Android 平台提供了四种传感器,用于监控各种环境属性。 您可以使用这些传感器来监控相对环境湿度、照度、环境压力和 Android 设备附近的环境温度。所有四个环境传感器均基于硬件 并且只有当设备制造商内置到设备中时才可用。除了 光传感器,大多数设备制造商都使用它来控制屏幕亮度和环境 传感器并不总是在设备上可用。因此,制定一个 在您尝试从 获取数据之前,在运行时验证是否存在环境传感器 。
与大多数移动传感器和位置传感器不同,后两者会返回一个多维传感器数组
每个 SensorEvent 的值,环境传感器会返回一个传感器
每个数据事件的价值例如,以°C 为单位的温度或以 hPa 为单位的压力。
此外,与移动传感器和位置传感器不同,移动传感器和位置传感器通常需要高通或低通
过滤,环境传感器通常不需要任何数据过滤或数据处理。桌子
1 提供了 Android 平台支持的环境传感器的摘要。
表 1. Android 平台支持的环境传感器。
| 传感器 | 传感器事件数据 | 度量单位 | 数据说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
TYPE_AMBIENT_TEMPERATURE |
event.values[0] |
°C | 环境空气温度。 |
TYPE_LIGHT |
event.values[0] |
lx | 照度。 |
TYPE_PRESSURE |
event.values[0] |
hPa 或 mbar | 环境空气压力。 |
TYPE_RELATIVE_HUMIDITY |
event.values[0] |
% | 环境相对湿度。 |
TYPE_TEMPERATURE |
event.values[0] |
°C | 设备温度。1 |
1 实现方式因设备而异 设备。此传感器已在 Android 4.0(API 级别 14)中弃用。
使用光、压力和温度传感器
从光、压力和温度传感器获取的原始数据通常不需要
校准、滤波或修改,这使得它们成为一些最容易使用的传感器。接收者
要从这些传感器中获取数据,您首先需要创建 SensorManager 类的实例,该实例可用于获取物理传感器的实例。
然后,在 onResume() 方法中注册传感器监听器,并开始在 onSensorChanged() 回调方法中处理传入的传感器数据。通过
以下代码展示了如何执行此操作:
Kotlin
class SensorActivity : Activity(), SensorEventListener { private lateinit var sensorManager: SensorManager private var pressure: Sensor? = null public override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.main) // Get an instance of the sensor service, and use that to get an instance of // a particular sensor. sensorManager = getSystemService(Context.SENSOR_SERVICE) as SensorManager pressure = sensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_PRESSURE) } override fun onAccuracyChanged(sensor: Sensor, accuracy: Int) { // Do something here if sensor accuracy changes. } override fun onSensorChanged(event: SensorEvent) { val millibarsOfPressure = event.values[0] // Do something with this sensor data. } override fun onResume() { // Register a listener for the sensor. super.onResume() sensorManager.registerListener(this, pressure, SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_NORMAL) } override fun onPause() { // Be sure to unregister the sensor when the activity pauses. super.onPause() sensorManager.unregisterListener(this) } }
Java
public class SensorActivity extends Activity implements SensorEventListener { private SensorManager sensorManager; private Sensor pressure; @Override public final void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); // Get an instance of the sensor service, and use that to get an instance of // a particular sensor. sensorManager = (SensorManager) getSystemService(Context.SENSOR_SERVICE); pressure = sensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_PRESSURE); } @Override public final void onAccuracyChanged(Sensor sensor, int accuracy) { // Do something here if sensor accuracy changes. } @Override public final void onSensorChanged(SensorEvent event) { float millibarsOfPressure = event.values[0]; // Do something with this sensor data. } @Override protected void onResume() { // Register a listener for the sensor. super.onResume(); sensorManager.registerListener(this, pressure, SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_NORMAL); } @Override protected void onPause() { // Be sure to unregister the sensor when the activity pauses. super.onPause(); sensorManager.unregisterListener(this); } }
您必须始终包含 onAccuracyChanged() 和 onSensorChanged() 两种回调方法的实现。此外,
确保在 activity 暂停时始终取消注册传感器。这可以防止传感器
持续检测数据并消耗电池电量。
使用湿度传感器
您可以像使用湿度传感器一样使用湿度传感器来获取原始相对湿度数据
光传感器、压力传感器和温度传感器。不过,如果设备同时具有湿度传感器
(TYPE_RELATIVE_HUMIDITY) 和温度传感器 (TYPE_AMBIENT_TEMPERATURE),您可以使用这两个数据流来计算
露点和绝对湿度
露点
露点是给定体积的空气必须在恒定恒定条件下必须冷却的温度 气压,使水蒸气凝结成水。以下等式显示了 可计算露点:
![t_d(t,RH) = Tn · (ln(RH/100) + m·t/(T_n+t)
))/(m - [ln(RH/100%) + m·t/(T_n+t)])](https://developer.android.google.cn/static/images/guide/topics/sensors/dew_point.png?authuser=6&hl=uk)
其中:
- td = 以摄氏度为单位的露点温度
- t = 以摄氏度为单位的实际温度
- RH = 以百分比 (%) 表示的实际相对湿度
- m = 17.62
- Tn = 243.12
绝对湿度
绝对湿度是一定体积的干燥空气中的水蒸气质量。绝对 湿度以克/米3 为单位。以下等式显示了 可计算绝对湿度:
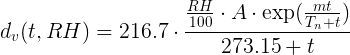
其中:
- dv = 以克/米3 为单位的绝对湿度
- t = 以摄氏度为单位的实际温度
- RH = 以百分比 (%) 表示的实际相对湿度
- m = 17.62
- Tn = 243.12 摄氏度
- A = 6.112 hPa

