Podobnie jak poprzednie wersje, Android 15 wprowadza zmiany w działaniu, które mogą mieć wpływ na Twoją aplikację. Poniższe zmiany dotyczą wyłącznie aplikacji, które są kierowane na Androida 15 lub nowszego. Jeśli Twoja aplikacja jest kierowana na Androida 15 lub nowszego, zmodyfikuj ją tak, aby prawidłowo obsługiwała te zachowania w odpowiednich przypadkach.
Zapoznaj się też z listą zmian w zachowaniu, które mają wpływ na wszystkie aplikacje działające na Androidzie 15, niezależnie od targetSdkVersion aplikacji.
Główna funkcja
Android 15 modyfikuje lub rozszerza różne podstawowe funkcje systemu Android.
Zmiany w usługach działających na pierwszym planie
W Androidzie 15 wprowadzamy następujące zmiany w usługach działających na pierwszym planie.
- Zachowanie usługi synchronizacji danych na pierwszym planie w przypadku przekroczenia limitu czasu
- Nowy typ usługi na pierwszym planie do przetwarzania multimediów
- Ograniczenia dotyczące odbiorników
BOOT_COMPLETEDuruchamiających usługi na pierwszym planie - Ograniczenia dotyczące uruchamiania usług na pierwszym planie, gdy aplikacja ma uprawnienie
SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW
Zachowanie limitu czasu usługi na pierwszym planie synchronizującej dane
Android 15 wprowadza nowe zachowanie dotyczące limitu czasu w przypadku dataSync w aplikacjach kierowanych na Androida 15 (poziom interfejsu API 35) lub nowszego. Takie zachowanie dotyczy też nowego mediaProcessingtypu usługi działającej na pierwszym planie.
System zezwala na działanie usług dataSync aplikacji przez łącznie 6 godzin w ciągu 24 godzin, po czym wywołuje metodę Service.onTimeout(int, int) działającej usługi (wprowadzoną w Androidzie 15). W tej chwili usługa ma kilka sekund na wywołanie metody Service.stopSelf(). Gdy wywołana zostanie usługa Service.onTimeout(), nie będzie ona już usługą na pierwszym planie. Jeśli usługa nie wywołuje funkcji Service.stopSelf(), system zgłasza wewnętrzny wyjątek. Wyjątek jest rejestrowany w Logcat z tym komunikatem:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type dataSync did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
Aby uniknąć problemów związanych z tą zmianą zachowania, możesz wykonać co najmniej jedną z tych czynności:
- Zaimplementuj nową metodę
Service.onTimeout(int, int)w swojej usłudze. Gdy aplikacja otrzyma połączenie zwrotne, w ciągu kilku sekund zadzwoń pod numerstopSelf(). Jeśli nie zatrzymasz aplikacji od razu, system wygeneruje błąd. - Upewnij się, że usługi
dataSyncTwojej aplikacji nie działają przez łącznie 6 godzin w dowolnym okresie 24 godzin (chyba że użytkownik wejdzie w interakcję z aplikacją, resetując minutnik). - Uruchamiaj
dataSyncusługi na pierwszym planie wyłącznie w wyniku bezpośredniej interakcji z użytkownikiem. Ponieważ aplikacja znajduje się na pierwszym planie w momencie uruchomienia usługi, usługa ma pełne 6 godzin od uruchomienia w tle. - Zamiast usługi na pierwszym planie
dataSyncużyj alternatywnego interfejsu API.
Jeśli w ciągu ostatnich 24 godzin usługi dataSync na pierwszym planie Twojej aplikacji działały przez 6 godzin, nie możesz uruchomić innej usługi dataSync na pierwszym planie chyba że użytkownik przełączył aplikację na pierwszy plan (co spowoduje zresetowanie minutnika). Jeśli spróbujesz uruchomić inną usługę na pierwszym planie dataSync, system wygeneruje ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException z komunikatem o błędzie, np. „Limit czasu dla usługi działającej na pierwszym planie typu dataSync został już wyczerpany”.
Testowanie
Aby przetestować działanie aplikacji, możesz włączyć czas oczekiwania na synchronizację danych, nawet jeśli aplikacja nie jest kierowana na Androida 15 (o ile działa na urządzeniu z Androidem 15). Aby włączyć limity czasu, uruchom to polecenie adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
Możesz też dostosować limit czasu oczekiwania, aby łatwiej testować działanie aplikacji po osiągnięciu limitu. Aby ustawić nowy okres oczekiwania, uruchom to polecenie adb:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager data_sync_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
Nowy typ usługi działającej na pierwszym planie do przetwarzania multimediów
W Androidzie 15 wprowadziliśmy nowy typ usługi na pierwszym planie: mediaProcessing. Ten typ usługi jest odpowiedni do operacji takich jak transkodowanie plików multimedialnych. Na przykład aplikacja multimedialna może pobrać plik audio i przed odtworzeniem musi przekonwertować go na inny format. Możesz użyć usługi mediaProcessing na pierwszym planie, aby mieć pewność, że konwersja będzie kontynuowana nawet wtedy, gdy aplikacja będzie działać w tle.
System zezwala na działanie usług mediaProcessing aplikacji przez łącznie 6 godzin w okresie 24 godzin. Po tym czasie system wywołuje metodę Service.onTimeout(int, int) (wprowadzoną w Androidzie 15). Obecnie usługa ma kilka sekund na wywołanie funkcji Service.stopSelf(). Jeśli usługa nie wywołuje funkcji Service.stopSelf(), system zgłasza wewnętrzny wyjątek. Wyjątek jest logowany w Logcat z tym komunikatem:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type mediaProcessing did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
Aby uniknąć wyjątku, wykonaj jedną z tych czynności:
- Zaimplementuj nową metodę
Service.onTimeout(int, int)w swojej usłudze. Gdy aplikacja otrzyma połączenie zwrotne, w ciągu kilku sekund zadzwoń pod numerstopSelf(). (jeśli nie zatrzymasz aplikacji od razu, system wygeneruje błąd). - Upewnij się, że usługi
mediaProcessingw aplikacji nie działają dłużej niż 6 godzin w ciągu 24 godzin (chyba że użytkownik wchodzi w interakcję z aplikacją, zresetowując w ten sposób timer). - Uruchamiaj usługi na pierwszym planie
mediaProcessingtylko w wyniku bezpośredniej interakcji z użytkownikiem. Ponieważ aplikacja jest na pierwszym planie, gdy usługa się uruchamia, ma ona 6 godzin na działanie po przejściu aplikacji w tło. - Zamiast usługi na pierwszym planie
mediaProcessingużyj alternatywnego interfejsu API, takiego jak WorkManager.
Jeśli w ciągu ostatnich 24 godzin usługi mediaProcessing na pierwszym planie aplikacji działały przez 6 godzin, nie możesz uruchomić innej usługi mediaProcessing na pierwszym planie chyba że użytkownik przełączył aplikację na pierwszy plan (co spowoduje zresetowanie minutnika). Jeśli spróbujesz uruchomić inną usługę działającą na pierwszym planie mediaProcessing, system wyświetli komunikat o błędzie podobny do „Czas limitu usługi działającej na pierwszym planie typu mediaProcessing został już wykorzystany”.ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException
Więcej informacji o typie usługi mediaProcessing znajdziesz w artykule Zmiany w typach usług na pierwszym planie w Androidzie 15: przetwarzanie multimediów.
Testowanie
Aby przetestować działanie aplikacji, możesz włączyć limity czasu przetwarzania multimediów, nawet jeśli aplikacja nie jest kierowana na Androida 15 (o ile jest uruchomiona na urządzeniu z Androidem 15). Aby włączyć limity czasu, uruchom to polecenie adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
Możesz też dostosować czas oczekiwania, aby łatwiej testować działanie aplikacji po osiągnięciu limitu. Aby ustawić nowy okres oczekiwania, uruchom to polecenie adb:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager media_processing_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
Ograniczenia dotyczące odbiorników BOOT_COMPLETED uruchamiających usługi na pierwszym planie
Wprowadziliśmy nowe ograniczenia dotyczące odbiorników BOOT_COMPLETED
usług działających na pierwszym planie. Odbiorcy BOOT_COMPLETED nie mogą uruchamiać modułu
te typy usług na pierwszym planie:
dataSynccameramediaPlaybackphoneCallmediaProjectionmicrophone(to ograniczenie obowiązuje w przypadkumicrophoneod Androida 14)
Jeśli odbiornik BOOT_COMPLETED próbuje uruchomić którykolwiek z tych typów działania na pierwszym planie
usług, system wywołuje ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException.
Testowanie
Aby przetestować działanie aplikacji, możesz włączyć te nowe ograniczenia, nawet jeśli aplikacja nie jest kierowana na Androida 15 (o ile jest ona uruchomiona na urządzeniu z Androidem 15). Uruchom to polecenie adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_BOOT_COMPLETED_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
Aby wysłać komunikat typu BOOT_COMPLETED bez ponownego uruchamiania urządzenia:
uruchom to polecenie adb:
adb shell am broadcast -a android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED your-package-name
Ograniczenia dotyczące uruchamiania usług na pierwszym planie, gdy aplikacja ma uprawnienia SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW
Wcześniej, jeśli aplikacja miała uprawnienia SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW, mogła uruchomić usługę na pierwszym planie, nawet jeśli była w tej chwili uruchomiona w tle (jak opisano w wyjątkach od ograniczeń dotyczących uruchamiania w tle).
Jeśli aplikacja jest kierowana na Androida 15, wykluczenie jest teraz bardziej precyzyjne. Aplikacja musi mieć teraz uprawnienia SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW, a także mieć widoczne okno nakładki. Oznacza to, że aplikacja musi najpierw uruchomić okno TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY i to okno musi być widoczne, zanim uruchomisz usługę na pierwszym planie.
Jeśli aplikacja próbuje uruchomić usługę działającą na pierwszym planie w tle bez spełnienia tych nowych wymagań (i nie ma żadnych innych wyjątków), system zgłasza ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException.
Jeśli Twoja aplikacja deklaruje uprawnienie SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW i uruchamia usługi na pierwszym planie z poziomu usług działających w tle, może być dotknięta tą zmianą. Jeśli Twoja aplikacja otrzymuje ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException, sprawdź kolejność jej działań i upewnij się, że aplikacja ma już aktywne okno nakładki, zanim spróbuje uruchomić usługę na pierwszym planie z tle. Aby sprawdzić, czy okno nakładki jest obecnie widoczne, wywołaj View.getWindowVisibility() lub zastąp View.onWindowVisibilityChanged(), aby otrzymywać powiadomienia o zmianie widoczności.
Testowanie
Aby przetestować działanie aplikacji, możesz włączyć te nowe ograniczenia, nawet jeśli aplikacja nie jest kierowana na Androida 15 (o ile jest ona uruchomiona na urządzeniu z Androidem 15). Aby włączyć nowe ograniczenia dotyczące uruchamiania usług na pierwszym planie w tle, uruchom to polecenie adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_SAW_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
Zmiany dotyczące tego, kiedy aplikacje mogą modyfikować globalny stan trybu Nie przeszkadzać
Aplikacje kierowane na Androida 15 (poziom API 35) lub nowszego nie mogą już zmieniać globalnego stanu ani zasad trybu Nie przeszkadzać na urządzeniu (ani przez modyfikowanie ustawień użytkownika, ani przez wyłączanie trybu Nie przeszkadzać). Zamiast tego aplikacje muszą przekazać AutomaticZenRule, które system połączy w globalne zasady z dotychczasowym schematem „najbardziej restrykcyjne zasady wygrywają”. Wywołania istniejących interfejsów API, które wcześniej wpływały na stan globalny (setInterruptionFilter,
setNotificationPolicy), powodują utworzenie lub zaktualizowanie niejawnego AutomaticZenRule, który jest włączany i wyłączany w zależności od cyklu wywołań tych interfejsów API.
Pamiętaj, że ta zmiana wpływa tylko na obserwowalne zachowanie, jeśli aplikacja wywołuje funkcję setInterruptionFilter(INTERRUPTION_FILTER_ALL) i oczekuje, że ta funkcja dezaktywuje AutomaticZenRule, który został wcześniej aktywowany przez właścicieli.
Zmiany w interfejsie OpenJDK API
Android 15 kontynuuje odświeżanie podstawowych bibliotek Androida, aby dostosować je do funkcji najnowszych wersji OpenJDK LTS.
Niektóre z tych zmian mogą mieć wpływ na kompatybilność aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 15 (poziom interfejsu API 35):
Zmiany w interfejsach API formatowania ciągów znaków: weryfikacja indeksu argumentu, flag, szerokości i precyzji jest teraz bardziej rygorystyczna w przypadku korzystania z tych interfejsów API:
String.format()iFormatter.format():String.format(String, Object[])String.format(Locale, String, Object[])Formatter.format(String, Object[])Formatter.format(Locale, String, Object[])
Na przykład ten wyjątek jest zgłaszany, gdy używany jest indeks argumentu 0 (
%0w ciągu formatującym):IllegalFormatArgumentIndexException: Illegal format argument index = 0W takim przypadku problem można rozwiązać, używając indeksu argumentu 1 (
%1w ciągu formatującym).Zmiany typu komponentu
Arrays.asList(...).toArray(): w przypadku użycia funkcjiArrays.asList(...).toArray()typ komponentu wynikowej tablicy to terazObject, a nie typ elementów tablicy bazowej. Dlatego ten kod zgłasza wyjątekClassCastException:String[] elements = (String[]) Arrays.asList("one", "two").toArray();W tym przypadku, aby zachować
Stringjako typ komponentu w wynikowej tablicy, możesz użyćCollection.toArray(Object[]):String[] elements = Arrays.asList("two", "one").toArray(new String[0]);Zmiany w obsłudze kodów języka: podczas korzystania z interfejsu
LocaleAPI kody języka hebrajskiego, jidysz i indonezyjskiego nie są już konwertowane na ich przestarzałe formy (hebrajski:iw, jidysz:jii indonezyjski:in). Podczas określania kodu języka dla jednego z tych języków używaj kodów z ISO 639-1 (hebrajski:he, jidysz:yii indonezyjski:id).Zmiany w sekwencjach liczb losowych: w wyniku zmian wprowadzonych w https://bugs.openjdk.org/browse/JDK-8301574 te metody
Random.ints()zwracają teraz inną sekwencję liczb niż metodyRandom.nextInt():Zwykle ta zmiana nie powinna powodować nieprawidłowego działania aplikacji, ale kod nie powinien oczekiwać, że sekwencja wygenerowana przez metody
Random.ints()będzie zgodna z sekwencjąRandom.nextInt().
Nowy interfejs API SequencedCollection może wpłynąć na zgodność aplikacji po zaktualizowaniu compileSdk w konfiguracji kompilacji aplikacji w celu używania Androida 15 (poziom interfejsu API 35):
Kolizja z funkcjami rozszerzeń
MutableList.removeFirst()iMutableList.removeLast()wkotlin-stdlibTyp
Listw Javie jest mapowany na typMutableListw Kotlinie. Interfejsy APIList.removeFirst()iList.removeLast()zostały wprowadzone w Androidzie 15 (poziom interfejsu API 35), więc kompilator Kotlina rozwiązuje wywołania funkcji, np.list.removeFirst(), statycznie do nowych interfejsów APIListzamiast do funkcji rozszerzeń wkotlin-stdlib.Jeśli aplikacja zostanie ponownie skompilowana z ustawieniem
compileSdkna35iminSdkna34lub niższą wersję, a następnie zostanie uruchomiona na Androidzie 14 lub starszym, wystąpi błąd środowiska wykonawczego:java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: No virtual method removeFirst()Ljava/lang/Object; in class Ljava/util/ArrayList;Istniejąca opcja
NewApilint we wtyczce Androida do obsługi Gradle może wykrywać te nowe zastosowania interfejsu API../gradlew lintMainActivity.kt:41: Error: Call requires API level 35 (current min is 34): java.util.List#removeFirst [NewApi] list.removeFirst()Aby naprawić wyjątek środowiska wykonawczego i błędy lint, wywołania funkcji
removeFirst()iremoveLast()można zastąpić odpowiednio wywołaniamiremoveAt(0)iremoveAt(list.lastIndex)w Kotlinie. Jeśli używasz Android Studio Ladybug | 2024.1.3 lub nowszej, możesz też skorzystać z opcji szybkiej naprawy tych błędów.Jeśli opcja lint została wyłączona, rozważ usunięcie
@SuppressLint("NewApi")ilintOptions { disable 'NewApi' }.Kolizja z innymi metodami w Javie
Do istniejących typów dodaliśmy nowe metody, np.
ListiDeque. Te nowe metody mogą być niezgodne z metodami o tej samej nazwie i typach argumentów w innych interfejsach i klasach. W przypadku kolizji sygnatury metody z niezgodnością kompilatorjavaczgłasza błąd w czasie kompilacji. Przykład:Przykładowy błąd 1:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:135: error: removeLast() in MyList cannot implement removeLast() in List public void removeLast() { ^ return type void is not compatible with Object where E is a type-variable: E extends Object declared in interface ListPrzykładowy błąd 2:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:7: error: types Deque<Object> and List<Object> are incompatible; public class MyList implements List<Object>, Deque<Object> { both define reversed(), but with unrelated return types 1 errorPrzykładowy błąd 3:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:43: error: types List<E#1> and MyInterface<E#2> are incompatible; public static class MyList implements List<Object>, MyInterface<Object> { class MyList inherits unrelated defaults for getFirst() from types List and MyInterface where E#1,E#2 are type-variables: E#1 extends Object declared in interface List E#2 extends Object declared in interface MyInterface 1 errorAby naprawić te błędy kompilacji, klasa implementująca te interfejsy powinna zastąpić metodę zgodnym typem zwracanym. Na przykład:
@Override public Object getFirst() { return List.super.getFirst(); }
Bezpieczeństwo
Android 15 zawiera zmiany, które zwiększają bezpieczeństwo systemu, aby chronić aplikacje i użytkowników przed złośliwymi aplikacjami.
Ograniczone wersje protokołu TLS
Android 15 ogranicza użycie TLS w wersjach 1.0 i 1.1. Te wersje zostały wcześniej wycofane w Androidzie, ale teraz są niedozwolone w przypadku aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 15.
Zabezpieczone uruchamianie aktywności w tle
Android 15 chroni użytkowników przed złośliwymi aplikacjami i zapewnia im większą kontrolę nad urządzeniami. Wprowadziliśmy zmiany, które uniemożliwiają złośliwym aplikacjom działającym w tle przenoszenie innych aplikacji na pierwszy plan, podnoszenie ich uprawnień i nadużywanie interakcji z użytkownikiem. Od Androida 10 (poziom interfejsu API 29) uruchamianie aktywności w tle jest ograniczone.
Inne zmiany
- Zmień domyślne ustawienie
PendingIntenttwórców na blokowanie uruchamiania aktywności w tle. Pomaga to zapobiegać przypadkowemu tworzeniu przez aplikacjePendingIntent, które mogłyby być wykorzystywane przez nieuczciwe podmioty. - Nie przenoś aplikacji na pierwszy plan, chyba że
PendingIntentnadawca na to zezwoli. Ta zmiana ma zapobiegać nadużywaniu przez złośliwe aplikacje możliwości rozpoczynania aktywności w tle. Domyślnie aplikacje nie mogą przenosić stosu zadań na pierwszy plan, chyba że twórca zezwoli na uprawnienia do uruchamiania działań w tle lub nadawca ma uprawnienia do uruchamiania działań w tle. - Określa, jak najwyższa aktywność w stosie zadań może zakończyć zadanie. Jeśli aktywność na górze stosu zakończy zadanie, Android wróci do ostatniego aktywnego zadania. Jeśli aktywność niebędąca na pierwszym planie zakończy swoje zadanie, Android wró do ekranu głównego. Nie zablokuje zakończenia tej aktywności.
- Zapobiegaj uruchamianiu dowolnych działań z innych aplikacji w swoim zadaniu. Ta zmiana uniemożliwia złośliwym aplikacjom wyłudzanie informacji od użytkowników przez tworzenie działań, które wyglądają jak działania innych aplikacji.
- Blokowanie okien niewidocznych, aby nie były brane pod uwagę podczas uruchamiania aktywności w tle. Pomaga to zapobiegać wykorzystywaniu przez złośliwe aplikacje uruchamiania aktywności w tle do wyświetlania użytkownikom niechcianych lub szkodliwych treści.
Bezpieczniejsze zamiary
W Androidzie 15 wprowadzono StrictMode w przypadku intencji.
Aby wyświetlić szczegółowe dzienniki naruszeń zasad korzystania z Intent, wykonaj te czynności:
Kotlin
fun onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build() ) }
Java
public void onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(new VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build()); }
Wrażenia użytkowników i interfejs systemu
Android 15 zawiera kilka zmian, które mają na celu zapewnienie bardziej spójnej i intuicyjnej obsługi.
Zmiany w oknie
W Androidzie 15 wprowadzono 2 zmiany związane z współrzędnymi okna: domyślnie wymuszono tryb pełnoekranowy, a także wprowadzono zmiany konfiguracji, takie jak domyślna konfiguracja pasków systemowych.
Egzekwowanie treści od krawędzi do krawędzi
Aplikacje są domyślnie wyświetlane bez ramki na urządzeniach z Androidem 15, jeśli są kierowane na tę wersję systemu (API na poziomie 35).
Jest to zmiana powodująca niezgodność wsteczną, która może negatywnie wpłynąć na interfejs aplikacji. Zmiany dotyczą tych obszarów interfejsu:
- Pasek nawigacyjny z uchwytem do gestów
- Domyślnie przezroczysty.
- Przesunięcie u dołu jest wyłączone, więc treść jest rysowana za paskiem nawigacji systemowej, chyba że zastosowano wstawki.
setNavigationBarColoriR.attr#navigationBarColorsą przestarzałe i nie mają wpływu na nawigację przy użyciu gestów.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcediR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcednadal nie mają wpływu na nawigację gestami.
- Nawigacja przy użyciu 3 przycisków
- Domyślnie ustawiona jest nieprzezroczystość na poziomie 80%, a kolor może być dopasowany do tła okna.
- Dolne przesunięcie jest wyłączone, więc treść jest rysowana za paskiem nawigacyjnym systemu, chyba że zastosowano wstawki.
setNavigationBarColoriR.attr#navigationBarColorsą domyślnie dopasowane do tła okna. Tło okna musi być rysunkiem w kolorze, aby można było zastosować tę wartość domyślną. Ten interfejs API został wycofany, ale nadal wpływa na nawigację 3-przyciskową.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcediR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedmają domyślnie wartość „prawda”, co dodaje 80-procentowe nieprzezroczyste tło w przypadku nawigacji za pomocą 3 przycisków.
- Pasek stanu
- Domyślnie przezroczysty.
- Górne przesunięcie jest wyłączone, więc treść jest rysowana za paskiem stanu, chyba że zastosowano wstawki.
setStatusBarColoriR.attr#statusBarColorsą przestarzałe i nie mają wpływu na Androida 15.setStatusBarContrastEnforcediR.attr#statusBarContrastEnforcedsą wycofane, ale nadal mają wpływ na Androida 15.
- Wycięcie na wyświetlaczu
- Wartość
layoutInDisplayCutoutModeokien niepływających musi być równaLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS.SHORT_EDGES,NEVERiDEFAULTsą interpretowane jakoALWAYS, dzięki czemu użytkownicy nie widzą czarnego paska spowodowanego wycięciem na wyświetlaczu, a aplikacja jest wyświetlana od krawędzi do krawędzi.
- Wartość
Poniższy przykład pokazuje aplikację przed i po kierowaniu na Androida 15 (API na poziomie 35) oraz przed i po zastosowaniu odcięć. Ten przykład nie jest wyczerpujący. W Androidzie Auto może wyglądać inaczej.
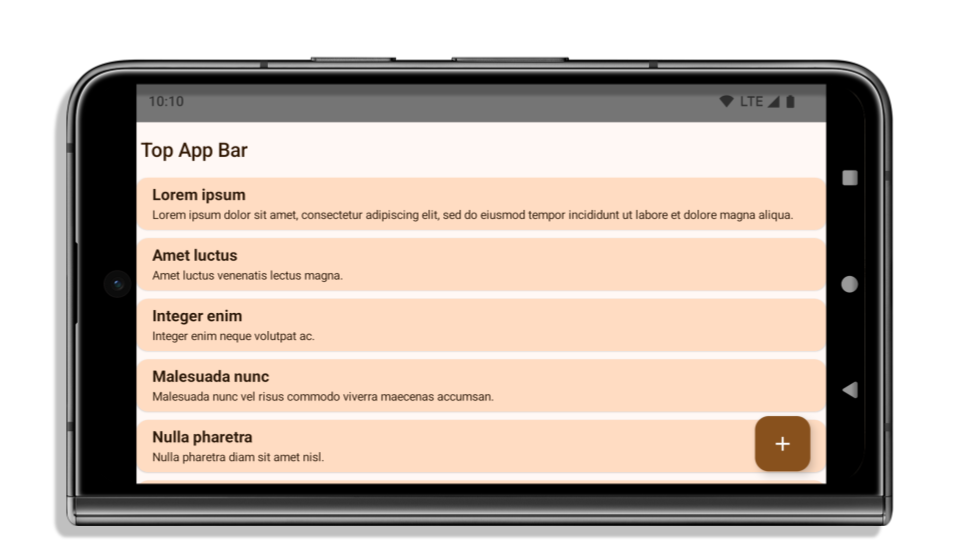

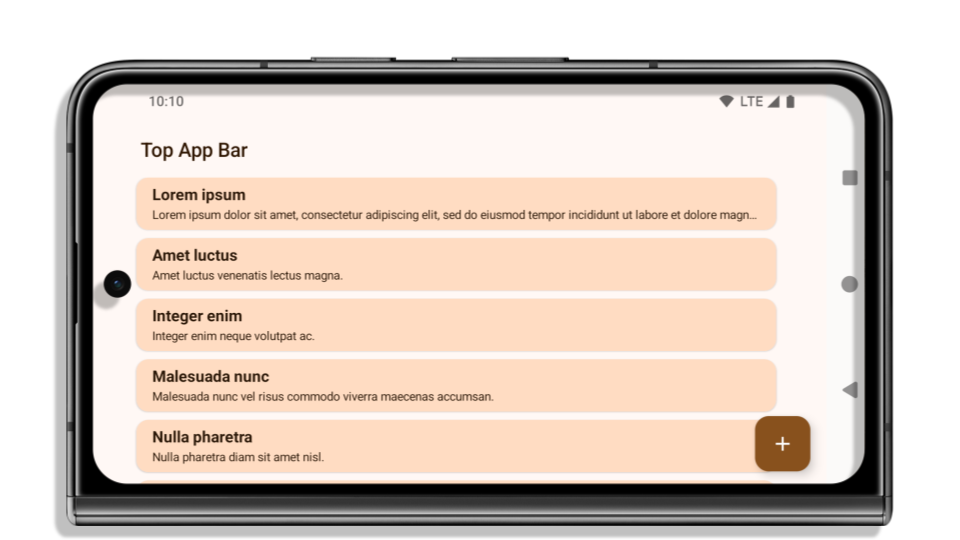
Co sprawdzić, jeśli aplikacja jest już wyświetlana od krawędzi do krawędzi
Jeśli Twoja aplikacja jest już wyświetlana na całym ekranie i stosuje wstawki, zmiany nie będą miały na nią większego wpływu, z wyjątkiem tych sytuacji: Nawet jeśli uważasz, że ten problem Cię nie dotyczy, zalecamy przetestowanie aplikacji.
- Masz okno niepływające, np.
Activity, które zamiastLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYSużywaSHORT_EDGES,NEVERlubDEFAULT. Jeśli aplikacja ulega awarii przy uruchamianiu, przyczyną może być ekran powitalny. Możesz uaktualnić zależność core splashscreen do wersji 1.2.0-alpha01 lub nowszej albo ustawićwindow.attributes.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = WindowManager.LayoutInDisplayCutoutMode.always. - Mogą występować ekrany o mniejszym natężeniu ruchu z zasłoniętym interfejsem. Sprawdź, czy na tych rzadziej odwiedzanych ekranach nie ma zasłoniętego interfejsu. Ekrany o mniejszym natężeniu ruchu to:
- ekrany wprowadzające lub logowania,
- Strony ustawień
Co sprawdzić, jeśli aplikacja nie jest jeszcze wyświetlana od krawędzi do krawędzi
Jeśli Twoja aplikacja nie jest jeszcze wyświetlana od krawędzi do krawędzi, najprawdopodobniej dotyczy Cię ta zmiana. Oprócz scenariuszy dotyczących aplikacji, które już są wyświetlane od krawędzi do krawędzi, warto wziąć pod uwagę te kwestie:
- Jeśli Twoja aplikacja korzysta z komponentów Material 3 (
androidx.compose.material3) w Compose, takich jakTopAppBar,BottomAppBariNavigationBar, te komponenty prawdopodobnie nie zostaną zmienione, ponieważ automatycznie obsługują wcięcia. - Jeśli Twoja aplikacja korzysta z komponentów Material 2 (
androidx.compose.material) w Compose, te komponenty nie obsługują automatycznie wcięć. Możesz jednak uzyskać dostęp do wstawek i zastosować je ręcznie. W androidx.compose.material 1.6.0 i nowszych wersjach użyj parametruwindowInsets, aby ręcznie zastosować wcięcia w przypadkuBottomAppBar,TopAppBar,BottomNavigationiNavigationRail. Podobnie użyj parametrucontentWindowInsetsdlaScaffold. - Jeśli Twoja aplikacja korzysta z widoków i komponentów Material Design (
com.google.android.material), większość komponentów Material Design opartych na widokach, takich jakBottomNavigationView,BottomAppBar,NavigationRailViewczyNavigationView, obsługuje wcięcia i nie wymaga dodatkowej pracy. Jeśli jednak używaszAppBarLayout, musisz dodaćandroid:fitsSystemWindows="true". - W przypadku kompozycji niestandardowych zastosuj wstawki ręcznie jako dopełnienie. Jeśli treść znajduje się w
Scaffold, możesz używać wstawek, korzystając zScaffoldwartości dopełnienia. W przeciwnym razie zastosuj dopełnienie za pomocą jednego z tych elementów:WindowInsets. - Jeśli Twoja aplikacja korzysta z widoków i kontenerów
BottomSheet,SideSheetlub niestandardowych, zastosuj dopełnienie za pomocą elementuViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener. W przypadku elementuRecyclerViewzastosuj dopełnienie za pomocą tego odbiornika, a także dodaj elementclipToPadding="false".
Co sprawdzić, jeśli aplikacja musi oferować niestandardową ochronę w tle
Jeśli aplikacja musi oferować niestandardową ochronę tła w przypadku nawigacji 3-przyciskowej lub paska stanu, powinna umieścić element kompozycyjny lub widok za paskiem systemowym, używając funkcji WindowInsets.Type#tappableElement(), aby uzyskać wysokość paska nawigacyjnego 3-przyciskowego, lub WindowInsets.Type#statusBars.
Dodatkowe materiały dotyczące wyświetlania od krawędzi do krawędzi
Dodatkowe informacje o stosowaniu wcięć znajdziesz w przewodnikach Widoki od krawędzi do krawędzi i Compose od krawędzi do krawędzi.
Wycofane interfejsy API
Te interfejsy API są wycofane, ale nie wyłączone:
R.attr#enforceStatusBarContrastR.attr#navigationBarColor(w przypadku nawigacji przy użyciu 3 przycisków z 80-procentową przezroczystością)Window#isStatusBarContrastEnforcedWindow#setNavigationBarColor(w przypadku nawigacji przy użyciu 3 przycisków, z 80-procentową przezroczystością)Window#setStatusBarContrastEnforced
Te interfejsy API są wycofane i wyłączone:
R.attr#navigationBarColor(w przypadku nawigacji przy użyciu gestów)R.attr#navigationBarDividerColorR.attr#statusBarColorWindow#setDecorFitsSystemWindowsWindow#getNavigationBarColorWindow#getNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#getStatusBarColorWindow#setNavigationBarColor(w przypadku nawigacji przy użyciu gestów)Window#setNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#setStatusBarColor
Stabilna konfiguracja
Jeśli Twoja aplikacja jest kierowana na Androida 15 (API na poziomie 35) lub nowszego, Configuration nie wyklucza już pasków systemowych. Jeśli do obliczania układu używasz rozmiaru ekranu w klasie Configuration, zastąp go lepszymi alternatywami, takimi jak odpowiedni ViewGroup, WindowInsets lub WindowMetricsCalculator, w zależności od potrzeb.
Configuration jest dostępny od interfejsu API 1. Zwykle jest ona uzyskiwana z Activity.onConfigurationChanged. Zawiera informacje takie jak gęstość okien, ich orientacja i rozmiary. Ważną cechą rozmiarów okien zwracanych przez Configuration jest to, że wcześniej wykluczały one paski systemowe.
Rozmiar konfiguracji jest zwykle używany do wyboru zasobów, np. /res/layout-h500dp, i nadal jest to prawidłowy przypadek użycia. Jednak używanie go do obliczania układu zawsze było odradzane. Jeśli tak jest, odsuń się od niego. Zamiast Configuration użyj czegoś bardziej odpowiedniego w zależności od przypadku użycia.
Jeśli używasz go do obliczania układu, użyj odpowiedniego ViewGroup, np. CoordinatorLayout lub ConstraintLayout. Jeśli używasz go do określania wysokości paska nawigacyjnego systemu, użyj WindowInsets. Jeśli chcesz poznać bieżący rozmiar okna aplikacji, użyj computeCurrentWindowMetrics.
Poniżej znajdziesz listę pól, których dotyczy ta zmiana:
- Rozmiary
Configuration.screenWidthDpiscreenHeightDpnie wykluczają już pasków systemowych. Configuration.smallestScreenWidthDpjest pośrednio powiązana ze zmianami wscreenWidthDpiscreenHeightDp.- Na
Configuration.orientationpośrednio wpływają zmiany wscreenWidthDpiscreenHeightDpna urządzeniach o proporcjach zbliżonych do kwadratu. Display.getSize(Point)jest pośrednio dotknięty(-a) zmianami wConfiguration. Zostało to wycofane od poziomu API 30.Display.getMetrics()działa w ten sposób od poziomu API 33.
Atrybut elegantTextHeight ma domyślnie wartość true.
W przypadku aplikacji przeznaczonych na Androida 15 (poziom interfejsu API 35) atrybut elegantTextHeight TextView domyślnie staje się true, co zastępuje czcionkę kompaktową używaną domyślnie w niektórych skryptach, które mają duże wymiary pionowe, czcionką o znacznie lepszej czytelności.
Czcionka kompaktowa została wprowadzona, aby zapobiec rozmieszczaniu elementów układu. Android 13 (poziom interfejsu API 33) zapobiega wielu takim problemom, ponieważ pozwala na rozciąganie wysokości układu tekstu za pomocą atrybutu fallbackLineSpacing.
W Androidzie 15 czcionka kompaktowa nadal pozostaje w systemie, więc aplikacja może ustawić wartość elegantTextHeight na false, aby uzyskać takie samo działanie jak wcześniej, ale jest mało prawdopodobne, aby była obsługiwana w przyszłych wersjach. Jeśli Twoja aplikacja obsługuje te pismo: arabski, kannada, oriya, tamilski, telugu, gudżarati, malajalam, birmański, gudźarati, kannada, malajalam, oriya, telugu lub tajski, przetestuj ją, ustawiając wartość elegantTextHeight na true.
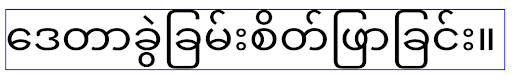
elegantTextHeightdla aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 14 (poziom API 34) i starszego.
elegantTextHeightzachowanie w przypadku aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 15.Szerokość widoku TextView zmienia się w przypadku złożonych kształtów liter
W poprzednich wersjach Androida niektóre czcionki kursywe lub języki ze złożonym kształtem mogą rysować litery w obszarze poprzedniego lub następnego znaku.
Zdarzało się, że takie litery były obcinane na początku lub na końcu.
Od Androida 15 TextView przydziela wystarczającą ilość miejsca na wyświetlenie takich liter, a aplikacje mogą prosić o dodatkowe wypełnienie po lewej stronie, aby zapobiec przycięciu.
Ta zmiana wpływa na sposób określania szerokości przez TextView, więc TextView domyślnie przydziela więcej szerokości, jeśli aplikacja jest kierowana na Androida 15 (poziom API 35) lub nowszego. Możesz włączyć lub wyłączyć tę funkcję, wywołując interfejs API setUseBoundsForWidth w komponencie TextView.
Dodanie dopełnienia z lewej strony może spowodować niewłaściwe ułożenie istniejących układów, dlatego dopełnienie nie jest dodawane domyślnie nawet w przypadku aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 15 lub nowszego.
Możesz jednak dodać dodatkowy margines, aby zapobiec przycięciu, wywołując funkcję setShiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang.
W poniższych przykładach pokazujemy, jak te zmiany mogą poprawić układ tekstu w przypadku niektórych czcionek i języków.

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" />

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />
Domyślna wysokość wiersza w widoku EditText uwzględniająca ustawienia regionalne
W poprzednich wersjach Androida układ tekstu rozciągał wysokość tekstu, aby dopasować ją do wysokości wiersza czcionki odpowiadającej bieżącemu ustawieniu języka. Jeśli na przykład treści były w języku japońskim, to ze względu na to, że wysokość linii czcionki japońskiej jest nieco większa niż czcionki łacińskiej, wysokość tekstu była nieco większa. Jednak pomimo tych różnic w wysokościach wierszy element EditText miał jednakowy rozmiar niezależnie od używanej lokalizacji, jak pokazano na poniższym obrazku:

EditText, które mogą zawierać tekst w języku angielskim (en), japońskim (ja) i birmańskim (my). Wysokość EditText jest taka sama, mimo że te języki mają różne wysokości linii.W przypadku aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 15 (poziom interfejsu API 35) minimalna wysokość linii jest teraz zarezerwowana dla EditText, aby pasowała do czcionki referencyjnej dla określonego języka, jak pokazano na poniższym obrazie:

EditText, które mogą zawierać tekst w języku angielskim (en), japońskim (ja) i birmańskim (my). Wysokość EditText uwzględnia teraz miejsce na domyślną wysokość wiersza dla czcionek w tych językach.W razie potrzeby aplikacja może przywrócić poprzednie działanie, ustawiając atrybut useLocalePreferredLineHeightForMinimum na false. Może też ustawić niestandardowe minimalne dane pionowe za pomocą interfejsu API setMinimumFontMetrics w językach Kotlin i Java.
Aparat i multimedia
Android 15 wprowadza te zmiany w działaniu aplikacji w zakresie kamery i multimediów, które są kierowane na Androida 15 lub nowszego.
Ograniczenia dotyczące żądania fokusu audio
Aplikacje kierowane na Androida 15 (poziom API 35) muszą być aplikacjami na pierwszym planie lub usługami na pierwszym planie, aby poprosić o uzyskanie kontroli nad dźwiękiem. Jeśli aplikacja próbuje poprosić o skupienie uwagi, gdy nie spełnia jednego z tych wymagań, wywołanie zwraca AUDIOFOCUS_REQUEST_FAILED.
Więcej informacji o fokusowaniu dźwięku znajdziesz w artykule Zarządzanie fokusem dźwięku.
Zaktualizowane ograniczenia dotyczące interfejsów API innych niż SDK
Android 15 zawiera zaktualizowane listy ograniczonych interfejsów innych niż SDK, które powstały na podstawie współpracy z deweloperami Androida i najnowszych testów wewnętrznych. Zanim ograniczymy interfejsy inne niż SDK, w miarę możliwości udostępniamy publiczne alternatywy.
Jeśli Twoja aplikacja nie jest kierowana na Androida 15, niektóre z tych zmian mogą nie mieć na Ciebie natychmiastowego wpływu. Jednak chociaż aplikacja może mieć dostęp do niektórych interfejsów spoza SDK w zależności od docelowego poziomu interfejsu API, używanie dowolnej metody lub pola spoza SDK zawsze wiąże się z wysokim ryzykiem awarii aplikacji.
Jeśli nie masz pewności, czy Twoja aplikacja używa interfejsów innych niż SDK, możesz to sprawdzić, testując aplikację. Jeśli Twoja aplikacja korzysta z interfejsów spoza SDK, zacznij planować migrację do alternatywnych pakietów SDK. Zdajemy sobie jednak sprawę, że w przypadku niektórych aplikacji używanie interfejsów innych niż SDK jest uzasadnione. Jeśli nie możesz znaleźć alternatywy dla używania interfejsu spoza pakietu SDK w przypadku funkcji w aplikacji, poproś o nowy publiczny interfejs API.
Więcej informacji o zmianach w tej wersji Androida znajdziesz w artykule Zmiany ograniczeń interfejsu niebędącego interfejsem SDK w Androidzie 15. Więcej informacji o interfejsach innych niż SDK znajdziesz w artykule Ograniczenia interfejsów innych niż SDK.

