Android 16 平台包含一些可能会影响您的应用的行为变更。以下行为变更将影响在 Android 16 上运行的所有应用,无论采用哪种 targetSdkVersion 都不例外。您应该测试您的应用,然后根据需要酌情修改,以便支持这些变更。
此外,请务必查看仅影响以 Android 16 为目标平台的应用的行为变更列表。
核心功能
Android 16(API 级别 36)包含以下变更,这些变更会修改或扩展 Android 系统的各种核心功能。
JobScheduler 配额优化
从 Android 16 开始,我们将根据以下因素调整常规作业和加急作业的执行运行时配额:
- 应用所处的应用待机存储分区:在 Android 16 中,活跃待机存储分区将开始通过宽松的运行时配额强制执行。
- 如果作业在应用处于前台状态时开始执行:在 Android 16 中,如果作业在应用对用户可见时开始执行,并在应用变为不可见后继续执行,则会遵守作业运行时配额。
- 如果作业在运行前台服务时执行:在 Android 16 中,与前台服务同时执行的作业将遵守作业运行时配额。如果您利用作业进行用户发起的数据传输,请考虑改用用户发起的数据传输作业。
此变更会影响使用 WorkManager、JobScheduler 和 DownloadManager 调度的任务。如需调试作业停止的原因,我们建议您通过调用 WorkInfo.getStopReason()(对于 JobScheduler 作业,请调用 JobParameters.getStopReason())来记录作业停止的原因。
如需了解应用的状态如何影响其可使用的资源,请参阅电源管理资源限制。 如需详细了解电池优化方面的最佳实践,请参阅有关针对任务调度 API 优化电池使用的指南。
我们还建议利用 Android 16 中引入的新 JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory API 来了解作业未执行的原因。
测试
如需测试应用的行为,只要应用在 Android 16 设备上运行,您就可以启用对某些作业配额优化功能的替换。
如需停用“顶级状态将遵守作业运行时配额”的强制执行,请运行以下 adb 命令:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
如需停用“在与前台服务同时执行时,作业将遵守作业运行时配额”的强制执行,请运行以下 adb 命令:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
如需测试特定应用待机分桶行为,您可以使用以下 adb 命令设置应用的应用待机分桶:
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
如需了解应用所在的待机分桶,您可以使用以下 adb 命令获取应用的待机分桶:
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
已放弃的空作业停止原因
如果与作业关联的 JobParameters 对象已被垃圾回收,但尚未调用 JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) 来指示作业已完成,则会发生作业被废弃的情况。这表示作业可能会在应用不知情的情况下运行和重新调度。
依赖于 JobScheduler 的应用不会维护对 JobParameters 对象的强引用,并且超时现在将获得新的作业停止原因 STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED,而不是 STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT。
如果新的作业被废弃停止原因频繁出现,系统会采取缓解措施来降低作业频率。
应用应使用新的停止原因来检测和减少被废弃的作业。
如果您使用的是 WorkManager、AsyncTask 或 DownloadManager,则不会受到影响,因为这些 API 会代表您的应用管理作业生命周期。
完全弃用 JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground
JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean) 方法用于在调度应用位于前台或暂时豁免于后台限制时指示作业的优先级。
自 Android 12(API 级别 31)起,此方法已废弃。从 Android 16 开始,它不再有效,系统会忽略调用此方法。
此功能移除也适用于 JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground()。从 Android 16 开始,如果调用该方法,该方法会返回 false。
有序广播优先级范围不再是全局
Android 应用可以为广播接收器定义优先级,以控制接收器接收和处理广播的顺序。对于清单声明的接收器,应用可以使用 android:priority 属性来定义优先级;对于上下文注册的接收器,应用可以使用 IntentFilter#setPriority() API 来定义优先级。发送广播时,系统会按接收器的优先级(从高到低)将其传送给接收器。
在 Android 16 中,无法保证使用 android:priority 属性或 IntentFilter#setPriority() 在不同进程中传送广播的顺序。广播优先级仅在同一应用进程内有效,而不会跨所有进程有效。
此外,广播优先级将自动限制在 (SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1) 的范围内。只有系统组件才能将 SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY、SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY 设置为广播优先级。
如果您的应用执行以下任一操作,可能会受到影响:
- 您的应用声明了具有相同广播 intent 的多个进程,并且希望根据优先级以特定顺序接收这些 intent。
- 您的应用进程与其他进程交互,并期望以特定顺序接收广播 intent。
如果进程需要相互协调,则应使用其他协调渠道进行通信。
ART 内部变更
Android 16 包含 Android 运行时 (ART) 的最新更新,这些更新可提升 Android 运行时 (ART) 的性能,并支持更多 Java 功能。通过 Google Play 系统更新,搭载 Android 12(API 级别 31)及更高版本的 10 亿多部设备也将受益于这些改进。
发布这些变更后,依赖于 ART 内部结构的库和应用代码在搭载 Android 16 的设备以及通过 Google Play 系统更新来更新 ART 模块的较低 Android 版本上可能无法正常运行。
依赖于内部结构(例如非 SDK 接口)始终会导致兼容性问题,但避免依赖于利用内部 ART 结构的代码(或包含代码的库)尤为重要,因为 ART 更改与设备所运行的平台版本无关,并且会通过 Google Play 系统更新推送到超过 10 亿部设备。
所有开发者都应在 Android 16 上对其应用进行全面测试,以检查其应用是否受到影响。此外,请查看已知问题,了解您的应用是否依赖于我们发现的任何依赖于内部 ART 结构的库。如果您的应用代码或库依赖项受到影响,请尽可能寻找公共 API 替代方案,并在问题跟踪器中创建功能请求,为新用例请求公共 API。
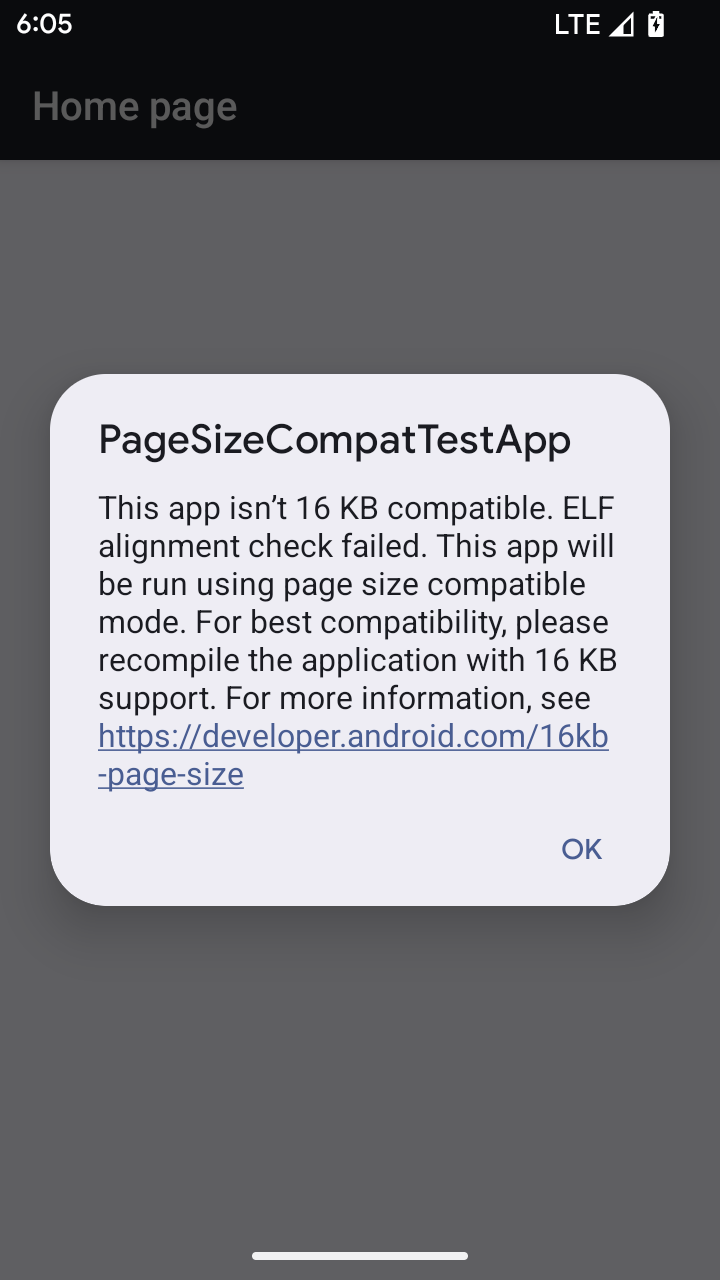
16 KB 页面大小兼容模式
Android 15 引入了对 16 KB 内存页面的支持,以优化平台性能。Android 16 添加了兼容模式,让一些针对 4 KB 内存页面构建的应用可以在配置为 16 KB 内存页面的设备上运行。
当您的应用在搭载 Android 16 或更高版本的设备上运行时,如果 Android 检测到您的应用具有 4 KB 对齐的内存页面,则会自动使用兼容模式并向用户显示通知对话框。在 AndroidManifest.xml 中设置 android:pageSizeCompat 属性以启用向后兼容模式,将会阻止应用启动时显示对话框。如需使用 android:pageSizeCompat 属性,请使用 Android 16 SDK 编译您的应用。
为了实现最佳性能、可靠性和稳定性,应用仍应以 16 KB 对齐。如需了解详情,请参阅我们近期发布的博文,了解如何更新应用以支持 16 KB 的内存页面。
用户体验和系统界面
Android 16(API 级别 36)包含以下旨在打造更一致、更直观的用户体验的变更。
弃用干扰性无障碍功能公告
Android 16 废弃了无障碍功能通告,其特征是使用 announceForAccessibility 或调度 TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT 无障碍功能事件。这可能会给 TalkBack 和 Android 屏幕阅读器用户带来不一致的用户体验,而替代方案可以更好地满足各种 Android 辅助技术的用户需求。
替代方案示例:
- 对于窗口更改等重大界面更改,请使用
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)和setAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence)。在 Compose 中,使用Modifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" } - 如需向用户告知关键界面的更改,请使用
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int)。在 Compose 中,请使用Modifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}。应谨慎使用这些事件,因为它们可能会在每次更新视图时生成通知。 - 如需向用户发送错误通知,请发送类型为
AccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERROR的AccessibilityEvent并设置AccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence),或使用TextView#setError(CharSequence)。
已废弃的 announceForAccessibility API 的参考文档中包含有关建议替代方案的更多详细信息。
支持“三按钮”导航
Android 16 为已正确迁移到预测性返回的应用的三按钮导航栏引入了预测性返回支持。长按返回按钮会启动预测性返回动画,让您预览返回滑动手势会打开的界面。
此行为适用于系统中支持预测性返回动画的所有区域,包括系统动画(返回主屏幕、跨任务和跨 activity)。
自动带主题的应用图标
从 Android 16 QPR 2 开始,Android 会自动将主题应用于应用图标,以打造一致的主屏幕体验。如果应用未提供自己的带主题的应用图标,就会发生这种情况。应用可以通过在自适应图标中添加单色图层来控制主题化应用图标的设计,并在 Android Studio 中预览应用图标的外观。
设备规格
Android 16(API 级别 36)在虚拟设备所有者将应用投影到显示屏时,对应用做出了以下更改。
虚拟设备所有者替换项
虚拟设备所有者是创建和管理虚拟设备的受信任应用或特权应用。虚拟设备所有者在虚拟设备上运行应用,然后将应用投影到远程设备的显示屏上,例如个人电脑、虚拟现实设备或车载信息娱乐系统。虚拟设备所有者位于本地设备上,例如手机。
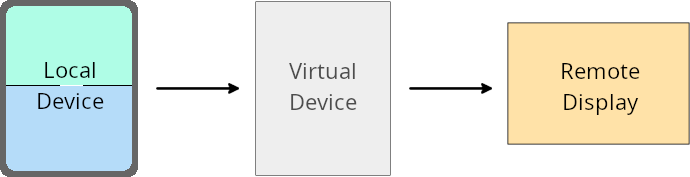
按应用替换项
在搭载 Android 16(API 级别 36)的设备上,虚拟设备所有者可以替换其管理的特定虚拟设备上的应用设置。例如,为了改进应用布局,虚拟设备所有者在将应用投影到外部显示屏上时,可以忽略屏幕方向、宽高比和可调整大小性限制。
常见的重大更改
Android 16 的行为可能会影响应用在汽车显示屏或 Chromebook 等大屏幕设备上的界面,尤其是那些专为竖屏小显示屏设计的布局。如需了解如何让应用适应所有设备类型,请参阅自适应布局简介。
参考文档
安全
Android 16(API 级别 36)包含多项变更,可提升系统安全性,有助于保护应用和用户免受恶意应用的侵害。
安全性更强,可防范 Intent 重定向攻击
Android 16 提供了针对一般 Intent 重定向攻击的默认安全性,并且只需进行最低限度的兼容性更改和开发者更改。
我们正在引入默认安全强化解决方案,以应对Intent重定向漏洞。在大多数情况下,使用 intent 的应用通常不会遇到任何兼容性问题;我们在整个开发过程中收集了指标,以监控哪些应用可能会出现中断。
当攻击者可以部分或完全控制用于在存在漏洞的应用上下文中启动新组件的 intent 内容时,就会出现 Android 中的 intent 重定向问题,而受害应用会在(“顶级”)intent 的 extras 字段中启动不可信的子级 intent。这可能会导致攻击者应用在受害者应用的上下文中启动私有组件、触发特权操作或获得对敏感数据的 URI 访问权限,从而可能导致数据窃取和任意代码执行。
选择停用 intent 重定向处理
Android 16 引入了一项新 API,允许应用选择停用启动安全保护功能。在默认安全行为会干扰正当应用用例的特定情况下,这可能是必要的。
对于针对 Android 16(API 级别 36)SDK 或更高版本进行编译的应用
您可以直接对 Intent 对象使用 removeLaunchSecurityProtection() 方法。
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
对于针对 Android 15(API 级别 35)或更低版本进行编译的应用
虽然不建议这样做,但您可以使用反射来访问 removeLaunchSecurityProtection() 方法。
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
不再向配套应用通知发现超时
Android 16 在配套设备配对流程期间引入了一种新行为,以防恶意应用侵犯用户的位置信息隐私。在 Android 16 上运行的所有配套应用都不再直接通过 RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT 收到发现超时通知。而是通过可视对话框通知用户超时事件。当用户关闭对话框时,系统会通过 RESULT_USER_REJECTED 提醒应用关联失败。
搜索时长也从原来的 20 秒延长到了 30 秒,并且用户可以在搜索期间的任何时间停止设备发现。如果在开始搜索的前 20 秒内发现了至少 1 部设备,CDM 会停止搜索其他设备。
连接
Android 16(API 级别 36)在蓝牙堆栈中进行了以下更改,以改善与外围设备的连接。
改进了债券损失处理
从 Android 16 开始,蓝牙堆栈已更新,以便在检测到远程配对丢失时提高安全性和用户体验。以前,系统会自动解除配对并启动新的配对流程,这可能会导致意外重新配对。在许多情况下,我们发现应用未以一致的方式处理债券损失事件。
为了统一体验,Android 16 改进了系统的绑定丢失处理。如果之前配对的蓝牙设备在重新连接时无法进行身份验证,系统会断开关联,保留本地配对信息,并显示系统对话框,告知用户配对已断开并指示他们重新配对。
