A plataforma Android 16 inclui mudanças de comportamento que podem afetar seu app.
As mudanças a seguir se aplicam a todos os apps quando executados no Android 16,
independente da targetSdkVersion. Teste seu app e modifique-o conforme
necessário para que ele ofereça suporte a essas mudanças.
Consulte também a lista de mudanças de comportamento que afetam apenas os apps destinados ao Android 16.
Principal recurso
O Android 16 (API de nível 36) inclui as seguintes mudanças que modificam ou expandem vários recursos principais do sistema Android.
Otimizações de cota do JobScheduler
A partir do Android 16, vamos ajustar a cota de tempo de execução de jobs regulares e acelerados com base nos seguintes fatores:
- Em qual bucket de espera do app o aplicativo está: no Android 16, os buckets de espera ativos vão começar a ser aplicados por uma cota de tempo de execução generosa.
- Se o job começar a execução enquanto o app estiver em um estado superior: no Android 16, os jobs iniciados enquanto o app estiver visível para o usuário e continuarem depois que o app ficar invisível vão obedecer à cota de tempo de execução do job.
- Se o job estiver sendo executado com um serviço em primeiro plano: no Android 16, os jobs que estiverem sendo executados simultaneamente com um serviço em primeiro plano vão obedecer à cota de tempo de execução do job. Se você estiver usando jobs para transferência de dados iniciada pelo usuário, considere usar jobs de transferência de dados iniciada pelo usuário.
Essa mudança afeta tarefas programadas usando o WorkManager, o JobScheduler e o
DownloadManager. Para depurar por que um job foi interrompido, recomendamos registrar por que ele foi interrompido chamando WorkInfo.getStopReason() (para jobs do JobScheduler, chame JobParameters.getStopReason()).
Para saber como o estado do app afeta os recursos que ele pode usar, consulte Limites de recursos de gerenciamento de energia. Para mais informações sobre práticas recomendadas de otimização da bateria, consulte as orientações sobre como otimizar o uso da bateria para APIs de programação de tarefas.
Também recomendamos usar a nova API
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory introduzida no
Android 16 para entender por que um job não foi executado.
Teste
Para testar o comportamento do app, é possível ativar a substituição de determinadas otimizações de cota de jobs enquanto o app estiver sendo executado em um dispositivo Android 16.
Para desativar a aplicação de "o estado principal vai obedecer à cota de tempo de execução do job", execute o seguinte comando adb:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Para desativar a aplicação de "jobs em execução simultânea com um
serviço em primeiro plano vão obedecer à cota de tempo de execução do job", execute o seguinte
comando adb:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Para testar determinado comportamento do bucket de espera do app, defina o bucket de espera do app
usando o seguinte comando adb:
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
Para entender em qual bucket de espera seu app está, use o seguinte comando adb:
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Motivo da interrupção de jobs vazios abandonados
Um job abandonado ocorre quando o objeto JobParameters associado ao job
é coletado, mas JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) não é chamado para sinalizar a conclusão do job. Isso indica que
o job pode estar sendo executado e reprogramado sem que o app saiba.
Os apps que dependem do JobScheduler não mantêm uma referência forte ao objeto
JobParameters, e o tempo limite agora será concedido ao novo motivo de interrupção de job
STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED, em vez de STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT.
Se houver ocorrências frequentes do novo motivo de interrupção, o sistema vai tomar medidas de mitigação para reduzir a frequência do job.
Os apps precisam usar o novo motivo de interrupção para detectar e reduzir jobs abandonados.
Se você estiver usando o WorkManager, o AsyncTask ou o DownloadManager, não será afetado porque essas APIs gerenciam o ciclo de vida do job em nome do app.
Suspensão total de JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground
O método JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean)
indica a importância de um job enquanto o app de programação está em primeiro plano
ou quando é temporariamente isento de restrições em segundo plano.
Esse método foi descontinuado a partir do Android 12 (nível 31 da API). A partir do Android 16, ele não funciona mais de forma eficaz, e a chamada desse método será ignorada.
Essa remoção de funcionalidade também se aplica a
JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground(). A partir do Android
16, se o método for chamado, ele retornará false.
O escopo de prioridade de transmissão ordenada não é mais global
Os apps Android podem definir prioridades em broadcast receivers para controlar
a ordem em que os receptores recebem e processam a transmissão. Para
recebedores declarados no manifesto, os apps podem usar o atributo
android:priority para definir a prioridade. Para
recebedores registrados no contexto, os apps podem usar a
API IntentFilter#setPriority() para definir a prioridade. Quando
uma transmissão é enviada, o sistema a entrega aos receptores na ordem de
prioridade, da mais alta para a mais baixa.
No Android 16, a ordem de entrega de transmissão usando o atributo android:priority
ou IntentFilter#setPriority() em diferentes processos não será
garantida. As prioridades de transmissão só serão respeitadas no mesmo
processo do aplicativo, e não em todos os processos.
Além disso, as prioridades de transmissão serão automaticamente limitadas ao intervalo
(SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1,
SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1). Somente os componentes do sistema poderão
definir SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY como prioridade de
transmissão.
O app pode ser afetado se fizer o seguinte:
- Seu aplicativo declarou vários processos com a mesma intent de transmissão e tem expectativas em relação ao recebimento dessas intents em uma determinada ordem com base na prioridade.
- O processo do aplicativo interage com outros processos e tem expectativas em relação ao recebimento de uma intent de transmissão em uma determinada ordem.
Se os processos precisarem se coordenar, eles vão precisar se comunicar usando outros canais de coordenação.
Mudanças internas no ART
O Android 16 inclui as atualizações mais recentes do Android Runtime (ART), que melhoram a performance do Android Runtime (ART) e oferecem suporte a outros recursos Java. Com as atualizações do sistema do Google Play, essas melhorias também estão disponíveis para mais de um bilhão de dispositivos com o Android 12 (nível 31 da API) e versões mais recentes.
À medida que essas mudanças são lançadas, bibliotecas e códigos de apps que dependem de estruturas internas do ART podem não funcionar corretamente em dispositivos com o Android 16, além de versões anteriores do Android que atualizam o módulo ART por meio de atualizações do sistema do Google Play.
A dependência de estruturas internas (como interfaces não SDK) pode sempre levar a problemas de compatibilidade, mas é particularmente importante evitar depender de código (ou bibliotecas que contenham código) que aproveite estruturas internas do ART, já que as mudanças do ART não estão vinculadas à versão da plataforma em que o dispositivo está executando e são enviadas para mais de um bilhão de dispositivos por meio de atualizações do sistema do Google Play.
Todos os desenvolvedores precisam verificar se o app é afetado testando-o completamente no Android 16. Além disso, verifique os problemas conhecidos para verificar se o app depende de bibliotecas que identificamos como dependentes de estruturas internas do ART. Se você tiver dependências de biblioteca ou código de app que foram afetadas, procure alternativas de API pública sempre que possível e solicite APIs públicas para novos casos de uso criando uma solicitação de recurso no nosso rastreador de problemas.
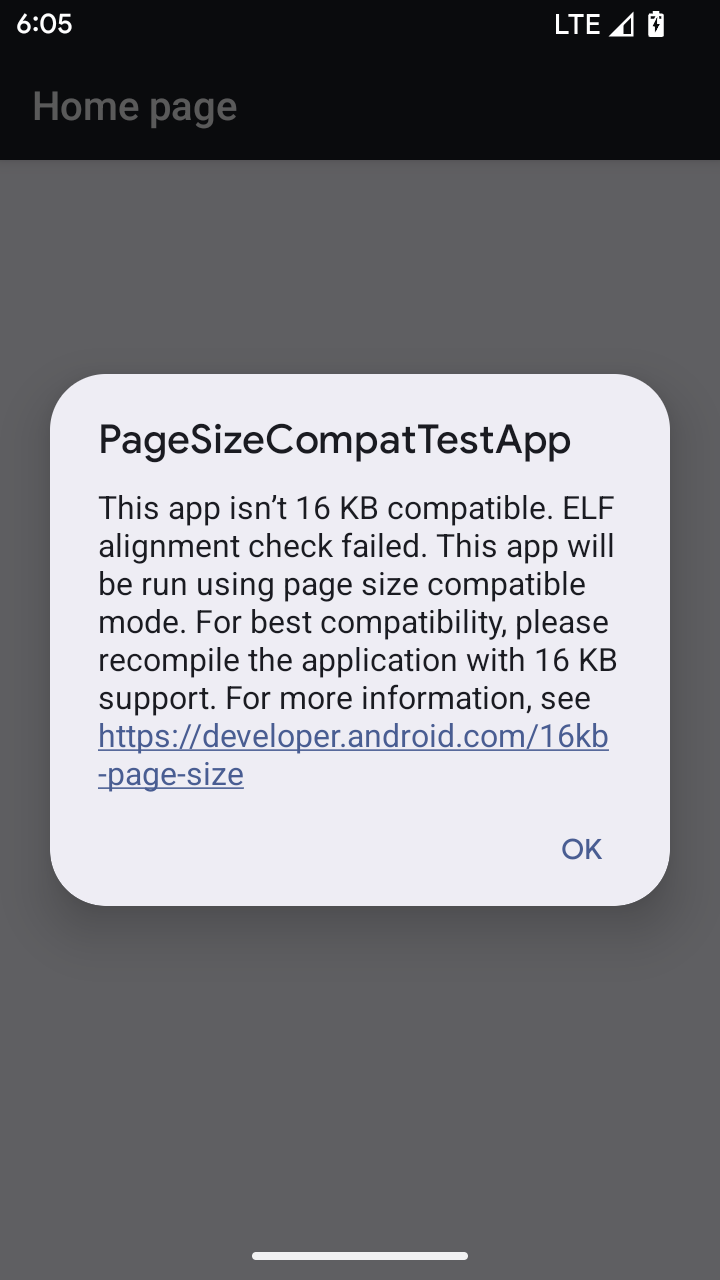
Modo de compatibilidade de tamanho de página de 16 KB
O Android 15 introduziu o suporte a páginas de memória de 16 KB para otimizar o desempenho da plataforma. O Android 16 adiciona um modo de compatibilidade, permitindo que alguns apps criados para páginas de memória de 4 KB sejam executados em um dispositivo configurado para páginas de memória de 16 KB.
Quando o app está em execução em um dispositivo com o Android 16 ou mais recente, se o Android
detectar que o app tem páginas de memória alinhadas de 4 KB, ele vai usar automaticamente
o modo de compatibilidade e mostrar uma caixa de diálogo de notificação para o usuário. Definir a
propriedade android:pageSizeCompat no AndroidManifest.xml para ativar o
modo de compatibilidade com versões anteriores vai impedir a exibição da caixa de diálogo quando o
app for iniciado. Para usar a propriedade android:pageSizeCompat, compile o app
usando o SDK do Android 16.
Para ter o melhor desempenho, confiabilidade e estabilidade, o app ainda precisa ter 16 KB alinhados. Confira nossa postagem recente do blog sobre como atualizar seus apps para oferecer suporte a páginas de memória de 16 KB para mais detalhes.
Experiência do usuário e interface do sistema
O Android 16 (nível 36 da API) inclui as seguintes mudanças que visam criar uma experiência do usuário mais consistente e intuitiva.
Descontinuação de avisos de acessibilidade que causam interrupção
O Android 16 descontinua os avisos de acessibilidade, caracterizados pelo uso de
announceForAccessibility ou o envio de
eventos de acessibilidade TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT. Isso pode criar
experiências de usuário inconsistentes para usuários do TalkBack e do leitor de tela do Android.
As alternativas atendem melhor a uma gama mais ampla de necessidades dos usuários em várias
tecnologias assistivas do Android.
Exemplos de alternativas:
- Para mudanças significativas na interface, como mudanças de janela, use
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)esetAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence). No Compose, useModifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" }. - Para informar o usuário sobre mudanças na interface crítica, use
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int). No Compose, useModifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}. Elas devem ser usadas com moderação, porque podem gerar avisos sempre que uma visualização é atualizada. - Para notificar os usuários sobre erros, envie um
AccessibilityEventdo tipoAccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORe definaAccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence)ou useTextView#setError(CharSequence).
A documentação de referência da API announceForAccessibility, que foi descontinuada, inclui mais detalhes sobre as alternativas sugeridas.
Compatibilidade com a navegação com três botões
O Android 16 oferece suporte à volta preditiva na navegação de três botões para apps que foram migrados corretamente para a volta preditiva. Tocar e pressionar o botão "Voltar" inicia uma animação de volta preditiva, mostrando uma prévia de onde a ação de deslizar para trás vai levar você.
Esse comportamento se aplica a todas as áreas do sistema que oferecem suporte a animações de volta preditiva, incluindo as animações do sistema (volta à tela inicial, entre tarefas e entre atividades).
Ícones temáticos automáticos de apps
A partir do Android 16 QPR 2, o Android aplica temas automaticamente aos ícones de apps para criar uma experiência coesa na tela inicial. Isso acontece se um app não fornecer um ícone temático próprio. Os apps podem controlar o design do ícone temático incluindo uma camada monocromática no ícone adaptável e conferindo uma prévia da aparência do ícone no Android Studio.
Formatos de dispositivos
O Android 16 (nível 36 da API) inclui as seguintes mudanças para apps quando projetados em telas por proprietários de dispositivos virtuais.
Substituições do proprietário do dispositivo virtual
Um proprietário de dispositivo virtual é um app confiável ou privilegiado que cria e gerencia um dispositivo virtual. Os proprietários de dispositivos virtuais executam apps em um dispositivo virtual e projetam os apps na tela de um dispositivo remoto, como um computador pessoal, um dispositivo de realidade virtual ou um sistema de infoentretenimento do carro. O proprietário do dispositivo virtual está em um dispositivo local, como um smartphone.
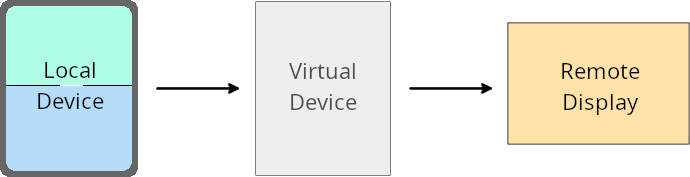
Substituições por app
Em dispositivos com o Android 16 (nível da API 36), os proprietários de dispositivos virtuais podem substituir as configurações de apps em dispositivos virtuais selecionados que eles gerenciam. Por exemplo, para melhorar o layout do app, um proprietário de dispositivo virtual pode ignorar as restrições de orientação, proporção e redimensionamento ao projetar apps em uma tela externa.
Mudanças interruptivas comuns
O comportamento do Android 16 pode afetar a interface do seu app em formatos de tela grande, como telas de carro ou Chromebooks, especialmente layouts projetados para telas pequenas na orientação retrato. Para saber como tornar seu app adaptável a todos os formatos de dispositivos, consulte Sobre layouts adaptáveis.
Referências
Streaming de apps complementares
Segurança
O Android 16 (nível da API 36) inclui mudanças que promovem a segurança do sistema para ajudar a proteger apps e usuários contra apps maliciosos.
Segurança aprimorada contra ataques de redirecionamento de intent
O Android 16 oferece segurança padrão contra ataques gerais de redirecionamento de Intent, com compatibilidade mínima e mudanças necessárias para desenvolvedores.
Estamos lançando soluções de reforço de segurança padrão para explorações de redirecionamento Intent. Na maioria dos casos, os apps que usam intents normalmente não
têm problemas de compatibilidade. Reunimos métricas durante nosso
processo de desenvolvimento para monitorar quais apps podem ter falhas.
O redirecionamento de intents no Android ocorre quando um invasor pode controlar total ou parcialmente o conteúdo de uma intent usada para iniciar um novo componente no contexto de um app vulnerável, enquanto o app da vítima inicia uma intent de subnível não confiável em um campo de extras de uma intent ("de nível superior"). Isso pode fazer com que o app do invasor inicie componentes particulares no contexto do app da vítima, acionando ações privilegiadas ou ganhando acesso de URI a dados sensíveis, o que pode levar ao roubo de dados e à execução arbitrária de código.
Desativar o processamento de redirecionamento de intents
O Android 16 introduz uma nova API que permite que os apps desativem as proteções de segurança de início. Isso pode ser necessário em casos específicos em que o comportamento de segurança padrão interfere em casos de uso legítimos do app.
Para aplicativos compilados com o SDK do Android 16 (nível 36 da API) ou versões mais recentes
Você pode usar diretamente o método removeLaunchSecurityProtection() no objeto Intent.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
Para aplicativos compilados com o Android 15 (nível 35 da API) ou versões anteriores
Embora não seja recomendado, você pode usar a reflexão para acessar o método
removeLaunchSecurityProtection().
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
Os apps complementares não recebem mais notificações de tempo limite de descoberta
O Android 16 apresenta um novo comportamento durante o
fluxo de pareamento de dispositivos complementares para proteger a privacidade de localização
do usuário contra apps maliciosos. Todos os apps complementares em execução no Android 16 não são
mais notificados diretamente do tempo limite de descoberta usando
RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT. Em vez disso, o usuário é
notificado sobre eventos de tempo limite com uma caixa de diálogo visual. Quando o usuário dispensa
a caixa de diálogo, o app é alertado sobre a falha de associação com
RESULT_USER_REJECTED.
A duração da pesquisa também foi estendida em relação aos 20 segundos originais, e a descoberta de dispositivos pode ser interrompida pelo usuário a qualquer momento durante a pesquisa. Se pelo menos um dispositivo for descoberto nos primeiros 20 segundos após o início da pesquisa, o CDM vai parar de procurar outros dispositivos.
Conectividade
O Android 16 (nível 36 da API) inclui as seguintes mudanças na pilha Bluetooth para melhorar a conectividade com dispositivos periféricos.
Melhoria no tratamento de perdas de títulos
A partir do Android 16, a pilha Bluetooth foi atualizada para melhorar a segurança e a experiência do usuário quando uma perda de vínculo remoto é detectada. Antes, o sistema retirava automaticamente a vinculação e iniciava um novo processo de pareamento, o que poderia levar a um novo pareamento não intencional. Em muitos casos, os apps não tratavam o evento de perda de vínculo de forma consistente.
Para unificar a experiência, o Android 16 melhorou o processamento de perda de vínculo para o sistema. Se um dispositivo Bluetooth pareado anteriormente não puder ser autenticado na reconexão, o sistema desconectará o link, manterá as informações de pareamento local e exibirá uma caixa de diálogo do sistema informando os usuários sobre a perda de pareamento e orientando-os a fazer o pareamento novamente.
