Android 14 bietet Entwicklern viele neue Funktionen und APIs. Die folgenden Ressourcen helfen Ihnen, sich über Funktionen für Ihre Apps zu informieren und mit den zugehörigen APIs zu beginnen.
Eine detaillierte Liste der hinzugefügten, geänderten und entfernten APIs finden Sie im API-Vergleichsbericht. Details zu den hinzugefügten APIs finden Sie in der Android-API-Referenz. Suchen Sie dort nach APIs, die in API-Level 34 hinzugefügt wurden. Informationen zu Bereichen, in denen sich Plattformänderungen auf Ihre Apps auswirken können, finden Sie unter „Verhaltensänderungen in Android 14“ für Apps, die auf Android 14 ausgerichtet sind, und für alle Apps.
Lokalisierung
App-spezifische Spracheinstellungen
Android 14 erweitert die Funktionen für die Sprache pro App, die in Android 13 (API-Level 33) eingeführt wurden, um die folgenden zusätzlichen Funktionen:
localeConfigeiner App automatisch generieren: Ab Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 und AGP 8.1.0-alpha07 können Sie Ihre App so konfigurieren, dass sie automatisch Spracheinstellungen pro App unterstützt. Basierend auf den Projektressourcen generiert das Android Gradle-Plug-in die DateiLocaleConfigund fügt in der endgültigen Manifestdatei einen Verweis darauf hinzu. Sie müssen die Datei also nicht mehr manuell erstellen oder aktualisieren. AGP verwendet die Ressourcen in denres-Ordnern Ihrer App-Module und alle Abhängigkeiten von Bibliotheksmodulen, um die Sprachen zu ermitteln, die in dieLocaleConfig-Datei aufgenommen werden sollen.Dynamische Updates für die
localeConfigeiner App: Verwenden Sie die MethodensetOverrideLocaleConfig()undgetOverrideLocaleConfig()inLocaleManager, um die Liste der unterstützten Sprachen Ihrer App in den Systemeinstellungen des Geräts dynamisch zu aktualisieren. Sie können diese Flexibilität nutzen, um die Liste der unterstützten Sprachen pro Region anzupassen, A/B-Tests durchzuführen oder eine aktualisierte Liste der Sprachen anzugeben, wenn Ihre App serverseitige Pushes für die Lokalisierung verwendet.Sichtbarkeit der App-Sprache für Eingabemethoden-Editoren (IMEs): IMEs können die Methode
getApplicationLocales()verwenden, um die Sprache der aktuellen App zu prüfen und die IME-Sprache mit dieser Sprache abzugleichen.
Grammatical Inflection API
3 Milliarden Menschen sprechen geschlechterspezifische Sprachen: Sprachen, in denen grammatische Kategorien wie Substantive, Verben, Adjektive und Präpositionen je nach Geschlecht der Personen und Objekte, mit denen oder über die gesprochen wird, konjugiert werden. Traditionell wird in vielen Sprachen mit Geschlechtern das männliche grammatische Geschlecht als Standard- oder generisches Geschlecht verwendet.
Wenn Sie Nutzer im falschen grammatischen Geschlecht ansprechen, z. B. Frauen im maskulinen grammatischen Geschlecht, kann sich das negativ auf ihre Leistung und Einstellung auswirken. Eine Benutzeroberfläche mit einer Sprache, die das grammatische Geschlecht des Nutzers korrekt widerspiegelt, kann das Nutzer-Engagement verbessern und eine personalisiertere und natürlicher klingende Nutzererfahrung bieten.
Mit der Grammatical Inflection API in Android 14 können Sie eine nutzerzentrierte Benutzeroberfläche für Sprachen mit grammatischem Geschlecht erstellen. So können Sie die Unterstützung für das grammatische Geschlecht hinzufügen, ohne Ihre App umbauen zu müssen.
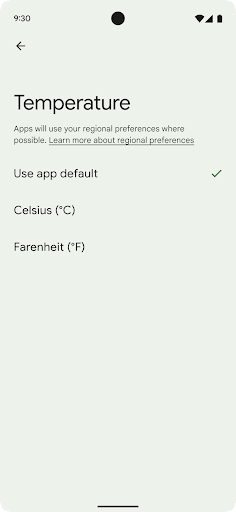
Regionale Einstellungen
Mit den regionalen Einstellungen können Nutzer Temperatureinheiten, den Wochentag und das Nummerierungssystem anpassen. Ein Europäer, der in den USA lebt, möchte möglicherweise, dass Temperatureinheiten in Celsius statt in Fahrenheit angegeben werden und dass Apps Montag als Wochenbeginn verwenden, anstatt den US-Standardsonntag.
Die neuen Android-Einstellungen für diese Einstellungen bieten Nutzern eine leicht auffindbare und zentrale Stelle, an der sie die App-Einstellungen ändern können. Diese Einstellungen bleiben auch nach dem Sichern und Wiederherstellen erhalten. Mehrere APIs und
Intents, wie z. B.
getTemperatureUnit
und
getFirstDayOfWeek–
Ihrer App Lesezugriff auf Nutzereinstellungen zu gewähren, damit sie anpassen kann, wie sie
werden Informationen angezeigt. Du kannst auch eine BroadcastReceiver unter ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED registrieren, um Änderungen an der Gebietsschemakonfiguration zu verarbeiten, wenn sich die regionalen Einstellungen ändern.
Sie finden diese Einstellungen in den Einstellungen unter System > Sprachen und Eingabe > Regionale Einstellungen.

Bedienungshilfen
Nicht lineare Skalierung der Schriftgröße auf 200%
Ab Android 14 unterstützt das System die Schriftartskalierung auf bis zu 200 % und bietet Nutzern so zusätzliche Optionen für die Barrierefreiheit.
Damit große Textelemente auf dem Bildschirm nicht zu groß skaliert werden, wendet das System eine nichtlineare Skalierungskurve an. Bei dieser Skalierungsstrategie wird großer Text nicht im gleichen Maße skaliert wie kleiner Text. Die nicht lineare Skalierung von Schriftarten trägt dazu bei, die proportionale Hierarchie zwischen Elementen unterschiedlicher Größe beizubehalten und gleichzeitig Probleme mit der linearen Textskalierung bei hohen Graden zu vermeiden, z. B. wenn Text abgeschnitten wird oder aufgrund einer extrem großen Displaygröße schwerer zu lesen ist.
App mit nicht linearer Schriftgrößenskalierung testen
Wenn Sie bereits skalierbare Pixel (sp) zum Definieren der Textgröße verwenden, werden diese zusätzlichen Optionen und Verbesserungen der Skalierung automatisch auf den Text in Ihrer App angewendet. Sie sollten jedoch trotzdem UI-Tests mit aktivierter maximaler Schriftgröße (200%) durchführen, um sicherzustellen, dass Ihre App die Schriftgrößen korrekt anwendet und größere Schriftgrößen ohne Beeinträchtigung der Nutzerfreundlichkeit unterstützt.
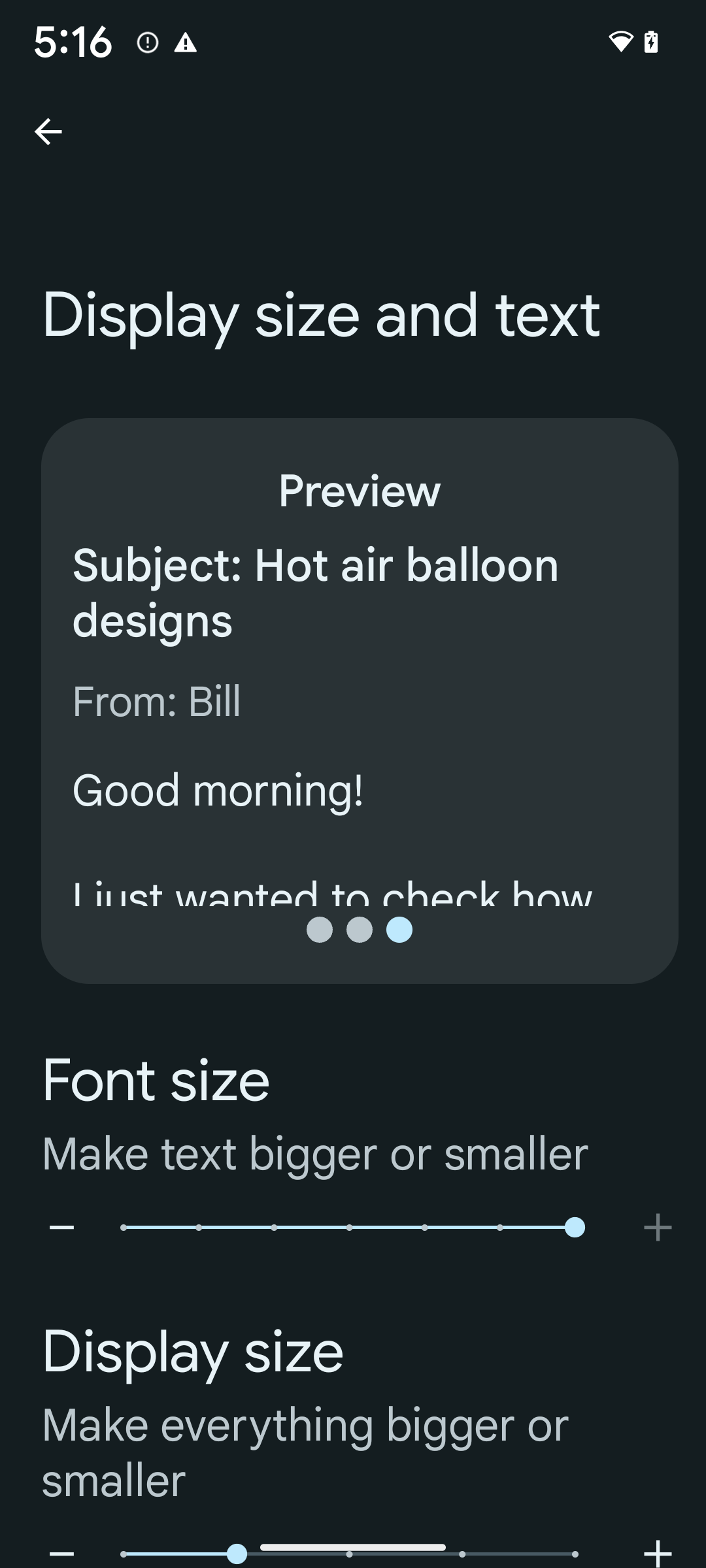
So aktivieren Sie die Schriftgröße von 200 %:
- Öffnen Sie die Einstellungen und gehen Sie zu Bedienungshilfen > Anzeigegröße und Text.
- Tippen Sie für die Option Schriftgröße auf das Pluszeichen (+), bis die maximale Schriftgröße eingestellt ist, wie im Bild zu diesem Abschnitt zu sehen.
Skalierbare Pixel (sp) für Textgrößen verwenden
Denken Sie daran, Textgrößen immer in sp-Einheiten anzugeben. Wenn Ihre App „sp“-Einheiten verwendet, kann Android die bevorzugte Textgröße des Nutzers anwenden und entsprechend skalieren.
Verwenden Sie keine „sp“-Einheiten für den Innenabstand und definieren Sie keine Ansichtshöhen, die einen impliziten Innenabstand voraussetzen: Bei nicht linearer Schriftartskalierung sind „sp“-Dimensionen möglicherweise nicht proportional. Daher ist 4sp + 20sp möglicherweise nicht gleich 24sp.
Einheiten für skalierte Pixel (sp) umrechnen
Verwenden Sie TypedValue.applyDimension(), um von sp-Einheiten in Pixel umzurechnen, und TypedValue.deriveDimension(), um Pixel in sp umzurechnen. Bei diesen Methoden wird automatisch die entsprechende nichtlineare Skalierungskurve angewendet.
Vermeiden Sie das Hardcodieren von Gleichungen mit Configuration.fontScale oder DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity. Da die Schriftartskalierung nicht linear ist, ist das Feld scaledDensity nicht mehr genau. Das Feld fontScale sollte nur zu Informationszwecken verwendet werden, da Schriftarten nicht mehr mit einem einzelnen Skalarwert skaliert werden.
„sp“-Einheiten für „lineHeight“ verwenden
Definieren Sie android:lineHeight immer in sp-Einheiten anstelle von dp, damit die Zeilenhöhe mit dem Text skaliert wird. Wenn Ihr Text in sp, Ihre lineHeight aber in dp oder px angegeben ist, wird er nicht skaliert und sieht gequetscht aus.
TextView korrigiert die lineHeight automatisch, sodass die beabsichtigten Proportionen beibehalten werden. Das funktioniert jedoch nur, wenn sowohl textSize als auch lineHeight in sp-Einheiten definiert sind.
Kamera und Medien
Ultra HDR für Bilder

Android 14 unterstützt jetzt HDR-Bilder (High Dynamic Range). Dabei bleiben beim Aufnehmen eines Fotos mehr Informationen vom Sensor erhalten, was zu lebendigeren Farben und einem höheren Kontrast führt. Android verwendet das Ultra-HDR-Format, das vollständig abwärtskompatibel mit JPEG-Bildern ist. So können Apps nahtlos mit HDR-Bildern interagieren und sie bei Bedarf im Standard-Dynamikbereich (SDR) anzeigen.
Das Rendern dieser Bilder in der Benutzeroberfläche in HDR erfolgt automatisch durch das Framework, wenn Ihre App die HDR-Benutzeroberfläche für ihr Aktivitätsfenster aktiviert, entweder über einen Manifesteintrag oder zur Laufzeit durch Window.setColorMode() aufrufen. Auf unterstützten Geräten können Sie auch komprimierte Ultra-HDR-Standbilder aufnehmen. Je mehr Farben vom Sensor erfasst werden, desto flexibler ist die Nachbearbeitung. Die mit Ultra-HDR-Bildern verknüpfte Gainmap kann zum Rendern mit OpenGL oder Vulkan verwendet werden.
Zoom, Fokus, Postview und mehr in Kameraerweiterungen
In Android 14 wurden die Kameraerweiterungen aktualisiert und verbessert. So können Apps längere Verarbeitungszeiten verarbeiten, was mithilfe von leistungsintensiven Algorithmen wie der Fotografie bei wenig Licht auf unterstützten Geräten zu besseren Bildern führt. Diese Funktionen bieten Nutzern noch mehr Stabilität bei der Verwendung von Kameraerweiterungsfunktionen. Beispiele für diese Verbesserungen:
- Die dynamische Schätzung der Verarbeitungslatenz für Standbilder liefert viel genauere Schätzungen der Latenz für Standbilder basierend auf der aktuellen Szene und den Umgebungsbedingungen. Rufen Sie
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()auf, um einStillCaptureLatency-Objekt mit zwei Methoden zur Latenzschätzung abzurufen. Die MethodegetCaptureLatency()gibt die geschätzte Latenz zwischenonCaptureStartedundonCaptureProcessStarted()zurück. Die MethodegetProcessingLatency()gibt die geschätzte Latenz zwischenonCaptureProcessStarted()und der Verfügbarkeit des letzten verarbeiteten Frames zurück. - Unterstützung für Callbacks zum Aufnahmefortschritt, damit Apps den aktuellen Fortschritt langwieriger Verarbeitungsvorgänge für Standbilder anzeigen können. Du kannst mit
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailableprüfen, ob diese Funktion verfügbar ist. Ist das der Fall, implementiere den CallbackonCaptureProcessProgressed(), der den Fortschritt (von 0 bis 100) als Parameter enthält. Erweiterungsspezifische Metadaten wie
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTH, um die Intensität eines Erweiterungseffekts zu steuern, z. B. die Weichzeichnung des Hintergrunds mitEXTENSION_BOKEH.Postview-Funktion für die Standbildaufnahme in Kameraerweiterungen, mit der ein weniger verarbeitetes Bild schneller als das Endbild angezeigt wird. Wenn eine Erweiterung die Verarbeitungslatenz erhöht, kann ein Postview-Bild als Platzhalter bereitgestellt werden, um die Nutzerfreundlichkeit zu verbessern, und später durch das endgültige Bild ersetzt werden. Mit
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailablekönnen Sie prüfen, ob diese Funktion verfügbar ist. Anschließend können SieOutputConfigurationanExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfigurationübergeben.Unterstützung für
SurfaceView, was einen optimierteren und energieeffizienteren Renderpfad für die Vorschau ermöglicht.Unterstützung für das Fokussieren und Zoomen durch Tippen bei Verwendung der Erweiterung.
In-Sensor-Zoom
Wenn REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE in CameraCharacteristics SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW enthält, kann Ihre App mithilfe erweiterter Sensorfunktionen einem zugeschnittenen RAW-Stream dieselben Pixel wie das vollständige Sichtfeld zuweisen. Verwenden Sie dazu einen CaptureRequest mit einem RAW-Ziel, für das der Stream-Nutzungsfall auf CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW festgelegt ist.
Durch die Implementierung der Steuerelemente für die Überschreibung von Anfragen können Nutzer mit der aktualisierten Kamera den Zoom bereits steuern, bevor andere Kamerasteuerelemente verfügbar sind.
Lossless-USB-Audio
Android 14 unterstützt jetzt verlustfreie Audioformate für eine audiophile Wiedergabe über USB-Kopfhörer. Du kannst ein USB-Gerät nach seinen bevorzugten Mixerattributen abfragen, einen Listener für Änderungen an bevorzugten Mixerattributen registrieren und Mixerattribute mit der Klasse AudioMixerAttributes konfigurieren. Diese Klasse stellt das Format dar, z. B. Kanalmaske, Abtastrate und Verhalten des Audiomixers. Mit dieser Klasse kann Audio direkt gesendet werden, ohne dass es gemischt, die Lautstärke angepasst oder Verarbeitungseffekte angewendet werden.
Produktivität von Entwicklern und Tools
Credential Manager
In Android 14 wird Credential Manager als Plattform-API hinzugefügt. Durch eine Jetpack-Bibliothek mit Google Play-Diensten wird zusätzliche Unterstützung für Geräte mit Android 4.4 (API-Level 19) bereitgestellt. Der Anmeldedaten-Manager soll die Anmeldung für Nutzer mit APIs erleichtern, die Anmeldedaten bei vom Nutzer konfigurierten Anmeldedatenanbietern abrufen und speichern. Credential Manager unterstützt mehrere Anmeldemethoden, darunter Nutzername und Passwort, Passkeys und Lösungen für die föderierte Anmeldung (z. B. „Über Google anmelden“) in einer einzigen API.
Passkeys bieten viele Vorteile. Passkeys basieren beispielsweise auf Branchenstandards, funktionieren über verschiedene Betriebssysteme und Browser hinweg und können sowohl für Websites als auch für Apps verwendet werden.
Weitere Informationen finden Sie in der Dokumentation zu Anmeldedaten-Manager und Passkeys und im Blogpost zu Anmeldedaten-Manager und Passkeys.
Health Connect
Health Connect ist ein On-Device-Repository für Gesundheits- und Fitnessdaten von Nutzern. Nutzer können Daten zwischen ihren Lieblings-Apps teilen und an einem zentralen Ort festlegen, welche Daten sie für diese Apps freigeben möchten.
Auf Geräten mit Android-Versionen vor Android 14 kann Health Connect als App im Google Play Store heruntergeladen werden. Ab Android 14 ist Health Connect Teil der Plattform und erhält Updates über Google Play-Systemupdates, ohne dass ein separater Download erforderlich ist. So kann Health Connect häufig aktualisiert werden und Ihre Apps können davon ausgehen, dass Health Connect auf Geräten mit Android 14 oder höher verfügbar ist. Nutzer können über die Einstellungen auf ihrem Gerät auf Health Connect zugreifen. Die Datenschutzeinstellungen sind in die Systemeinstellungen integriert.
Health Connect bietet in Android 14 mehrere neue Funktionen, z. B. Trainingsrouten. Damit können Nutzer eine Route ihres Trainings teilen, die auf einer Karte visualisiert werden kann. Eine Route wird als Liste von Orten definiert, die innerhalb eines bestimmten Zeitraums gespeichert wurden. Ihre App kann Routen in Trainingseinheiten einfügen und so miteinander verknüpfen. Damit Nutzer die vollständige Kontrolle über diese sensiblen Daten haben, müssen sie die Freigabe einzelner Routen für andere Apps zulassen.
Weitere Informationen finden Sie in der Health Connect-Dokumentation und im Blogpost Neuerungen in Android Health.
OpenJDK 17-Updates
Mit Android 14 werden die Kernbibliotheken von Android weiter aktualisiert, um sie an die Funktionen der neuesten OpenJDK LTS-Releases anzupassen. Dazu gehören sowohl Bibliotheksupdates als auch die Java 17-Sprachunterstützung für App- und Plattformentwickler.
Die folgenden Funktionen und Verbesserungen sind enthalten:
- Etwa 300
java.base-Klassen wurden auf Java 17 umgestellt. - Textblöcke, die mehrzeilige Stringliterale in die Java-Programmiersprache einführen.
- Musterabgleich für „instanceof“: Damit kann ein Objekt in einer
instanceofohne zusätzliche Variablen als Objekt eines bestimmten Typs behandelt werden. - Verschlossene Klassen, mit denen Sie einschränken können, welche Klassen und Schnittstellen sie erweitern oder implementieren können.
Dank Google Play-Systemupdates (Project Mainline) können über 600 Millionen Geräte die neuesten Android Runtime-Updates (ART) erhalten, die diese Änderungen enthalten. Wir möchten Apps eine einheitliche, sichere Umgebung auf allen Geräten bieten und Nutzern unabhängig von Plattformveröffentlichungen neue Funktionen und Möglichkeiten zur Verfügung stellen.
Java und OpenJDK sind Marken oder eingetragene Marken von Oracle und/oder seinen Tochtergesellschaften.
Verbesserungen für App-Shops
Mit Android 14 werden mehrere PackageInstaller APIs eingeführt, mit denen App-Shops die Nutzerfreundlichkeit verbessern können.
Vor dem Herunterladen Installationsberechtigung anfordern
Für die Installation oder Aktualisierung einer App ist möglicherweise die Genehmigung des Nutzers erforderlich.
Beispielsweise, wenn ein Installationsprogramm, das die Berechtigung REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES nutzt, versucht, eine neue App zu installieren. In früheren Android-Versionen können App-Shops die Nutzergenehmigung nur anfordern, nachdem APKs in die Installationssitzung geschrieben und die Sitzung festgeschrieben wurde.
Ab Android 14 können Installateure mit der Methode requestUserPreapproval() die Nutzereinwilligung vor dem Ausführen der Installationssitzung anfordern. Durch diese Verbesserung kann ein App-Shop das Herunterladen von APKs so lange verschieben, bis die Installation vom Nutzer genehmigt wurde. Sobald ein Nutzer die Installation genehmigt hat, kann der App-Shop die App im Hintergrund herunterladen und installieren, ohne den Nutzer zu unterbrechen.
Verantwortung für zukünftige Updates übernehmen
Mit der Methode setRequestUpdateOwnership() kann ein Installationsprogramm dem System mitteilen, dass es für zukünftige Updates einer installierten App verantwortlich sein möchte. Mit dieser Funktion kann die Inhaberschaft von Updates erzwungen werden. Das bedeutet, dass nur der Inhaber des Updates automatische Updates für die App installieren darf. So wird sichergestellt, dass Nutzer Updates nur über den erwarteten App-Shop erhalten.
Alle anderen Installationsprogramme, einschließlich derjenigen, die die Berechtigung INSTALL_PACKAGES verwenden, müssen die ausdrückliche Genehmigung des Nutzers einholen, um ein Update zu installieren. Wenn ein Nutzer sich für eine Aktualisierung aus einer anderen Quelle entscheidet, geht die Inhaberschaft für die Aktualisierung verloren.
Apps zu einer weniger störenden Zeit aktualisieren
App-Shops möchten in der Regel vermeiden, eine App zu aktualisieren, die aktiv verwendet wird, da dadurch die laufenden Prozesse der App beendet werden, was die Aktivitäten des Nutzers unterbrechen kann.
Ab Android 14 können Sie mit der InstallConstraints API dafür sorgen, dass Ihre App-Updates zum richtigen Zeitpunkt erfolgen. Ein App-Shop kann beispielsweise die Methode commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() aufrufen, um dafür zu sorgen, dass ein Update nur dann ausgeführt wird, wenn der Nutzer nicht mehr mit der betreffenden App interagiert.
Optionale Trennlinien nahtlos einfügen
Bei Split-APKs können Funktionen einer App in separaten APK-Dateien bereitgestellt werden, anstatt als monolithisches APK. Mit unterteilten APKs können App-Shops die Bereitstellung verschiedener App-Komponenten optimieren. App-Shops können beispielsweise basierend auf den Eigenschaften des Zielgeräts optimieren. Die PackageInstaller API unterstützt seit ihrer Einführung in API-Ebene 22 die Aufteilung.
Unter Android 14 kann ein Installer mit der Methode setDontKillApp() angeben, dass die laufenden Prozesse der App nicht beendet werden sollen, wenn neue Splits installiert werden. App-Shops können diese Funktion verwenden, um neue Funktionen einer App nahtlos zu installieren, während der Nutzer die App verwendet.
App-Metadaten-Bundles
Ab Android 14 können Sie mit dem Android-Paketinstallationsprogramm App-Metadaten wie Praktiken zur Datensicherheit angeben, die auf App-Shop-Seiten wie Google Play angezeigt werden.
Erkennen, wenn Nutzer Screenshots aufnehmen
Um die Erkennung von Screenshots zu standardisieren, wird in Android 14 eine datenschutzfreundliche API zur Erkennung von Screenshots eingeführt. Mit dieser API können Apps Rückrufe pro Aktivität registrieren. Diese Rückrufe werden aufgerufen und der Nutzer wird benachrichtigt, wenn er einen Screenshot aufnimmt, während diese Aktivität sichtbar ist.
Nutzererfahrung
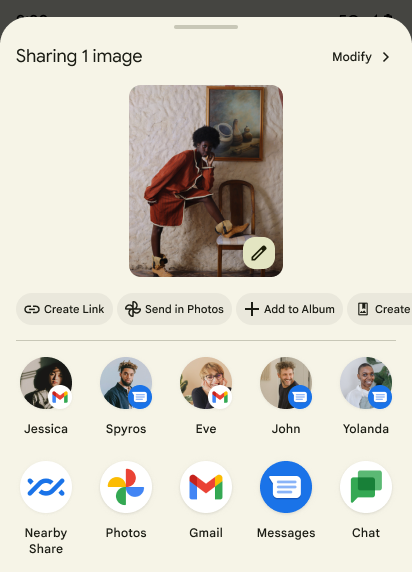
Benutzerdefinierte Aktionen im Freigabeblatt und verbessertes Ranking
Unter Android 14 wird das System-Freigabe-Dialogfeld aktualisiert, um benutzerdefinierte App-Aktionen und informativere Vorschauergebnisse für Nutzer zu unterstützen.
Benutzerdefinierte Aktionen hinzufügen
Unter Android 14 kann Ihre App dem freigegebenen System-Sheet benutzerdefinierte Aktionen hinzufügen.
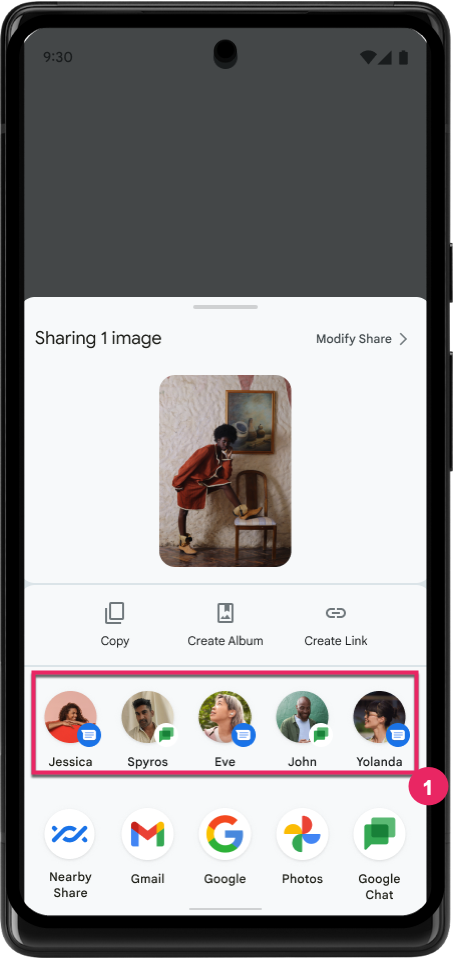
Rang der Ziele für die direkte Freigabe verbessern
Unter Android 14 werden mehr Signale aus Apps verwendet, um das Ranking der Ziele für die direkte Freigabe zu bestimmen und so hilfreichere Ergebnisse für den Nutzer zu liefern. Folgen Sie der Anleitung unter Rankings Ihrer Ziele für die direkte Freigabe verbessern, um das nützlichste Signal für das Ranking bereitzustellen. Kommunikations-Apps können auch die Nutzung von Tastenkürzeln für ausgehende und eingehende Nachrichten melden.
Unterstützung für integrierte und benutzerdefinierte Animationen für die intelligente „Zurück“-Touchgeste
In Android 13 wurde die intelligente „Zurück“-Geste für die Systemanimation als Entwickleroption eingeführt. Wenn Sie die Touch-Geste „Zurück“ in einer unterstützten App verwenden, bei der die Entwickleroption aktiviert ist, wird beim Wischen nach hinten eine Animation angezeigt, die darauf hinweist, dass Sie durch die Touch-Geste „Zurück“ die App verlassen und zum Startbildschirm zurückkehren.
Android 14 enthält mehrere Verbesserungen und neue Hinweise für die Vorhersagefunktion für Back:
- Sie können
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueso einstellen, dass die vorausschauenden Systemanimationen für die Rückwärtsnavigation pro Aktivität und nicht für die gesamte App aktiviert werden. - Wir haben neue Systemanimationen hinzugefügt, die die Animation zum Zurückkehren zum Startbildschirm aus Android 13 begleiten. Die neuen Systemanimationen sind aktivitäts- und aufgabenübergreifend und werden Ihnen automatisch angezeigt, nachdem Sie zur intelligenten „Zurück“-Touch-Geste migriert sind.
- Wir haben neue Material Component-Animationen für Untere Seitenleisten, Seitenleisten und die Suche hinzugefügt.
- Wir haben Designrichtlinien für die Erstellung benutzerdefinierter In-App-Animationen und ‑Übergänge erstellt.
- Wir haben neue APIs hinzugefügt, um benutzerdefinierte In-App-Übergangsanimationen zu unterstützen:
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- Verwenden Sie
overrideActivityTransitionanstelle vonoverridePendingTransitionfür Übergänge, die ausgelöst werden, wenn der Nutzer wischt.
In dieser Android 14-Vorabversion sind alle Funktionen der Vorhersagefunktion für die rückwärtsgerichtete Navigation weiterhin nur über eine Entwickleroption verfügbar. Weitere Informationen finden Sie im Entwicklerleitfaden zur Migration Ihrer App zu der Funktion „Vorhersagender Rückwärtsgang“ und im Entwicklerleitfaden zum Erstellen benutzerdefinierter In-App-Übergänge.
Herstellerspezifische Überschreibungen für Apps auf Geräten mit großem Display
Mit Überschreibungen pro App können Gerätehersteller das Verhalten von Apps auf Geräten mit großen Bildschirmen ändern. Die Überschreibung FORCE_RESIZE_APP weist das System beispielsweise an, die App an die Displayabmessungen anzupassen (um den Kompatibilitätsmodus zu vermeiden), auch wenn resizeableActivity="false" im App-Manifest festgelegt ist.
Überschreibungen sollen die Nutzererfahrung auf großen Bildschirmen verbessern.
Mit neuen Manifesteigenschaften können Sie einige Überschreibungen von Geräteherstellern für Ihre App deaktivieren.
App-spezifische Überschreibungen für Nutzer mit großen Bildschirmen
Mit App-spezifischen Überschreibungen können Sie das Verhalten von Apps auf Geräten mit großen Bildschirmen ändern. Beispielsweise wird durch die Override-Anweisung des Geräteherstellers OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE das Seitenverhältnis der App unabhängig von der Konfiguration der App auf 16:9 festgelegt.
Mit Android 14 QPR1 können Nutzer auf Geräten mit großem Bildschirm über ein neues Einstellungsmenü App-spezifische Überschreibungen anwenden.
App-Bildschirmfreigabe
Bei der App-Bildschirmfreigabe können Nutzer beim Aufzeichnen von Bildschirminhalten ein App-Fenster anstelle des gesamten Gerätebildschirms freigeben.
Bei der Bildschirmfreigabe für Apps werden die Statusleiste, die Navigationsleiste, Benachrichtigungen und andere Elemente der System-UI vom geteilten Display ausgeschlossen. Es werden nur die Inhalte der ausgewählten App freigegeben.
Die Bildschirmfreigabe von Apps verbessert die Produktivität und den Datenschutz, da Nutzer mehrere Apps ausführen, die Freigabe von Inhalten jedoch auf eine einzelne App beschränken können.
LLM-basierte Funktion „Intelligente Antworten“ in Gboard auf dem Pixel 8 Pro
Auf Google Pixel 8 Pro-Geräten mit dem Feature Drop vom Dezember können Entwickler intelligente Antworten in Gboard ausprobieren, die auf On-Device-Large Language Models (LLMs) basieren, die auf Google Tensor ausgeführt werden.
Diese Funktion ist in WhatsApp, Line und KakaoTalk als eingeschränkte Vorabversion für amerikanisches Englisch verfügbar. Dazu benötigen Sie ein Google Pixel 8 Pro mit Gboard als Tastatur.
Wenn Sie die Funktion ausprobieren möchten, aktivieren Sie sie zuerst unter Einstellungen > Entwickleroptionen > AICore-Einstellungen > „Persistente AICore-Daten aktivieren“.
Öffnen Sie als Nächstes eine Unterhaltung in einer unterstützten App, um LLM-basierte intelligente Antworten in der Vorschlagsleiste von Gboard als Antwort auf eingehende Nachrichten zu sehen.
Grafik
Pfade können abgefragt und interpoliert werden
Die Path API von Android ist ein leistungsstarker und flexibler Mechanismus zum Erstellen und Rendern von Vektorgrafiken. Sie können damit einen Pfad zeichnen oder füllen, einen Pfad aus Liniensegmenten oder quadratischen oder kubischen Kurven erstellen, boolesche Operationen ausführen, um noch komplexere Formen zu erhalten, oder all dies gleichzeitig. Eine Einschränkung besteht darin, herauszufinden, was sich tatsächlich in einem Pfadobjekt befindet. Das Innere des Objekts ist nach der Erstellung für Aufrufer undurchsichtig.
Wenn Sie eine Path erstellen möchten, rufen Sie Methoden wie moveTo(), lineTo() und cubicTo() auf, um Pfadsegmente hinzuzufügen. Da es jedoch nicht möglich war, den Pfad nach den Segmenten zu fragen, müssen Sie diese Informationen zum Zeitpunkt der Erstellung beibehalten.
Ab Android 14 können Sie Pfade abfragen, um herauszufinden, was sie enthalten.
Rufen Sie zuerst ein PathIterator-Objekt mit der Path.getPathIterator API ab:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
Als Nächstes können Sie PathIterator aufrufen, um die Segmente nacheinander durchzugehen und alle erforderlichen Daten für jedes Segment abzurufen. In diesem Beispiel werden PathIterator.Segment-Objekte verwendet, die die Daten für Sie verpacken:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator hat auch eine Version von next() ohne Zuordnung, in der Sie einen Zwischenspeicher übergeben können, um die Punktdaten zu speichern.
Einer der wichtigsten Anwendungsfälle für die Abfrage von Path-Daten ist die Interpolation. So können Sie beispielsweise einen Übergang (Morphing) zwischen zwei verschiedenen Pfaden animieren. Zur weiteren Vereinfachung dieses Anwendungsfalls enthält Android 14 auch die Methode interpolate() für Path. Unter der Annahme, dass die beiden Pfade die gleiche interne Struktur haben, erstellt die Methode interpolate() eine neue Path mit diesem interpolierten Ergebnis. In diesem Beispiel wird ein Pfad zurückgegeben, dessen Form halbiert ist (eine lineare Interpolation von 0,5) zwischen path und otherPath:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
Die Jetpack-Bibliothek graphics-path ermöglicht ähnliche APIs auch für ältere Android-Versionen.
Benutzerdefinierte Meshes mit Vertex- und Fragment-Shadern
Android unterstützt schon lange das Zeichnen von Dreiecksnetzen mit benutzerdefinierter Schattierung. Das Eingabe-Mesh-Format war jedoch auf einige vordefinierte Kombinationen von Attributen beschränkt. Android 14 unterstützt benutzerdefinierte 3D-Meshes, die als Dreiecke oder Dreiecksstreifen definiert werden können und optional indexiert werden können. Diese Meshes werden mit benutzerdefinierten Attributen, Vertex-Strides, Variierenden sowie Vertex- und Fragment-Shadern in AGSL angegeben.
Der Vertex-Shader definiert die Variablen wie Position und Farbe, während der Fragment-Shader optional die Farbe für das Pixel definieren kann, in der Regel unter Verwendung der vom Vertex-Shader erstellten Variablen. Wenn die Farbe vom Fragment-Shader bereitgestellt wird, wird sie mit der aktuellen Paint-Farbe mithilfe des Blendmodus gemischt, der beim Zeichnen des Mesh ausgewählt wurde. Uniforms können für zusätzliche Flexibilität an die Fragment- und Vertex-Shader übergeben werden.
Hardware-Buffer-Renderer für Canvas
Unter Android 14 wird HardwareBufferRenderer eingeführt, um die Verwendung der Canvas API von Android zum Zeichnen mit Hardwarebeschleunigung in einem HardwareBuffer zu unterstützen. Diese API ist
besonders nützlich, wenn Ihr Anwendungsfall die Kommunikation mit dem System umfasst
Compositor über SurfaceControl für niedrige Latenzzeiten
zeichnen können.
