Android 14 面向开发者引入了一些出色的功能和 API。以下内容可帮助您了解适用于您的应用的功能并开始使用相关 API。
如需查看新增、修改和移除的 API 的详细列表,请参阅 API 差异报告。如需详细了解添加的 API,请访问 Android API 参考文档。对于 Android 14,请查找在 API 级别 34 中添加的 API。如需了解平台变更可能会在哪些方面影响您的应用,请务必查看会影响以 Android 14 为目标平台的应用和所有应用的 Android 14 行为变更。
国际化
单个应用语言设置
Android 14 扩展了 Android 13(API 级别 33)中引入的按应用设定语言功能,并包含以下额外功能:
自动生成应用的
localeConfig:从 Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 和 AGP 8.1.0-alpha07 开始,您可以将应用配置为自动支持各应用语言偏好设定。Android Gradle 插件会根据您的项目资源生成LocaleConfig文件,并在最终清单文件中添加对该文件的引用,这样您就不再需要手动创建或更新该文件。AGP 使用应用模块的res文件夹中的资源以及任何库模块依赖项来确定要在LocaleConfig文件中添加的语言区域。动态更新应用的
localeConfig:使用LocaleManager方法中的setOverrideLocaleConfig()和getOverrideLocaleConfig()可以在设备的系统设置中动态更新应用的受支持语言列表。有了这种灵活性,您可以按区域自定义支持的语言列表、运行 A/B 实验,或者如果您的应用通过服务器端推送进行本地化,则可以提供更新后的语言区域列表。输入法 (IME) 的应用语言可见性:IME 可以利用
getApplicationLocales()方法查看当前应用的语言,并将 IME 语言与该语言进行匹配。
Grammatical Inflection API
有 30 亿人在使用区分性别的语言,此类语言的语法类别(例如名词、动词、形容词和介词)会根据您交谈所涉及的人或物的性别而变化。传统上,许多区分性别的语言使用阳性语法性别作为默认或通用性别。
以错误的语法性别来称呼用户,例如以阳性语法性别来称呼女性,可能会对她们的表现和态度产生负面影响。相比之下,界面语言如果能正确反映用户的语法性别,就可以提高用户互动度,并提供更个性化、更自然的用户体验。
为帮助您针对区分性别的语言构建以用户为中心的界面,Android 14 引入了 Grammatical Inflection API,让您无需重构应用便能添加对语法性别的支持。
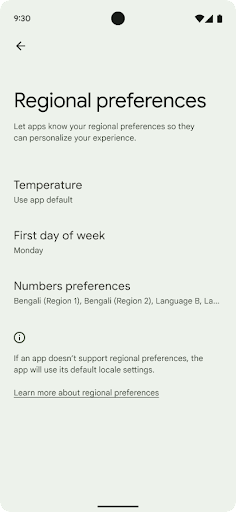
地区偏好设置
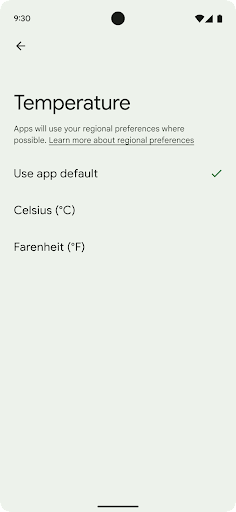
用户可通过地区偏好设置对温度单位、一周的第一天和编号系统进行个性化设置。居住在美国的欧洲用户可能更希望使用摄氏度,而不是华氏度,并且希望应用将星期一视为一周的开始,而不是像美国那样默认从星期日开始。
新 Android 设置菜单包含这些偏好设置,使用户能够在一个位置集中发现这些应用更改偏好设置。这些偏好设置在备份和恢复设备后也会保持不变。多个 API 和 intent(例如 getTemperatureUnit 和 getFirstDayOfWeek)会为您的应用授予读取权限来访问用户偏好设置,因此您的应用可以调整其显示信息的方式。您还可以在 ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED 上注册 BroadcastReceiver,以便在地区偏好设置发生更改时处理语言区域配置更改。
如需找到这些设置,请打开“设置”应用,然后依次前往系统 > 语言和输入法 > 地区偏好设置。
无障碍
非线性字体放大至 200%
从 Android 14 开始,系统支持字体放大高达 200%,为用户提供了其他无障碍功能选项。
为防止屏幕上的大文本元素过于放大,系统会采用非线性放大曲线。这种放大策略意味着大号文本的放大比例不会与较小的文本相同。非线性字体放大有助于保持不同大小元素之间的比例层次结构,同时缓解高级别线性文本放大存在的问题(例如文本被截断或文本因非常大的显示大小而难以阅读)。
使用非线性字体放大测试应用
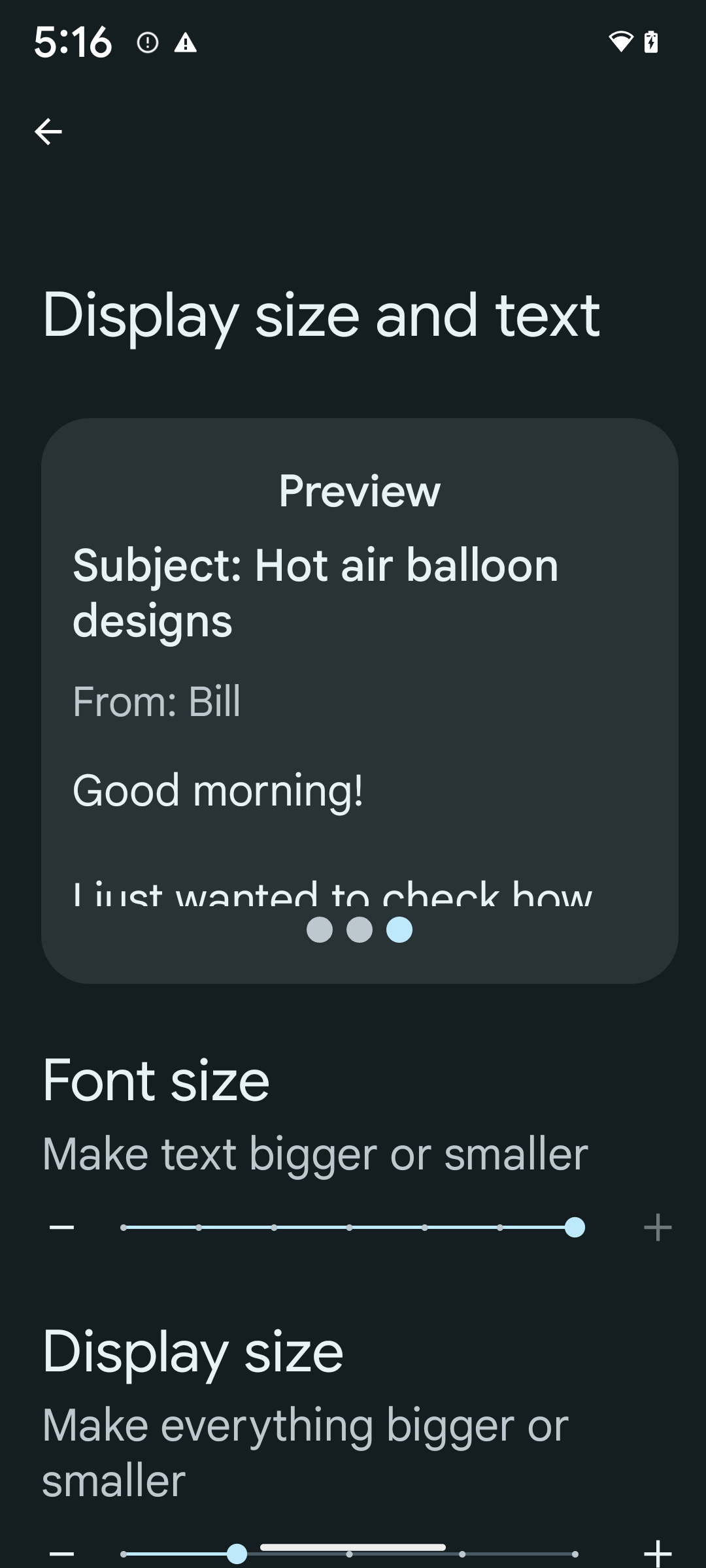
如果您已使用可缩放像素 (sp) 单位来定义文本大小,那么这些额外的选项和缩放改进会自动应用于应用中的文本。不过,您仍应在启用最大字体大小 (200%) 的情况下执行界面测试,以确保应用正确应用字体大小,并且可以容纳更大的字体大小,而不会影响易用性。
要启用 200% 字号,请按以下步骤操作:
- 打开“设置”应用,然后依次前往无障碍 > 显示大小和文字。
- 在字号选项中,点按加号 (+) 图标,直到启用最大字号设置,如本部分随附的图片所示。
针对文本大小使用放大像素 (sp) 单位
请务必始终以 sp 为单位指定文本大小。当应用使用 sp 单位时,Android 可以应用用户的首选文本大小,并相应地进行缩放。
不要为内边距使用 sp 单位,也不要定义假设存在隐式内边距的视图高度:使用非线性字体放大 sp 尺寸可能并不成比例,因此 4sp + 20sp 可能并不等于 24sp。
转换放大像素 (sp) 单位
使用 TypedValue.applyDimension() 从 sp 单位转换为像素,并使用 TypedValue.deriveDimension() 将像素转换为 sp。这些方法会自动应用适当的非线性放大曲线。
避免使用 Configuration.fontScale 或 DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity 对等式进行硬编码。由于字体放大是非线性的,因此 scaledDensity 字段不再准确。fontScale 字段应仅用于提供信息,因为字体不再使用单个标量值进行缩放。
针对 lineHeight 使用 sp 单位
请始终使用 sp 单位(而非 dp)定义 android:lineHeight,以便行高随文本一起缩放。否则,如果您的文字是 sp,但 lineHeight 是 dp 或像素,则文字不会缩放,看起来会很拥挤。
TextView 会自动更正 lineHeight,以便保留您预期的比例,但前提是 textSize 和 lineHeight 均以 sp 单位定义。
摄像头和媒体
图片 Ultra HDR

Android 14 新增了对高动态范围 (HDR) 图片的支持,可在拍摄照片时保留更多来自传感器的信息,从而实现鲜艳的色彩和更高的对比度。Android 使用 Ultra HDR 格式,该格式与 JPEG 图片完全向后兼容,可让应用与 HDR 图片无缝互操作,并根据需要以标准动态范围 (SDR) 显示这些图片。
当您的应用选择为其 activity 窗口使用 HDR 界面(通过清单条目或通过在运行时调用 Window.setColorMode())时,框架会自动在界面中以 HDR 格式渲染这些图片。您还可以在受支持的设备上拍摄压缩的 Ultra HDR 静态图片。从传感器中恢复的颜色越多,后期编辑的灵活性就越高。与 Ultra HDR 图片关联的 Gainmap 可用于使用 OpenGL 或 Vulkan 渲染这些图片。
相机扩展中的缩放、聚焦、postview 等功能
Android 14 升级并改进了相机扩展程序,让应用能够处理更长的处理时间,从而支持在受支持的设备上使用计算密集型算法(例如弱光摄影)来改善图片。这些功能可让用户在使用相机扩展功能时获得更出色的体验。这些改进的示例包括:
- 动态静态拍摄处理延迟时间估算功能可根据当前场景和环境条件提供更准确的静态拍摄延迟时间估算值。调用
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()可获取具有两种延迟时间估算方法的StillCaptureLatency对象。getCaptureLatency()方法会返回onCaptureStarted和onCaptureProcessStarted()之间的估算延迟时间,而getProcessingLatency()方法会返回onCaptureProcessStarted()和可用的最终处理帧之间的估算延迟时间。 - 支持拍摄进度回调,以便应用可以显示长时间运行的静态拍摄处理操作的当前进度。您可以检查
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailable是否支持此功能,如果支持,则实现onCaptureProcessProgressed()回调,并将进度(从 0 到 100)作为参数传入。 扩展程序专用元数据,例如用于调节扩展程序效果(例如背景虚化程度)的
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTH和EXTENSION_BOKEH。相机扩展程序中的静态图片拍摄预览功能,该功能比最终图片更快地提供经过较少处理的图片。如果扩展程序的处理延迟时间增加,可以提供 postview 图片作为占位符以提升用户体验,并在稍后改用最终图片。您可以使用
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable检查此功能是否可用。然后,您可以将OutputConfiguration传递给ExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration。支持
SurfaceView,可实现更优化且能效更高的预览渲染路径。支持在使用扩展程序时点按对焦和缩放。
传感器内变焦
When REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE in
CameraCharacteristics contains
SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW, your app
can use advanced sensor capabilities to give a cropped RAW stream the same
pixels as the full field of view by using a CaptureRequest
with a RAW target that has stream use case set to
CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW.
By implementing the request override controls, the updated camera gives users
zoom control even before other camera controls are ready.
无损 USB 音频
Android 14 支持无损音频格式,可通过 USB 有线耳机提供发烧友级体验。您可以查询 USB 设备的首选混音器属性,注册监听器以监听首选混音器属性的更改,以及使用 AudioMixerAttributes 类配置混音器属性。此类表示音频混音器的格式,例如声道掩码、采样率和行为。该类允许直接发送音频,而无需混音、调节音量或处理效果。
开发者工作效率和工具
Credential Manager
Android 14 将 Credential Manager 添加为平台 API,并通过使用 Google Play 服务的 Jetpack 库,向后额外支持 Android 4.4(API 级别 19)设备。Credential Manager 旨在通过 API 使用用户配置的凭据提供程序检索和存储凭据,让用户更轻松地登录。Credential Manager 在单个 API 中支持多种登录方法,包括用户名和密码、通行密钥和联合登录解决方案(如“使用 Google 账号登录”)。
通行密钥具有许多优势。例如,通行密钥是基于业界标准构建的,可在各种不同的操作系统和浏览器生态系统中使用,并且可用于网站和应用。
如需了解详情,请参阅 Credential Manager 和通行密钥文档以及介绍 Credential Manager 和通行密钥的博文。
健康数据共享
Health Connect 是用户健康与健身数据的设备端仓库。借助该功能,用户可以在一个位置控制要与这些应用共享哪些数据,并在自己喜爱的应用之间共享数据。
在搭载 Android 14 之前的 Android 版本的设备上,Health Connect 可作为应用从 Google Play 商店下载。从 Android 14 开始,Health Connect 将成为 Android 平台的一部分,并通过 Google Play 系统更新接收更新,而无需单独下载。这样一来,Health Connect 就可以频繁更新,您的应用可以依赖于搭载 Android 14 或更高版本的设备上提供的 Health Connect。用户可以通过设备的“设置”访问 Health Connect,隐私控制功能集成到系统设置中。
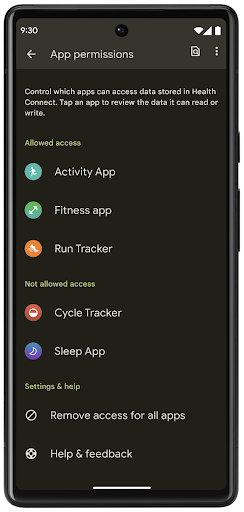
Health Connect 在 Android 14 中包含多项新功能,例如锻炼路线,可让用户分享可在地图上直观呈现的锻炼路线。路线定义为在一定时间范围内保存的位置列表,您的应用可以将路线插入锻炼时段,将它们关联起来。为确保用户能够完全控制此类敏感数据,用户必须允许与其他应用共享单个路线。
如需了解详情,请参阅 Health Connect 文档以及有关 Android Health 中的新功能的博文。
OpenJDK 17 更新
Android 14 将继续更新 Android 的核心库,以与最新 OpenJDK LTS 版本中的功能保持一致,包括适合应用和平台开发者的库更新和 Java 17 语言支持。
其中包含以下功能和改进:
- 将大约 300 个
java.base类更新为支持 Java 17。 - 文本块 - 为 Java 编程语言引入了多行字符串字面量。
- instanceof 模式匹配:可让对象在
instanceof中被视为具有特定类型,而无需任何额外的变量。 - 密封类:允许您限制哪些类和接口可以扩展或实现它们。
得益于 Google Play 系统更新 (Project Mainline),6 亿多台设备能够接收包含这些更改的最新 Android 运行时 (ART) 更新。我们致力于为应用提供更加一致、安全的跨设备环境,并为用户提供独立于平台版本的新功能。
Java 和 OpenJDK 是 Oracle 及/或其关联公司的商标或注册商标。
针对应用商店的改进
Android 14 introduces several PackageInstaller APIs that
allow app stores to improve their user experience.
Request install approval before downloading
Installing or updating an app might require user approval.
For example, when an installer making use of the
REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES permission attempts to install a
new app. In prior Android versions, app stores can only request user approval
after APKs are written to the install session and the
session is committed.
Starting with Android 14, the requestUserPreapproval()
method lets installers request user approval before committing the install
session. This improvement lets an app store defer downloading any APKs until
after the installation has been approved by the user. Furthermore, once a user
has approved installation, the app store can download and install the app in the
background without interrupting the user.
Claim responsibility for future updates
The setRequestUpdateOwnership() method allows an installer
to indicate to the system that it intends to be responsible for future updates
to an app it is installing. This capability enables update ownership
enforcement, meaning that only the update owner is permitted
to install automatic updates to the app. Update ownership enforcement helps to
ensure that users receive updates only from the expected app store.
Any other installer, including those making use of the
INSTALL_PACKAGES permission, must receive explicit user
approval in order to install an update. If a user decides to proceed with an
update from another source, update ownership is lost.
Update apps at less-disruptive times
App stores typically want to avoid updating an app that is actively in use because this leads to the app's running processes being killed, which potentially interrupts what the user was doing.
Starting with Android 14, the InstallConstraints API
gives installers a way to ensure that their app updates happen at an opportune
moment. For example, an app store can call the
commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() method to
make sure that an update is only committed when the user is no longer
interacting with the app in question.
Seamlessly install optional splits
With split APKs, features of an app can be delivered in separate APK files,
rather than as a monolithic APK. Split APKs allow app stores to optimize the
delivery of different app components. For example, app stores might optimize
based on the properties of the target device. The
PackageInstaller API has supported splits since its
introduction in API level 22.
In Android 14, the setDontKillApp() method allows an
installer to indicate that the app's running processes shouldn't be killed when
new splits are installed. App stores can use this feature to seamlessly install
new features of an app while the user is using the app.
应用元数据软件包
从 Android 14 开始,Android 软件包安装程序可让您指定应用元数据(例如数据安全做法),以在 Google Play 等应用商店页面上架。
检测用户何时截取设备屏幕截图
为了打造更加标准化的屏幕截图检测体验,Android 14 引入了可保护隐私的屏幕截图检测 API。借助此 API,应用可以按 activity 注册回调。如果用户在该 activity 可见时截取屏幕截图,系统会调用这些回调并通知用户。
用户体验
Sharesheet 自定义操作和经过改进的排名系统
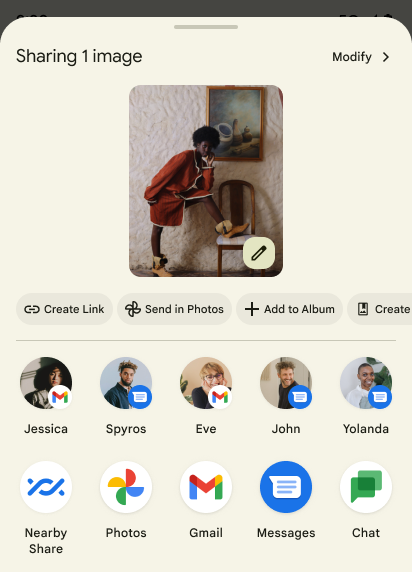
Android 14 更新了系统 Sharesheet,以便为用户提供自定义应用操作和信息更丰富的预览结果。
添加自定义操作
对于 Android 14,您的应用可以向其调用的系统 Sharesheet 添加自定义操作。
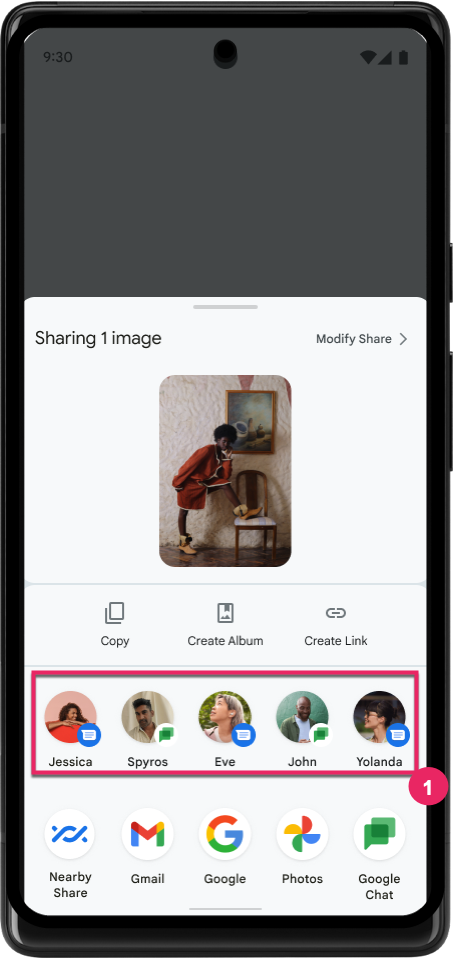
提高直接共享目标的排名
Android 14 根据来自应用的更多信号来确定直接共享目标的排名,以便为用户提供更实用的结果。为了提供最实用的排名信号,请遵循提高直接共享目标排名的准则。通讯应用还可以报告出站和入站消息的快捷方式使用情况。
支持内置和自定义预测性返回动画
Android 13 在开发者选项背后引入了预测性“返回主屏幕”动画。在已启用开发者选项的受支持应用中使用时,滑回手势会显示动画,表明返回手势会使应用退回到主屏幕。
Android 14 包含针对“预测性返回”的多项改进和新指南:
- 您可设置
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=true,以便为每个 activity 选择启用预测性返回系统动画,而不是为整个应用选择启用。 - 我们添加了新的系统动画,以配合 Android 13 中的“返回主屏幕”动画。新的系统动画是跨 activity 和跨任务的,您可在迁移到预测性返回后自动获得该动画。
- 我们为底部动作条、侧边动作条和搜索添加了新的 Material 组件动画。
- 我们制作了有关如何创建自定义应用内动画和转换的设计指南。
- 我们添加了许多新 API 来支持自定义的应用内转换动画:
在此 Android 14 预览版中,所有预测性返回功能都是位于开发者选项背后。请参阅与将您的应用迁移到预测性返回有关的开发者指南,以及与创建自定义应用内转换有关的开发者指南。
大屏设备制造商按应用替换项
借助按应用替换项,设备制造商可以更改应用在大屏设备上的行为。例如,FORCE_RESIZE_APP 替换项会指示系统调整应用大小以适应显示屏尺寸(避免进入尺寸兼容模式),即使在应用清单中设置了 resizeableActivity="false" 也是如此。
替换项旨在改善大屏设备上的用户体验。
借助新的清单属性,您可以为应用停用某些设备制造商替换项。
大屏设备用户按应用替换项
按应用替换项会更改应用在大屏设备上的行为。例如,无论应用的配置如何,OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE 设备制造商替换项都会将应用宽高比设置为 16:9。
借助 Android 14 QPR1,用户可以在大屏设备上通过新的设置菜单应用按应用替换项。
应用屏幕共享
借助应用界面共享功能,用户可以在录制屏幕内容时共享应用窗口,而不是整个设备屏幕。
在应用屏幕共享模式下,状态栏、导航栏、通知和其他系统界面元素会从共享显示屏中排除。系统只会分享所选应用的内容。
应用屏幕共享功能可让用户运行多个应用,但将内容共享限制为单个应用,从而提高工作效率并保护隐私。
Pixel 8 Pro 上由 LLM 提供支持的 Gboard 智能回复功能
On Pixel 8 Pro devices with the December Feature Drop, developers can try out higher-quality smart replies in Gboard powered by on-device Large Language Models (LLMs) running on Google Tensor.
This feature is available as a limited preview for US English in WhatsApp, Line, and KakaoTalk. It requires using a Pixel 8 Pro device with Gboard as your keyboard.
To try it out, first enable the feature in Settings > Developer Options > AiCore Settings > Enable Aicore Persistent.
Next, open a conversation in a supported app to see LLM-powered Smart Reply in Gboard's suggestion strip in response to incoming messages.
图形
路径可查询和插值
Android 的 Path API 是一种强大且灵活的机制,可用于创建和渲染矢量图形,能够描边或填充路径、根据线段或二次曲线或立方曲线构建路径、执行布尔运算以获取更复杂的形状,或同时执行所有这些操作。但有一个限制是,您无法了解 Path 对象中实际包含的内容;该对象的内部信息在创建后对调用方是不透明的。
如需创建 Path,您可以调用 moveTo()、lineTo() 和 cubicTo() 等方法来添加路径段。但是,无法询问该路径有哪些片段,因此您必须在创建时保留该信息。
从 Android 14 开始,您可以查询路径以了解其内部内容。首先,您需要使用 Path.getPathIterator API 获取 PathIterator 对象:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
接下来,您可以调用 PathIterator 逐个遍历片段,并检索每个片段的所有必要数据。以下示例使用了 PathIterator.Segment 对象,它会为您打包数据:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator 还有一个非分配版 next(),您可以在其中传入缓冲区来保存点数据。
查询 Path 数据的一个重要用例是插值。例如,您可能想在两个不同的路径之间添加动画(或变形)。为了进一步简化该用例,Android 14 针对 Path 还包含 interpolate() 方法。假设两个路径具有相同的内部结构,interpolate() 方法会使用该插值结果创建一个新的 Path。以下示例返回了一个形状介于 path 和 otherPath 之间的一半(线性插值为 0.5)的路径:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
Jetpack graphics-path 库也为早期版本的 Android 启用了类似的 API。
具有顶点着色器和片段着色器的自定义网格
Android 长期以来一直支持使用自定义着色绘制三角网格,但输入网格格式仅限于一些预定义的属性组合。Android 14 增加了对自定义网格的支持,可将其定义为三角形或三角形条,并且可以选择是否编入索引。这些网格是使用自定义属性、顶点步长、可变以及使用 AGSL 编写的顶点着色器和片段着色器指定的。
顶点着色器定义了位置和颜色等变量,而片段着色器可以选择为像素定义颜色,通常是使用顶点着色器创建的变量。如果片段着色器提供颜色,则系统会使用绘制网格时选择的混合模式将其与当前 Paint 颜色混合。Uniform 可以传递到片段着色器和顶点着色器,以提高灵活性。
Canvas 的硬件缓冲区渲染器
协助使用 Android 的 Canvas API 通过
硬件加速至 HardwareBuffer、Android 14
引入了 HardwareBufferRenderer。如果您的用例涉及通过 SurfaceControl 与系统合成器通信以实现低延迟绘制,此 API 特别有用。
