerendert werden, sofern keine Insets angewendet werden.
setNavigationBarColorundR.attr#navigationBarColorsind standardmäßig so eingestellt, dass sie dem Fensterhintergrund entsprechen. Der Fensterhintergrund muss ein Farb-Drawable sein, damit diese Standardeinstellung angewendet wird. Diese API ist zwar eingestellt, wirkt sich aber weiterhin auf die 3-Tasten-Navigation aus.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedundR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedsind standardmäßig auf „true“ gesetzt. Dadurch wird bei der Bedienung über 3 Schaltflächen ein zu 80% undurchsichtiger Hintergrund hinzugefügt.
- Statusleiste
- Standardmäßig transparent.
- Der obere Offset ist deaktiviert. Inhalte werden also hinter der Statusleiste gerendert, sofern keine Insets angewendet werden.
setStatusBarColorundR.attr#statusBarColorsind veraltet und haben keine Auswirkungen auf Android 15.setStatusBarContrastEnforcedundR.attr#statusBarContrastEnforcedsind veraltet, haben aber weiterhin Auswirkungen auf Android 15.
- Displayausschnitt
layoutInDisplayCutoutModevon nicht schwebenden Fenstern mussLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYSsein.SHORT_EDGES,NEVERundDEFAULTwerden alsALWAYSinterpretiert, damit Nutzer keinen schwarzen Balken sehen, der durch den Displayausschnitt verursacht wird, und das Bild von Kante zu Kante angezeigt wird.
Im folgenden Beispiel wird eine App vor und nach der Ausrichtung auf Android 15 (API‑Level 35) sowie vor und nach dem Anwenden von Einsätzen gezeigt. Dieses Beispiel ist nicht vollständig. Die Darstellung kann in Android Auto anders aussehen.
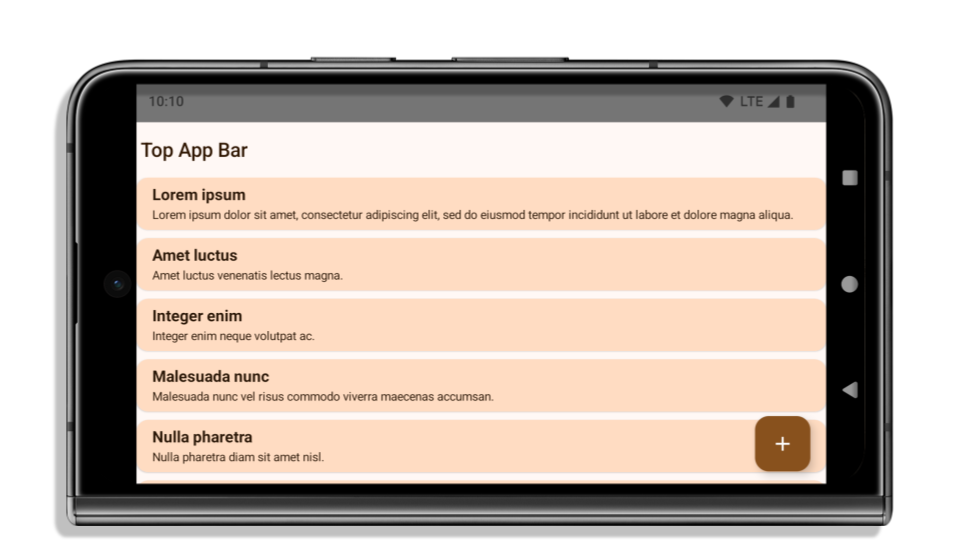

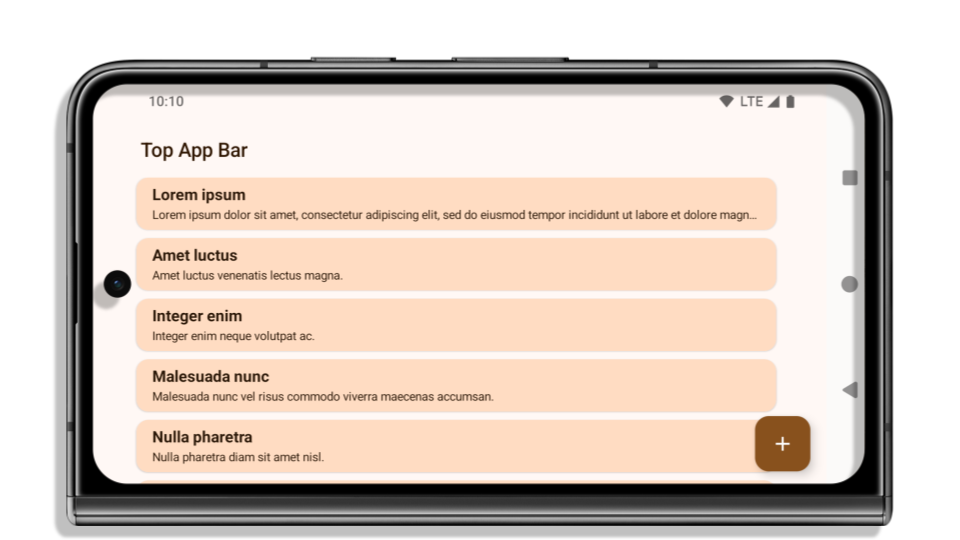
Was Sie prüfen sollten, wenn Ihre App bereits Edge-to-Edge-Darstellung unterstützt
Wenn Ihre App bereits randlos ist und Insets verwendet, sind Sie größtenteils nicht betroffen, außer in den folgenden Fällen. Auch wenn Sie nicht davon ausgehen, dass Ihre App betroffen ist, empfehlen wir Ihnen, sie zu testen.
- Sie haben ein nicht schwebendes Fenster, z. B. ein
Activity, dasSHORT_EDGES,NEVERoderDEFAULTanstelle vonLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYSverwendet. Wenn Ihre App beim Starten abstürzt, liegt das möglicherweise an Ihrem Splashscreen. Sie können entweder die Abhängigkeit core splashscreen auf 1.2.0-alpha01 oder höher aktualisieren oderwindow.attributes.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = WindowManager.LayoutInDisplayCutoutMode.alwaysfestlegen. - Es kann sein, dass es Bildschirme mit geringerem Traffic gibt, auf denen die Benutzeroberfläche verdeckt ist. Prüfen Sie, ob die Benutzeroberfläche auf diesen weniger besuchten Bildschirmen verdeckt ist. Zu den Bildschirmen mit geringerem Traffic gehören:
- Einrichtungs- oder Anmeldebildschirme
- Einstellungsseiten
Was Sie prüfen sollten, wenn Ihre App noch nicht randlos ist
Wenn Ihre App noch nicht randlos ist, sind Sie höchstwahrscheinlich betroffen. Zusätzlich zu den Szenarien für Apps, die bereits randlos sind, sollten Sie Folgendes berücksichtigen:
- Wenn in Ihrer App Material 3-Komponenten (
androidx.compose.material3) in Compose verwendet werden, z. B.TopAppBar,BottomAppBarundNavigationBar, sind diese Komponenten wahrscheinlich nicht betroffen, da sie Insets automatisch verarbeiten. - Wenn in Ihrer App Material 2-Komponenten (
androidx.compose.material) in Compose verwendet werden, werden Insets nicht automatisch von diesen Komponenten verarbeitet. Sie können jedoch auf die Insets zugreifen und sie manuell anwenden. In androidx.compose.material 1.6.0 und höher können Sie den ParameterwindowInsetsverwenden, um die Insets manuell fürBottomAppBar,TopAppBar,BottomNavigationundNavigationRailanzuwenden. Verwenden Sie den ParametercontentWindowInsetsauch fürScaffold. - Wenn in Ihrer App Ansichten und Material-Komponenten (
com.google.android.material) verwendet werden, werden die meisten ansichtsbasierte Material-Komponenten wieBottomNavigationView,BottomAppBar,NavigationRailViewoderNavigationViewmit Insets gerendert. Es sind keine zusätzlichen Maßnahmen erforderlich. Wenn SieAppBarLayoutverwenden, müssen Sie jedochandroid:fitsSystemWindows="true"hinzufügen. - Bei benutzerdefinierten Composables müssen Sie die Insets manuell als Padding anwenden. Wenn sich Ihre Inhalte in einem
Scaffoldbefinden, können Sie Insets mit denScaffold-Abstandswerten verwenden. Andernfalls wenden Sie den Innenabstand mit einem derWindowInsetsan. - Wenn Ihre App Ansichten und
BottomSheet-,SideSheet- oder benutzerdefinierte Container verwendet, wenden Sie den Innenabstand mitViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListeneran. Wenden Sie fürRecyclerViewmit diesem Listener einen Innenabstand an und fügen Sie auchclipToPadding="false"hinzu.
Prüfen, ob Ihre App einen benutzerdefinierten Schutz im Hintergrund bieten muss
Wenn Ihre App einen benutzerdefinierten Hintergrundschutz für die 3‑Tasten-Navigation oder die Statusleiste bieten muss, sollte sie mithilfe von WindowInsets.Type#tappableElement() für die Höhe der 3‑Tasten-Navigationsleiste oder WindowInsets.Type#statusBars eine Komposition oder Ansicht hinter der Systemleiste platzieren.
Weitere Ressourcen für Edge-to-Edge-Anzeigen
Weitere Informationen zum Anwenden von Insets finden Sie in den Leitfäden Edge-to-Edge-Ansichten und Edge-to-Edge-Compose.
Eingestellte APIs
Die folgenden APIs sind veraltet, aber nicht deaktiviert:
R.attr#enforceStatusBarContrastR.attr#navigationBarColor(für die Bedienung über 3 Schaltflächen, mit 80 % Alpha)Window#isStatusBarContrastEnforcedWindow#setNavigationBarColor(für die Bedienung über 3 Schaltflächen, mit 80% Alpha)Window#setStatusBarContrastEnforced
Die folgenden APIs sind eingestellt und deaktiviert:
R.attr#navigationBarColor(für die Bedienung über Gesten)R.attr#navigationBarDividerColorR.attr#statusBarColorWindow#setDecorFitsSystemWindowsWindow#getNavigationBarColorWindow#getNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#getStatusBarColorWindow#setNavigationBarColor(für die Bedienung über Gesten)Window#setNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#setStatusBarColor
Stabile Konfiguration
Wenn Ihre App auf Android 15 (API‑Level 35) oder höher ausgerichtet ist, werden die Systemleisten nicht mehr aus Configuration ausgeschlossen. Wenn Sie die Bildschirmgröße in der Klasse Configuration für die Layoutberechnung verwenden, sollten Sie sie je nach Bedarf durch bessere Alternativen wie ein geeignetes ViewGroup, WindowInsets oder WindowMetricsCalculator ersetzen.
Configuration ist seit API 1 verfügbar. Sie wird in der Regel aus Activity.onConfigurationChanged abgerufen. Sie enthält Informationen wie Fensterdichte, Ausrichtung und Größen. Ein wichtiges Merkmal der Fenstergrößen, die von Configuration zurückgegeben werden, ist, dass die Systemleisten zuvor ausgeschlossen wurden.
Die Konfigurationsgröße wird in der Regel für die Ressourcenauswahl verwendet, z. B. /res/layout-h500dp. Dies ist weiterhin ein gültiger Anwendungsfall. Die Verwendung für die Layoutberechnung wurde jedoch immer abgeraten. Wenn das der Fall ist, sollten Sie jetzt davon Abstand nehmen. Sie sollten die Verwendung von Configuration durch etwas ersetzen, das je nach Anwendungsfall besser geeignet ist.
Wenn Sie sie zum Berechnen des Layouts verwenden, nutzen Sie eine geeignete ViewGroup, z. B. CoordinatorLayout oder ConstraintLayout. Wenn Sie damit die Höhe der Systemnavigationsleiste ermitteln möchten, verwenden Sie WindowInsets. Wenn Sie die aktuelle Größe Ihres App-Fensters wissen möchten, verwenden Sie computeCurrentWindowMetrics.
In der folgenden Liste werden die Felder beschrieben, die von dieser Änderung betroffen sind:
- Bei den Größen
Configuration.screenWidthDpundscreenHeightDpwerden die Systemleisten nicht mehr ausgeschlossen. Configuration.smallestScreenWidthDpist indirekt von Änderungen anscreenWidthDpundscreenHeightDpbetroffen.Configuration.orientationist indirekt von Änderungen anscreenWidthDpundscreenHeightDpauf Geräten mit einem quadratähnlichen Display betroffen.Display.getSize(Point)ist indirekt von den Änderungen inConfigurationbetroffen. Diese Funktion wurde ab API-Level 30 verworfen.Display.getMetrics()funktioniert seit API-Level 33 bereits so.
Das Attribut „elegantTextHeight“ ist standardmäßig auf „true“ gesetzt.
Bei Apps, die auf Android 15 (API-Level 35) ausgerichtet sind, wird das Attribut elegantTextHeight TextView standardmäßig in true geändert. Dadurch wird die standardmäßig verwendete kompakte Schriftart durch eine Schriftart mit größeren vertikalen Maßen ersetzt, die viel besser lesbar ist.
Die kompakte Schrift wurde eingeführt, um Layouts zu vermeiden. Android 13 (API-Ebene 33) verhindert viele dieser Unterbrechungen, indem das Textlayout die vertikale Höhe mithilfe des Attributs fallbackLineSpacing maximieren kann.
In Android 15 ist die kompakte Schrift weiterhin im System vorhanden. Sie können in Ihrer App also elegantTextHeight auf false festlegen, um das bisherige Verhalten beizubehalten. Es ist jedoch unwahrscheinlich, dass sie in zukünftigen Releases unterstützt wird. Wenn Ihre App die folgenden Schriftarten unterstützt: Arabisch, Lao, Myanmar, Tamil, Gujarati, Kannada, Malayalam, Oriya, Telugu oder Thai, testen Sie Ihre App, indem Sie elegantTextHeight auf true setzen.
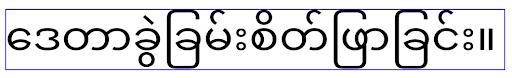
elegantTextHeight-Verhalten für Apps, die auf Android 14 (API-Level 34) und niedriger ausgerichtet sind.
elegantTextHeight-Verhalten für Apps, die auf Android 15 ausgerichtet sind.TextView-Breite ändert sich bei komplexen Buchstabenformen
In früheren Android-Versionen wurden bei einigen Schriftarten mit Kurrentschrift oder Sprachen mit komplexer Schriftbildgestaltung die Buchstaben möglicherweise im Bereich des vorherigen oder nächsten Zeichens gezeichnet.
In einigen Fällen wurden solche Buchstaben am Anfang oder Ende abgeschnitten.
Ab Android 15 weist eine TextView eine Breite zu, um genügend Platz für solche Buchstaben zu erhalten. Außerdem können Apps auf der linken Seite zusätzliche Abstände anfordern, um das Abschneiden zu verhindern.
Da sich diese Änderung darauf auswirkt, wie TextView die Breite festlegt, weist TextView standardmäßig mehr Breite zu, wenn die App auf Android 15 (API-Level 35) oder höher ausgerichtet ist. Sie können dieses Verhalten aktivieren oder deaktivieren, indem Sie die setUseBoundsForWidth API auf TextView aufrufen.
Da das Hinzufügen eines linken Abstands zu einer Fehlausrichtung bestehender Layouts führen kann, wird der Abstand auch bei Apps, die auf Android 15 oder höher ausgerichtet sind, nicht standardmäßig hinzugefügt.
Sie können jedoch zusätzliche Abstände hinzufügen, um ein Abschneiden zu verhindern. Rufen Sie dazu setShiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang auf.
Die folgenden Beispiele zeigen, wie sich diese Änderungen auf das Textlayout für bestimmte Schriftarten und Sprachen auswirken können.

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" />

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />
Gebietsschemaabhängige Standardzeilenhöhe für EditText
In früheren Android-Versionen wurde die Texthöhe im Textlayout so gedehnt, dass sie der Zeilenhöhe der Schrift entspricht, die dem aktuellen Gebietsschema entspricht. Wenn der Inhalt beispielsweise auf Japanisch war, war die Texthöhe etwas größer, da die Zeilenhöhe der japanischen Schrift etwas größer ist als die einer lateinischen Schrift. Trotz dieser Unterschiede bei den Zeilenhöhen wurde das Element EditText unabhängig von der verwendeten Sprache einheitlich dimensioniert, wie in der folgenden Abbildung dargestellt:

EditText-Elemente darstellen, die Text auf Englisch (en), Japanisch (ja) und Burmese (my) enthalten können. Die Höhe der EditText ist gleich, obwohl diese Sprachen unterschiedliche Zeilenhöhen haben.Für Apps, die auf Android 15 (API-Level 35) ausgerichtet sind, ist jetzt eine Mindestzeilenhöhe für EditText reserviert, die der Referenzschriftart für die angegebene Sprache entspricht, wie in der folgenden Abbildung dargestellt:

EditText-Elemente darstellen, die Text auf Englisch (en), Japanisch (ja) und Burmese (my) enthalten können. Die Höhe des EditText enthält jetzt Platz für die Standardzeilenhöhe der Schriftarten dieser Sprachen.Bei Bedarf können Sie das vorherige Verhalten Ihrer App wiederherstellen, indem Sie das Attribut useLocalePreferredLineHeightForMinimum auf false festlegen. Außerdem können Sie mit der setMinimumFontMetrics API in Kotlin und Java benutzerdefinierte Mindestmesswerte für vertikale Ausrichtungen festlegen.
Kamera und Medien
Unter Android 15 werden die folgenden Änderungen am Kamera- und Medienverhalten für Apps eingeführt, die auf Android 15 oder höher ausgerichtet sind.
Einschränkungen beim Anfordern des Audiofokus
Apps, die auf Android 15 (API-Level 35) ausgerichtet sind, müssen die oberste App sein oder einen Dienst im Vordergrund ausführen, um den Audiofokus anfordern zu können. Wenn eine App versucht, den Fokus anzufordern, ohne eine dieser Anforderungen zu erfüllen, gibt der Aufruf AUDIOFOCUS_REQUEST_FAILED zurück.
Weitere Informationen zum Audiofokus finden Sie unter Audiofokus verwalten.
Aktualisierte Einschränkungen für Nicht-SDKs
Android 15 enthält aktualisierte Listen eingeschränkter Nicht-SDK-Schnittstellen, die auf der Zusammenarbeit mit Android-Entwicklern und den neuesten internen Tests basieren. Wir sorgen nach Möglichkeit dafür, dass öffentliche Alternativen verfügbar sind, bevor wir Nicht-SDK-Schnittstellen einschränken.
Wenn Ihre App nicht auf Android 15 ausgerichtet ist, wirken sich einige dieser Änderungen möglicherweise nicht sofort auf Sie aus. Zwar kann Ihre App je nach Ziel-API-Level Ihrer App auf einige Nicht-SDK-Schnittstellen zugreifen, die Verwendung einer Nicht-SDK-Methode oder eines Nicht-SDK-Felds birgt jedoch immer ein hohes Risiko, dass Ihre App nicht mehr funktioniert.
Wenn Sie sich nicht sicher sind, ob Ihre App Nicht-SDK-Schnittstellen verwendet, können Sie Ihre App testen, um das herauszufinden. Wenn Ihre App auf Nicht-SDK-Schnittstellen basiert, sollten Sie mit der Planung einer Migration zu SDK-Alternativen beginnen. Wir wissen jedoch, dass es für einige Apps gültige Anwendungsfälle für die Verwendung von Nicht-SDK-Schnittstellen gibt. Wenn Sie für eine Funktion in Ihrer App keine Alternative zur Verwendung einer Nicht-SDK-Schnittstelle finden, sollten Sie eine neue öffentliche API anfordern.
Weitere Informationen zu den Änderungen in dieser Android-Version finden Sie unter Änderungen an den Einschränkungen für nicht SDK-spezifische Oberflächen in Android 15. Weitere Informationen zu Nicht-SDK-Schnittstellen finden Sie unter Einschränkungen für Nicht-SDK-Schnittstellen.

