Android 15 平台包含一些可能会影响您的应用的行为变更。以下行为变更将影响在 Android 15 上运行的所有应用,无论采用哪种 targetSdkVersion 都不例外。您应该测试您的应用,然后根据需要进行修改,以适当地支持这些变更。
此外,请务必查看仅影响以 Android 15 为目标平台的应用的行为变更列表。
核心功能
Android 15 修改或扩展了 Android 系统的各种核心功能。
软件包停止状态的更改
The intention of the package FLAG_STOPPED state (which users
can engage in AOSP builds by long-pressing an app icon and selecting "Force
Stop") has always been to keep apps in this state until the user explicitly
removes the app from this state by directly launching the app or indirectly
interacting with the app (through the sharesheet or a widget, selecting the app
as live wallpaper, etc.). In Android 15, we've updated the behavior of the
system to be aligned with this intended behavior. Apps should only be removed
from the stopped state through direct or indirect user action.
To support the intended behavior, in addition to the existing restrictions, the
system also cancels all pending intents when the app enters the
stopped state on a device running Android 15. When the user's actions remove the
app from the stopped state, the ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED
broadcast is delivered to the app providing an opportunity to re-register any
pending intents.
You can call the new
ApplicationStartInfo.wasForceStopped()
method to confirm whether the app was put into the stopped state.
支持 16 KB 页面大小
从历史上看,Android 仅支持 4 KB 内存页面大小,这优化了系统内存性能,以适应 Android 设备通常拥有的平均总内存量。从 Android 15 开始,AOSP 支持配置为使用 16 KB 页面大小的设备(16 KB 设备)。如果您的应用直接或通过 SDK 间接使用任何 NDK 库,则需要重新构建应用,才能在这些 16 KB 设备上运行。
随着设备制造商不断制造出具有更大物理内存 (RAM) 的设备,许多此类设备将采用 16 KB(最终甚至更大)的页面大小来优化设备性能。添加对 16 KB 页面大小设备的支持,可让您的应用在这些设备上运行,并帮助您的应用受益于相关的性能改进。如果不重新编译,应用将无法在未来 Android 版本的 16 KB 设备上运行。
为帮助您为应用添加支持,我们提供了相关指南,介绍了如何检查应用是否受到影响、如何重新构建应用(如果适用),以及如何使用模拟器(包括 Android 模拟器的 Android 15 系统映像)在 16 KB 环境中测试应用。
Benefits and performance gains
Devices configured with 16 KB page sizes use slightly more memory on average, but also gain various performance improvements for both the system and apps:
- Lower app launch times while the system is under memory pressure: 3.16% lower on average, with more significant improvements (up to 30%) for some apps that we tested
- Reduced power draw during app launch: 4.56% reduction on average
- Faster camera launch: 4.48% faster hot starts on average, and 6.60% faster cold starts on average
- Improved system boot time: improved by 8% (approximately 950 milliseconds) on average
These improvements are based on our initial testing, and results on actual devices will likely differ. We'll provide additional analysis of potential gains for apps as we continue our testing.
Check if your app is impacted
If your app uses any native code, then you should rebuild your app with support for 16 KB devices. If you are unsure if your app uses native code, you can use the APK Analyzer to identify whether any native code is present and then check the alignment of ELF segments for any shared libraries that you find. Android Studio also provides features that help you to automatically detect alignment issues.
If your app only uses code written in the Java programming language or in Kotlin, including all libraries or SDKs, then your app already supports 16 KB devices. Nevertheless, we recommend that you test your app in a 16 KB environment to verify that there are no unexpected regressions in app behavior.
某些应用支持私密空间所需的更改
Private space is a new feature in Android 15 that lets users create a separate space on their device where they can keep sensitive apps away from prying eyes, under an additional layer of authentication. Because apps in the private space have restricted visibility, some types of apps need to take additional steps to be able to see and interact with apps in a user's private space.
All apps
Because apps in the private space are kept in a separate user profile, similar to work profiles, apps shouldn't assume that any installed copies of their app that aren't in the main profile are in the work profile. If your app has logic related to work profile apps that make this assumption, you'll need to adjust this logic.
Medical apps
When a user locks the private space, all apps in the private space are stopped, and those apps can't perform foreground or background activities, including showing notifications. This behavior might critically impact the use and function of medical apps installed in the private space.
The private space setup experience warns users that the private space is not suitable for apps that need to perform critical foreground or background activities, such as showing notifications from medical apps. However, apps can't determine whether or not they're being used in the private space, so they can't show a warning to the user for this case.
For these reasons, if you develop a medical app, review how this feature might impact your app and take appropriate actions—such as informing your users not to install your app in the private space—to avoid disrupting critical app capabilities.
Launcher apps
If you develop a launcher app, you must do the following before apps in the private space will be visible:
- Your app must be assigned as the default launcher app for the device—that
is, possessing the
ROLE_HOMErole. - Your app must declare the
ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILESnormal permission in your app's manifest file.
Launcher apps that declare the ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILES permission must handle
the following private space use cases:
- Your app must have a separate launcher container for apps installed in the
private space. Use the
getLauncherUserInfo()method to determine which type of user profile is being handled. - The user must be able to hide and show the private space container.
- The user must be able to lock and unlock the private space container. Use
the
requestQuietModeEnabled()method to lock (by passingtrue) or unlock (by passingfalse) the private space. While locked, no apps in the private space container should be visible or discoverable through mechanisms such as search. Your app should register a receiver for the
ACTION_PROFILE_AVAILABLEandACTION_PROFILE_UNAVAILABLEbroadcasts and update the UI in your app when the locked or unlocked state of the private space container changes. Both of these broadcasts includeEXTRA_USER, which your app can use to refer to the private profile user.You can also use the
isQuietModeEnabled()method to check whether the private space profile is locked or not.
App store apps
The private space includes an "Install Apps" button that launches an implicit
intent to install apps into the user's private space. In order for your app to
receive this implicit intent, declare an <intent-filter>
in your app's manifest file with a <category> of
CATEGORY_APP_MARKET.
移除了基于 PNG 的表情符号字体
The legacy, PNG-based emoji font file (NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf) has been
removed, leaving just the vector-based file. Beginning with Android 13 (API
level 33), the emoji font file used by the system emoji renderer changed from a
PNG-based file to a vector based file. The system retained
the legacy font file in Android 13 and 14 for compatibility reasons, so that
apps with their own font renderers could continue to use the legacy font file
until they were able to upgrade.
To check if your app is affected, search your app's code for references to the
NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf file.
You can choose to adapt your app in a number of ways:
- Use platform APIs for text rendering. You can render text to a bitmap-backed
Canvasand use that to get a raw image if necessary. - Add COLRv1 font support to your app. The FreeType open source library supports COLRv1 in version 2.13.0 and higher.
- As a last resort, you can bundle the legacy emoji font file
(
NotoColorEmoji.ttf) into your APK, although in that case your app will be missing the latest emoji updates. For more information, see the Noto Emoji GitHub project page.
将最低目标 SDK 版本从 23 提升至 24
Android 15 builds on the
the changes that were made in Android 14 and extends this
security further. In Android 15, apps with a
targetSdkVersion lower than 24 can't be installed.
Requiring apps to meet modern API levels helps to ensure better security and
privacy.
Malware often targets lower API levels in order to bypass security and privacy
protections that have been introduced in higher Android versions. For example,
some malware apps use a targetSdkVersion of 22 to avoid being subjected to the
runtime permission model introduced in 2015 by Android 6.0 Marshmallow (API
level 23). This Android 15 change makes it harder for malware to avoid security
and privacy improvements. Attempting to install an app targeting a lower API
level results in an installation failure, with a message like the following one
appearing in Logcat:
INSTALL_FAILED_DEPRECATED_SDK_VERSION: App package must target at least SDK version 24, but found 7
On devices upgrading to Android 15, any apps with a targetSdkVersion lower
than 24 remain installed.
If you need to test an app targeting an older API level, use the following ADB command:
adb install --bypass-low-target-sdk-block FILENAME.apk
安全和隐私设置
Android 15 introduces robust measures to combat one-time passcode (OTP) fraud and to protect the user's sensitive content, focusing on hardening the Notification Listener Service and screenshare protections. Key enhancements include redacting OTPs from notifications accessible to untrusted apps, hiding notifications during screenshare, and securing app activities when OTPs are posted. These changes aim to keep the user's sensitive content safe from unauthorized actors.
Developers need to be aware of the following to ensure their apps are compatible with the changes in Android 15:
OTP Redaction
Android will stop untrusted apps that implement a
NotificationListenerService from reading unredacted content
from notifications where an OTP has been detected. Trusted apps such as
companion device manager associations are exempt from these restrictions.
Screenshare Protection
- Notification content is hidden during screen sharing sessions to preserve
the user's privacy. If the app implements
setPublicVersion(), Android shows the public version of the notification which serves as a replacement notification in insecure contexts. Otherwise, the notification content is redacted without any further context. - Sensitive content like password input is hidden from remote viewers to prevent revealing the user's sensitive information.
- Activities from apps that post notifications during screenshare where an OTP has been detected will be hidden. App content is hidden from the remote viewer when launched.
- Beyond Android's automatic identification of sensitive fields, developers
can manually mark parts of their app as sensitive using
setContentSensitivity, which is hidden from remote viewers during screenshare. - Developers can choose to toggle the Disable screen share protections option under Developer Options to be exempted from the screenshare protections for demo or testing purposes. The default system screen recorder is exempted from these changes, since the recordings remain on-device.
摄像头和媒体
Android 15 对所有应用的相机和媒体行为做出了以下更改。
当达到资源限制时,直接播放和分流播放音频会使之前打开的直接或分流音频轨道失效
在 Android 15 之前,如果某个应用在另一个应用播放音频且达到资源限制时请求直接或分流音频播放,该应用将无法打开新的 AudioTrack。
从 Android 15 开始,当应用请求直接播放或分流播放且达到资源限制时,系统会使任何当前打开的 AudioTrack 对象失效,以防止执行新轨道请求。
(直接音轨和分流音轨通常会打开,以播放压缩音频格式。播放直接音频的常见用例包括通过 HDMI 将编码的音频流式传输到电视。分流轨道通常用于在具有硬件 DSP 加速的移动设备上播放压缩音频。)
用户体验和系统界面
Android 15 包含一些旨在打造更一致、更直观的用户体验的变更。
为选择启用的应用启用了预测性返回动画
Beginning in Android 15, the developer option for predictive back animations has been removed. System animations such as back-to-home, cross-task, and cross-activity now appear for apps that have opted in to the predictive back gesture either entirely or at an activity level. If your app is affected, take the following actions:
- Ensure that your app has been properly migrated to use the predictive back gesture.
- Ensure that your fragment transitions work with predictive back navigation.
- Migrate away from animation and framework transitions and use animator and androidx transitions instead.
- Migrate away from back stacks that
FragmentManagerdoesn't know about. Use back stacks managed byFragmentManageror by the Navigation component instead.
当用户强制停止应用时,widget 会被停用
If a user force-stops an app on a device running Android 15, the system temporarily disables all the app's widgets. The widgets are grayed out, and the user cannot interact with them. This is because beginning with Android 15, the system cancels all an app's pending intents when the app is force-stopped.
The system re-enables those widgets the next time the user launches the app.
For more information, see Changes to package stopped state.
媒体投影状态栏功能块会提醒用户屏幕共享、投屏和录制功能
Screen projection exploits expose private user data such as financial information because users don't realize their device screen is being shared.
For apps running on devices with Android 15 QPR1 or higher, a status bar chip that is large and prominent alerts users to any in‑progress screen projection. Users can tap the chip to stop their screen from being shared, cast, or recorded. Also, screen projection automatically stops when the device screen is locked.
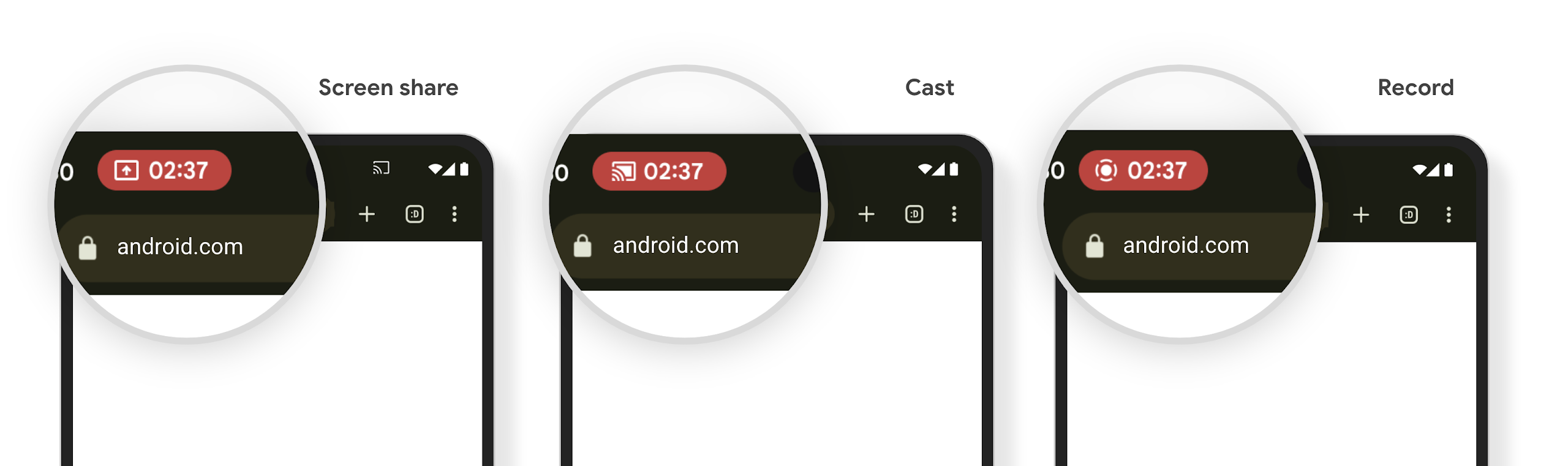
Check if your app is impacted
By default, your app includes the status bar chip and automatically suspends screen projection when the lock screen activates.
To learn more about how to test your app for these use cases, see Status bar chip and auto stop.
后台网络访问限制
In Android 15, apps that start a network request outside of a valid process
lifecycle receive an exception. Typically, an
UnknownHostException or other socket-related
IOException. Network requests that happen outside of a valid lifecycle are
usually due to apps unknowingly continuing a network request even after the app
is no longer active.
To mitigate this exception, ensure your network requests are lifecycle aware and cancelled upon leaving a valid process lifecycle by using lifecycle aware components. If it is important that the network request should happen even when the user leaves the application, consider scheduling the network request using WorkManager or continue a user visible task using Foreground Service.
废弃
随着每个版本的发布,特定的 Android API 可能会过时或需要进行重构,以提供更好的开发者体验或支持新的平台功能。在这些情况下,我们会正式废弃过时的 API,并引导开发者改用替代 API。
废弃意味着我们已结束对这些 API 的正式支持,但它们将继续可供开发者使用。如需详细了解此 Android 版本中值得注意的弃用,请参阅弃用页面。

