Android 15 bietet tolle Funktionen und APIs für Entwickler. In den folgenden Abschnitten werden diese Funktionen zusammengefasst, um Ihnen den Einstieg in die zugehörigen APIs zu erleichtern.
Eine detaillierte Liste der hinzugefügten, geänderten und entfernten APIs finden Sie im API-Vergleichsbericht. Details zu hinzugefügten APIs finden Sie in der Android-API-Referenz. Suchen Sie für Android 15 nach APIs, die in API-Level 35 hinzugefügt wurden. Informationen zu Bereichen, in denen sich Plattformänderungen auf Ihre Apps auswirken können, finden Sie unter Verhaltensänderungen in Android 15 für Apps, die auf Android 15 ausgerichtet sind und für alle Apps.
Kamera und Medien
Android 15 bietet eine Vielzahl von Funktionen, die die Kamera- und Mediennutzung verbessern und die Entwicklern Zugriff auf Tools und Hardware geben, um ihre Visionen auf Android zu verwirklichen.
Weitere Informationen zu den neuesten Funktionen und Entwicklerlösungen für Android-Medien und -Kameras finden Sie im Google I/O-Vortrag zum Erstellen moderner Android-Medien- und Kamerafunktionen.
Low Light-Modus
Mit Android 15 wird Low Light Boost eingeführt, ein Modus für die automatische Belichtung, der sowohl für Camera 2 als auch für die Kameraerweiterung „Nachtmodus“ verfügbar ist. Der Modus für wenig Licht passt die Belichtung des Vorschaustreams bei schlechten Lichtverhältnissen an. Das unterscheidet sich von der Funktionsweise der Kameraerweiterung für den Nachtmodus, mit der Standbilder erstellt werden. Im Nachtmodus werden mehrere Fotos zu einem einzigen verbesserten Bild kombiniert. Der Nachtmodus eignet sich zwar sehr gut zum Erstellen eines Standbilds, kann aber keinen kontinuierlichen Frames-Stream erstellen. Das ist mit dem Low Light Boost jedoch möglich. So ermöglicht der Low Light Boost unter anderem folgende Kamerafunktionen:
- Verbesserte Bildvorschau, damit Nutzer ihre Fotos bei schlechten Lichtverhältnissen besser ausrichten können
- QR-Codes bei wenig Licht scannen
Wenn Sie die Funktion „Optimierung bei wenig Licht“ aktivieren, wird sie automatisch aktiviert, wenn die Lichtverhältnisse schlecht sind, und deaktiviert, wenn mehr Licht vorhanden ist.
Apps können sogar die Vorschau eines Streams bei schlechten Lichtverhältnissen aufnehmen und dann ein aufgehelltes Video speichern.
Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter Boost bei schlechten Lichtverhältnissen.
In-App-Kamerasteuerung
Android 15 bietet eine Erweiterung, mit der Sie die Kamerahardware und ihre Algorithmen auf unterstützten Geräten besser steuern können:
- Erweiterte Anpassungen der Blitzstärke, mit denen sich die Blitzintensität sowohl im Modus
SINGLEals auch im ModusTORCHbei der Aufnahme von Bildern präzise steuern lässt.
HDR-Headroom-Steuerung
Android 15 wählt einen HDR-Headroom aus, der den zugrunde liegenden Gerätefunktionen und der Bittiefe des Panels entspricht. Bei Seiten mit vielen SDR-Inhalten, z. B. einer Messaging-App, in der ein einzelnes HDR-Vorschaubild angezeigt wird, kann dieses Verhalten die wahrgenommene Helligkeit der SDR-Inhalte beeinträchtigen. Mit Android 15 können Sie den HDR-Headroom mit setDesiredHdrHeadroom steuern, um ein Gleichgewicht zwischen SDR- und HDR-Inhalten zu finden.

Loudness-Regler

Mit Android 15 werden nun CTA-2075-Lautheitsstandard, der Ihnen hilft, Vermeiden Sie Inkonsistenzen bei der Audiolautstärke und stellen Sie sicher, dass Nutzer sich nicht ständig darum kümmern müssen, Lautstärke beim Wechsel zwischen Inhalten anpassen. Das System nutzt bekannte Eigenschaften der Ausgabegeräte (Kopfhörer und Lautsprecher) sowie Lautstärkemetadaten, die in AAC-Audioinhalten verfügbar sind, um die Lautstärke und die Komprimierungsebenen des dynamischen Bereichs intelligent anzupassen.
Wenn du diese Funktion aktivieren möchtest, müssen in deinen AAC-Inhalten Lautstärke-Metadaten verfügbar sein und die Plattformfunktion in deiner App aktiviert sein. Dazu erstellst du ein LoudnessCodecController-Objekt, indem du die create-Factorymethode mit der Audiositzungs-ID aus der zugehörigen AudioTrack aufrufst. Dadurch werden automatisch Audioupdates angewendet. Sie können eine
OnLoudnessCodecUpdateListener zum Ändern oder Filtern
lautheitsparameter, bevor sie auf den
MediaCodec
// Media contains metadata of type MPEG_4 OR MPEG_D
val mediaCodec = …
val audioTrack = AudioTrack.Builder()
.setSessionId(sessionId)
.build()
...
// Create new loudness controller that applies the parameters to the MediaCodec
try {
val lcController = LoudnessCodecController.create(mSessionId)
// Starts applying audio updates for each added MediaCodec
}
AndroidX media3 ExoPlayer wird ebenfalls für die Verwendung der
LoudnessCodecController APIs für eine nahtlose Anwendungsintegration
Virtuelle MIDI 2.0-Geräte
Mit Android 13 wurde die Unterstützung für die Verbindung über USB mit MIDI 2.0-Geräten hinzugefügt, die mit Universal MIDI-Paketen (UMP) kommunizieren. Android 15 erweitert die Unterstützung von UMP auf virtuelle MIDI-Apps. So können Kompositions-Apps Synthesizer-Apps wie ein virtuelles MIDI 2.0-Gerät steuern, genau wie bei einem USB-MIDI 2.0-Gerät.
Effizientere AV1-Softwaredecodierung

dav1d, der beliebte AV1-Software-Decoder von VideoLAN, ist für Android-Geräte verfügbar, die die AV1-Dekodierung nicht in Hardware unterstützen. dav1d ist bis zu dreimal leistungsfähiger als der bisherige AV1-Software-Decoder und ermöglicht die HD-AV1-Wiedergabe für mehr Nutzer, einschließlich einiger Geräte der unteren und mittleren Preisklasse.
Deine App muss die Verwendung von dav1d aktivieren, indem sie es beim Namen aufruft"c2.android.av1-dav1d.decoder". In einem nachfolgenden Update wird dav1d zum Standard-AV1-Software-Decoder. Diese Unterstützung ist standardisiert und wird auf Android 11-Geräte übertragen, die Google Play-Systemupdates erhalten.
Produktivität von Entwicklern und Tools
Die meisten unserer Bemühungen zur Steigerung Ihrer Produktivität konzentrieren sich auf Tools wie Android Studio, Jetpack Compose und die Android Jetpack-Bibliotheken. Wir suchen aber auch immer nach Möglichkeiten, Ihnen die Umsetzung Ihrer Visionen auf der Plattform zu erleichtern.
OpenJDK 17-Updates
In Android 15 werden die Kernbibliotheken von Android weiter aktualisiert, um sie an die Funktionen der neuesten OpenJDK-LTS-Releases anzupassen.
Die folgenden wichtigen Funktionen und Verbesserungen sind enthalten:
- Verbesserungen bei NIO-Buffers
- Streams
- Zusätzliche
math- undstrictmath-Methoden util-Paketupdates, einschließlich der sequenziertencollection,mapundsetByteBuffer-Unterstützung inDeflater- Sicherheitsupdates wie
X500PrivateCredentialund Sicherheitsschlüsselupdates
Diese APIs werden über Google Play-Systemupdates auf über einer Milliarde Geräten mit Android 12 (API-Level 31) und höher aktualisiert, damit Sie Ihre Apps auf die neuesten Programmierfunktionen ausrichten können.
Verbesserungen bei PDF-Dateien
Android 15 enthält erhebliche Verbesserungen an den PdfRenderer-APIs. Apps können erweiterte Funktionen wie Rendering enthalten
passwortgeschützte Dateien, Anmerkungen, Formularbearbeitung,
Suche und Auswahl mit Text Linearisiertes PDF
Optimierungen werden unterstützt, um die lokale PDF-Ansicht zu beschleunigen und den Ressourcenverbrauch zu reduzieren.
Mit der Jetpack-PDF-Bibliothek können Sie Ihrer App ganz einfach Funktionen zum Ansehen von PDFs hinzufügen.
Die PdfRenderer wurde in ein Modul verschoben, das unabhängig von der Plattformversion über Google Play-Systemupdates aktualisiert werden kann. Wir unterstützen diese Änderungen bis Android 11 (API-Level 30), indem wir eine kompatible Version der API-Oberfläche vor Android 15 namens PdfRendererPreV erstellen.
Verbesserungen beim automatischen Sprachenwechsel
Mit Android 14 wurde die geräteinterne mehrsprachige Spracherkennung mit automatischem Wechsel zwischen Sprachen hinzugefügt. Dies kann jedoch dazu führen, dass Wörter weggelassen werden, insbesondere wenn die Sprachen mit weniger Pause zwischen den beiden Äußerungen gewechselt werden. Android 15 bietet zusätzliche Steuerelemente, mit denen Entwickler das Umschalten an ihren Anwendungsfall anpassen können.
Mit EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_INITIAL_ACTIVE_DURATION_TIME_MILLIS wird die automatische Umstellung auf den Beginn der Audiositzung beschränkt. Mit EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_MATCH_SWITCHES wird die Sprachumstellung nach einer bestimmten Anzahl von Umstellungen deaktiviert. Diese Optionen sind besonders nützlich, wenn Sie davon ausgehen, dass während der Sitzung nur eine Sprache gesprochen wird, die automatisch erkannt werden soll.
Verbesserte OpenType Variable Font API
Android 15 verbessert die Nutzerfreundlichkeit der OpenType-Variablenschrift. Mit der buildVariableFamily API können Sie eine FontFamily-Instanz aus einer variablen Schriftart erstellen, ohne Gewichtsachsen anzugeben. Der Text-Renderer überschreibt den Wert der wght-Achse, damit er mit dem angezeigten Text übereinstimmt.
Mit der API wird der Code zum Erstellen einer Typeface erheblich vereinfacht:
Kotlin
val newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build()
Java
Typeface newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build();
Bisher war viel mehr Code erforderlich, um dieselbe Typeface zu erstellen:
Kotlin
val oldTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build()) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ).build() ).build()
Java
Typeface oldTypeface = new Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ) .build() ).build();
Hier ein Beispiel dafür, wie ein Typeface mit der alten und der neuen API erstellt wurde
Renderings:
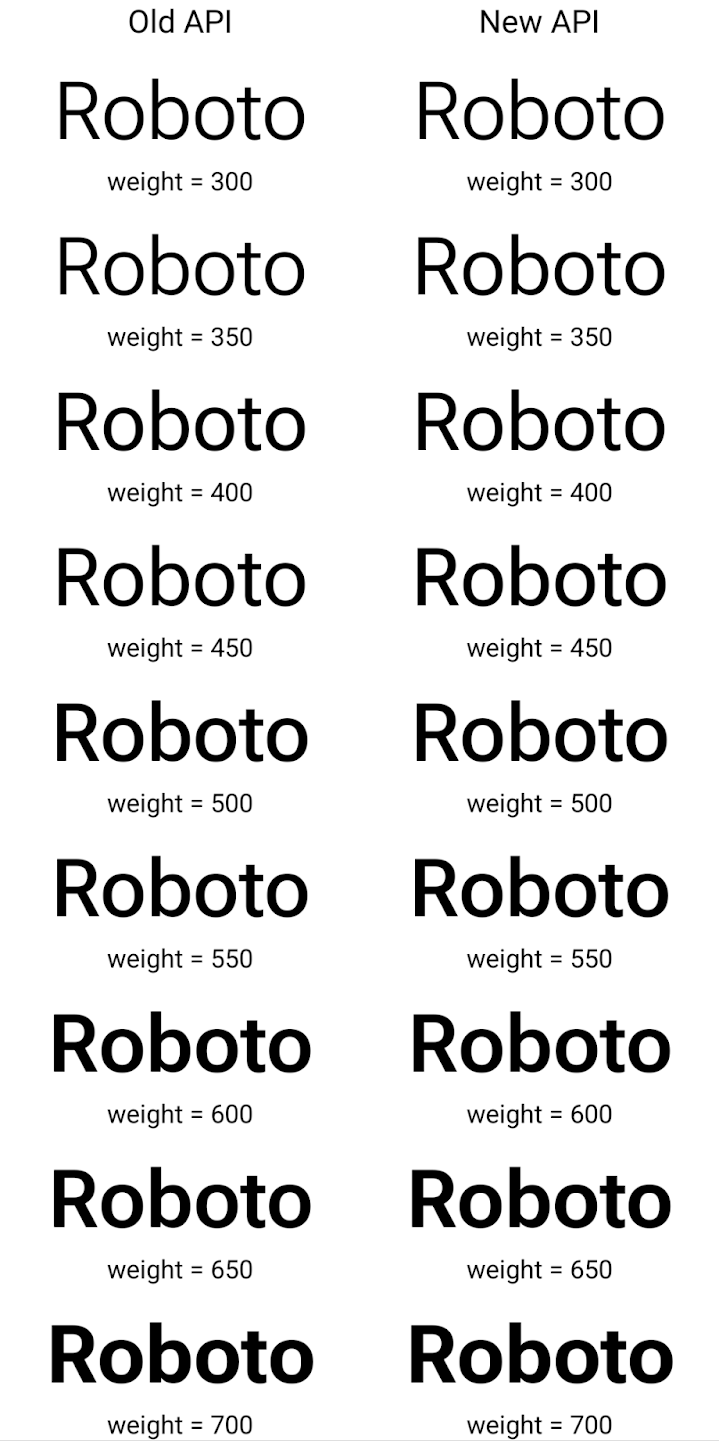
In diesem Beispiel hat der mit der alten API erstellte Typeface nicht die
für die Schriftstärke 350, 450, 550 und 650
Font-Instanzen, sodass der Renderer auf die nächste Gewichtung zurückgreift. In diesem Fall wird also 300 anstelle von 350 gerendert, 400 anstelle von 450 usw. Im Gegensatz dazu erstellt die mit den neuen APIs erstellte Typeface dynamisch
eine Font-Instanz für eine bestimmte Gewichtung, sodass genaue Gewichtungen für 350,
450, 550 und 650 an.
Detaillierte Steuerung von Zeilenumbrüchen
Ab Android 15 kann ein TextView und der zugrunde liegende Zeilenumbruch den angegebenen Textabschnitt in derselben Zeile beibehalten, um die Lesbarkeit zu verbessern. Sie können diese Anpassung der Zeilenumbrüche nutzen, indem Sie das <nobreak>-Tag in Stringressourcen oder createNoBreakSpan verwenden. Ebenso können Sie Wörter aus Bindestrichen beibehalten, indem Sie das <nohyphen>-Tag oder createNoHyphenationSpan verwenden.
Die folgende Stringressource enthält beispielsweise keinen Zeilenumbruch und wird so gerendert, dass der Text „Pixel 8 Pro.“ an einer unerwünschten Stelle unterbrochen wird:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind Pixel 8 Pro.</string>
</resources>
Diese Stringressource enthält dagegen das Tag <nobreak>, das den Ausdruck „Pixel 8 Pro“ umbricht und Zeilenumbrüche verhindert:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind <nobreak>Pixel 8 Pro.</nobreak></string>
</resources>
Die Unterschiede bei der Darstellung dieser Strings sind in den folgenden Bildern zu sehen:

<nobreak>-Tag umgebrochen wird.
<nobreak>-Tag umgebrochen wird.App-Archivierung
Android und Google Play haben angekündigt, dass die App-Archivierung zuletzt unterstützt wird. Jahr, sodass Nutzer Speicherplatz freigeben können, indem sie selten verwendete Apps auf dem Gerät, die über die Android-App veröffentlicht wurden Set bei Google Play. Android 15 unterstützt das Archivieren und Entarchivieren von Apps auf Betriebssystemebene. Dadurch lässt sich die Funktion in allen App-Shops einfacher implementieren.
Apps mit der Berechtigung REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES können die
PackageInstaller requestArchive, um die Archivierung eines
installiertes App-Paket entfernt, wodurch das APK und alle im Cache gespeicherten Dateien entfernt werden,
Nutzerdaten. Archivierte Apps werden über die LauncherApps APIs als darstellbare Apps zurückgegeben. Nutzer sehen eine UI-Anzeige, die darauf hinweist, dass diese Apps archiviert sind. Wenn ein Nutzer auf eine archivierte App tippt,
erhält eine Anfrage zum Wieder aktivieren und der Wiederherstellungsprozess kann
die von der ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED-Übertragung überwacht werden.
16‑KB-Modus auf einem Gerät über die Entwickleroptionen aktivieren

Aktivieren Sie die Entwickleroption Mit Seitengröße von 16 KB starten, um ein Gerät im 16‑KB-Modus zu starten.
Ab Android 15 QPR1 können Sie die Entwickleroption verwenden, die auf bestimmten Geräten verfügbar ist, um das Gerät im 16‑KB-Modus zu starten und Tests auf dem Gerät durchzuführen. Bevor Sie die Entwickleroption verwenden, rufen Sie Einstellungen > System > Softwareupdates auf und installieren Sie alle verfügbaren Updates.
Diese Entwickleroption ist auf den folgenden Geräten verfügbar:
Google Pixel 8 und Google Pixel 8 Pro (mit Android 15 QPR1 oder höher)
Google Pixel 8a (mit Android 15 QPR1 oder höher)
Google Pixel 9, Google Pixel 9 Pro und Google Pixel 9 Pro XL (mit Android 15 QPR2 Beta 2 oder höher)
Grafik
Android 15 bietet die neuesten Grafikverbesserungen, darunter ANGLE und Ergänzungen des Canvas-Grafiksystems.
Modernisierung des GPU-Zugriffs unter Android

Die Android-Hardware hat sich seit den frühen Tagen, als das Betriebssystem auf einer einzelnen CPU ausgeführt wurde und der Zugriff auf GPUs über APIs mit Pipeline mit fester Funktion erfolgte, stark weiterentwickelt. Die Vulkan®-Grafik-API ist seit Android 7.0 (API-Level 24) im NDK verfügbar. Sie bietet eine Abstraktion auf niedrigerem Niveau, die moderne GPU-Hardware besser widerspiegelt, besser skaliert, um mehrere CPU-Kerne zu unterstützen, und einen reduzierten CPU-Treiber-Overhead bietet – was zu einer verbesserten App-Leistung führt. Vulkan wird von allen modernen Game-Engines unterstützt.
Vulkan ist die bevorzugte Schnittstelle von Android zur GPU. Daher enthält Android 15 ANGLE als optionale Schicht zum Ausführen von OpenGL® ES auf Vulkan. Durch die Umstellung auf ANGLE wird die OpenGL-Implementierung von Android standardisiert, um die Kompatibilität und in einigen Fällen auch die Leistung zu verbessern. Sie können die Stabilität und Leistung Ihrer OpenGL ES-App mit ANGLE testen, indem Sie die Entwickleroption unter Android 15 in den Einstellungen -> System -> Entwickleroptionen -> Experimentell: ANGLE aktivieren aktivieren.
Roadmap für ANGLE auf Vulkan für Android
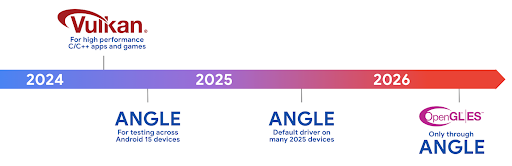
Im Rahmen der Optimierung unseres GPU-Stacks werden wir ANGLE künftig als GL-Systemtreiber auf mehr neuen Geräten ausliefern. Wir gehen davon aus, dass OpenGL/ES in Zukunft nur noch über ANGLE verfügbar sein wird. Wir planen jedoch, OpenGL ES auf allen Geräten weiterhin zu unterstützen.
Empfohlene nächste Schritte
Wählen Sie in den Entwickleroptionen den ANGLE-Treiber für OpenGL ES aus und testen Sie Ihre App. Für neue Projekte empfehlen wir dringend die Verwendung von Vulkan für C/C++.
Verbesserungen für Canvas
Mit Android 15 setzen wir unsere Modernisierung des Canvas-Grafiksystems von Android mit zusätzlichen Funktionen fort:
Matrix44bietet eine 4 × 4-Matrix zum Transformieren von Koordinaten, die verwendet werden sollte, wenn Sie den Canvas in 3D bearbeiten möchten.- Mit
clipShaderwird der aktuelle Clip mit dem angegebenen Shader überlagert. MitclipOutShaderwird der Clip auf die Differenz zwischen dem aktuellen Clip und dem Shader gesetzt. Dabei wird der Shader als Alphamaske behandelt. So lassen sich komplexe Formen effizient zeichnen.
Leistung und Akku
Android konzentriert sich weiterhin darauf, Ihnen dabei zu helfen, die Leistung und Qualität Ihrer Apps zu verbessern. In Android 15 werden APIs eingeführt, mit denen Aufgaben in Ihrer App effizienter ausgeführt werden können, die App-Leistung optimiert und Statistiken zu Ihren Apps erhoben werden können.
Informationen zu Best Practices für einen effizienten Akkuverbrauch, zum Debuggen der Netzwerk- und Stromnutzung sowie dazu, wie wir die Akkueffizienz von Hintergrundaufgaben in Android 15 und den letzten Android-Versionen verbessern, finden Sie im Google I/O-Vortrag zum Thema „Improving battery efficiency of background work on Android“.
ApplicationStartInfo API
In früheren Android-Versionen war das Starten von Apps ein wenig mysteriös. Es war schwierig zu ermitteln, ob Ihre App im Kalt-, Warm- oder Heißstart gestartet wurde. Außerdem war es schwierig zu ermitteln, wie lange Ihre App in den verschiedenen Startphasen benötigt hat: zum Beispiel zum Verzweigen des Prozesses, zum Aufrufen von onCreate oder zum Zeichnen des ersten Frames. Bei der Instanziierung Ihrer Application-Klasse konnten Sie nicht wissen, ob die App über eine Übertragung, einen Inhaltsanbieter, einen Job, eine Sicherung, den vollständigen Start, einen Wecker oder eine Activity gestartet wurde.
Die ApplicationStartInfo API unter Android 15 bietet all das und noch mehr. Sie können dem Ablauf auch eigene Zeitstempel hinzufügen, um Zeitdaten an einem Ort zu erfassen. Neben der Erhebung von Messwerten können Sie ApplicationStartInfo auch verwenden, um den App-Start direkt zu optimieren. So können Sie beispielsweise die kostenintensive Instanziierung von UI-bezogenen Bibliotheken in Ihrem Application-Klassen beim Starten Ihrer App aufgrund einer Übertragung vermeiden.
Detaillierte Informationen zur App-Größe
Seit Android 8.0 (API-Ebene 26) ist die StorageStats.getAppBytes API in Android enthalten. Diese API gibt die installierte Größe einer App als einzelne Bytezahl an, die sich aus der APK-Größe, der Größe der aus dem APK extrahierten Dateien und der Größe der auf dem Gerät generierten Dateien wie AOT-kompiliertem Code zusammensetzt. Diese Zahl gibt nicht viel Aufschluss darüber, wie Ihre App den Speicherplatz nutzt.
Android 15 enthält die StorageStats.getAppBytesByDataType([type]) API, mit der Sie nachvollziehen können, wie viel Speicherplatz Ihre App belegt, einschließlich APK-Dateien, AOT- und Beschleunigungscode, Dex-Metadaten, Bibliotheken und Anleitungsprofilen.
Von der App verwaltetes Profiling
Android 15 enthält die Klasse ProfilingManager, mit der Sie Profilinformationen aus Ihrer App heraus erfassen können, z. B. Heap-Dumps, Heap-Profile und Stack-Sampling. Er stellt einen Callback an Ihre Anwendung mit einem bereitgestellten Tag bereit, um die Ausgabedatei zu identifizieren. Diese wird im Dateiverzeichnis Ihrer Anwendung bereitgestellt. Die API führt eine Ratenbegrenzung durch, um Leistungseinbußen zu minimieren.
Wenn Sie das Erstellen von Profilerstellungsanfragen in Ihrer Anwendung vereinfachen möchten, empfehlen wir die Verwendung der entsprechenden Profiling AndroidX API, die in Core 1.15.0-rc01 oder höher verfügbar ist.
Verbesserungen der SQLite-Datenbank
Mit Android 15 werden SQLite-APIs eingeführt, die erweiterte Funktionen der SQLite-Engine zugrunde, die auf spezifische Leistungsprobleme abzielen, in Apps. Diese APIs sind im Update von SQLite auf Version 3.44.3 enthalten.
Entwickler sollten die Best Practices für die SQLite-Leistung lesen. um das Beste aus ihrer SQLite-Datenbank herauszuholen, insbesondere bei der Arbeit mit großen Datenbanken oder bei der Ausführung von latenzempfindlichen Abfragen.
- Schreibgeschützte ausgesetzte Transaktionen: wenn Transaktionen ausgegeben werden, die
(keine Anweisungen schreiben), verwenden Sie
beginTransactionReadOnly()undbeginTransactionWithListenerReadOnly(SQLiteTransactionListener)um schreibgeschützte Transaktionen vom TypDEFERREDauszuführen. Solche Transaktionen können gleichzeitig ausgeführt werden. Wenn sich die Datenbank im WAL-Modus befindet, können sie auch gleichzeitig mitIMMEDIATE- oderEXCLUSIVE-Transaktionen ausgeführt werden. - Zeilenanzahl und ‑IDs: Es wurden APIs hinzugefügt, um die Anzahl der geänderten Zeilen oder die ID der zuletzt eingefügten Zeile abzurufen, ohne eine zusätzliche Abfrage auszuführen.
getLastChangedRowCount()gibt die Anzahl der Zeilen zurück, die von der letzten SQL-Anweisung innerhalb die aktuelle Transaktion, währendgetTotalChangedRowCount()gibt die Anzahl der aktuellen Verbindung zurück.getLastInsertRowId()gibtrowidder letzten Zeile zurück das bei der aktuellen Verbindung eingefügt werden soll. - Raw-Anweisungen: Hiermit wird eine SQlite-Anweisung ausgegeben, ohne dass praktische Wrapper und eventueller zusätzlicher Verarbeitungsaufwand verwendet werden.
Updates für das Android Dynamic Performance Framework
Mit Android 15 setzen wir unsere Investitionen in das Android Dynamic Performance Framework (ADPF) fort. Das ADPF ist eine Reihe von APIs, mit denen Spiele und leistungsintensive Apps direkter mit den Energie- und Temperatursystemen von Android-Geräten interagieren können. Auf unterstützten Geräten bietet Android 15 ADPF-Funktionen:
- Ein Energiesparmodus für Sitzungen mit Hinweisen, um anzugeben, dass die zugehörigen Threads den Energiesparmodus der Leistung vorziehen sollen. Ideal für lang andauernde Hintergrundlasten.
- Die GPU- und CPU-Arbeitsdauern können in Hinweissitzungen erfasst werden, sodass das System die CPU- und GPU-Taktfrequenzen gemeinsam anpassen kann, um die Anforderungen der Arbeitslast bestmöglich zu erfüllen.
- Grenzwerte für den thermischen Spielraum, um den möglichen thermischen Drosselungsstatus anhand der Spielraumvorhersage zu interpretieren.
Weitere Informationen zur Verwendung von ADPF in Ihren Apps und Spielen finden Sie in der Dokumentation.
Datenschutz
Android 15 umfasst eine Vielzahl von Funktionen, die App-Entwicklern helfen, den Datenschutz der Nutzer zu schützen.
Erkennung von Bildschirmaufzeichnungen
Mit Android 15 wird Unterstützung für Apps hinzugefügt, um zu erkennen, dass sie aufgezeichnet werden. Ein Callback wird immer dann aufgerufen, wenn die Anwendung wechselt in einer Bildschirmaufzeichnung sichtbar oder unsichtbar sein. Eine App ist als sichtbar gelten, wenn Aktivitäten, die zur UID des Registrierungsprozesses gehören, aufgezeichnet wird. So können Sie Nutzer informieren, wenn in Ihrer App ein sensibler Vorgang ausgeführt wird.
val mCallback = Consumer<Int> { state ->
if (state == SCREEN_RECORDING_STATE_VISIBLE) {
// We're being recorded
} else {
// We're not being recorded
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val initialState =
windowManager.addScreenRecordingCallback(mainExecutor, mCallback)
mCallback.accept(initialState)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
windowManager.removeScreenRecordingCallback(mCallback)
}
Erweiterte IntentFilter-Funktionen
Android 15 unterstützt eine genauere Intent-Auflösung über UriRelativeFilterGroup. Diese enthält eine Reihe von UriRelativeFilter-Objekten, die eine Reihe von Intent-Abgleichsregeln bilden, die jeweils erfüllt werden müssen, einschließlich URL-Suchparameter, URL-Fragmente und Blockierungs- oder Ausschlussregeln.
Diese Regeln können in der AndroidManifest-XML-Datei mit dem <uri-relative-filter-group>-Tag definiert werden, das optional ein android:allow-Tag enthalten kann. Diese Tags können <data>-Tags enthalten, die vorhandene Daten-Tag-Attribute sowie die Attribute android:query und android:fragment verwenden.
Hier ein Beispiel für die AndroidManifest-Syntax:
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="astore.com" />
<uri-relative-filter-group>
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="region=na" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="mobileoptout=true" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:fragmentPrefix="faq" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
</intent-filter>
Vertrauliches Profil
Vertrauliche Profile bieten Nutzern einen separaten Bereich auf ihrem Gerät für Apps, die andere nicht auf ihrem Gerät sehen sollen. Sie werden durch eine zusätzliche Authentifizierung geschützt. Für vertrauliche Profile ist ein separates Nutzerprofil erforderlich. Nutzer können die Gerätesperre oder einen separaten Sperrfaktor für vertrauliche Profile verwenden.
Apps im vertraulichen Profil werden in einem separaten Container im Launcher angezeigt und sind in „Letzte Apps“, Benachrichtigungen, Einstellungen und anderen Apps nicht zu sehen, wenn das vertrauliche Profil gesperrt ist. Von Nutzern erstellte und heruntergeladene Inhalte (z. B. Medien oder Dateien) und Konten im vertraulichen Profil sind vom Hauptprofil getrennt. Das Sharesheet des Systems und die Bildauswahl können verwendet werden, um Apps den Zugriff auf Inhalte über verschiedene Bereiche hinweg zu ermöglichen, wenn das vertrauliche Profil entsperrt ist.
Nutzer können vorhandene Apps und ihre Daten nicht in den privaten Bereich verschieben. Stattdessen wählen Nutzer im vertraulichen Profil eine Installationsoption aus, um eine App über den gewünschten App-Shop zu installieren. Apps im vertraulichen Profil werden als separate Kopien von Apps im Hauptprofil installiert (neue Kopien derselben App).
Wenn ein Nutzer das vertrauliche Profil sperrt, wird es beendet. Solange das Profil angehalten ist, sind die Apps im privaten Bereich nicht mehr aktiv und können keine Aktivitäten im Vordergrund oder Hintergrund ausführen, z. B. keine Benachrichtigungen anzeigen.
Wir empfehlen Ihnen, Ihre App in einem privaten Gruppenbereich zu testen, um sicherzustellen, dass sie wie erwartet funktioniert. Das gilt insbesondere, wenn Ihre App in eine der folgenden Kategorien fällt:
- Apps mit Logik für Arbeitsprofile, bei denen davon ausgegangen wird, dass alle installierten Kopien der App, die sich nicht im Hauptprofil befinden, sich im Arbeitsprofil befinden.
- Medizinische Apps
- Launcher-Apps
- App-Shop-Apps
Letzte Nutzerauswahl für den Zugriff auf ausgewählte Fotos abfragen
Apps können jetzt nur die zuletzt ausgewählten Fotos und Videos hervorheben,
Es wird teilweiser Zugriff auf Medienberechtigungen gewährt. Mit dieser Funktion können
für Apps, die häufig Zugriff auf Fotos und Videos anfordern,
Videos. Wenn Sie diese Funktion in Ihrer App verwenden möchten, aktivieren Sie das Argument QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, wenn Sie MediaStore über ContentResolver abfragen.
Kotlin
val externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external") val mediaColumns = arrayOf( FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE, ) val queryArgs = bundleOf( // Return only items from the last selection (selected photos access) QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY to true, // Sort returned items chronologically based on when they were added to the device's storage QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER to "${FileColumns.DATE_ADDED} DESC", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION to "${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ? OR ${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ?", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS to arrayOf( FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE.toString(), FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.toString() ) )
Java
Uri externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external"); String[] mediaColumns = { FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE }; Bundle queryArgs = new Bundle(); queryArgs.putBoolean(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, true); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER, FileColumns.DATE_ADDED + " DESC"); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION, FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ? OR " + FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ?"); queryArgs.putStringArray(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS, new String[] { String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE), String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) });
Privacy Sandbox für Android
Android 15 enthält die neuesten Erweiterungen für Android-Werbedienste, einschließlich der neuesten Version der Privacy Sandbox für Android. Diese Ergänzung ist Teil unserer Bemühungen, Technologien zu entwickeln, die den Datenschutz für Nutzer verbessern und effektive, personalisierte App-Werbung ermöglichen. Auf unserer Privacy Sandbox-Seite finden Sie weitere Informationen zu den Entwicklervorschau- und Betaprogrammen der Privacy Sandbox für Android.
Health Connect
Android 15 integriert die neuesten Erweiterungen Health Connect by Android, eine sichere und zentrale Plattform zum Verwalten und Teilen von durch Apps erhobenen Gesundheits- und Fitnessdaten. Dieses Update Unterstützung weiterer Datentypen über Fitness, Ernährung, Hauttemperatur, Trainingspläne und mehr.
Mit dem Tracking der Hauttemperatur können Nutzer genauere Temperaturdaten von einem Wearable oder einem anderen Tracking-Gerät speichern und teilen.
Trainingspläne sind strukturierte Trainingspläne, die Nutzern helfen, ihre Fitnessziele zu erreichen. Trainingspläne unterstützen eine Vielzahl von Zielvorhaben für den Abschluss und die Leistung:
- Abschlussziele im Umkreis von verbrannten Kalorien distance, duration, Wiederholungen und Schritte.
- Leistungsziele in etwa viele Wiederholungen wie möglich (AMRAP), Kadenz, Herzfrequenz Macht, empfundene Belastungsrate und Geschwindigkeit.
Weitere Informationen zu den neuesten Updates für Health Connect auf Android finden Sie im Vortrag Building adaptable experiences with Android Health (Adaptive Funktionen mit Android Health entwickeln) von der Google I/O.
App-Bildschirmfreigabe
Android 15 unterstützt die Bildschirmfreigabe für Apps, sodass Nutzer nur ein App-Fenster und nicht den gesamten Gerätebildschirm teilen oder aufzeichnen können. Diese Funktion, die erstmals in Android 14 QPR2 aktiviert wurde, umfasst MediaProjectionCallbacks, mit denen Sie die Bildschirmfreigabe Ihrer App anpassen können. Bei Apps, die auf Android 14 (API-Level 34) oder höher ausgerichtet sind, ist für jede MediaProjection-Aufnahmesitzung die Einwilligung des Nutzers erforderlich.
Nutzerfreundlichkeit und System-UI
Unter Android 15 haben App-Entwickler und Nutzer mehr Kontrolle und Flexibilität bei der Konfiguration ihrer Geräte.
Weitere Informationen dazu, wie Sie die neuesten Verbesserungen in Android 15 nutzen können, um die Nutzerfreundlichkeit Ihrer App zu verbessern, finden Sie im Google I/O-Vortrag „Improve the user experience of your Android app“.
Umfangreichere Widget-Vorschauen mit der Generated Previews API
Vor Android 15 bestand die einzige Möglichkeit, Vorschauen für die Widget-Auswahl bereitzustellen, Eine statische Bild- oder Layoutressource Diese Vorschauen unterscheiden sich oft erheblich vom Erscheinungsbild des tatsächlichen Widgets, wenn es auf dem Startbildschirm platziert wird. Außerdem können mit Jetpack Glance keine statischen Ressourcen erstellt werden. Daher musste ein Glance-Entwickler einen Screenshot seines Widgets erstellen oder ein XML-Layout erstellen, um eine Widget-Vorschau zu erhalten.
Android 15 unterstützt jetzt generierte Vorschauen. Das bedeutet, dass App-Widget-Anbieter RemoteViews generieren können, um sie anstelle einer statischen Ressource als Auswahlvorschau zu verwenden.

Push API
Apps können generierte Vorschauen über eine Push-API bereitstellen. Apps bieten
und erhalten keine explizite Anfrage
vom Host gesendet,
um eine Vorschau anzuzeigen. Vorschauen werden in AppWidgetService gespeichert und können von den Gastgebern auf Anfrage abgerufen werden. Im folgenden Beispiel wird eine XML-Widget-Layoutressource geladen und als Vorschau festgelegt:
AppWidgetManager.getInstance(appContext).setWidgetPreview(
ComponentName(
appContext,
SociaLiteAppWidgetReceiver::class.java
),
AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN,
RemoteViews("com.example", R.layout.widget_preview)
)
Der erwartete Ablauf sieht so aus:
- Der Widget-Anbieter ruft jederzeit
setWidgetPreviewauf. Die bereitgestellten Vorschauen werden zusammen mit anderen Anbieterinformationen inAppWidgetServicegespeichert. setWidgetPreviewbenachrichtigt Hosts über eine aktualisierte Vorschau über dasAppWidgetHost.onProvidersChanged-Rückruf. Daraufhin reagiert das Widget alle Anbieterinformationen neu lädt.- Bei der Anzeige einer Widget-Vorschau prüft der Host
AppWidgetProviderInfo.generatedPreviewCategories. Wenn das ausgewählte Element Kategorie verfügbar ist, ruftAppWidgetManager.getWidgetPreviewan gibt die gespeicherte Vorschau für diesen Anbieter zurück.
Wann Sie setWidgetPreview anrufen sollten
Da es keinen Callback für die Vorschau gibt, können Apps wenn sie ausgeführt werden. Wie oft die Vorschau aktualisiert wird, hängt vom Anwendungsfall des Widgets ab.
In der folgenden Liste werden die beiden Hauptkategorien von Anwendungsfällen für Vorschauen beschrieben:
- Anbieter, die in ihrer Widget-Vorschau echte Daten anzeigen, z. B. personalisierte oder aktuelle Informationen. Diese Anbieter können die Vorschau einrichten, sobald der Nutzer angemeldet sind oder die Erstkonfiguration in der App vorgenommen hat. Danach werden sie können eine regelmäßige Aufgabe einrichten, um die Vorschauen im gewünschten Rhythmus zu aktualisieren. Beispiele für diese Art von Widget sind Foto-, Kalender-, Wetter- oder Nachrichten-Widgets.
- Anbieter, die in Vorschau- oder Schnellaktions-Widgets statische Informationen anzeigen, die keine Daten enthalten. Diese Anbieter können die Vorschau einmal einrichten, App-Starts. Beispiele für diese Art von Widget sind Widget „Aktionen“ oder das Widget für Chrome-Verknüpfungen.
Einige Anbieter zeigen in der Auswahl für den Hub-Modus möglicherweise statische Vorschaubilder, aber in der Auswahl für den Startbildschirm echte Informationen an. Diese Anbieter müssen sich an die Richtlinien halten, für beide Anwendungsfälle, um eine Vorschau festzulegen.
Die Funktion „Bild im Bild“
Android 15 führt Änderungen bei Bild im Bild (BiB) ein, die eine einheitliche weichere Übergänge beim Wechsel in den BiB-Modus. Dies ist hilfreich für Apps mit UI-Elementen, die über der Hauptbenutzeroberfläche eingeblendet werden und in BiB einfügen
Entwickler verwenden den onPictureInPictureModeChanged-Callback, um Logik zu definieren
die die Sichtbarkeit
der eingeblendeten UI-Elemente ein-/ausschaltet. Dieser Callback ist
wird ausgelöst, wenn die BiB-Animation zum Ein- oder Ausschalten abgeschlossen ist. Beginnt in
Unter Android 15 enthält die Klasse PictureInPictureUiState einen weiteren Status.
Bei diesem UI-Status wird für Apps, die auf Android 15 (API-Level 35) ausgerichtet sind, die
Activity#onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged-Callback wird aufgerufen mit
isTransitioningToPip(), sobald die BiB-Animation beginnt. Es gibt
viele UI-Elemente, die für die App im BiB-Modus nicht relevant sind,
Beispielansichten oder Layouts, die Informationen wie Vorschläge, bevorstehende
Videos, Bewertungen und Titel. Wenn die App in den BiB-Modus wechselt, verwende die
onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged-Callback zum Ausblenden dieser UI-Elemente. Wenn der Parameter
wenn die App vom BiB-Fenster in den Vollbildmodus wechselt, verwenden Sie
onPictureInPictureModeChanged-Callback zum Einblenden dieser Elemente, wie in
die folgenden Beispiele:
override fun onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged(pipState: PictureInPictureUiState) {
if (pipState.isTransitioningToPip()) {
// Hide UI elements
}
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean) {
if (isInPictureInPictureMode) {
// Unhide UI elements
}
}
Diese Ein/Aus-Schaltfläche für die schnelle Sichtbarkeit irrelevanter UI-Elemente (für ein BiB-Fenster) hilft sorgen für eine flüssigere und flimmernde BiB-Animation.
Verbesserte „Bitte nicht stören“-Regeln
Mit AutomaticZenRule können Apps die Funktion „Aufmerksamkeitserkennung“ anpassen
Verwaltungsregeln (Bitte nicht stören) und entscheiden, wann sie aktiviert oder deaktiviert werden
. In Android 15 wurden diese Regeln erheblich erweitert, um die Nutzerfreundlichkeit zu verbessern. Die folgenden Verbesserungen sind enthalten:
AutomaticZenRuleTypen hinzufügen, damit das System einige Regeln besonders behandeln kann.AutomaticZenRulewurde ein Symbol hinzugefügt, damit die Modi besser erkennbar sind.- Durch Hinzufügen eines
triggerDescription-Strings zuAutomaticZenRule, der Folgendes beschreibt: Bedingungen, unter denen die Regel für den Nutzer aktiviert werden soll. - Hinzugefügt
ZenDeviceEffectsaufAutomaticZenRule, sodass Regeln z. B. die Graustufe auslösen, Nachtmodus verwenden oder den Hintergrund dimmen.
VibrationEffect für Benachrichtigungskanäle festlegen
Android 15 unterstützt die Einstellung starker Vibrationen für eingehende Benachrichtigungen, indem
mit NotificationChannel.setVibrationEffect, sodass
können Ihre Nutzer zwischen
verschiedenen Benachrichtigungstypen unterscheiden,
ohne auf ihr Gerät schauen zu müssen.
Chip für die Statusleiste für die Medienprojektion und automatisches Beenden
Bei der Medienprojektion können private Nutzerdaten offengelegt werden. Ein neuer, gut sichtbarer Status-Chip informiert Nutzer über eine laufende Bildschirmprojektion. Nutzer können auf den Chip tippen, um die Bildschirmfreigabe, -freigabe oder -aufzeichnung zu beenden. Außerdem wird eine laufende Bildschirmprojektion jetzt automatisch beendet, wenn das Display des Geräts gesperrt wird.

Große Displays und Formfaktoren
Mit Android 15 können Ihre Apps die Formfaktoren von Android optimal nutzen, darunter große Displays, Flipables und Foldables.
Verbessertes Multitasking auf großen Displays
Mit Android 15 können Nutzer auf Geräten mit großen Bildschirmen noch einfacher mehrere Dinge gleichzeitig erledigen. Für So können Nutzende ihre bevorzugten Kombinationen von Splitscreen-Apps speichern, Sie können auf die Taskleiste zugreifen und sie anpinnen, um schnell zwischen Apps zu wechseln. Das bedeutet, ist es wichtiger denn je, eine adaptive App zu entwickeln.
Auf der Google I/O gibt es Sitzungen zum Thema Entwicklung adaptiver Android- und Benutzeroberfläche mit Material 3 erstellen, adaptive Bibliothek das hilfreich sein kann. In unserer Dokumentation finden Sie weitere Informationen dazu, wie Sie Designs für große Unternehmen .
Unterstützung des Außendisplays
Ihre App kann eine Property deklarieren, die von Android 15 verwendet wird, damit Ihre Application oder Activity auf den kleinen Cover-Displays unterstützter Klappgeräte angezeigt werden kann. Diese Bildschirme sind zu klein, um als kompatible Ziele für Android-Apps zu gelten. Sie können jedoch die Unterstützung für diese Bildschirme aktivieren, damit Ihre App an mehr Orten verfügbar ist.
Konnektivität
Mit Android 15 wird die Plattform aktualisiert, damit Ihre App Zugriff auf die neuesten Fortschritte in der Kommunikations- und Funktechnologie hat.
Satellitenunterstützung
Android 15 erweitert die Plattformunterstützung für die Satellitenverbindung weiter und enthält einige UI-Elemente, die für eine einheitliche Nutzererfahrung bei der Satellitenverbindung sorgen.
Mit ServiceState.isUsingNonTerrestrialNetwork() können Apps erkennen, wenn ein Gerät mit einem Satelliten verbunden ist. So können sie besser nachvollziehen, warum vollständige Netzwerkdienste möglicherweise nicht verfügbar sind. Außerdem unterstützt Android 15 SMS- und MMS-Apps sowie vorinstallierte RCS-Apps, um die Satellitenverbindung zum Senden und Empfangen von Nachrichten zu nutzen.
Reibungslosere NFC-Funktionen
Mit Android 15 wird das Bezahlen per NFC noch einfacher und zuverlässiger. Gleichzeitig wird das robuste NFC-App-Ökosystem von Android weiter unterstützt. Auf unterstützten Geräten können Apps den NfcAdapter auffordern, den Beobachtungsmodus zu aktivieren. In diesem Modus überwacht das Gerät NFC-Lesegeräte, antwortet ihnen aber nicht. Der NFC-Dienst der App sendet dann PollingFrame-Objekte zur Verarbeitung. Die PollingFrame-Objekte können vor der ersten Kommunikation mit dem NFC-Lesegerät zur Authentifizierung verwendet werden, was in vielen Fällen eine Transaktion mit nur einem Tippen ermöglicht.
Außerdem können Apps auf unterstützten Geräten einen Filter registrieren, damit sie über die Aktivitäten der Polling-Schleife benachrichtigt werden. Dies ermöglicht einen reibungslosen Betrieb mit mehreren NFC-kompatiblen Apps.
Wallet-Rolle
In Android 15 wird eine Wallet-Rolle eingeführt, die eine engere Integration mit der bevorzugten Wallet-App des Nutzers ermöglicht. Diese Rolle ersetzt die NFC-Standardeinstellung für kontaktloses Bezahlen. Nutzer können den Wallet-Rolleninhaber unter Einstellungen > Apps > Standard-Apps verwalten.
Die Wallet-Rolle wird verwendet, wenn NFC-Transaktionen für AIDs weitergeleitet werden, die in der Zahlungskategorie registriert sind. Tippaktionen werden immer an den Wallet-Rolleninhaber weitergeleitet, es sei denn, eine andere App, die für dieselbe AID registriert ist, wird im Vordergrund ausgeführt.
Anhand dieser Rolle wird auch festgelegt, wo die Kachel für den Schnellzugriff auf Wallet platziert werden soll, wenn sie aktiviert ist. Wenn die Rolle auf „Kein“ festgelegt ist, ist die Schnellzugriffskachele nicht verfügbar und NFC-Transaktionen für die Zahlungskategorie werden nur an die App im Vordergrund gesendet.
Sicherheit
Mit Android 15 können Sie die Sicherheit Ihrer App verbessern, die Daten Ihrer App schützen und Nutzern mehr Transparenz und Kontrolle über ihre Daten bieten. Im Google I/O-Vortrag Safeguarding user security on Android (Nutzersicherheit auf Android schützen) erfahren Sie mehr darüber, wie wir den Nutzerschutz verbessern und Ihre App vor neuen Bedrohungen schützen.
Credential Manager in die Funktion zum automatischen Ausfüllen einbinden
Ab Android 15 können Entwickler bestimmte Ansichten wie Nutzernamen- oder Passwortfelder mit Anfragen des Anmeldedaten-Managers verknüpfen. So lässt sich die Anmeldung für Nutzer noch besser anpassen. Wenn der Nutzer den Fokus auf eine dieser Ansichten legt, wird eine entsprechende Anfrage an den Anmeldedaten-Manager gesendet. Die resultierenden Anmeldedaten werden anbieterübergreifend zusammengefasst und in Fallback-Benutzeroberflächen für das automatische Ausfüllen angezeigt, z. B. in Inline- oder Drop-down-Vorschlägen. Die Jetpack-Bibliothek androidx.credentials ist der bevorzugte Endpunkt für Entwickler und wird bald verfügbar sein, um diese Funktion in Android 15 und höher weiter zu verbessern.
Registrierung und Anmeldung über One Tap mit biometrischen Aufforderungen einbinden
Der Anmeldedaten-Manager integriert biometrische Aufforderungen in die Erstellung von Anmeldedaten und Anmeldeprozessen, sodass Anbieter keine biometrische Aufforderungen. Anbieter von Anmeldedaten müssen sich daher nur auf die der Erstellungs- und Abrufvorgänge, ergänzt mit dem biometrischen Flussergebnis. Dieser vereinfachte Prozess ermöglicht eine effizientere und optimierte Erstellung und Abruf von Anmeldedaten.
Schlüsselverwaltung für die Ende-zu-Ende-Verschlüsselung
Mit Android 15 führen wir die E2eeContactKeysManager ein. Diese API auf Betriebssystemebene ermöglicht die Speicherung kryptografischer öffentlicher Schlüssel und erleichtert so die Ende-zu-Ende-Verschlüsselung (E2EE) in Ihren Android-Apps.
Die E2eeContactKeysManager ist für die Einbindung in die Kontakt-App der Plattform konzipiert, um Nutzern eine zentrale Möglichkeit zur Verwaltung und Bestätigung der öffentlichen Schlüssel ihrer Kontakte zu bieten.
Berechtigungsprüfungen für Inhalts-URIs
Mit Android 15 werden mehrere APIs eingeführt, die Berechtigungsprüfungen für Inhalts-URIs durchführen:
Context.checkContentUriPermissionFull: Es wird eine vollständige Berechtigungsprüfung für Inhalts-URIs durchgeführt.Activity-ManifestattributrequireContentUriPermissionFromCaller: Hiermit werden beim Starten der Aktivität die angegebenen Berechtigungen für die angegebenen Inhalts-URIs erzwungen.ComponentCaller-Klasse fürActivity-Caller: Dies ist die App, über die die Aktivität gestartet wurde.
Bedienungshilfen
Android 15 bietet neue Funktionen, die die Barrierefreiheit für Nutzer verbessern.
Better Braille
In Android 15 unterstützt TalkBack Braillezeilen, die den HID-Standard sowohl über USB als auch über sicheres Bluetooth verwenden.
Dieser Standard, der dem von Mäusen und Tastaturen ähnelt, wird dazu beitragen, dass Android im Laufe der Zeit eine größere Auswahl an Braillezeilen unterstützt.
Lokalisierung
Mit Android 15 werden Funktionen und Möglichkeiten hinzugefügt, die die Nutzerfreundlichkeit verbessern, wenn ein Gerät in verschiedenen Sprachen verwendet wird.
Variable CJK-Schriftart
Ab Android 15 ist die Schriftdatei für die chinesischen, japanischen und koreanischen Sprachen (CJK), NotoSansCJK, eine variable Schriftart. Variable Schriftarten eröffnen neue Möglichkeiten für kreative Typografie in CJK-Sprachen. Designer können eine größere Bandbreite an Stilen ausprobieren und visuell ansprechende Layouts erstellen, die zuvor schwierig oder unmöglich zu erreichen waren.

Zeichenübergreifende Begründung
Ab Android 15 kann Text mithilfe von Buchstabenabstand ausgerichtet werden. Verwenden Sie dazu JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER. Interwort-Begründung lautete
erstmals mit Android 8.0 (API-Level 26) eingeführt und Zeichen
Justification bietet ähnliche Funktionen für Sprachen,
Leerzeichen für die Segmentierung, z. B. Chinesisch oder Japanisch.

JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.Automatische Konfiguration von Zeilenumbrüchen
Android unterstützt jetzt wortbasierte Zeilenumbrüche für Japanisch und Koreanisch in
Android 13 (API-Level 33) Durch Zeilenumbrüche dagegen verbessern sich
von kurzen Textzeilen gut lesbar sind, eignen sie sich nicht gut für lange Textzeilen.
In Android 15 können Apps textbasierte Zeilenumbrüche nur auf kurze Zeilen anwenden
des Textes, unter Verwendung des LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
Option. Mit dieser Option wird die beste Wortstiloption für den Text ausgewählt.
Für kurze Textzeilen werden satzbasierte Zeilenumbrüche verwendet, die wie LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE funktionieren, wie im folgenden Bild dargestellt:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO satzbasierte Zeilenumbrüche ein, um die Lesbarkeit des Textes zu verbessern.
Dies entspricht der Anwendung
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASEBei längeren Textzeilen verwendet LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO das Zeichen „Nein“
Zeilenumbruch-Wortformat, das genauso funktioniert wie
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE, wie in den
folgendes Bild:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
wendet keinen Zeilenumbruch an, um die Lesbarkeit des Textes zu verbessern.
Dies entspricht der Anwendung von LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE.Zusätzliche japanische Hentaigana-Schriftart
In Android 15 eine Schriftartdatei für das alte japanische Hiragana (bekannt als Hentaigana) ist standardmäßig gebündelt. Die einzigartigen Formen von Hentaigana-Figuren sorgen dafür, einem Design oder einem Design unverwechselbar machen und gleichzeitig Übertragung und Verständnis alter japanischer Dokumente.

VideoLAN-Kegel – Copyright (c) 1996–2010 VideoLAN. Dieses Logo oder eine modifizierte Version kann von jeder Person verwendet oder geändert werden, um auf das VideoLAN-Projekt oder ein Produkt zu verweisen, das vom VideoLAN-Team entwickelt wurde. Es ist jedoch keine Empfehlung des Projekts.
Vulkan und das Vulkan-Logo sind eingetragene Marken der Khronos Group Inc.
OpenGL ist eine eingetragene Marke und das OpenGL ES-Logo ist eine Marke von Hewlett Packard Enterprise, die mit Genehmigung von Khronos verwendet wird.

