Assim como nas versões anteriores, o Android 16 inclui mudanças de comportamento que podem afetar seu app. As mudanças de comportamento a seguir se aplicam exclusivamente a apps destinados ao Android 16 ou versões mais recentes. Se o app for direcionado ao Android 16 ou a versões mais recentes, faça modificações para oferecer suporte a esses comportamentos, quando aplicável.
Consulte também a lista de mudanças de comportamento que afetam todos os apps
executados no Android 16, independente da targetSdkVersion do seu app.
Experiência do usuário e interface do sistema
O Android 16 (nível 36 da API) inclui as seguintes mudanças que visam criar uma experiência do usuário mais consistente e intuitiva.
A opção de recusa de ponta a ponta vai ser desativada
Android 15 强制执行全屏显示,但您的应用可以通过将 R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement 设置为 true 来选择停用此功能。对于以 Android 16(API 级别 36)为目标平台的应用,R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement 已被废弃并停用,并且您的应用无法选择不采用从边缘到边缘的布局。
- 如果您的应用以 Android 16(API 级别 36)为目标平台,并且在 Android 15 设备上运行,则
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement会继续正常运行。 - 如果您的应用以 Android 16(API 级别 36)为目标平台,并且在 Android 16 设备上运行,则
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement会被停用。
如需在 Android 16 中进行测试,请确保您的应用支持无边框设计,并移除所有 R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement 用法,以便您的应用在 Android 15 设备上也能支持无边框设计。如需支持从边缘到边缘的显示,请参阅 Compose 和 Views 指南。
Migração ou desativação necessárias para a volta preditiva
对于以 Android 16(API 级别 36)或更高版本为目标平台且在搭载 Android 16 或更高版本的设备上运行的应用,预测性返回系统动画(返回主屏幕、跨任务和跨 activity)默认处于启用状态。此外,系统不再调用 onBackPressed,也不再调度 KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK。
如果您的应用会拦截返回事件,但您尚未迁移到预测性返回,请更新应用以使用受支持的返回导航 API,或者通过在应用的 AndroidManifest.xml 文件的 <application> 或 <activity> 标记中将 android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback 属性设置为 false 来暂时选择停用。
APIs de fontes elegantes descontinuadas e desativadas
Os apps destinados ao Android 15 (nível 35 da API) têm o atributo
elegantTextHeight
TextView definido como true por
padrão, substituindo a fonte compacta por uma muito mais legível. É possível substituir isso definindo o atributo elegantTextHeight como false.
O Android 16 descontinua o
atributo elegantTextHeight,
que será ignorado quando o app for destinado ao Android 16. As "fontes da interface" controladas por essas APIs serão descontinuadas. Por isso, adapte todos os layouts para garantir a renderização de texto consistente e à prova de futuro em árabe, laosiano, birmanês, tâmil, gujarati, canarês, malaiala, odia, télugo ou tailandês.
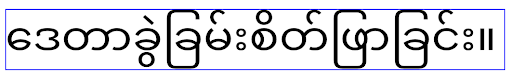
elegantTextHeight para apps destinados ao Android
14 (nível 34 da API) e versões anteriores ou para apps destinados ao Android 15 (nível 35 da API)
que substituíram o padrão definindo o atributo elegantTextHeight
como false.elegantTextHeight para apps direcionados ao Android
16 (nível 36 da API) ou ao Android 15 (nível 35 da API) que não
substituíram o padrão definindo o atributo elegantTextHeight
como false.
Principal recurso
O Android 16 (API de nível 36) inclui as seguintes mudanças que modificam ou expandem vários recursos principais do sistema Android.
Otimização da programação de trabalho com taxa fixa
Antes de segmentar o Android 16, quando o scheduleAtFixedRate
perdia uma execução de tarefa por estar fora de um
ciclo de vida do processo válido, todas as execuções perdidas eram executadas imediatamente
quando o app retornava a um ciclo de vida válido.
Ao segmentar o Android 16, no máximo uma execução perdida de
scheduleAtFixedRate é executada imediatamente quando o app
retorna a um ciclo de vida válido. Essa mudança de comportamento deve melhorar o desempenho
do app. Teste esse comportamento no seu app para verificar se ele é afetado.
Também é possível testar usando o framework de compatibilidade de apps
e ativando a flag de compatibilidade STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS.
Formatos de dispositivos
O Android 16 (nível 36 da API) inclui as seguintes mudanças para apps quando mostrados em dispositivos de tela grande.
Layouts adaptáveis
现在,Android 应用可在各种设备(例如手机、平板电脑、可折叠设备、桌面设备、汽车和电视)上运行,并且在大屏设备上支持多种窗口模式(例如分屏和桌面窗口),因此开发者应构建能够适应任何屏幕和窗口尺寸的 Android 应用,无论设备方向如何。在当今多设备的世界中,限制屏幕方向和尺寸可调整性等范式过于严格。
忽略屏幕方向、尺寸可调整性和宽高比限制
对于以 Android 16(API 级别 36)为目标平台的应用,屏幕方向、尺寸可调整性和宽高比限制不再适用于最小宽度 >= 600dp 的显示屏。无论宽高比或用户偏好的屏幕方向如何,应用都会填满整个显示窗口,且不会采用竖条模式。
此变更引入了新的标准平台行为。Android 正在向一种模型转变,在该模型中,应用需要适应各种屏幕方向、显示大小和宽高比。固定屏幕方向或有限的尺寸调整等限制会阻碍应用的适应性。使应用具有自适应性,以提供尽可能最佳的用户体验。
您还可以使用应用兼容性框架并启用 UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT 兼容性标志来测试此行为。
常见的重大更改
忽略屏幕方向、可调整大小性和宽高比限制可能会影响应用在某些设备上的界面,尤其是那些专为锁定为纵向的小布局设计的元素,例如布局拉伸、动画和组件超出屏幕等问题。任何关于宽高比或屏幕方向的假设都可能导致应用出现视觉问题。详细了解如何避免这些问题并改进应用的自适应行为。
允许设备旋转会导致更多 activity 重新创建,如果未正确保留,可能会导致用户状态丢失。如需了解如何正确保存界面状态,请参阅保存界面状态。
实现细节
在全屏模式和多窗口模式下,以下清单属性和运行时 API 会被大屏设备忽略:
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
系统会忽略 screenOrientation、setRequestedOrientation() 和 getRequestedOrientation() 的以下值:
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
对于显示屏可调整大小性,android:resizeableActivity="false"、android:minAspectRatio 和 android:maxAspectRatio 没有影响。
对于以 Android 16(API 级别 36)为目标平台的应用,默认情况下,大屏设备会忽略应用的屏幕方向、可调整尺寸性和宽高比限制,但尚未完全准备就绪的每个应用都可以选择停用此行为,从而暂时替换此行为(这会导致应用恢复到之前放置在兼容模式下的行为)。
异常
在以下情况下,Android 16 的屏幕方向、尺寸调整能力和宽高比限制不适用:
- 游戏(基于
android:appCategory标志) - 用户在设备的宽高比设置中明确选择启用应用的默认行为
- 小于
sw600dp的屏幕
暂时停用
如需选择停用特定 activity,请声明 PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY 清单属性:
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
如果您的应用有太多部分尚未准备好支持 Android 16,您可以在应用级别应用相同的属性,从而完全选择不启用该功能:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
Saúde e fitness
O Android 16 (nível da API 36) inclui as seguintes mudanças relacionadas a dados de saúde e condicionamento físico.
Permissões de saúde e fitness
对于以 Android 16(API 级别 36)或更高版本为目标平台的应用,BODY_SENSORS 权限使用 android.permissions.health 下更精细的权限,健康数据共享也使用这些权限。自 Android 16 起,凡是以前需要具有 BODY_SENSORS 或 BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND 权限的 API,现在都需要获取相应的 android.permissions.health 权限。这会影响以下数据类型、API 和前台服务类型:
- 从 Wear OS 上的健康服务中获取
HEART_RATE_BPM - 来自 Android Sensor Manager 的
Sensor.TYPE_HEART_RATE - 在 Wear OS 上,
ProtoLayout中的heartRateAccuracy和heartRateBpm FOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTH,其中需要使用相应的android.permission.health权限来代替BODY_SENSORS
如果您的应用使用这些 API,则应请求相应的精细权限:
- 对于使用期间的心率、血氧饱和度或体表温度监测:请求
android.permissions.health下的精细权限,例如READ_HEART_RATE,而不是BODY_SENSORS。 - 对于后台传感器访问权限:请求
READ_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUND而不是BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND。
这些权限与用于保护对 Health Connect(Android 健康、健身和身心状态数据存储区)中读取数据的访问权限相同。
移动应用
迁移到使用 READ_HEART_RATE 和其他精细权限的移动应用还必须声明 activity 以显示应用的隐私权政策。此要求与健康数据共享的要求相同。
Conectividade
O Android 16 (nível 36 da API) inclui as seguintes mudanças na pilha Bluetooth para melhorar a conectividade com dispositivos periféricos.
Novas intents para lidar com perda de vinculação e mudanças na criptografia
Como parte do Processamento de perda de vínculo aprimorado, o Android 16 também apresenta duas novas intents para dar aos apps mais consciência da perda de vínculo e mudanças de criptografia.
Os apps destinados ao Android 16 agora podem:
- Receber uma intent
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGquando a perda de vínculo remoto é detectada, permitindo que eles forneçam feedback mais informativo ao usuário e realizem ações adequadas. - Receba uma intent
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEsempre que o status de criptografia do link mudar. Isso inclui a mudança de status de criptografia, de algoritmo de criptografia e de tamanho da chave de criptografia. Os apps precisam considerar a vinculação restaurada se o link for criptografado ao receber a intentACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEmais tarde.
Como se adaptar a diferentes implementações de OEM
Embora o Android 16 apresente essas novas intents, a implementação e a transmissão delas podem variar de acordo com os diferentes fabricantes de dispositivos (OEMs). Para garantir que o app ofereça uma experiência consistente e confiável em todos os dispositivos, os desenvolvedores precisam projetar o processamento de perda de vínculo para se adaptar a essas variações.
Recomendamos os seguintes comportamentos do app:
Se a intent
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGfor transmitida:O link ACL (Asynchronous Connection-Less) será desconectado pelo sistema, mas as informações de vinculação do dispositivo serão mantidas, conforme descrito aqui.
Seu app precisa usar essa intent como o indicador principal para a detecção de perda de conexão e orientar o usuário a confirmar se o dispositivo remoto está no alcance antes de iniciar o esquecimento ou o novo pareamento do dispositivo.
Se um dispositivo se desconectar depois que o
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGfor recebido, o app precisará ter cuidado ao se reconectar, porque o dispositivo pode não estar mais vinculado ao sistema.Se a intent
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGNÃO for transmitida:O link ACL vai permanecer conectado, e as informações de vinculação do dispositivo serão removidas pelo sistema, assim como no comportamento do Android 15.
Nesse cenário, o app precisa continuar com os mecanismos de processamento de perda de vínculo existentes, como nas versões anteriores do Android, para detectar e gerenciar eventos de perda de vínculo.
Nova maneira de remover a vinculação Bluetooth
现在,以 Android 16 为目标平台的所有应用都可以使用 CompanionDeviceManager 中的公共 API 解除蓝牙设备配对。如果配套设备作为 CDM 关联进行管理,则应用可以在关联的设备上使用新的 removeBond(int) API 触发蓝牙配对的移除。该应用可以通过监听蓝牙设备广播事件 ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED 来监控配对状态变化。
Segurança
O Android 16 (nível da API 36) inclui as seguintes mudanças de segurança.
Bloqueio da versão do MediaStore
对于以 Android 16 或更高版本为目标平台的应用,MediaStore#getVersion() 现在将是每个应用的唯一标识。这会从版本字符串中移除标识属性,以防止滥用和用于指纹识别技术。应用不应对此版本的格式做出任何假设。在使用此 API 时,应用应已处理版本变更,并且在大多数情况下无需更改其当前行为,除非开发者尝试推断超出此 API 预期范围的其他信息。
Intents mais seguras
“更安全的 intent”功能是一项多阶段安全计划,旨在提高 Android 的 intent 解析机制的安全性。目标是在 intent 处理期间添加检查,并过滤不符合特定条件的 intent,从而保护应用免受恶意操作的侵害。
在 Android 15 中,该功能侧重于发送应用,现在在 Android 16 中,控制权转移到了接收应用,允许开发者使用其应用清单选择加入严格的 intent 解析。
我们正在实施两项关键变更:
显式 intent 必须与目标组件的 intent 过滤器相匹配:如果 intent 显式定位到某个组件,则应与该组件的 intent 过滤器相匹配。
没有操作的 intent 无法匹配任何 intent 过滤器:未指定操作的 intent 不应解析为任何 intent 过滤器。
这些变更仅在涉及多个应用时适用,不会影响单个应用内的 intent 处理。
影响
选择启用性质意味着,开发者必须在应用清单中明确启用它,才能使其生效。 因此,此功能的影响将仅限于以下应用:
- 了解“更安全的 intent”功能及其优势。
- 主动选择在应用中采用更严格的 intent 处理实践。
这种选择性采用的方法可最大限度地降低破坏可能依赖于当前不太安全的 intent 解析行为的现有应用的风险。
虽然在 Android 16 中,初始影响可能有限,但“更安全的 intent”计划的路线图显示,未来 Android 版本的影响范围会更广。我们计划最终将严格的意图解析设为默认行为。
“更安全的 intent”功能可让恶意应用更难利用 intent 解析机制中的漏洞,从而有望显著提升 Android 生态系统的安全性。
不过,向选择退出和强制执行的过渡必须谨慎管理,以解决现有应用的潜在兼容性问题。
实现
开发者需要在应用清单中使用 intentMatchingFlags 属性明确启用更严格的 intent 匹配。
以下示例展示了如何为整个应用选择启用该功能,但在接收器上停用/选择停用该功能:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
有关支持的标志的更多信息:
| 标志名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | 对传入的 intent 强制执行更严格的匹配 |
| none | 停用针对传入 intent 的所有特殊匹配规则。指定多个标志时,系统会优先考虑“无”标志,以解决值冲突问题 |
| allowNullAction | 放宽了匹配规则,允许匹配没有操作的 intent。此标志与“enforceIntentFilter”结合使用可实现特定行为 |
测试和调试
在强制执行处于有效状态时,如果 intent 调用方已正确填充 intent,应用应能正常运行。
不过,被屏蔽的 intent 会触发警告日志消息(例如 "Intent does not match component's intent filter:" 和 "Access blocked:"),并带有标记 "PackageManager."。这表示存在可能会影响应用的潜在问题,需要引起注意。
Logcat 过滤条件:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
Filtragem de syscalls da GPU
为了加固 Mali GPU 表面,在生产 build 中,已废弃或仅用于 GPU 开发的 Mali GPU IOCTL 已被屏蔽。此外,用于 GPU 性能分析的 IOCTL 已限制为 shell 进程或可调试的应用。如需详细了解平台级政策,请参阅 SAC 更新。
此更改适用于使用 Mali GPU 的 Pixel 设备(Pixel 6-9)。Arm 已在其 r54p2 版本的 Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst 中提供了 IOCTL 的官方分类。此列表将在未来的驱动程序版本中继续维护。
此项变更不会影响受支持的图形 API(包括 Vulkan 和 OpenGL),预计也不会影响开发者或现有应用。 Streamline Performance Analyzer 和 Android GPU 检查器等 GPU 性能剖析工具不会受到影响。
测试
如果您看到类似如下所示的 SELinux 拒绝,则说明您的应用可能受到了此变更的影响:
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
如果您的应用需要使用被屏蔽的 IOCTL,请提交 bug 并将其分配给 android-partner-security@google.com。
常见问题解答
此政策变更是否适用于所有原始设备制造商 (OEM)? 此变更将采用选择启用模式,但任何想要使用此强化方法的 OEM 都可以使用。如需了解如何实现此变更,请参阅实现文档。
是否必须在 OEM 代码库中进行更改才能实现此功能,还是默认随新的 AOSP 版本提供? 平台级变更将默认随新的 AOSP 版本一起发布。如果供应商想要应用此变更,可以在其代码库中选择启用此变更。
SoC 是否负责使 IOCTL 列表保持最新状态?例如,如果我的设备使用 ARM Mali GPU,我是否需要就任何更改与 ARM 联系? 各个 SoC 必须在驱动程序发布后根据设备更新其 IOCTL 列表。 例如,ARM 会在驱动程序更新时更新其已发布的 IOCTL 列表。 不过,OEM 应确保在 SEPolicy 中纳入这些更新,并根据需要将任何选定的自定义 IOCTL 添加到列表中。
此变更是否会自动应用于所有在售 Pixel 设备,还是需要用户执行操作来切换某些设置才能应用此变更? 此变更适用于所有使用 Mali GPU 的 Pixel 在售设备(Pixel 6-9)。用户无需采取任何行动即可应用此变更。
使用此政策会影响内核驱动程序的性能吗? 我们使用 GFXBench 在 Mali GPU 上测试了此政策,未发现 GPU 性能有任何可衡量的变化。
IOCTL 列表是否需要与当前的用户空间和内核驱动程序版本保持一致? 是的,允许的 IOCTL 列表必须与用户空间和内核驱动程序支持的 IOCTL 同步。如果用户空间或内核驱动程序中的 IOCTL 发生更新,则必须更新 SEPolicy IOCTL 列表以保持一致。
ARM 已将 IOCTL 分类为“受限”/“检测”,但我们希望在生产用例中使用其中一些 IOCTL,并拒绝其他 IOCTL。 各个 OEM/SoC 负责根据其用户空间 Mali 库的配置来决定如何对其使用的 IOCTL 进行分类。ARM 的列表可用于帮助确定这些值,但每个 OEM/SoC 的使用情形可能有所不同。
Privacidade
O Android 16 (nível da API 36) inclui as seguintes mudanças de privacidade.
Permissão de rede local
具有 INTERNET 权限的任何应用都可以访问局域网上的设备。
这使得应用可以轻松连接到本地设备,但也存在隐私影响,例如形成用户指纹,以及成为位置信息的代理。
本地网络保护项目旨在通过在新的运行时权限后限制对本地网络的访问,来保护用户的隐私。
发布计划
此变更将分别在 25Q2 和 26Q2 这两个版本之间部署。 开发者必须遵循 25Q2 的相关指南并分享反馈,因为这些保护措施将在后续 Android 版本中强制执行。此外,他们还需要按照以下指南更新依赖于隐式本地网络访问权限的场景,并为用户拒绝和撤消新权限做好准备。
影响
在当前阶段,LNP 是一项选择启用功能,这意味着只有选择启用的应用会受到影响。选择启用阶段的目标是让应用开发者了解应用的哪些部分依赖于隐式本地网络访问权限,以便他们可以为下一个版本做好权限保护准备。
如果应用使用以下方式访问用户的本地网络,则会受到影响:
- 在本地网络地址(例如 mDNS 或 SSDP 服务发现协议)上直接或通过库使用原始套接字
- 使用可访问本地网络的框架级类(例如 NsdManager)
向本地网络地址发送流量和从本地网络地址接收流量需要本地网络访问权限。下表列出了一些常见情况:
| 应用低级层网络操作 | 需要本地网络权限 |
|---|---|
| 建立出站 TCP 连接 | 是 |
| 接受传入的 TCP 连接 | 是 |
| 发送 UDP 单播、多播、广播 | 是 |
| 接收传入的 UDP 单播、多播、广播 | 是 |
这些限制是在网络堆栈深处实现的,因此适用于所有网络 API。这包括在原生代码或受管理代码中创建的套接字、Cronet 和 OkHttp 等网络库,以及基于这些库实现的任何 API。尝试解析本地网络上的服务(即带有 .local 后缀的服务)将需要本地网络权限。
上述规则的例外情况:
- 如果设备的 DNS 服务器位于本地网络上,则进出该服务器(位于端口 53)的流量不需要本地网络访问权限。
- 如果应用使用输出切换器作为其应用内选择器,则无需本地网络权限(更多指南将在 2025 年第 4 季度发布)。
开发者指南(选择启用)
如需选择启用本地网络限制,请执行以下操作:
- 将设备刷写到 25Q2 Beta 3 或更高版本的 build。
- 安装要测试的应用。
在 adb 中切换 Appcompat 标志:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>重启设备
现在,您的应用对本地网络的访问受到限制,任何访问本地网络的尝试都会导致套接字错误。如果您使用的 API 在应用进程之外执行本地网络操作(例如:NsdManager),在选择启用阶段,这些 API 不会受到影响。
如需恢复访问权限,您必须向应用授予 NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES 权限。
- 确保应用在其清单中声明了
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES权限。 - 依次前往设置 > 应用 > [应用名称] > 权限 > 附近的设备 > 允许。
现在,应用对本地网络的访问权限应该已恢复,并且所有场景都应像选择启用应用之前一样正常运行。
本地网络保护功能开始强制执行后,应用的网络流量将受到以下影响。
| 权限 | 出站 LAN 请求 | 出站/入站互联网请求 | 入站 LAN 请求 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 已授予 | Works | Works | Works |
| 未授予 | 最差排行榜 | Works | 最差排行榜 |
使用以下命令切换关闭应用兼容性标志
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
错误
每当调用套接字调用 send 或 send 变体向本地网络地址发送数据时,系统都会向该套接字返回因这些限制而产生的错误。
错误示例:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
本地网络定义
此项目中的本地网络是指使用支持广播的网络接口(例如 Wi-Fi 或以太网)的 IP 网络,但不包括移动网络 (WWAN) 或 VPN 连接。
以下网络被视为本地网络:
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // 链路本地
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- 链路本地
- 直接连接的路线
- Thread 等桩网络
- 多个子网(待定)
此外,多播地址 (224.0.0.0/4、ff00::/8) 和 IPv4 广播地址 (255.255.255.255) 都归类为本地网络地址。
Fotos do app
当面向 SDK 36 或更高版本的应用在搭载 Android 16 或更高版本的设备上提示用户授予照片和视频权限时,如果用户选择限制对所选媒体的访问权限,则会在照片选择器中看到该应用拥有的所有照片。用户可以取消选择任何这些预选项,这会撤消该应用对这些照片和视频的访问权限。
