A plataforma Android 15 inclui mudanças de comportamento que podem afetar seu app.
As mudanças a seguir se aplicam a todos os apps quando executados no Android 15,
independente da targetSdkVersion. Teste o app e modifique-o conforme necessário para que ele ofereça suporte a essas mudanças, se necessário.
Consulte também a lista de mudanças de comportamento que afetam apenas os apps destinados ao Android 15.
Principal recurso
O Android 15 modifica ou expande vários recursos principais do sistema Android.
Mudanças no estado parado do pacote
A intenção do estado FLAG_STOPPED do pacote (que os usuários
podem acionar em builds do AOSP pressionando um ícone de app por muito tempo e selecionando "Forçar
Parar") sempre foi manter os apps nesse estado até que o usuário os remova
explicitamente, iniciando o app diretamente ou interagindo indiretamente
com ele (pela sharesheet ou um widget, selecionando o app
como papel de parede animado etc.). No Android 15, atualizamos o comportamento do
sistema para estar alinhado com esse comportamento pretendido. Os apps só podem ser removidos
do estado de interrupção por uma ação direta ou indireta do usuário.
Para oferecer suporte ao comportamento pretendido, além das restrições atuais, o
sistema também cancela todas as intenções pendentes quando o app entra no
estado parado em um dispositivo com o Android 15. Quando as ações do usuário removem o
app do estado parado, a transmissão ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED
é enviada ao app, oferecendo a oportunidade de registrar novamente todas as
intents pendentes.
Chame o novo método
ApplicationStartInfo.wasForceStopped()
para confirmar se o app foi colocado no estado parado.
Suporte a tamanhos de página de 16 KB
Historicamente, o Android só ofereceu suporte a tamanhos de página de memória de 4 KB, o que otimizou o desempenho da memória do sistema para a quantidade média de memória total que os dispositivos Android normalmente tinham. A partir do Android 15, o AOSP oferece suporte a dispositivos configurados para usar um tamanho de página de 16 KB (dispositivos de 16 KB). Se o app usar alguma biblioteca do NDK, seja direta ou indiretamente por um SDK, será necessário recriar o app para que ele funcione nesses dispositivos de 16 KB.
À medida que os fabricantes de dispositivos continuam criando dispositivos com quantidades maiores de memória física (RAM), muitos deles vão adotar tamanhos de página de 16 KB (e eventualmente maiores) para otimizar o desempenho do dispositivo. Ao adicionar suporte para dispositivos com tamanho de página de 16 KB, você permite que o app seja executado nesses dispositivos e aproveite as melhorias de desempenho associadas. Sem recompilação, os apps não vão funcionar em dispositivos de 16 KB em versões futuras do Android.
Para ajudar você a adicionar suporte ao app, fornecemos orientações sobre como verificar se o app foi afetado, como recompilar o app (se aplicável) e como testar o app em um ambiente de 16 KB usando emuladores (incluindo imagens do sistema Android 15 para o Android Emulator).
Benefícios e ganhos de desempenho
Os dispositivos configurados com tamanhos de página de 16 KB usam um pouco mais de memória em média, mas também têm várias melhorias de desempenho para o sistema e os apps:
- Tempos de inicialização do app mais rápidos enquanto o sistema está sob pressão de memória: 3,16% mais baixos em média, com melhorias mais significativas (até 30%) em alguns apps testados.
- Redução do consumo de energia durante o lançamento do app: redução média de 4,56%
- Lançamento mais rápido da câmera: 4,48% mais rápido em média e 6,60% mais rápido em média
- Tempo de inicialização do sistema melhorado: melhoria de 8% (aproximadamente 950 milissegundos) em média
Essas melhorias são baseadas nos testes iniciais, e os resultados em dispositivos reais provavelmente serão diferentes. Forneceremos análises adicionais de ganhos em potencial para apps à medida que continuarmos nossos testes.
Verificar se o app é afetado
Se o app usar código nativo, recompile o app com suporte para dispositivos de 16 KB. Se você não tiver certeza se o app usa código nativo, use o APK Analyzer para identificar se há código nativo e verifique o alinhamento dos segmentos ELF de bibliotecas compartilhadas encontradas. O Android Studio também oferece recursos que ajudam a detectar automaticamente problemas de alinhamento.
Se o app usa apenas código escrito na linguagem de programação Java ou Kotlin, incluindo bibliotecas ou SDKs, ele já oferece suporte a dispositivos de 16 KB. No entanto, recomendamos que você teste o app em um ambiente de 16 KB para verificar se não há regressões inesperadas no comportamento do app.
Mudanças necessárias para alguns apps funcionarem no espaço privado
O espaço privado é um novo recurso do Android 15 que permite aos usuários criar um espaço separado no dispositivo para manter os apps sensíveis longe de olhares curiosos e sob uma camada adicional de autenticação. Como os apps no espaço particular têm visibilidade restrita, alguns tipos de apps precisam seguir outras etapas para poderem ser vistos e interagir com os apps no espaço particular de um usuário.
Todos os apps
Como os apps no espaço pessoal são mantidos em um perfil de usuário separado, semelhante aos perfis de trabalho, os apps não podem presumir que as cópias instaladas do app que não estão no perfil principal estão no perfil de trabalho. Se o app tiver uma lógica relacionada a apps de perfil de trabalho que fazem essa suposição, você precisará ajustar essa lógica.
Apps de medicina
Quando um usuário bloqueia o espaço particular, todos os apps nele são interrompidos e não podem realizar atividades em primeiro ou segundo plano, incluindo a exibição de notificações. Esse comportamento pode afetar significativamente o uso e a função de apps médicos instalados no espaço privado.
A experiência de configuração do espaço privado alerta os usuários de que ele não é adequado para apps que precisam realizar atividades importantes em primeiro ou segundo plano, como mostrar notificações de apps médicos. No entanto, os apps não podem determinar se estão sendo usados no espaço particular, portanto, não podem mostrar um aviso ao usuário nesse caso.
Por esses motivos, se você desenvolve um app médico, analise como esse recurso pode afetar seu app e tome as medidas adequadas, como informar aos usuários para não instalar o app no espaço privado, para evitar interromper os recursos essenciais do app.
Apps da tela de início
Se você desenvolver um app de tela de início, faça o seguinte antes que os apps no espaço privado fiquem visíveis:
- Seu app precisa ser atribuído como o app de inicialização padrão do dispositivo, ou
seja, ter o papel de
ROLE_HOME. - O app precisa declarar a permissão normal
ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILESno arquivo de manifesto do app.
Os apps de inicialização que declaram a permissão ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILES precisam processar
os seguintes casos de uso do espaço privado:
- O app precisa ter um contêiner de inicialização separado para apps instalados no
espaço privado. Use o método
getLauncherUserInfo()para determinar qual tipo de perfil de usuário está sendo processado. - O usuário precisa poder ocultar e mostrar o contêiner de espaço privado.
- O usuário precisa poder bloquear e desbloquear o contêiner do espaço privado. Use
o método
requestQuietModeEnabled()para bloquear (transmitindotrue) ou desbloquear (transmitindofalse) o espaço privado. Enquanto estiver bloqueado, nenhum app no contêiner do espaço privado poderá ser visível ou detectável por mecanismos como a pesquisa. O app precisa registrar um receptor para as transmissões
ACTION_PROFILE_AVAILABLEeACTION_PROFILE_UNAVAILABLEe atualizar a interface quando o estado bloqueado ou desbloqueado do contêiner do espaço privado mudar. Ambas as transmissões incluemEXTRA_USER, que o app pode usar para se referir ao usuário do perfil privado.Também é possível usar o método
isQuietModeEnabled()para verificar se o perfil do espaço particular está bloqueado ou não.
Apps da app store
O espaço privado inclui um botão "Instalar apps" que inicia uma intent implícita
para instalar apps no espaço privado do usuário. Para que o app
receba essa intent implícita, declare uma <intent-filter>
no arquivo de manifesto do app com uma <category> de
CATEGORY_APP_MARKET.
Fonte de emoji baseada em PNG removida
O arquivo de fonte de emoji legada (NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf) com base em PNG foi
removido, deixando apenas o arquivo baseado em vetor. A partir do Android 13 (nível
33 da API), o arquivo de fonte de emoji usado pelo renderizador de emoji do sistema mudou de um
arquivo baseado em PNG para um baseado em vetor. O sistema reteve
o arquivo de fonte legada no Android 13 e 14 por motivos de compatibilidade. Assim, apps com renderizadores de fontes próprios podiam continuar usando o arquivo de fonte legada
até que pudessem fazer upgrade.
Para verificar se o app foi afetado, procure referências ao arquivo
NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf no código do app.
Você pode adaptar seu app de várias maneiras:
- Use APIs da plataforma para renderização de texto. É possível renderizar texto em uma
Canvascom suporte a bitmap e usá-la para receber uma imagem bruta, se necessário. - Adicione suporte a fontes COLRv1 ao app. A biblioteca de código aberto FreeType oferece suporte a COLRv1 na versão 2.13.0 e mais recentes.
- Como último recurso, você pode agrupar o arquivo de fonte de emoji legado
(
NotoColorEmoji.ttf) no APK, mas, nesse caso, o app não terá as atualizações mais recentes de emoji. Para mais informações, consulte a página do projeto Noto Emoji no GitHub (em inglês).
Aumentamos a versão mínima do SDK de destino de 23 para 24.
O Android 15 se baseia no
das mudanças feitas no Android 14 e amplia essa
aumentar a segurança. No Android 15, os apps com uma
Não é possível instalar uma targetSdkVersion anterior a 24.
Exigir que os aplicativos atendam aos níveis modernos da API ajuda a garantir melhor segurança e
privacidade.
O malware geralmente tem como alvo níveis mais baixos de API para contornar a segurança e a privacidade
de segurança que foram introduzidas em versões mais recentes do Android. Por exemplo,
alguns apps de malware usam uma targetSdkVersion de 22 para evitar serem submetidos ao
modelo de permissão de execução apresentado em 2015 pelo Android 6.0 Marshmallow (nível
23 da API). Essa mudança do Android 15 dificulta que malwares evitem melhorias de segurança
e privacidade. Tentar instalar um app destinado a uma API anterior
resulta em falha na instalação, com uma mensagem como a seguinte
que aparecem no Logcat:
INSTALL_FAILED_DEPRECATED_SDK_VERSION: App package must target at least SDK version 24, but found 7
Em dispositivos que fizerem upgrade para o Android 15, todos os apps com uma targetSdkVersion anterior
de 24 permanecem instalados.
Se você precisar testar um app destinado a um nível de API mais antigo, use o seguinte comando adb:
adb install --bypass-low-target-sdk-block FILENAME.apk
Segurança e privacidade
O Android 15 apresenta medidas robustas para combater a fraude de senha única (OTP, na sigla em inglês) e proteger o conteúdo sensível do usuário, com foco em aumentar a proteção do serviço de listener de notificações e do compartilhamento de tela. As principais melhorias incluem a edição de OTPs de notificações acessíveis a apps não confiáveis, o ocultamento de notificações durante o compartilhamento de tela e a proteção de atividades do app quando OTPs são publicadas. O objetivo dessas mudanças é proteger o conteúdo sensível do usuário contra atores não autorizados.
Os desenvolvedores precisam estar cientes do seguinte para garantir que os apps sejam compatíveis com as mudanças no Android 15:
OTP Redaction
O Android vai impedir que apps não confiáveis que implementam um
NotificationListenerService leiam conteúdo não editado
de notificações em que um OTP foi detectado. Os apps confiáveis, como
as associações de gerenciador de dispositivos secundário, estão isentos dessas restrições.
Proteção de compartilhamento de tela
- O conteúdo da notificação é ocultado durante as sessões de compartilhamento de tela para preservar
a privacidade do usuário. Se o app implementar
setPublicVersion(), o Android vai mostrar a versão pública da notificação, que serve como uma notificação de substituição em contextos não seguros. Caso contrário, o conteúdo da notificação será editado sem nenhum outro contexto. - Conteúdo sensível, como a entrada de senha, fica oculto para os espectadores remotos para evitar a revelação de informações sensíveis do usuário.
- As atividades de apps que postam notificações durante o compartilhamento de tela em que um OTP foi detectado serão ocultas. O conteúdo do app fica oculto do espectador remoto quando é iniciado.
- Além da identificação automática de campos sensíveis do Android, os desenvolvedores
podem marcar manualmente partes do app como sensíveis usando
setContentSensitivity, que é ocultado dos espectadores remotos durante o compartilhamento de tela. - Os desenvolvedores podem ativar a opção Desativar proteções do compartilhamento de tela em Opções do desenvolvedor para serem dispensados das proteções do compartilhamento de tela para fins de demonstração ou teste. O gravador de tela padrão do sistema está isento dessas mudanças, já que as gravações permanecem no dispositivo.
Câmera e mídia
O Android 15 faz as seguintes mudanças no comportamento de mídia e câmera para todos os apps.
A reprodução de áudio direta e de descarga invalida as faixas de áudio diretas ou de descarga abertas anteriormente quando os limites de recursos são atingidos.
Antes do Android 15, se um app solicitasse a reprodução de áudio direta ou de transferência enquanto
outro app estava reproduzindo áudio e os limites de recursos fossem alcançados, o app
não conseguiria abrir uma nova AudioTrack.
A partir do Android 15, quando um app solicita a reprodução direta ou de
descarga e os limites de
recurso são alcançados, o sistema invalida todos os objetos
AudioTrack abertos que impedem o atendimento da nova solicitação de faixa.
As faixas de áudio diretas e de transferência geralmente são abertas para a reprodução de formatos de áudio compactados. Os casos de uso comuns para a reprodução de áudio direto incluem o streaming de áudio codificado por HDMI para uma TV. As faixas de transferência são geralmente usadas para reproduzir áudio compactado em um dispositivo móvel com aceleração de DSP de hardware.
Experiência do usuário e interface do sistema
O Android 15 inclui algumas mudanças que visam criar uma experiência do usuário mais consistente e intuitiva.
Animações de volta preditiva ativadas para apps que ativaram a opção
A partir do Android 15, a opção para desenvolvedores de animações de volta preditiva foi removida. Animações do sistema, como voltar à tela inicial, entre tarefas e atividades, agora aparecem para apps que ativaram o gesto de volta preditivo inteiramente ou em um nível de atividade. Se o app for afetado, realize as seguintes ações:
- Confira se o app foi migrado corretamente para usar o gesto de volta previsivo.
- Verifique se as transições de fragmentos funcionam com a navegação de volta preditiva.
- Migrar de animações e transições de framework e usar animações e transições do androidx.
- Migração de backstacks que
FragmentManagernão conhece. Use backstacks gerenciadas porFragmentManagerou pelo componente de navegação.
Widgets desativados quando o usuário força a interrupção de um app
Se um usuário interromper um app em um dispositivo com o Android 15, o sistema desativará temporariamente todos os widgets do app. Os widgets estão esmaecidos, e o usuário não pode interagir com eles. Isso ocorre porque, a partir do Android 15, o sistema cancela todas as intents pendentes de um app quando ele é forçado a parar.
O sistema reativa esses widgets na próxima vez que o usuário abrir o app.
Para mais informações, consulte Mudanças no estado de pacotes interrompidos.
O ícone da barra de status de projeção de mídia alerta os usuários sobre compartilhamento, transmissão e gravação de tela
As explorações de projeção de tela expõem dados privados do usuário, como informações financeiras, porque os usuários não percebem que a tela do dispositivo está sendo compartilhada.
Para apps executados em dispositivos com o Android 15 QPR1 ou mais recente, um ícone grande e visível na barra de status alerta os usuários sobre qualquer projeção de tela em andamento. Os usuários podem tocar no ícone para impedir que a tela seja compartilhada, transmitida ou gravada. Além disso, a projeção da tela é interrompida automaticamente quando a tela do dispositivo é bloqueada.
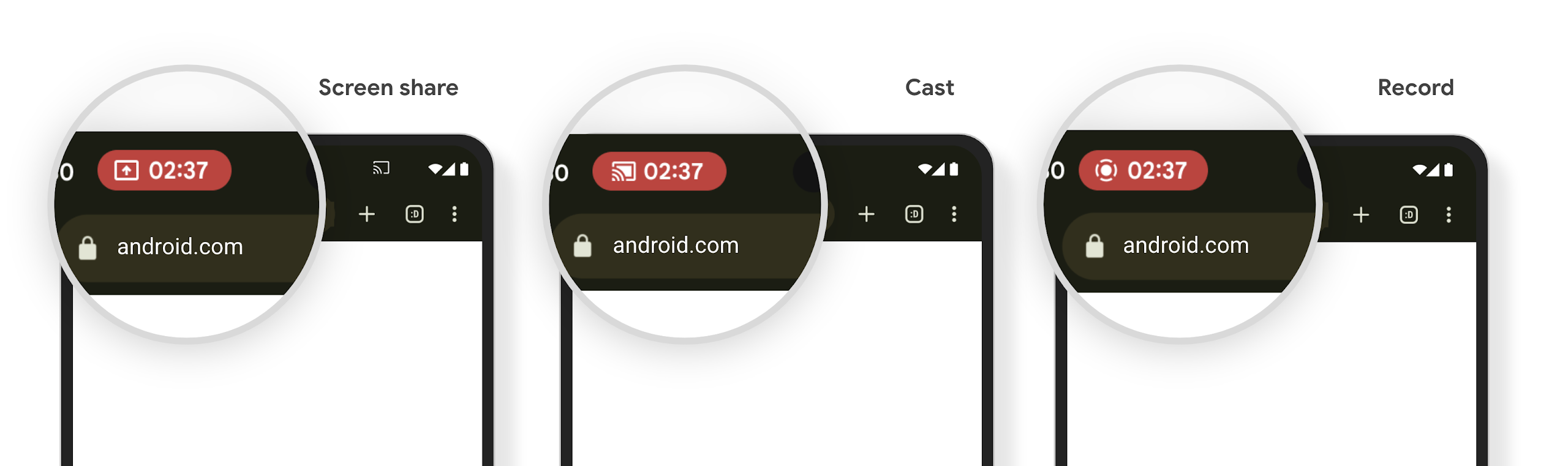
Verificar se o app é afetado
Por padrão, o app inclui o ícone da barra de status e suspende automaticamente a projeção de tela quando a tela de bloqueio é ativada.
Para saber mais sobre como testar seu app para esses casos de uso, consulte Ícone da barra de status e parada automática.
Restrições de acesso à rede em segundo plano
No Android 15, os apps que iniciam uma solicitação de rede fora de um ciclo de vida
de processo válido recebem uma exceção. Normalmente, um
UnknownHostException ou outro IOException
relacionado ao soquete. As solicitações de rede que acontecem fora de um ciclo de vida válido geralmente
são devido a apps que continuam uma solicitação de rede sem saber, mesmo depois que o app
não está mais ativo.
Para reduzir essa exceção, use componentes com reconhecimento de ciclo de vida para garantir que as solicitações de rede tenham reconhecimento de ciclo de vida e sejam canceladas ao sair de um ciclo de vida de processo válido. Se for importante que a solicitação de rede aconteça mesmo quando o usuário sair do aplicativo, programe a solicitação de rede usando o WorkManager ou continue uma tarefa visível para o usuário usando o Serviço em primeiro plano.
Suspensões de uso
A cada versão, algumas APIs específicas do Android podem se tornar obsoletas ou precisarem ser refatoradas para fornecer uma melhor experiência aos desenvolvedores ou oferecer compatibilidade com as novas funcionalidades da plataforma. Nesses casos, descontinuamos oficialmente as APIs obsoletas e direcionamos os desenvolvedores para APIs alternativas.
Descontinuação significa que encerramos o suporte oficial para as APIs, mas elas continuarão disponíveis para os desenvolvedores. Para saber mais sobre as descontinuações importantes nesta versão do Android, consulte a página de descontinuações.
