与之前的版本一样,Android 16 包含一些行为变更,这些变更可能会影响您的应用。以下行为变更仅影响以 Android 16 或更高版本为目标平台的应用。如果您的应用以 Android 16 或更高版本为目标平台,您应该修改自己的应用以支持这些行为(如果适用)。
请务必查看对 Android 16 上运行的所有应用都有影响的行为变更列表(无论应用的 targetSdkVersion 如何)。
用户体验和系统界面
Android 16(API 级别 36)包含以下变更,旨在打造更一致、更直观的用户体验。
无边框设计选择退出功能即将停用
Android 15 enforced edge-to-edge for apps targeting Android 15 (API
level 35), but your app could opt-out by setting
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement to true. For apps
targeting Android 16 (API level 36),
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement is deprecated and disabled, and your
app can't opt-out of going edge-to-edge.
- If your app targets Android 16 (API level 36) and is running on an
Android 15 device,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementcontinues to work. - If your app targets Android 16 (API level 36) and is running on an
Android 16 device,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementis disabled.
For testing in Android 16, ensure your app supports edge-to-edge and
remove any use of R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement so that your app
also supports edge-to-edge on an Android 15 device. To support edge-to-edge,
see the Compose and Views guidance.
预测性返回需要迁移或选择停用
对于以 Android 16(API 级别 36)或更高版本为目标平台且在搭载 Android 16 或更高版本的设备上运行的应用,预测性返回系统动画(返回主屏幕、跨任务和跨 activity)默认处于启用状态。此外,系统不再调用 onBackPressed,也不再调度 KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK。
如果您的应用会拦截返回事件,但您尚未迁移到预测性返回,请更新应用以使用受支持的返回导航 API,或者暂时选择停用,方法是在应用的 AndroidManifest.xml 文件的 <application> 或 <activity> 标记中将 android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback 属性设置为 false。
优雅字体 API 已弃用并停用
以 Android 15(API 级别 35)为目标平台的应用默认将 elegantTextHeight
TextView 属性设置为 true,从而将紧凑型字体替换为可读性更高的字体。您可以通过将 elegantTextHeight 属性设置为 false 来替换此设置。
Android 16 弃用了 elegantTextHeight 属性,当您的应用以 Android 16 为目标平台后,系统会忽略该属性。由这些 API 控制的“界面字体”即将停用,因此您应调整所有布局,以确保阿拉伯语、老挝语、缅甸语、泰米尔语、古吉拉特语、卡纳达语、马拉雅拉姆语、奥里亚语、泰卢固语或泰语文本的呈现效果一致且不受未来变化的影响。
elegantTextHeight 属性设置为 false 替换默认值的应用,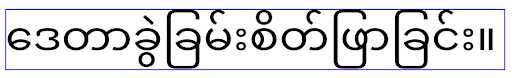
elegantTextHeight 行为。elegantTextHeight 属性设置为 false 来替换默认值的应用,其 elegantTextHeight 行为。
核心功能
Android 16(API 级别 36)包含以下变更,这些变更会修改或扩展 Android 系统的各种核心功能。
固定费率工作安排优化
Prior to targeting Android 16, when scheduleAtFixedRate
missed a task execution due to being outside a valid
process lifecycle, all missed executions immediately
execute when the app returns to a valid lifecycle.
When targeting Android 16, at most one missed execution of
scheduleAtFixedRate is immediately executed when the app
returns to a valid lifecycle. This behavior change is expected to improve app
performance. Test this behavior in your app to check if your app is impacted.
You can also test by using the app compatibility framework
and enabling the STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS compat flag.
设备规格
Android 16(API 级别 36)在应用显示在大屏设备上时,包含以下变更。
自适应布局
现在,Android 应用可在各种设备(例如手机、平板电脑、可折叠设备、桌面设备、汽车和电视)上运行,并且在大屏设备上支持多种窗口模式(例如分屏和桌面窗口),因此开发者应构建能够适应任何屏幕和窗口尺寸的 Android 应用,无论设备方向如何。在当今多设备的世界中,限制屏幕方向和尺寸可调整性等范式过于严格。
忽略屏幕方向、尺寸可调整性和宽高比限制
对于以 Android 16(API 级别 36)为目标平台的应用,Android 16 包含对系统管理屏幕方向、尺寸调整能力和宽高比限制的方式的变更。在最小宽度大于或等于 600dp 的显示屏上,这些限制不再适用。应用还会填满整个显示窗口,无论宽高比或用户偏好的屏幕方向如何,都不会使用竖条模式。
此变更引入了新的标准平台行为。Android 正在向一种模型转变,在该模型中,应用需要适应各种屏幕方向、显示大小和宽高比。固定屏幕方向或有限的尺寸可调整性等限制会阻碍应用的适应性,因此我们建议让应用具备自适应能力,以提供尽可能出色的用户体验。
您还可以使用应用兼容性框架并启用 UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT 兼容性标志来测试此行为。
常见的重大更改
忽略屏幕方向、可调整大小性和宽高比限制可能会影响应用在某些设备上的界面,尤其是那些专为锁定为纵向的小布局设计的元素,例如布局拉伸、动画和组件超出屏幕等问题。任何关于宽高比或屏幕方向的假设都可能导致应用出现视觉问题。详细了解如何避免这些问题并改进应用的自适应行为。
允许设备旋转会导致更多 activity 重新创建,如果未正确保留,可能会导致用户状态丢失。如需了解如何正确保存界面状态,请参阅保存界面状态。
实现细节
在全屏模式和多窗口模式下,以下清单属性和运行时 API 会被大屏设备忽略:
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
系统会忽略 screenOrientation、setRequestedOrientation() 和 getRequestedOrientation() 的以下值:
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
对于显示屏可调整大小性,android:resizeableActivity="false"、android:minAspectRatio 和 android:maxAspectRatio 没有影响。
对于以 Android 16(API 级别 36)为目标平台的应用,默认情况下,大屏设备会忽略应用屏幕方向、可调整尺寸性和宽高比限制,但尚未完全准备就绪的每个应用都可以选择停用此行为,从而暂时替换此行为(这会导致应用采用之前的行为,即放置在兼容模式下)。
异常
在以下情况下,Android 16 的屏幕方向、尺寸调整能力和宽高比限制不适用:
- 游戏(基于
android:appCategory标志) - 用户在设备的宽高比设置中明确选择启用应用的默认行为
- 小于
sw600dp的屏幕
暂时停用
如需选择停用特定 activity,请声明 PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY 清单属性:
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
如果您的应用有太多部分尚未准备好支持 Android 16,您可以在应用级别应用相同的属性,从而完全选择不启用该功能:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
健康与健身
Android 16(API 级别 36)包含与健康和健身数据相关的以下变更。
健康与健身权限
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36) or higher,
BODY_SENSORS permissions use more granular permissions
under android.permissions.health, which Health Connect
also uses. As of Android 16, any API previously requiring BODY_SENSORS
or BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND requires the corresponding
android.permissions.health permission instead. This affects the following data
types, APIs, and foreground service types:
HEART_RATE_BPMfrom Health Services on Wear OSSensor.TYPE_HEART_RATEfrom Android Sensor ManagerheartRateAccuracyandheartRateBpmfromProtoLayouton Wear OSFOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTHwhere the respectiveandroid.permission.healthpermission is needed in place ofBODY_SENSORS
If your app uses these APIs, it should request the respective granular permissions:
- For while-in-use monitoring of Heart Rate, SpO2, or Skin Temperature:
request the granular permission under
android.permissions.health, such asREAD_HEART_RATEinstead ofBODY_SENSORS. - For background sensor access: request
READ_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUNDinstead ofBODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND.
These permissions are the same as those that guard access to reading data from Health Connect, the Android datastore for health, fitness, and wellness data.
Mobile apps
Mobile apps migrating to use the READ_HEART_RATE and other granular
permissions must also declare an activity to display
the app's privacy policy. This is the same requirement as Health Connect.
连接
Android 16(API 级别 36)在蓝牙堆栈中进行了以下更改,以改善与外围设备的连接。
用于处理绑定丢失和加密更改的新 intent
As part of the Improved bond loss handling, Android 16 also introduces 2 new intents to provide apps with greater awareness of bond loss and encryption changes.
Apps targeting Android 16 can now:
- Receive an
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent when remote bond loss is detected, allowing them to provide more informative user feedback and take appropriate actions. - Receive an
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEintent whenever encryption status of the link changes. This includes encryption status change, encryption algorithm change, and encryption key size change. Apps must consider the bond restored if the link is successfully encrypted upon receivingACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEintent later.
Adapting to varying OEM implementations
While Android 16 introduces these new intents, their implementation and broadcasting can vary across different device manufacturers (OEMs). To ensure your app provides a consistent and reliable experience across all devices, developers should design their bond loss handling to gracefully adapt to these potential variations.
We recommend the following app behaviors:
If the
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent is broadcast:The ACL (Asynchronous Connection-Less) link will be disconnected by the system, but the bond information for the device will be retained (as described here).
Your app should use this intent as the primary signal for bond loss detection and guiding the user to confirm the remote device is in range before initiating device forgetting or re-pairing.
If a device disconnects after
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGis received, your app should be cautious about reconnecting, as the device may no longer be bonded with the system.If the
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent is NOT broadcast:The ACL link will remain connected, and the bond information for the device will be removed by the system, same to behavior in Android 15.
In this scenario, your app should continue its existing bond loss handling mechanisms as in previous Android releases, to detect and manage bond loss events.
移除蓝牙绑定的新方式
现在,以 Android 16 为目标平台的所有应用都可以使用 CompanionDeviceManager 中的公共 API 解除蓝牙设备配对。如果配套设备作为 CDM 关联进行管理,则应用可以在关联的设备上使用新的 removeBond(int) API 触发蓝牙配对的移除。该应用可以通过监听蓝牙设备广播事件 ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED 来监控配对状态变化。
安全
Android 16(API 级别 36)包含以下安全方面的变更。
MediaStore 版本锁定
For apps targeting Android 16 or higher, MediaStore#getVersion() will now
be unique to each app. This eliminates identifying properties from the version
string to prevent abuse and usage for fingerprinting techniques. Apps shouldn't
make any assumptions around the format of this version. Apps should already
handle version changes when using this API and in most cases shouldn't need to
change their current behavior, unless the developer has attempted to infer
additional information that is beyond the intended scope of this API.
更安全的 intent
“更安全的 intent”功能是一项多阶段安全计划,旨在提升 Android 的 intent 解析机制的安全性。目标是在 intent 处理期间添加检查,并过滤不符合特定条件的 intent,从而保护应用免受恶意操作的侵害。
在 Android 15 中,该功能侧重于发送应用,现在在 Android 16 中,控制权转移到了接收应用,允许开发者使用其应用清单选择启用严格的 intent 解析。
我们正在实施两项关键变更:
显式 intent 必须与目标组件的 intent 过滤器相匹配:如果 intent 显式定位到某个组件,则应与该组件的 intent 过滤器相匹配。
没有操作的 intent 无法匹配任何 intent 过滤器:未指定操作的 intent 不应解析为任何 intent 过滤器。
这些变更仅在涉及多个应用时适用,不会影响单个应用内的 intent 处理。
影响
选择启用性质意味着,开发者必须在应用清单中明确启用它,才能使其生效。 因此,此功能的影响将仅限于以下应用(开发者):
- 了解“更安全的 intent”功能及其优势。
- 主动选择在应用中采用更严格的 intent 处理实践。
这种选择性采用的方法可最大限度地降低破坏可能依赖于当前不太安全的 intent 解析行为的现有应用的风险。
虽然在 Android 16 中,初始影响可能有限,但“更安全的 intent”计划的路线图显示,未来 Android 版本中会产生更广泛的影响。我们计划最终将严格的 intent 解析设为默认行为。
“更安全的 intent”功能可让恶意应用更难利用 intent 解析机制中的漏洞,从而显著提升 Android 生态系统的安全性。
不过,向选择退出和强制执行的过渡必须谨慎管理,以解决现有应用的潜在兼容性问题。
实现
开发者需要在应用清单中使用 intentMatchingFlags 属性明确启用更严格的 intent 匹配。
以下示例展示了如何为整个应用选择启用该功能,但在接收器上停用/选择停用该功能:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
有关支持的标志的更多信息:
| 标志名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | 对传入的 intent 强制执行更严格的匹配 |
| none | 停用针对传入 intent 的所有特殊匹配规则。指定多个标志时,系统会优先考虑“无”标志,以解决值冲突问题 |
| allowNullAction | 放宽了匹配规则,允许匹配没有操作的 intent。此标志与“enforceIntentFilter”结合使用可实现特定行为 |
测试和调试
在强制执行处于有效状态时,如果 intent 调用方已正确填充 intent,应用应能正常运行。
不过,被屏蔽的 intent 会触发警告日志消息(例如 "Intent does not match component's intent filter:" 和 "Access blocked:"),并带有标记 "PackageManager."。这表示存在可能会影响应用的潜在问题,需要引起注意。
Logcat 过滤条件:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
GPU 系统调用过滤
为了加固 Mali GPU 表面,在正式版 build 中,已弃用或仅用于 GPU 开发的 Mali GPU IOCTL 已被屏蔽。此外,用于 GPU 性能分析的 IOCTL 已限制为仅供 shell 进程或可调试的应用使用。如需详细了解平台级政策,请参阅 SAC 更新。
此变化发生在使用 Mali GPU 的 Pixel 设备(Pixel 6-9)上。Arm 已在其 r54p2 版本的 Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst 中提供了 IOCTL 的官方分类。此列表将在未来的驱动程序版本中继续维护。
此项变更不会影响受支持的图形 API(包括 Vulkan 和 OpenGL),预计也不会影响开发者或现有应用。 Streamline Performance Analyzer 和 Android GPU 检查器等 GPU 性能剖析工具不会受到影响。
测试
如果您看到类似如下所示的 SELinux 拒绝,则说明您的应用可能受到了此变更的影响:
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
如果您的应用需要使用被屏蔽的 IOCTL,请提交 bug 并将其分配给 android-partner-security@google.com。
常见问题解答
这项政策变更是否适用于所有原始设备制造商 (OEM)? 此变更将采用选择启用模式,但任何想要使用此强化方法的 OEM 都可以使用。如需了解如何实现此变更,请参阅实现文档。
是否必须在 OEM 代码库中进行更改才能实现此功能,还是默认随新的 AOSP 版本提供? 平台级变更将默认随新的 AOSP 版本一起发布。如果供应商想要应用此变更,可以在其代码库中选择启用此变更。
SoC 是否负责使 IOCTL 列表保持最新状态?例如,如果我的设备使用 ARM Mali GPU,我是否需要就任何更改与 ARM 联系? 各个 SoC 必须在驱动程序发布后根据设备更新其 IOCTL 列表。 例如,ARM 会在驱动程序更新时更新其已发布的 IOCTL 列表。 不过,OEM 应确保在 SEPolicy 中纳入这些更新,并根据需要将任何选定的自定义 IOCTL 添加到列表中。
此变更是否会自动应用于所有在售 Pixel 设备,还是需要用户执行操作来切换某些设置才能应用此变更? 此变更适用于所有使用 Mali GPU 的 Pixel 在售设备(Pixel 6-9)。无需用户采取任何行动即可应用此变更。
使用此政策会影响内核驱动程序的性能吗? 我们使用 GFXBench 在 Mali GPU 上测试了此政策,未发现 GPU 性能有任何可衡量的变化。
IOCTL 列表是否需要与当前的用户空间和内核驱动程序版本保持一致? 可以,允许的 IOCTL 列表必须与用户空间和内核驱动程序支持的 IOCTL 同步。如果用户空间或内核驱动程序中的 IOCTL 发生更新,则必须更新 SEPolicy IOCTL 列表以保持一致。
ARM 已将 IOCTL 分类为“受限”/“检测”,但我们希望在生产用例中使用其中一些,并拒绝其他 IOCTL。 各个 OEM/SoC 负责根据其用户空间 Mali 库的配置来决定如何对其使用的 IOCTL 进行分类。ARM 的列表可用于帮助确定这些值,但每个 OEM/SoC 的使用情形可能有所不同。
隐私权
Android 16(API 级别 36)包含以下隐私权方面的变更。
本地网络权限
Devices on the LAN can be accessed by any app that has the INTERNET permission.
This makes it easy for apps to connect to local devices but it also has privacy
implications such as forming a fingerprint of the user, and being a proxy for
location.
The Local Network Protections project aims to protect the user's privacy by gating access to the local network behind a new runtime permission.
Release plan
This change will be deployed between two releases, 25Q2 and TBD respectively. It is imperative that developers follow this guidance for 25Q2 and share feedback because these protections will be enforced at a later Android release. Moreover, they will need to update scenarios which depend on implicit local network access by using the following guidance and prepare for user rejection and revocation of the new permission.
Impact
At the current stage, LNP is an opt-in feature which means only the apps that opt in will be affected. The goal of the opt-in phase is for app developers to understand which parts of their app depend on implicit local network access such that they can prepare to permission guard them for the next release.
Apps will be affected if they access the user's local network using:
- Direct or library use of raw sockets on local network addresses (e.g. mDNS or SSDP service discovery protocol)
- Use of framework level classes that access the local network (e.g. NsdManager)
Traffic to and from a local network address requires local network access permission. The following table lists some common cases:
| App Low Level Network Operation | Local Network Permission Required |
|---|---|
| Making an outgoing TCP connection | yes |
| Accepting incoming TCP connections | yes |
| Sending a UDP unicast, multicast, broadcast | yes |
| Receiving an incoming UDP unicast, multicast, broadcast | yes |
These restrictions are implemented deep in the networking stack, and thus they apply to all networking APIs. This includes sockets created in native or managed code, networking libraries like Cronet and OkHttp, and any APIs implemented on top of those. Trying to resolve services on the local network (i.e. those with a .local suffix) will require local network permission.
Exceptions to the rules above:
- If a device's DNS server is on a local network, traffic to or from it (at port 53) doesn't require local network access permission.
- Applications using Output Switcher as their in-app picker won't need local network permissions (more guidance to come in 2025Q4).
Developer Guidance (Opt-in)
To opt into local network restrictions, do the following:
- Flash the device to a build with 25Q2 Beta 3 or later.
- Install the app to be tested.
Toggle the Appcompat flag in adb:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>Reboot The device
Now your app's access to the local network is restricted and any attempt to access the local network will lead to socket errors. If you are using APIs that perform local network operations outside of your app process (ex: NsdManager), they won't be impacted during the opt-in phase.
To restore access, you must grant your app permission to NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES.
- Ensure the app declares the
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESpermission in its manifest. - Go to Settings > Apps > [Application Name] > Permissions > Nearby devices > Allow.
Now your app's access to the local network should be restored and all your scenarios should work as they did prior to opting the app in.
Once enforcement for local network protection begins, here is how the app network traffic will be impacted.
| Permission | Outbound LAN Request | Outbound/Inbound Internet Request | Inbound LAN Request |
|---|---|---|---|
| Granted | Works | Works | Works |
| Not Granted | Fails | Works | Fails |
Use the following command to toggle-off the App-Compat flag
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
Errors
Errors arising from these restrictions will be returned to the calling socket whenever it invokes send or a send variant to a local network address.
Example errors:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
Local Network Definition
A local network in this project refers to an IP network that utilizes a broadcast-capable network interface, such as Wi-Fi or Ethernet, but excludes cellular (WWAN) or VPN connections.
The following are considered local networks:
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // Link Local
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- Link-local
- Directly-connected routes
- Stub networks like Thread
- Multiple-subnets (TBD)
Additionally, both multicast addresses (224.0.0.0/4, ff00::/8) and the IPv4 broadcast address (255.255.255.255) are classified as local network addresses.
应用拥有的照片
当面向 SDK 36 或更高版本的应用在搭载 Android 16 或更高版本的设备上提示用户授予照片和视频权限时,如果用户选择限制对所选媒体的访问权限,则会在照片选择器中看到该应用拥有的所有照片。用户可以取消选择任何这些预选项,这会撤消该应用对这些照片和视频的访问权限。

