与之前的版本一样,Android 15 包含一些可能会影响您的应用的行为变更。以下行为变更仅影响以 Android 15 或更高版本为目标平台的应用。如果您的应用以 Android 15 或更高版本为目标平台,您应该修改自己的应用以适当地支持这些行为(如果适用)。
请务必查看对 Android 15 上运行的所有应用都有影响的行为变更列表(无论应用的 targetSdkVersion 如何)。
核心功能
Android 15 修改或扩展了 Android 系统的各种核心功能。
前台服务变更
我们将对 Android 15 中的前台服务进行以下更改。
数据同步前台服务超时行为
对于以 Android 15(API 级别 35)或更高版本为目标平台的应用,Android 15 为 dataSync 引入了新的超时行为。此行为也适用于新的 mediaProcessing 前台服务类型。
系统允许应用的 dataSync 服务在 24 小时内总共运行 6 小时,之后系统会调用正在运行的服务的 Service.onTimeout(int, int) 方法(在 Android 15 中引入)。此时,该服务有几秒钟时间来调用 Service.stopSelf()。调用 Service.onTimeout() 后,该服务将不再被视为前台服务。如果服务未调用 Service.stopSelf(),系统会抛出内部异常。系统会在 Logcat 中记录此异常,并显示以下消息:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type dataSync did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
为避免因行为变更而导致问题,您可以执行以下一项或多项操作:
- 让您的服务实现新的
Service.onTimeout(int, int)方法。当您的应用收到回调时,请务必在几秒钟内调用stopSelf()。(如果您不立即停止应用,系统会生成故障。) - 确保应用的
dataSync服务在任何 24 小时内总运行时间不超过 6 小时(除非用户与应用互动,重置计时器)。 - 仅通过直接的用户互动来启动
dataSync前台服务;由于您的应用在服务启动时位于前台,因此服务会在应用进入后台后的 6 小时内完整运行。 - 请改用替代 API,而不是使用
dataSync前台服务。
如果您的应用的 dataSync 前台服务在过去 24 小时内运行了 6 小时,则您无法启动其他 dataSync 前台服务,除非用户已将您的应用切换到前台(这会重置计时器)。如果您尝试启动其他 dataSync 前台服务,系统会抛出 ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException,并显示类似“前台服务类型 dataSync 的时间限制已用尽”的错误消息。
测试
如需测试应用的行为,您可以启用数据同步超时功能,即使应用未以 Android 15 为目标平台也是如此(前提是应用在 Android 15 设备上运行)。如需启用超时,请运行以下 adb 命令:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
您还可以调整超时期限,更轻松地测试应用在达到此限制时的行为。如需设置新的超时期限,请运行以下 adb 命令:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager data_sync_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
新的媒体处理前台服务类型
Android 15 引入了一种新的前台服务类型 mediaProcessing。此服务类型适用于转码媒体文件等操作。例如,媒体应用可能会下载音频文件,并需要先将其转换为其他格式,然后才能播放。您可以使用 mediaProcessing 前台服务,确保即使应用在后台运行时转换也会继续。
系统允许应用的 mediaProcessing 服务在 24 小时内总共运行 6 小时,之后系统会调用正在运行的服务的 Service.onTimeout(int, int) 方法(在 Android 15 中引入)。此时,服务有几秒钟的时间来调用 Service.stopSelf()。如果服务未调用 Service.stopSelf(),系统会抛出内部异常。系统会在 Logcat 中记录此异常,并显示以下消息:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type mediaProcessing did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
为避免出现此异常,您可以执行以下任一操作:
- 让您的服务实现新的
Service.onTimeout(int, int)方法。当您的应用收到回调时,请务必在几秒钟内调用stopSelf()。(如果您未立即停止应用,系统会生成失败情况。) - 确保应用的
mediaProcessing服务在任何 24 小时内总运行时间不超过 6 小时(除非用户与应用互动,重置计时器)。 - 仅在有直接用户互动时启动
mediaProcessing前台服务;由于服务启动时应用位于前台,因此您的服务在应用进入后台后有完整的 6 小时时间。 - 请改用 替代 API(例如 WorkManager),而不是使用
mediaProcessing前台服务。
如果您的应用的 mediaProcessing 前台服务在过去 24 小时内运行了 6 小时,则您无法启动其他 mediaProcessing 前台服务,除非用户将您的应用切换到前台(这会重置计时器)。如果您尝试启动另一个 mediaProcessing 前台服务,系统会抛出 ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException,并显示类似于“前台服务类型 mediaProcessing 的时间限制已用尽”的错误消息。
如需详细了解 mediaProcessing 服务类型,请参阅 Android 15 前台服务类型变更:媒体处理。
测试
如需测试应用的行为,您可以启用媒体处理超时,即使您的应用并非以 Android 15 为目标平台也是如此(前提是应用在 Android 15 设备上运行)。如需启用超时,请运行以下 adb 命令:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
您还可以调整超时期限,以便更轻松地测试应用在达到上限时的行为方式。如需设置新的超时期限,请运行以下 adb 命令:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager media_processing_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
对启动前台服务的 BOOT_COMPLETED 广播接收器的限制
在启动 BOOT_COMPLETED 广播接收器方面存在新限制
前台服务。BOOT_COMPLETED 接收器不能启动
以下类型的前台服务:
dataSynccameramediaPlaybackphoneCallmediaProjectionmicrophone(自 Android 14 起,microphone就受到此限制)
如果 BOOT_COMPLETED 接收器尝试启动任何上述类型的前台
服务,系统会抛出 ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException。
测试
如需测试应用的行为,您可以启用这些新限制,即使您的应用并未以 Android 15 为目标平台(只要应用在 Android 15 设备上运行)也是如此。运行以下 adb 命令:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_BOOT_COMPLETED_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
如需在不重启设备的情况下发送 BOOT_COMPLETED 广播,请运行以下 adb 命令:
adb shell am broadcast -a android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED your-package-name
在应用拥有 SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW 权限时启动前台服务的限制
以前,如果应用拥有 SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW 权限,即使应用当前在后台运行,也可以启动前台服务(如免于后台启动限制中所述)。
如果应用以 Android 15 为目标平台,则此豁免范围现在更窄。现在,应用需要具有 SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW 权限,并且还需要有一个可见的叠加窗口。也就是说,应用需要先启动 TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY 窗口,并且该窗口需要处于可见状态,然后您才能启动前台服务。
如果您的应用尝试从后台启动前台服务,但不符合这些新要求(并且没有其他豁免情况),系统会抛出 ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException。
如果您的应用声明了 SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW 权限并从后台启动前台服务,则可能会受到此变更的影响。如果您的应用获得了 ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException,请检查应用的操作顺序,并确保应用在尝试从后台启动前台服务之前已具有有效的叠加层窗口。您可以通过调用 View.getWindowVisibility() 检查叠加层窗口当前是否可见,也可以替换 View.onWindowVisibilityChanged(),以便在可见性发生变化时收到通知。
测试
如需测试应用的行为,您可以启用这些新限制,即使您的应用并未以 Android 15 为目标平台(只要应用在 Android 15 设备上运行)也是如此。如需针对从后台启动前台服务启用这些新限制,请运行以下 adb 命令:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_SAW_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
更改了应用可以修改“勿扰”模式全局状态的时间
以 Android 15(API 级别 35)及更高版本为目标平台的应用无法再更改设备上的勿扰 (DND) 功能的全局状态或政策(无论是通过修改用户设置还是关闭勿扰模式)。相反,应用必须提供 AutomaticZenRule,系统会将其与现有的“最严格的政策优先”方案合并为一个全局政策。对之前会影响全局状态的现有 API 的调用(setInterruptionFilter、setNotificationPolicy)会导致创建或更新隐式 AutomaticZenRule,该 AutomaticZenRule 会根据这些 API 调用的调用周期开启和关闭。
请注意,只有当应用调用 setInterruptionFilter(INTERRUPTION_FILTER_ALL) 并希望该调用停用之前由其所有者激活的 AutomaticZenRule 时,此更改才会影响可观察到的行为。
OpenJDK API 变更
Android 15 将继续更新 Android 的核心库,以与最新 OpenJDK LTS 版本中的功能保持一致。
以下变更可能会影响以 Android 15(API 级别 35)为目标平台的应用的兼容性:
对字符串格式化 API 进行了更改:现在,使用以下
String.format()和Formatter.format()API 时,对实参索引、标志、宽度和精度的验证要求变得更加严格:String.format(String, Object[])String.format(Locale, String, Object[])Formatter.format(String, Object[])Formatter.format(Locale, String, Object[])
例如,当使用参数索引 0(格式字符串中的
%0)时,系统会抛出以下异常:IllegalFormatArgumentIndexException: Illegal format argument index = 0在这种情况下,可以使用实参索引 1(格式字符串中的
%1)来解决此问题。对
Arrays.asList(...).toArray()的组件类型所做的更改:使用Arrays.asList(...).toArray()时,所得数组的组件类型现在是Object,而不是底层数组元素的类型。因此,以下代码会抛出ClassCastException:String[] elements = (String[]) Arrays.asList("one", "two").toArray();在这种情况下,为了在生成的数组中保留
String作为组件类型,您可以改用Collection.toArray(Object[]):String[] elements = Arrays.asList("two", "one").toArray(new String[0]);语言代码处理方面的变更:使用
LocaleAPI 时,希伯来语、意第绪语和印度尼西亚语的语言代码不再转换为其过时的形式(希伯来语:iw、意第绪语:ji和印度尼西亚语:in)。指定这些语言区域的语言代码时,请改用 ISO 639-1 中的代码(希伯来语:he、意第绪语:yi和印度尼西亚语:id)。随机整数序列的更改:根据 https://bugs.openjdk.org/browse/JDK-8301574 中所做的更改,以下
Random.ints()方法现在返回的数字序列与Random.nextInt()方法返回的数字序列不同:一般来说,此更改不应导致应用出现破坏性行为,但您的代码不应期望从
Random.ints()方法生成的序列与Random.nextInt()相匹配。
在您更新应用 build 配置中的 compileSdk 以使用 Android 15(API 级别 35)后,新的 SequencedCollection API 可能会影响应用的兼容性:
kotlin-stdlib中MutableList.removeFirst()和MutableList.removeLast()扩展函数的冲突Java 中的
List类型会映射到 Kotlin 中的MutableList类型。 由于List.removeFirst()和List.removeLast()API 已在 Android 15(API 级别 35)中引入,因此 Kotlin 编译器会将函数调用(例如list.removeFirst())静态解析为新的ListAPI,而不是kotlin-stdlib中的扩展函数。如果某个应用重新编译时将
compileSdk设置为35,并将minSdk设置为34或更低值,然后该应用在 Android 14 及更低版本上运行,则会抛出运行时错误:java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: No virtual method removeFirst()Ljava/lang/Object; in class Ljava/util/ArrayList;Android Gradle 插件中现有的
NewApilint 选项可以捕获这些新的 API 用法。./gradlew lintMainActivity.kt:41: Error: Call requires API level 35 (current min is 34): java.util.List#removeFirst [NewApi] list.removeFirst()如需修正运行时异常和 lint 错误,可以在 Kotlin 中将
removeFirst()和removeLast()函数调用分别替换为removeAt(0)和removeAt(list.lastIndex)。如果您使用的是 Android Studio Ladybug | 2024.1.3 或更高版本,它还会针对这些错误提供快速修复选项。如果已停用 lint 选项,请考虑移除
@SuppressLint("NewApi")和lintOptions { disable 'NewApi' }。与 Java 中的其他方法发生冲突
现有类型中添加了新方法,例如
List和Deque。这些新方法可能与具有相同名称和实参类型的其他接口和类中的方法不兼容。如果方法签名发生不兼容的冲突,javac编译器会输出 build 时错误。例如:错误示例 1:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:135: error: removeLast() in MyList cannot implement removeLast() in List public void removeLast() { ^ return type void is not compatible with Object where E is a type-variable: E extends Object declared in interface List错误示例 2:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:7: error: types Deque<Object> and List<Object> are incompatible; public class MyList implements List<Object>, Deque<Object> { both define reversed(), but with unrelated return types 1 error错误示例 3:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:43: error: types List<E#1> and MyInterface<E#2> are incompatible; public static class MyList implements List<Object>, MyInterface<Object> { class MyList inherits unrelated defaults for getFirst() from types List and MyInterface where E#1,E#2 are type-variables: E#1 extends Object declared in interface List E#2 extends Object declared in interface MyInterface 1 error如需修复这些 build 错误,实现这些接口的类应使用兼容的返回类型替换相应方法。例如:
@Override public Object getFirst() { return List.super.getFirst(); }
安全
Android 15 包含多项旨在提升系统安全性的变更,以帮助保护应用和用户免受恶意应用的侵害。
受限的 TLS 版本
Android 15 限制了对 TLS 版本 1.0 和 1.1 的使用。这些版本之前已在 Android 中被弃用,但现在不允许面向 Android 15 的应用使用。
限制后台 activity 启动
Android 15 做出了一些变更,可防止恶意后台应用将其他应用置于前台、提升自身权限并滥用用户互动,从而保护用户免受恶意应用的侵害,并让用户更好地控制自己的设备。自 Android 10(API 级别 29)起,后台 activity 启动受到限制。
其他更改
- 将
PendingIntent创建者更改为默认阻止后台活动启动。这有助于防止应用意外创建可能被恶意行为者滥用的PendingIntent。 - 除非
PendingIntent发送方允许,否则请勿将应用转至前台。此变更旨在防止恶意应用滥用在后台启动 activity 的功能。默认情况下,除非创建者允许后台 activity 启动权限或发送者具有后台 activity 启动权限,否则不允许应用将任务堆栈带到前台。 - 控制任务堆栈的顶层 activity 如何完成其任务。如果顶部 activity 完成了一项任务,Android 将返回到上次处于活跃状态的任务。此外,如果非顶部 activity 完成其任务,Android 会返回到主屏幕;它不会阻止此非顶部 activity 完成。
- 防止从其他应用启动任意 activity 进入您自己的任务。此变更可防止恶意应用通过创建看似来自其他应用的 activity 来对用户进行钓鱼式攻击。
- 阻止将非可见窗口纳入后台 activity 启动的考虑范围。这有助于防止恶意应用滥用后台活动启动来向用户显示不必要或恶意的内容。
更安全的 intent
Android 15 针对 intent 引入了 StrictMode。
如需查看有关 Intent 使用违规行为的详细日志,请使用以下方法:
Kotlin
fun onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build() ) }
Java
public void onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(new VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build()); }
用户体验和系统界面
Android 15 包含一些旨在打造更一致、更直观的用户体验的变更。
窗口边衬区变更
Android 15 中与窗口内边距相关的两项变更:默认强制执行边到边,此外还有配置变更,例如系统栏的默认配置。
全面实施政策
如果应用以 Android 15(API 级别 35)为目标平台,则在搭载 Android 15 的设备上默认以无边框显示。
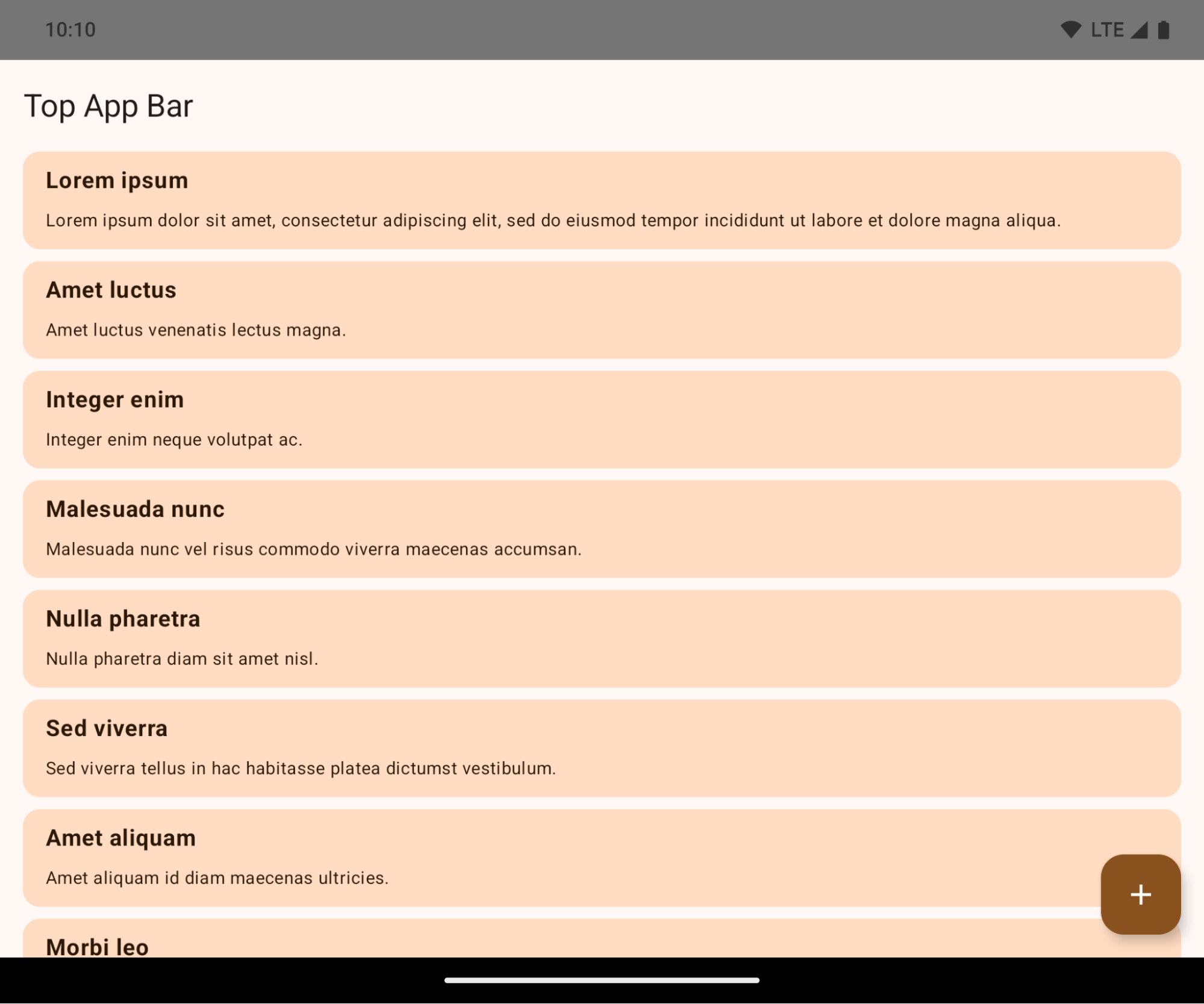
这是一项重大变更,可能会对应用的界面产生负面影响。这些更改会影响以下界面区域:
- 手势柄导航栏
- 默认透明。
- 底部偏移量处于停用状态,因此内容会绘制在系统导航栏后面,除非应用了边衬区。
setNavigationBarColor和R.attr#navigationBarColor已弃用,不会影响手势导航。setNavigationBarContrastEnforced和R.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforced继续对使用手势进行导航没有任何影响。
- “三按钮”导航
- 默认情况下,不透明度设置为 80%,颜色可能与窗口背景颜色一致。
- 底部偏移量已停用,因此内容会绘制在系统导航栏后面,除非应用了边衬区。
setNavigationBarColor和R.attr#navigationBarColor默认设置为与窗口背景保持一致。窗口背景必须是颜色可绘制对象,才能应用此默认值。此 API 已弃用,但仍会影响三按钮导航。setNavigationBarContrastEnforced和R.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforced默认值为 true,这会在三按钮导航栏中添加 80% 不透明度的背景。
- 状态栏
- 默认透明。
- 顶部偏移量处于停用状态,因此内容会绘制在状态栏后面,除非应用了边衬区。
setStatusBarColor和R.attr#statusBarColor已弃用,对 Android 15 没有影响。setStatusBarContrastEnforced和R.attr#statusBarContrastEnforced已废弃,但仍会对 Android 15 产生影响。
- 刘海屏
- 非浮动窗口的
layoutInDisplayCutoutMode必须为LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS。SHORT_EDGES、NEVER和DEFAULT会被解读为ALWAYS,这样用户就不会看到因刘海屏而产生的黑条,并且应用会显示在屏幕的整个边缘。
- 非浮动窗口的
以下示例展示了应用在以 Android 15(API 级别 35)为目标平台之前和之后,以及在应用边衬区之前和之后的效果。此示例并不全面,在 Android Auto 上可能会显示不同的内容。
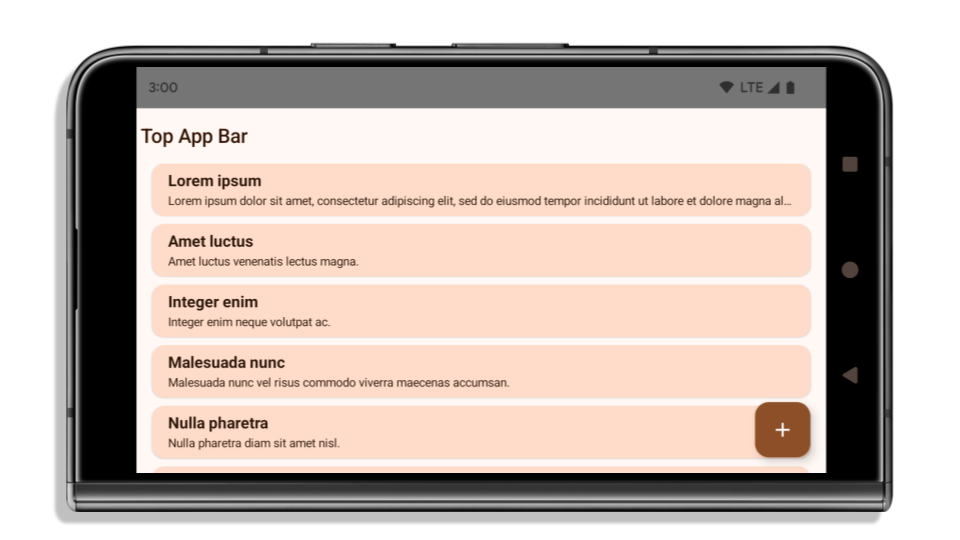

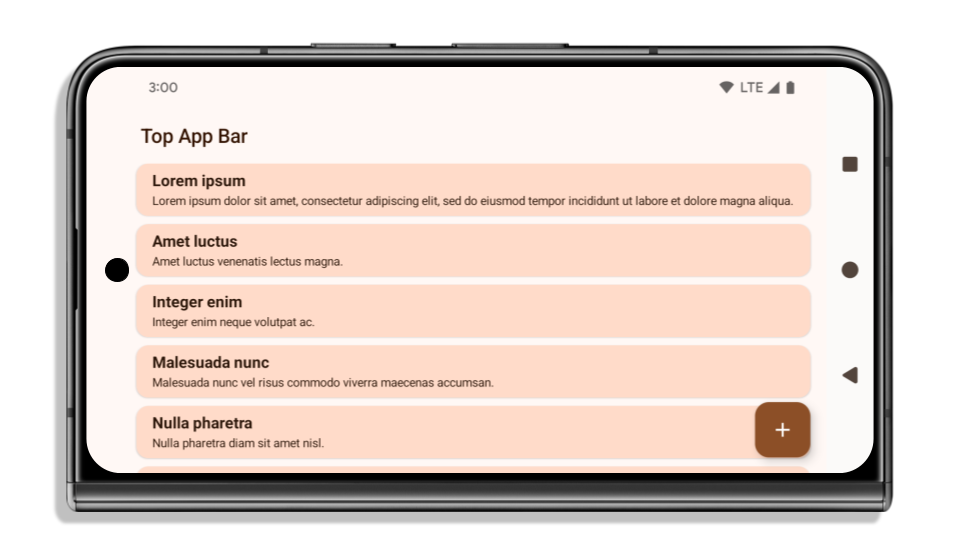
如果应用已实现全屏显示,需要检查哪些方面
如果您的应用已实现全屏显示并应用边衬区,则基本上不会受到影响,但以下情形除外。不过,即使您认为自己不受影响,我们仍建议您测试应用。
- 您有一个非浮动窗口,例如使用
SHORT_EDGES、NEVER或DEFAULT而不是LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS的Activity。如果您的应用在启动时崩溃,这可能是由启动画面引起的。您可以将核心启动画面依赖项升级到 1.2.0-alpha01 或更高版本,也可以设置window.attributes.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = WindowManager.LayoutInDisplayCutoutMode.always。 - 可能存在流量较低且界面被遮挡的屏幕。验证这些访问频率较低的界面是否没有被遮挡的界面。低流量屏幕包括:
- 初始配置或登录界面
- “设置”页面
如果您的应用尚未实现全屏显示,需要检查哪些方面
如果您的应用尚未实现全屏显示,则很可能会受到影响。除了已实现全屏显示的边缘到边缘应用的相关场景之外,您还应考虑以下事项:
- 如果您的应用在 Compose 中使用 Material 3 组件 (
androidx.compose.material3),例如TopAppBar、BottomAppBar和NavigationBar,这些组件很可能不会受到影响,因为它们会自动处理边衬区。 - 如果您的应用使用的是 Compose 中的 Material 2 组件 (
androidx.compose.material),这些组件不会自动处理边衬区。不过,您可以获得边衬区的访问权限,然后手动应用边衬区。在 androidx.compose.material 1.6.0 及更高版本中,使用windowInsets参数可为BottomAppBar、TopAppBar、BottomNavigation和NavigationRail手动应用边衬区。 同样,请为Scaffold使用contentWindowInsets参数。 - 如果应用使用了视图和 Material 组件 (
com.google.android.material),则大多数基于视图的 Material 组件(例如BottomNavigationView、BottomAppBar、NavigationRailView或NavigationView)都会处理边衬区,因此不需要执行额外的操作。不过,如果使用的是AppBarLayout,则需要添加android:fitsSystemWindows="true"。 - 对于自定义可组合项,请手动应用边衬区作为内边距。如果您的内容位于
Scaffold中,则可以使用Scaffold内边距值来使用边衬区。否则,请使用WindowInsets之一应用内边距。 - 如果应用使用的是视图和
BottomSheet、SideSheet或自定义容器,请使用ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener应用内边距。对于RecyclerView,请使用此监听器应用内边距,同时添加clipToPadding="false"。
如果应用必须提供自定义后台保护,您需要检查哪些方面
如果您的应用必须为三按钮导航或状态栏提供自定义背景保护,则应使用 WindowInsets.Type#tappableElement() 获取三按钮导航栏高度或 WindowInsets.Type#statusBars,在系统栏后面放置一个可组合项或视图。
其他全屏显示资源
如需了解有关应用边衬区的其他注意事项,请参阅全屏视图和全屏 Compose 指南。
已弃用的 API
以下 API 已弃用,但未停用:
R.attr#enforceStatusBarContrastR.attr#navigationBarColor(适用于三按钮导航,alpha 为 80%)Window#isStatusBarContrastEnforcedWindow#setNavigationBarColor(适用于三按钮导航,alpha 为 80%)Window#setStatusBarContrastEnforced
以下 API 已弃用并停用:
R.attr#navigationBarColor(用于手势导航)R.attr#navigationBarDividerColorR.attr#statusBarColorWindow#setDecorFitsSystemWindowsWindow#getNavigationBarColorWindow#getNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#getStatusBarColorWindow#setNavigationBarColor(用于手势导航)Window#setNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#setStatusBarColor
稳定配置
如果您的应用以 Android 15(API 级别 35)或更高版本为目标平台,Configuration 不再排除系统栏。如果您在 Configuration 类中使用屏幕尺寸进行布局计算,则应根据需要将其替换为更好的替代方案,例如适当的 ViewGroup、WindowInsets 或 WindowMetricsCalculator。
Configuration 自 API 1 起便已开始提供。通常从 Activity.onConfigurationChanged 获取。它提供窗口密度、方向和大小等信息。从 Configuration 返回的窗口大小的一个重要特征是,它之前不包括系统栏。
配置大小通常用于资源选择(例如 /res/layout-h500dp),这仍然是一个有效的使用情形。不过,我们一直不建议使用它进行布局计算。如果您正在这样做,请立即远离该设备。您应根据自己的使用场景,将 Configuration 的使用替换为更合适的用法。
如果您使用它来计算布局,请使用适当的 ViewGroup,例如 CoordinatorLayout 或 ConstraintLayout。如果您使用它来确定系统导航栏的高度,请使用 WindowInsets。如果您想知道应用窗口的当前大小,请使用 computeCurrentWindowMetrics。
以下列表介绍了受此变更影响的字段:
Configuration.screenWidthDp和screenHeightDp尺寸不再排除系统栏。Configuration.smallestScreenWidthDp会受到screenWidthDp和screenHeightDp更改的间接影响。Configuration.orientation会受到近乎正方形的设备上screenWidthDp和screenHeightDp更改的间接影响。Display.getSize(Point)受到Configuration中的更改间接影响。此方法已从 API 级别 30 开始弃用。- 自 API 级别 33 以来,
Display.getMetrics()一直以这种方式运行。
elegantTextHeight 属性默认值为 true
对于以 Android 15(API 级别 35)为目标平台的应用,elegantTextHeight TextView 属性默认会变为 true,将默认使用的紧凑字体替换为一些具有较大垂直测量的脚本,使其更易于阅读。紧凑字体旨在防止布局中断;Android 13(API 级别 33)允许文本布局利用 fallbackLineSpacing 属性拉伸垂直高度,从而防止许多此类中断。
在 Android 15 中,系统中仍保留了紧凑字体,因此您的应用可以将 elegantTextHeight 设置为 false 以获得与之前相同的行为,但即将发布的版本不太可能支持此字体。因此,如果您的应用支持以下脚本:阿拉伯语、老挝语、缅甸语、泰米尔语、古吉拉特语、卡纳达语、马拉雅拉姆语、奥里亚语、泰卢固语或泰语,请将 elegantTextHeight 设置为 true 以测试您的应用。
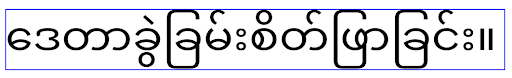
elegantTextHeight 行为。
elegantTextHeight 行为。TextView 宽度因复杂的字母形状而发生变化
在以前的 Android 版本中,某些具有复杂形状的手写字体或语言可能会在上一个或下一个字符的区域绘制字母。在某些情况下,此类字母会在开头或结尾处被剪裁。从 Android 15 开始,TextView 会分配宽度,以便为此类字母绘制足够的空间,并允许应用请求向左额外添加内边距以防止剪裁。
由于此更改会影响 TextView 确定宽度的方式,因此如果应用以 Android 15(API 级别 35)或更高版本为目标平台,TextView 会默认分配更多宽度。您可以通过对 TextView 调用 setUseBoundsForWidth API 来启用或停用此行为。
由于添加左内边距可能会导致现有布局未对齐,因此默认情况下不会添加内边距,即使以 Android 15 或更高版本为目标平台的应用也是如此。不过,您可以通过调用 setShiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang 添加额外的内边距以防止剪裁。
以下示例展示了这些更改如何改进某些字体和语言的文本布局。

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" />

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />
EditText 的语言区域感知默认行高
在较低版本的 Android 中,文本布局会拉伸文本的高度,以满足与当前语言区域匹配的字体的行高。例如,如果内容是日语,由于日语字体的行高略高于拉丁字体,因此文本的高度会略高。不过,尽管行高存在这些差异,但无论使用的是哪种语言区域,EditText 元素的大小都是统一的,如下图所示:

EditText 元素。EditText 的高度相同,即使这些语言的行高各不相同。对于以 Android 15(API 级别 35)为目标平台的应用,现在为 EditText 预留了最小行高,以匹配指定语言区域的参考字体,如下图所示:

EditText 元素。EditText 的高度现在包含足够的空间来容纳这些语言字体的默认行高。如有需要,您的应用可以将 useLocalePreferredLineHeightForMinimum 属性指定为 false,以恢复之前的行为;您的应用还可以在 Kotlin 和 Java 中使用 setMinimumFontMetrics API 设置自定义最小垂直指标。
摄像头和媒体
Android 15 对以 Android 15 或更高版本为目标平台的应用的相机和媒体行为做出了以下更改。
有关请求音频焦点的限制
以 Android 15(API 级别 35)为目标平台的应用必须是顶部应用或正在运行前台服务,才能请求音频焦点。如果应用在未满足上述任一要求的情况下尝试请求焦点,调用将返回 AUDIOFOCUS_REQUEST_FAILED。
如需详细了解音频焦点,请参阅管理音频焦点。
更新后的非 SDK 限制
Android 15 包含更新后的受限非 SDK 接口列表(基于与 Android 开发者之间的协作以及最新的内部测试)。在限制使用非 SDK 接口之前,我们会尽可能确保有可用的公开替代方案。
如果您的应用并非以 Android 15 为目标平台,其中一些变更可能不会立即对您产生影响。不过,虽然您的应用可以访问某些非 SDK 接口(具体取决于应用的目标 API 级别),但只要您使用任何非 SDK 方法或字段,就始终会有很高风险导致应用功能异常。
如果您不确定自己的应用是否使用了非 SDK 接口,则可以通过测试该应用来进行确认。如果您的应用依赖非 SDK 接口,则应开始计划迁移到 SDK 替代方案。不过,我们知道某些应用存在使用非 SDK 接口的合理场景。如果您无法为应用中的某项功能找到使用非 SDK 接口的替代方案,则应该请求新的公共 API。
如需详细了解此 Android 版本中的变更,请参阅 Android 15 中有关限制非 SDK 接口的更新。如需全面了解有关非 SDK 接口的详细信息,请参阅对非 SDK 接口的限制。
