これまでのリリースと同様、Android 16 には、アプリに影響する可能性がある動作変更が含まれています。下記の動作変更は、Android 16 以上をターゲットとするアプリにのみ適用されます。アプリが Android 16 以上をターゲットとする場合は、必要に応じてアプリを変更し、下記の動作に対応できるようにしてください。
アプリの targetSdkVersion に関係なく、Android 16 で実行されるすべてのアプリに影響する動作変更のリストも必ずご確認ください。
ユーザー エクスペリエンスとシステム UI
Android 16(API レベル 36)には、より一貫性のある直感的なユーザー エクスペリエンスを実現するための以下の変更が含まれています。
エッジ ツー エッジのオプトアウトの廃止
Android 15 では、Android 15(API レベル 35)をターゲットとするアプリに対してエッジ ツー エッジが強制適用されましたが、R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement を true に設定することで、アプリはエッジ ツー エッジを無効にできます。Android 16(API レベル 36)をターゲットとするアプリの場合、R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement は非推奨となり無効化されます。アプリでエッジ ツー エッジを無効にすることはできません。
- アプリが Android 16(API レベル 36)をターゲットとしており、Android 15 デバイスで実行されている場合、
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementは引き続き動作します。 - アプリが Android 16(API レベル 36)をターゲットとしており、Android 16 デバイスで実行されている場合、
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementは無効になります。
Android 16 でテストする場合は、アプリがエッジ ツー エッジに対応していることを確認し、R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement の使用をすべて削除して、Android 15 デバイスでもエッジ ツー エッジに対応するようにします。エッジ ツー エッジをサポートするには、Compose と Views のガイダンスをご覧ください。
予測型「戻る」には移行またはオプトアウトが必要
对于以 Android 16(API 级别 36)或更高版本为目标平台且在搭载 Android 16 或更高版本的设备上运行的应用,预测性返回系统动画(返回主屏幕、跨任务和跨 activity)默认处于启用状态。此外,系统不再调用 onBackPressed,也不再调度 KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK。
如果您的应用会拦截返回事件,但您尚未迁移到预测性返回,请更新应用以使用受支持的返回导航 API,或者通过在应用的 AndroidManifest.xml 文件的 <application> 或 <activity> 标记中将 android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback 属性设置为 false 来暂时选择停用。
Elegant font API のサポート終了と無効化
Android 15(API レベル 35)をターゲットとするアプリでは、elegantTextHeight
TextView 属性がデフォルトで true に設定され、コンパクトなフォントが可読性の高いフォントに置き換えられます。elegantTextHeight 属性を false に設定することで、この動作をオーバーライドできます。
Android 16 では elegantTextHeight 属性が非推奨となり、アプリのターゲットが Android 16 になると、この属性は無視されます。これらの API で制御される「UI フォント」は廃止されるため、アラビア語、ラオス語、ミャンマー語、タミル語、グジャラート語、カンナダ語、マラヤーラム語、オディア語、テルグ語、タイ語でテキストが常に正しくレンダリングされるように、レイアウトを調整する必要があります。
elegantTextHeight 属性を false に設定してデフォルトをオーバーライドした Android 15(API レベル 35)をターゲットとするアプリの elegantTextHeight の動作。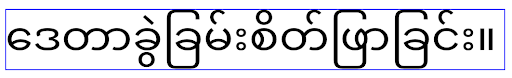
elegantTextHeight 属性を false に設定してデフォルトをオーバーライドしていない Android 15(API レベル 35)をターゲットとするアプリの elegantTextHeight の動作。
コア機能
Android 16(API レベル 36)には、Android システムのさまざまなコア機能を変更または拡張する以下の変更が含まれています。
固定レートの作業スケジュールの最適化
Android 16 をターゲットとする前は、scheduleAtFixedRate が有効なプロセス ライフサイクルの外部にあるためにタスクの実行を逃した場合、アプリが有効なライフサイクルに戻ると、逃した実行がすべて直ちに実行されました。
Android 16 をターゲットとしている場合、アプリが有効なライフサイクルに戻ると、scheduleAtFixedRate の実行が最大 1 回スキップされた場合、その実行が直ちに実行されます。この動作変更により、アプリのパフォーマンスが向上することが期待されます。アプリでこの動作をテストして、アプリが影響を受けているかどうかを確認します。アプリ互換性フレームワークを使用して STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS 互換性フラグを有効にしてテストすることもできます。
デバイスのフォーム ファクタ
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、大画面デバイスに表示されるアプリに対して次の変更が加えられています。
アダプティブ レイアウト
现在,Android 应用可在各种设备(例如手机、平板电脑、可折叠设备、桌面设备、汽车和电视)上运行,并且在大屏设备上支持多种窗口模式(例如分屏和桌面窗口),因此开发者应构建能够适应任何屏幕和窗口尺寸的 Android 应用,无论设备方向如何。在当今多设备的世界中,限制屏幕方向和尺寸可调整性等范式过于严格。
忽略屏幕方向、尺寸可调整性和宽高比限制
对于以 Android 16(API 级别 36)为目标平台的应用,屏幕方向、尺寸可调整性和宽高比限制不再适用于最小宽度 >= 600dp 的显示屏。无论宽高比或用户偏好的屏幕方向如何,应用都会填满整个显示窗口,且不会采用竖条模式。
此变更引入了新的标准平台行为。Android 正在向一种模型转变,在该模型中,应用需要适应各种屏幕方向、显示大小和宽高比。固定屏幕方向或有限的尺寸调整等限制会阻碍应用的适应性。使应用具有自适应性,以提供尽可能最佳的用户体验。
您还可以使用应用兼容性框架并启用 UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT 兼容性标志来测试此行为。
常见的重大更改
忽略屏幕方向、可调整大小性和宽高比限制可能会影响应用在某些设备上的界面,尤其是那些专为锁定为纵向的小布局设计的元素,例如布局拉伸、动画和组件超出屏幕等问题。任何关于宽高比或屏幕方向的假设都可能导致应用出现视觉问题。详细了解如何避免这些问题并改进应用的自适应行为。
允许设备旋转会导致更多 activity 重新创建,如果未正确保留,可能会导致用户状态丢失。如需了解如何正确保存界面状态,请参阅保存界面状态。
实现细节
在全屏模式和多窗口模式下,以下清单属性和运行时 API 会被大屏设备忽略:
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
系统会忽略 screenOrientation、setRequestedOrientation() 和 getRequestedOrientation() 的以下值:
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
对于显示屏可调整大小性,android:resizeableActivity="false"、android:minAspectRatio 和 android:maxAspectRatio 没有影响。
对于以 Android 16(API 级别 36)为目标平台的应用,默认情况下,大屏设备会忽略应用的屏幕方向、可调整尺寸性和宽高比限制,但尚未完全准备就绪的每个应用都可以选择停用此行为,从而暂时替换此行为(这会导致应用恢复到之前放置在兼容模式下的行为)。
异常
在以下情况下,Android 16 的屏幕方向、尺寸调整能力和宽高比限制不适用:
- 游戏(基于
android:appCategory标志) - 用户在设备的宽高比设置中明确选择启用应用的默认行为
- 小于
sw600dp的屏幕
暂时停用
如需选择停用特定 activity,请声明 PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY 清单属性:
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
如果您的应用有太多部分尚未准备好支持 Android 16,您可以在应用级别应用相同的属性,从而完全选择不启用该功能:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
健康&フィットネス
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、健康とフィットネスに関するデータに関連して、以下の変更が加えられています。
健康とフィットネスの権限
Android 16(API レベル 36)以上をターゲットとするアプリの場合、BODY_SENSORS 権限は android.permissions.health の下にあるより細かい権限を使用します。これは ヘルスコネクトでも使用されます。Android 16 以降、これまで BODY_SENSORS または BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND を必要としていた API はすべて、対応する android.permissions.health 権限が必要となります。この変更は、次のデータ型、API、フォアグラウンド サービス タイプに影響します。
- Wear OS のヘルスサービスからの
HEART_RATE_BPM - Android Sensor Manager からの
Sensor.TYPE_HEART_RATE - Wear OS の
ProtoLayoutからheartRateAccuracyとheartRateBpm FOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTH:BODY_SENSORSの代わりにそれぞれのandroid.permission.health権限が必要な場合
アプリでこれらの API を使用する場合は、次の粒度の細かい権限をリクエストする必要があります。
- 心拍数、血中酸素ウェルネス、皮膚温の使用中のモニタリングの場合:
BODY_SENSORSではなく、android.permissions.healthの下でREAD_HEART_RATEなどの詳細な権限をリクエストします。 - バックグラウンド センサー アクセスの場合:
BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUNDではなくREAD_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUNDをリクエストします。
これらの権限は、健康、フィットネス、ウェルネスのデータ用の Android データストアである ヘルスコネクト からのデータ読み取りへのアクセスを保護する権限と同じです。
モバイルアプリ
READ_HEART_RATE やその他の詳細な権限を使用するように移行するモバイルアプリは、アプリのプライバシー ポリシーを表示するためのアクティビティも宣言する必要があります。これはヘルスコネクトと同じ要件です。
接続
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、周辺機器との接続性を改善するために、Bluetooth スタックに次の変更が加えられています。
ボンドの損失と暗号化の変更を処理する新しいインテント
ボンドの損失処理の改善の一環として、Android 16 では、ボンドの損失と暗号化の変更をアプリがより認識できるように、2 つの新しいインテントを導入しています。
Android 16 をターゲットとするアプリは、次のことができます。
- リモート ボンドの損失が検出されたときに
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGインテントを受け取り、より有益なユーザー フィードバックを提供するとともに、適切なアクションを実行できます。 - リンクの暗号化ステータスが変更されるたびに
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEインテントを受け取ります。これには、暗号化ステータスの変更、暗号化アルゴリズムの変更、暗号鍵サイズの変更が含まれます。後でACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEインテントを受け取った際にリンクが正常に暗号化された場合、アプリはボンディングが復元されたと見なす必要があります。
さまざまな OEM 実装への適応
Android 16 ではこれらの新しいインテントを導入していますが、その実装とブロードキャスト方法はデバイス メーカー(OEM)によって異なる場合があります。すべてのデバイスでアプリが一貫した信頼性の高いエクスペリエンスを提供できるようにするには、デベロッパーは、このような潜在的な変化に適切に対応するように、ボンディングの損失処理を設計する必要があります。
アプリの動作は次のとおりにすることをおすすめします。
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGインテントがブロードキャストされた場合:ACL(非同期接続レス)リンクはシステムによって切断されますが、デバイスのボンディング情報は保持されます(こちらを参照)。
アプリでは、このインテントを結合喪失の検出の主要なシグナルとして使用し、デバイスの消去や再ペア設定を開始する前に、リモート デバイスが範囲内にあることを確認するようユーザーに案内する必要があります。
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGの受信後にデバイスが切断された場合、デバイスがシステムとボンディングされていない可能性があるため、アプリは再接続に注意する必要があります。ACTION_KEY_MISSINGインテントがブロードキャストされていない場合:ACL リンクは接続されたままになり、デバイスのボンディング情報は Android 15 の場合と同じようにシステムによって削除されます。
このシナリオでは、アプリは以前の Android リリースと同様に既存のボンディング損失処理メカニズムを継続して、ボンディング損失イベントを検出して管理する必要があります。
Bluetooth のペア設定を削除する新しい方法
Android 16 をターゲットとするすべてのアプリで、CompanionDeviceManager の公開 API を使用して Bluetooth デバイスのペア設定を解除できるようになりました。コンパニオン デバイスが CDM の関連付けとして管理されている場合、アプリは、関連付けられたデバイスで新しい removeBond(int) API を使用して、Bluetooth の接続解除をトリガーできます。アプリは、Bluetooth デバイスのブロードキャスト イベント ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED をリッスンすることで、ボンディング状態の変化をモニタリングできます。
セキュリティ
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、セキュリティが次のように変更されています。
MediaStore バージョンのロックダウン
Android 16 以降をターゲットとするアプリの場合、MediaStore#getVersion() はアプリごとに一意になります。これにより、バージョン文字列から識別プロパティが削除され、フィンガープリント手法の不正使用と使用が防止されます。アプリでは、このバージョンの形式について前提条件を設定しないでください。アプリは、この API を使用する際にバージョンの変更をすでに処理している必要があります。ほとんどの場合、デベロッパーがこの API の対象範囲を超える追加情報を推測しようとしない限り、現在の動作を変更する必要はありません。
Safer Intents
Safer Intents 機能は、Android のインテント解決メカニズムのセキュリティを強化するために設計された多段階のセキュリティ イニシアチブです。この目標は、インテント処理中にチェックを追加し、特定の条件を満たさないインテントをフィルタすることで、アプリを悪意のあるアクションから保護することです。
Android 15 では、この機能は送信側アプリに重点が置かれていましたが、Android 16 では受信側アプリに制御が移り、デベロッパーはアプリのマニフェストを使用して厳格なインテント解決を有効にできるようになりました。
主な変更点は次の 2 つです。
明示的インテントはターゲット コンポーネントのインテント フィルタと一致する必要がある: インテントがコンポーネントを明示的にターゲットに設定している場合、そのコンポーネントのインテント フィルタと一致する必要があります。
アクションのないインテントはインテント フィルタに一致しない: アクションが指定されていないインテントは、インテント フィルタに解決されるべきではありません。
これらの変更は、複数のアプリが関与している場合にのみ適用され、単一のアプリ内のインテント処理には影響しません。
影響
オプトイン方式であるため、デベロッパーはアプリ マニフェストで明示的に有効にしないと、この機能は有効になりません。そのため、この機能の影響は、デベロッパーが以下の条件を満たすアプリに限定されます。
- Safer Intents 機能とそのメリットを理解している。
- より厳格なインテント処理方法をアプリに組み込むことを積極的に選択する。
このオプトイン アプローチにより、現在の安全性の低いインテント解決動作に依存している可能性のある既存のアプリが破損するリスクを最小限に抑えることができます。
Android 16 での初期の影響は限定的かもしれませんが、Safer Intents イニシアチブには、今後の Android リリースでより広範な影響を与えるためのロードマップがあります。最終的には、厳密なインテント解決をデフォルトの動作にする予定です。
Safer Intents 機能は、悪意のあるアプリがインテント解決メカニズムの脆弱性を悪用することを困難にすることで、Android エコシステムのセキュリティを大幅に強化する可能性があります。
ただし、既存のアプリとの互換性の問題に対処するため、オプトアウトと強制適用の移行は慎重に管理する必要があります。
実装
デベロッパーは、アプリのマニフェストで intentMatchingFlags 属性を使用して、より厳密なインテント マッチングを明示的に有効にする必要があります。アプリ全体で機能を有効にし、レシーバで無効にする/無効にする例を次に示します。
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
サポートされているフラグの詳細:
| フラグ名 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | 受信インテントの厳密な照合を適用する |
| なし | 受信インテントの特別な照合ルールをすべて無効にします。複数のフラグを指定した場合、競合する値は「none」フラグが優先されることで解決されます。 |
| allowNullAction | 一致ルールを緩和し、アクションのないインテントを一致させます。特定の動作を実現するために「enforceIntentFilter」と組み合わせて使用されるフラグ |
テストとデバッグ
適用が有効になっている場合、インテント呼び出し元がインテントを適切に設定していれば、アプリは正しく機能します。ただし、ブロックされたインテントは、タグ "PackageManager." を含む "Intent does not match component's intent filter:" や "Access blocked:" などの警告ログメッセージをトリガーします。これは、アプリに影響する可能性のある問題を示しており、注意が必要です。
Logcat フィルタ:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
GPU システムコール フィルタリング
Mali GPU サーフェスを強化するため、非推奨になった Mali GPU IOCTL や GPU 開発専用の Mali GPU IOCTL は、本番環境ビルドでブロックされています。また、GPU プロファイリングに使用される IOCTL が、シェルプロセスまたはデバッグ可能なアプリに制限されました。プラットフォーム レベルのポリシーについて詳しくは、SAC の更新を参照してください。
この変更は、Mali GPU を使用する Google Pixel デバイス(Google Pixel 6 ~ 9)で実施されます。Arm は、r54p2 リリースの Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst で IOCTL の公式な分類を提供しています。このリストは、今後のドライバ リリースでも引き続き維持されます。
この変更は、サポートされているグラフィック API(Vulkan や OpenGL など)には影響しません。また、デベロッパーや既存のアプリケーションにも影響しないと見込まれます。Streamline Performance Analyzer や Android GPU Inspector などの GPU プロファイリング ツールは影響を受けません。
テスト
次のような SELinux の拒否が表示された場合は、アプリがこの変更の影響を受けている可能性があります。
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
アプリケーションでブロックされた IOCTL を使用する必要がある場合は、バグを報告して android-partner-security@google.com に割り当ててください。
よくある質問
このポリシーの変更はすべての OEM に適用されますか?この変更はオプトインですが、この強化方法を使用したい OEM は誰でも利用できます。変更の実装手順については、実装に関するドキュメントをご覧ください。
これを実装するには OEM コードベースで変更を行う必要がありますか?それとも、新しい AOSP リリースにデフォルトで含まれていますか?プラットフォーム レベルの変更は、デフォルトで新しい AOSP リリースに含まれます。ベンダーは、この変更を適用したい場合は、コードベースでこの変更を有効にできます。
SoC は IOCTL リストを最新の状態に保つ責任を負っていますか?たとえば、デバイスで ARM Mali GPU を使用している場合、変更について ARM に問い合わせる必要はありますか?個々の SoC は、ドライバのリリース時にデバイスごとに IOCTL リストを更新する必要があります。たとえば、ARM はドライバの更新時に公開済みの IOCTL リストを更新します。ただし、OEM は、SEPolicy に更新を組み込み、必要に応じて選択したカスタム IOCTL をリストに追加する必要があります。
この変更は、販売中のすべての Google Pixel に自動的に適用されますか?それとも、この変更を適用するためにユーザーが何かを切り替える必要がありますか?この変更は、Mali GPU(Google Pixel 6 ~ 9)を使用するすべての Google Pixel 販売中デバイスに適用されます。この変更を適用するためにユーザー側で必要な対応はありません。
このポリシーを使用すると、カーネル ドライバのパフォーマンスに影響しますか?このポリシーは GFXBench を使用して Mali GPU でテストされましたが、GPU パフォーマンスに測定可能な変化は見られませんでした。
IOCTL リストを現在のユーザースペースとカーネル ドライバのバージョンに合わせる必要がありますか?はい。許可される IOCTL のリストは、ユーザー空間とカーネル ドライバの両方でサポートされる IOCTL と同期する必要があります。ユーザー空間またはカーネル ドライバの IOCTL が更新された場合は、SEPolicy IOCTL リストも一致するように更新する必要があります。
ARM は IOCTL を「制限付き」 / 「計測」に分類していますが、一部を本番環境のユースケースで使用したり、一部を拒否したりしたいと考えています。個々の OEM/SoC は、ユーザー空間 Mali ライブラリの構成に基づいて、使用する IOCTL を分類する方法を決定する責任があります。ARM のリストは、これらの決定に役立ちますが、OEM/SoC のユースケースはそれぞれ異なる場合があります。
プライバシー
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、プライバシーが次のように変更されています。
ローカル ネットワークの権限
LAN 上のデバイスには、INTERNET 権限を持つアプリからアクセスできます。これにより、アプリがローカル デバイスに簡単に接続できるようになりますが、ユーザーのフィンガープリントの作成や位置情報のプロキシなど、プライバシーに関する影響もあります。
ローカル ネットワーク保護プロジェクトは、新しいランタイム権限によってローカル ネットワークへのアクセスを制限することで、ユーザーのプライバシーを保護することを目的としています。
リリース計画
この変更は、25Q2 と 26Q2 の 2 つのリリース間でそれぞれデプロイされます。デベロッパーは 25Q2 でこのガイダンスに沿って、フィードバックを共有することが不可欠です。これらの保護は、今後の Android リリースで適用される予定です。また、暗黙的なローカル ネットワーク アクセスに依存するシナリオを、以下のガイダンスに沿って更新し、ユーザーによる新しい権限の拒否や取り消しに備える必要があります。
影響
現時点では、LNP はオプトイン機能であるため、オプトインしたアプリのみが影響を受けます。オプトイン フェーズの目的は、アプリのどの部分が暗黙的なローカル ネットワーク アクセスに依存しているかをアプリ デベロッパーが把握し、次のリリースでそれらの部分の権限を保護する準備をすることです。
アプリが次の方法でユーザーのローカル ネットワークにアクセスする場合、アプリは影響を受けます。
- ローカル ネットワーク アドレスでのロー ソケットの直接使用またはライブラリ使用(mDNS や SSDP サービス ディスカバリ プロトコルなど)
- ローカル ネットワークにアクセスするフレームワーク レベルのクラス(NsdManager など)の使用
ローカル ネットワーク アドレスとの間のトラフィックには、ローカル ネットワーク アクセス権限が必要です。次の表に、一般的なケースを示します。
| アプリの低レベル ネットワーク オペレーション | ローカル ネットワークへのアクセス権が必要です |
|---|---|
| アウトバウンド TCP 接続を行う | はい |
| 受信 TCP 接続を受け入れる | はい |
| UDP ユニキャスト、マルチキャスト、ブロードキャストの送信 | はい |
| 受信 UDP ユニキャスト、マルチキャスト、ブロードキャスト | はい |
これらの制限はネットワーク スタックの奥深くに実装されているため、すべてのネットワーク API に適用されます。これには、ネイティブ コードまたはマネージド コードで作成されたソケット、Cronet や OkHttp などのネットワーキング ライブラリ、それらの上に実装された API が含まれます。ローカル ネットワーク上のサービス(.local サフィックスが付いているサービスなど)を解決しようとする場合は、ローカル ネットワークの権限が必要になります。
上記のルールの例外:
- デバイスの DNS サーバーがローカル ネットワーク上にある場合、そのサーバーとの間のトラフィック(ポート 53)にはローカル ネットワーク アクセス権限は必要ありません。
- アプリ内ピッカーとして出力スイッチャーを使用するアプリは、ローカル ネットワークの権限を必要としません(2025 年第 4 四半期に詳細なガイダンスが提供される予定です)。
デベロッパー ガイダンス(オプトイン)
ローカル ネットワークの制限を有効にする手順は次のとおりです。
- デバイスを 25Q2 ベータ版 3 以降のビルドにフラッシュします。
- テストするアプリをインストールします。
adb で Appcompat フラグを切り替えます。
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>デバイスを再起動する
これで、アプリのローカル ネットワークへのアクセスが制限され、ローカル ネットワークにアクセスしようとするとソケット エラーが発生します。アプリのプロセス外でローカル ネットワーク オペレーションを実行する API(NsdManager など)を使用している場合、オプトイン フェーズでは影響を受けません。
アクセス権を復元するには、アプリに NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES へのアクセス権を付与する必要があります。
- アプリがマニフェストで
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES権限を宣言していることを確認します。 - [設定] > [アプリ] > [アプリ名] > [権限] > [付近のデバイス] > [許可] に移動します。
これで、アプリのローカル ネットワークへのアクセスが復元され、アプリをオプトインする前と同じようにすべてのシナリオが動作するはずです。
ローカル ネットワーク保護の適用が開始されると、アプリのネットワーク トラフィックは次のように影響を受けます。
| 権限 | アウトバウンド LAN リクエスト | アウトバウンド/インバウンドのインターネット リクエスト | インバウンド LAN リクエスト |
|---|---|---|---|
| 許可 | Works | Works | Works |
| Not Granted(未許可) | ハプニング集 | Works | ハプニング集 |
次のコマンドを使用して、App-Compat フラグをオフに切り替えます。
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
エラー
これらの制限に起因するエラーは、呼び出し元ソケットがローカル ネットワーク アドレスに対して send または send バリアントを呼び出すたびに返されます。
エラーの例:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
ローカル ネットワークの定義
このプロジェクトのローカル ネットワークとは、Wi-Fi やイーサネットなどのブロードキャスト対応のネットワーク インターフェースを利用する IP ネットワークを指します。ただし、携帯通信(WWAN)や VPN 接続は除きます。
次のネットワークはローカル ネットワークとみなされます。
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // リンクローカル
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- リンクローカル
- 直接接続されたルート
- Thread などのスタブ ネットワーク
- 複数サブネット(未定)
また、マルチキャスト アドレス(224.0.0.0/4、ff00::/8)と IPv4 ブロードキャスト アドレス(255.255.255.255)の両方がローカル ネットワーク アドレスとして分類されます。
アプリ所有の写真
Android 16 以降を搭載したデバイスで、SDK 36 以降をターゲットとするアプリから写真と動画の権限を求めるメッセージが表示された場合、選択したメディアへのアクセスを制限することを選択したユーザーには、アプリが所有する写真が写真選択ツールで事前選択された状態で表示されます。ユーザーは、これらの事前選択された項目の選択を解除できます。これにより、それらの写真と動画へのアプリのアクセス権が取り消されます。
