La plataforma de Android 16 incluye cambios de comportamiento que podrían afectar tu app.
Los siguientes cambios de comportamiento se aplican a todas las apps cuando se ejecutan en Android 16,
independientemente de targetSdkVersion. Debes probar tu app y, luego, modificarla según corresponda para admitir estos cambios.
Asegúrate también de revisar la lista de cambios de comportamiento que solo afectan a las apps orientadas a Android 16.
Funcionalidad principal
Android 16 (nivel de API 36) incluye los siguientes cambios que modifican o expanden varias capacidades principales del sistema Android.
Optimizaciones de cuotas de JobScheduler
A partir de Android 16, ajustaremos la cuota de tiempo de ejecución de trabajos regulares y acelerados en función de los siguientes factores:
- En qué intervalo de espera de la app se encuentra la aplicación: En Android 16, los intervalos de espera activos comenzarán a aplicarse con una cuota de tiempo de ejecución generosa.
- Si el trabajo comienza a ejecutarse mientras la app está en un estado superior: En Android 16, los trabajos que se inician mientras la app es visible para el usuario y continúan después de que la app se vuelve invisible cumplirán con la cuota de tiempo de ejecución del trabajo.
- Si el trabajo se ejecuta mientras se ejecuta un servicio en primer plano: En Android 16, los trabajos que se ejecutan de forma simultánea con un servicio en primer plano cumplirán con la cuota de tiempo de ejecución del trabajo. Si aprovechas los trabajos para la transferencia de datos iniciada por el usuario, considera usar trabajos de transferencia de datos iniciados por el usuario.
Este cambio afecta las tareas programadas con WorkManager, JobScheduler y DownloadManager. Para depurar por qué se detuvo un trabajo, te recomendamos que registres el motivo por el que se detuvo llamando a WorkInfo.getStopReason() (para los trabajos de JobScheduler, llama a JobParameters.getStopReason()).
Para obtener información sobre cómo el estado de tu app afecta los recursos que puede usar, consulta Límites de recursos de administración de energía. Para obtener más información sobre las prácticas recomendadas para optimizar la batería, consulta la guía sobre cómo optimizar el uso de la batería para las APIs de programación de tareas.
También recomendamos aprovechar la nueva API de JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory que se introdujo en Android 16 para comprender por qué no se ejecutó un trabajo.
Prueba
Para probar el comportamiento de tu app, puedes habilitar la anulación de ciertas optimizaciones de la cuota de trabajos siempre que la app se ejecute en un dispositivo Android 16.
Para inhabilitar la aplicación de la regla "El estado superior se ajustará a la cuota de tiempo de ejecución del trabajo", ejecuta el siguiente comando de adb:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Para inhabilitar la aplicación de "los trabajos que se ejecutan de forma simultánea con un servicio en primer plano se ajustarán a la cuota de tiempo de ejecución del trabajo", ejecuta el siguiente comando de adb:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Para probar el comportamiento de un intervalo de Standby específico, puedes establecer el intervalo de Standby de tu app con el siguiente comando adb:
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
Para comprender el intervalo de Standby de la app en el que se encuentra tu app, puedes obtenerlo con el siguiente comando adb:
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Motivo de detención de trabajos vacíos abandonados
Una tarea abandonada ocurre cuando se recopiló como elemento no utilizado el objeto JobParameters asociado con la tarea, pero no se llamó a JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) para indicar que se completó. Esto indica que
el trabajo puede estar en ejecución y reprogramarse sin que la app lo sepa.
Las apps que dependen de JobScheduler no mantienen una referencia sólida al objeto JobParameters, y el tiempo de espera ahora se otorgará al nuevo motivo de detención de la tarea STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED, en lugar de STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT.
Si se producen casos frecuentes del nuevo motivo de detención abandonada, el sistema tomará medidas de mitigación para reducir la frecuencia de las tareas.
Las apps deben usar el nuevo motivo de detención para detectar y reducir las tareas abandonadas.
Si usas WorkManager, AsyncTask o DownloadManager, no se te verá afectado porque estas APIs administran el ciclo de vida de la tarea en nombre de tu app.
Se dejó de usar por completo JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground
El método JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean) indica la importancia de una tarea mientras la app de programación está en primer plano o cuando está exenta temporalmente de las restricciones en segundo plano.
Este método dejó de estar disponible a partir de Android 12 (nivel de API 31). A partir de Android 16, ya no funciona de manera eficaz y se ignorará llamar a este método.
Esta eliminación de funcionalidad también se aplica a JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground(). A partir de Android 16, si se llama al método, este muestra false.
El alcance de prioridad de transmisión ordenada ya no es global
Las apps para Android pueden definir prioridades en los receptores de emisión para controlar el orden en que los receptores reciben y procesan la emisión. En el caso de los receptores declarados en el manifiesto, las apps pueden usar el atributo android:priority para definir la prioridad y, en el caso de los receptores registrados en el contexto, las apps pueden usar la API de IntentFilter#setPriority() para definir la prioridad. Cuando se envía una transmisión, el sistema la entrega a los receptores en orden de prioridad, de la más alta a la más baja.
En Android 16, no se garantizará el orden de entrega de transmisiones con el atributo android:priority o IntentFilter#setPriority() en diferentes procesos. Las prioridades de transmisión solo se respetarán dentro del mismo proceso de la aplicación y no en todos los procesos.
Además, las prioridades de transmisión se limitarán automáticamente al rango (SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1). Solo los componentes del sistema podrán establecer SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY como prioridad de transmisión.
Es posible que tu app se vea afectada si realiza alguna de las siguientes acciones:
- Tu aplicación declaró varios procesos con el mismo intent de transmisión y tiene expectativas sobre la recepción de esos intents en un orden determinado según la prioridad.
- El proceso de tu app interactúa con otros procesos y tiene expectativas con respecto a la recepción de un intent de transmisión en un orden determinado.
Si los procesos deben coordinarse entre sí, deben comunicarse a través de otros canales de coordinación.
Cambios internos en ART
Android 16 incluye las actualizaciones más recientes del entorno de ejecución de Android (ART) que mejoran el rendimiento de este y proporcionan compatibilidad con funciones adicionales de Java. A través de las actualizaciones del sistema de Google Play, estas mejoras también están disponibles para más de mil millones de dispositivos que ejecutan Android 12 (nivel de API 31) y versiones posteriores.
A medida que se lanzan estos cambios, es posible que las bibliotecas y el código de la app que dependen de las estructuras internas de ART no funcionen correctamente en dispositivos con Android 16, junto con versiones anteriores de Android que actualizan el módulo de ART a través de actualizaciones del sistema de Google Play.
Depender de estructuras internas (como interfaces que no son de SDK) siempre puede generar problemas de compatibilidad, pero es particularmente importante evitar depender de código (o bibliotecas que contienen código) que aproveche estructuras internas de ART, ya que los cambios de ART no están vinculados a la versión de la plataforma en la que se ejecuta el dispositivo y se envían a más de mil millones de dispositivos a través de actualizaciones del sistema de Google Play.
Todos los desarrolladores deben verificar si sus apps se ven afectadas probando sus apps de forma exhaustiva en Android 16. Además, consulta los problemas conocidos para ver si tu app depende de alguna biblioteca que identificamos que se basa en estructuras internas de ART. Si tienes dependencias de código de app o biblioteca que se verán afectadas, busca alternativas de API públicas siempre que sea posible y solicita APIs públicas para casos de uso nuevos. Para ello, crea una solicitud de función en nuestro seguimiento de problemas.
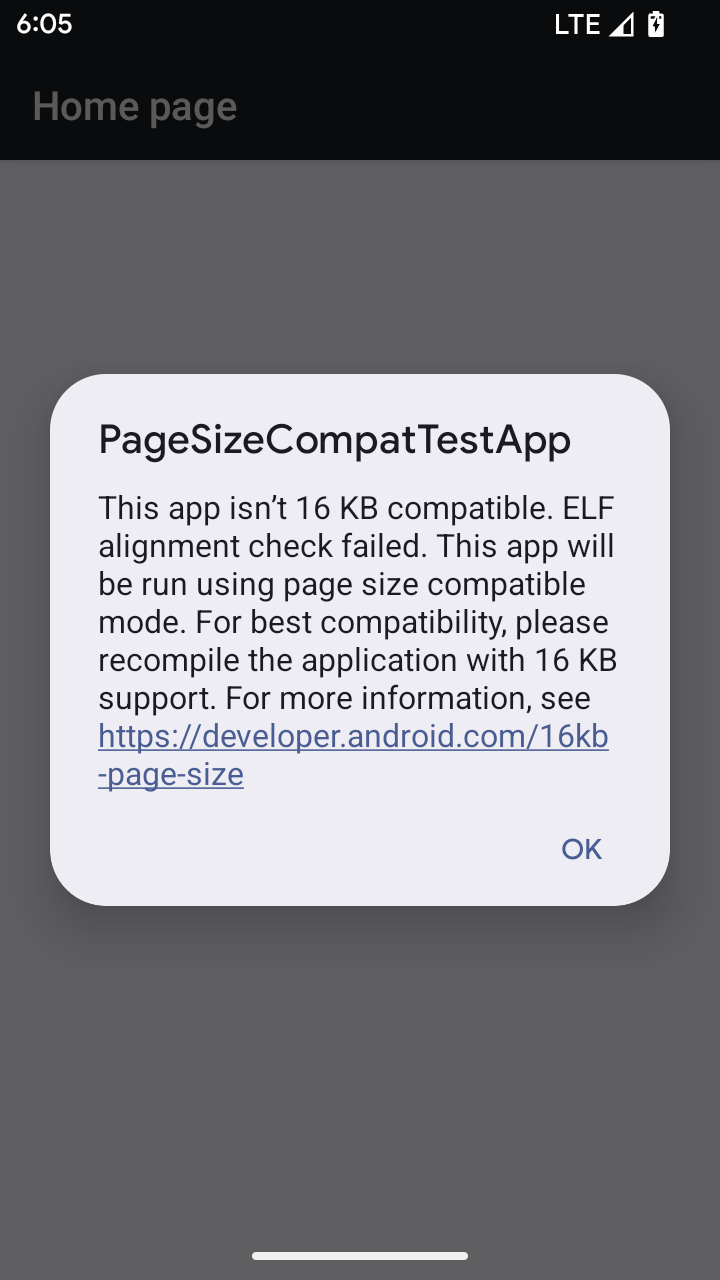
Modo de compatibilidad de tamaño de página de 16 KB
Android 15 introdujo la compatibilidad con páginas de memoria de 16 KB para optimizar el rendimiento de la plataforma. Android 16 agrega un modo de compatibilidad, lo que permite que algunas apps compiladas para páginas de memoria de 4 KB se ejecuten en un dispositivo configurado para páginas de memoria de 16 KB.
Cuando tu app se ejecuta en un dispositivo con Android 16 o versiones posteriores, si Android detecta que tu app tiene páginas de memoria alineadas de 4 KB, usa automáticamente el modo de compatibilidad y muestra un diálogo de notificación al usuario. Si configuras la
propiedad android:pageSizeCompat en AndroidManifest.xml para habilitar el
modo de compatibilidad con versiones anteriores, se evitará que se muestre el diálogo cuando se inicie
tu app. Para usar la propiedad android:pageSizeCompat, compila tu app con el SDK de Android 16.
Para obtener el mejor rendimiento, confiabilidad y estabilidad, tu app aún debe estar alineada en 16 KB. Consulta nuestra entrada de blog reciente sobre cómo actualizar tus apps para que admitan páginas de memoria de 16 KB y obtener más detalles.
Experiencia del usuario y la IU del sistema
Android 16 (nivel de API 36) incluye los siguientes cambios que tienen como objetivo crear una experiencia del usuario más coherente e intuitiva.
Se dieron de baja los anuncios de accesibilidad que interrumpen
Android 16 da de baja los anuncios de accesibilidad, que se caracterizan por el uso de announceForAccessibility o el envío de eventos de accesibilidad TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT. Esto puede crear experiencias del usuario incoherentes para los usuarios de TalkBack y el lector de pantalla de Android, y las alternativas satisfacen mejor una gama más amplia de necesidades de los usuarios en una variedad de tecnologías de accesibilidad de Android.
Ejemplos de alternativas:
- Para cambios significativos en la IU, como cambios de ventana, usa
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)ysetAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence). En Compose, usaModifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" }. - Para informar al usuario sobre los cambios en la IU crítica, usa
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int). En Compose, usaModifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}. Se deben usar con moderación, ya que pueden generar anuncios cada vez que se actualiza una vista. - Para notificar a los usuarios sobre errores, envía un
AccessibilityEventde tipoAccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORy estableceAccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence), o usaTextView#setError(CharSequence).
La documentación de referencia de la API de announceForAccessibility, que dejó de estar disponible, incluye más detalles sobre las alternativas sugeridas.
Compatibilidad con la navegación con 3 botones
Android 16 admite el gesto atrás predictivo en la navegación de 3 botones para las apps que migraron correctamente al gesto atrás predictivo. Si mantienes presionado el botón Atrás, se inicia una animación de atrás predictivo, que te brinda una vista previa de adónde te dirige el gesto de deslizar para volver.
Este comportamiento se aplica a todas las áreas del sistema que admiten animaciones de atrás predictivas, incluidas las animaciones del sistema (volver a la pantalla principal, cambiar de tarea y cambiar de actividad).
Íconos de apps temáticos automáticos
A partir de Android 16 QPR 2, Android aplica automáticamente temas a los íconos de las apps para crear una experiencia cohesiva en la pantalla principal. Esto sucede si una app no proporciona su propio ícono de app temático. Las apps pueden controlar el diseño de su ícono de app temático si incluyen una capa monocromática dentro de su ícono adaptable y obtienen una vista previa de la apariencia de su ícono de app en Android Studio.
Factores de forma del dispositivo
Android 16 (nivel de API 36) incluye los siguientes cambios para las apps cuando los propietarios de dispositivos virtuales las proyectan en pantallas.
Anulaciones del propietario del dispositivo virtual
El propietario de un dispositivo virtual es una app de confianza o privilegiada que crea y administra un dispositivo virtual. Los propietarios de dispositivos virtuales ejecutan apps en un dispositivo virtual y, luego, las proyectan en la pantalla de un dispositivo remoto, como una computadora personal, un dispositivo de realidad virtual o un sistema de infoentretenimiento para automóviles. El propietario del dispositivo virtual se encuentra en un dispositivo local, como un teléfono celular.
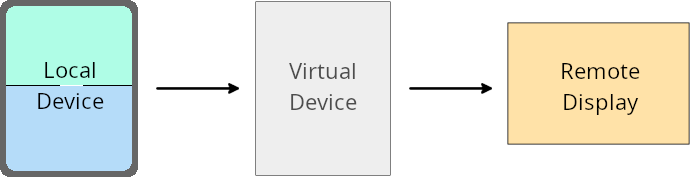
Anulaciones por app
En los dispositivos que ejecutan Android 16 (nivel de API 36), los propietarios de dispositivos virtuales pueden anular la configuración de las apps en dispositivos virtuales seleccionados que administran. Por ejemplo, para mejorar el diseño de la app, el propietario de un dispositivo virtual puede ignorar las restricciones de orientación, relación de aspecto y cambio de tamaño cuando proyecta apps en una pantalla externa.
Cambios rotundos comunes
El comportamiento de Android 16 podría afectar la IU de tu app en factores de forma de pantalla grande, como las pantallas de automóviles o las Chromebooks, en especial los diseños que se crearon para pantallas pequeñas en orientación vertical. Para obtener más información sobre cómo hacer que tu app sea adaptable a todos los factores de forma de los dispositivos, consulta Acerca de los diseños adaptables.
Referencias
Transmisión de apps complementarias
Seguridad
Android 16 (nivel de API 36) incluye cambios que promueven la seguridad del sistema para ayudar a proteger las apps y los usuarios de las apps maliciosas.
Mayor seguridad contra ataques de redireccionamiento de intents
Android 16 proporciona seguridad predeterminada contra ataques generales de redireccionamiento de Intent, con cambios mínimos de compatibilidad y para desarrolladores.
Incorporaremos soluciones de refuerzo de seguridad predeterminadas para los ataques de redireccionamiento de Intent. En la mayoría de los casos, las apps que usan intents no tendrán problemas de compatibilidad. Recopilamos métricas durante todo nuestro proceso de desarrollo para supervisar qué apps podrían tener interrupciones.
El redireccionamiento de intents en Android se produce cuando un atacante puede controlar de forma parcial o total el contenido de un intent que se usa para iniciar un componente nuevo en el contexto de una app vulnerable, mientras que la app víctima inicia un intent de nivel secundario no confiable en un campo de extras de un intent ("de nivel superior"). Esto puede provocar que la app del atacante inicie componentes privados en el contexto de la app de la víctima, que se activen acciones con privilegios o que se obtenga acceso a URI de datos sensibles, lo que podría provocar el robo de datos y la ejecución de código arbitrario.
Cómo inhabilitar el control del redireccionamiento de intents
Android 16 presenta una nueva API que permite que las apps inhabiliten las protecciones de seguridad de inicio. Esto puede ser necesario en casos específicos en los que el comportamiento de seguridad predeterminado interfiere con los casos de uso legítimos de la app.
Para las aplicaciones que se compilan con el SDK de Android 16 (nivel de API 36) o versiones posteriores
Puedes usar directamente el método removeLaunchSecurityProtection() en el objeto Intent.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
Para aplicaciones que se compilan en Android 15 (nivel de API 35) o versiones anteriores
Si bien no se recomienda, puedes usar la reflexión para acceder al método removeLaunchSecurityProtection().
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
Ya no se notifica a las apps complementarias sobre los tiempos de espera de detección
Android 16 presenta un nuevo comportamiento durante el flujo de vinculación de dispositivos complementarios para proteger la privacidad de la ubicación del usuario de las apps maliciosas. A todas las apps complementarias que se ejecutan en Android 16 ya no se les notifica directamente el tiempo de espera de descubrimiento con RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT. En su lugar, se le notifica al usuario sobre los eventos de tiempo de espera con un diálogo visual. Cuando el usuario descarta el diálogo, se alerta a la app sobre la falla de asociación con RESULT_USER_REJECTED.
La duración de la búsqueda también se extendió de los 20 segundos originales, y el usuario puede detener el descubrimiento de dispositivos en cualquier momento durante la búsqueda. Si se descubrió al menos un dispositivo en los primeros 20 segundos después de iniciar la búsqueda, el CDM deja de buscar dispositivos adicionales.
Conectividad
Android 16 (nivel de API 36) incluye los siguientes cambios en la pila de Bluetooth para mejorar la conectividad con dispositivos periféricos.
Se mejoró el manejo de la pérdida de vinculación
A partir de Android 16, se actualizó la pila de Bluetooth para mejorar la seguridad y la experiencia del usuario cuando se detecta una pérdida de vinculación remota. Anteriormente, el sistema quitaba automáticamente la vinculación e iniciaba un nuevo proceso de vinculación, lo que podía provocar una vinculación accidental. En muchos casos, observamos que las apps no se ocupan del evento de pérdida de vínculo de manera coherente.
Para unificar la experiencia, Android 16 mejoró el manejo de la pérdida de vinculación en el sistema. Si no se pudo autenticar un dispositivo Bluetooth vinculado anteriormente cuando se volvió a conectar, el sistema desconectará el vínculo, retendrá la información de vinculación local y mostrará un diálogo del sistema en el que se informará a los usuarios sobre la pérdida de vinculación y se les indicará que vuelvan a vincular el dispositivo.
