Android 16 bietet viele neue Funktionen und APIs für Entwickler. In den folgenden Abschnitten werden diese Funktionen zusammengefasst, um Ihnen den Einstieg in die zugehörigen APIs zu erleichtern.
Eine detaillierte Liste der neuen, geänderten und entfernten APIs finden Sie im API-Diff-Bericht. Details zu neuen APIs finden Sie in der Android-API-Referenz. Neue APIs sind zur besseren Übersichtlichkeit hervorgehoben.Sie sollten auch Bereiche prüfen, in denen sich Plattformänderungen auf Ihre Apps auswirken könnten. Weitere Informationen finden Sie auf den folgenden Seiten:
- Verhaltensänderungen, die sich auf Apps auswirken, wenn sie auf Android 16 ausgerichtet sind
- Verhaltensänderungen, die sich unabhängig von
targetSdkVersionauf alle Apps auswirken
Hauptfunktion
Android umfasst neue APIs, die die Kernfunktionen des Android-Systems erweitern.
Zwei Android-API-Releases im Jahr 2025
- This preview is for the next major release of Android with a planned launch in Q2 of 2025. This release is similar to all of our API releases in the past, where we can have planned behavior changes that are often tied to a targetSdkVersion.
- We're planning the major release a quarter earlier (Q2 rather than Q3 in prior years) to better align with the schedule of device launches across our ecosystem, so more devices can get the major release of Android sooner. With the major release coming in Q2, you'll need to do your annual compatibility testing a few months earlier than in previous years to make sure your apps are ready.
- We plan to have another release in Q4 of 2025 which also will include new developer APIs. The Q2 major release will be the only release in 2025 to include planned behavior changes that could affect apps.
In addition to new developer APIs, the Q4 minor release will pick up feature updates, optimizations, and bug fixes; it will not include any app-impacting behavior changes.
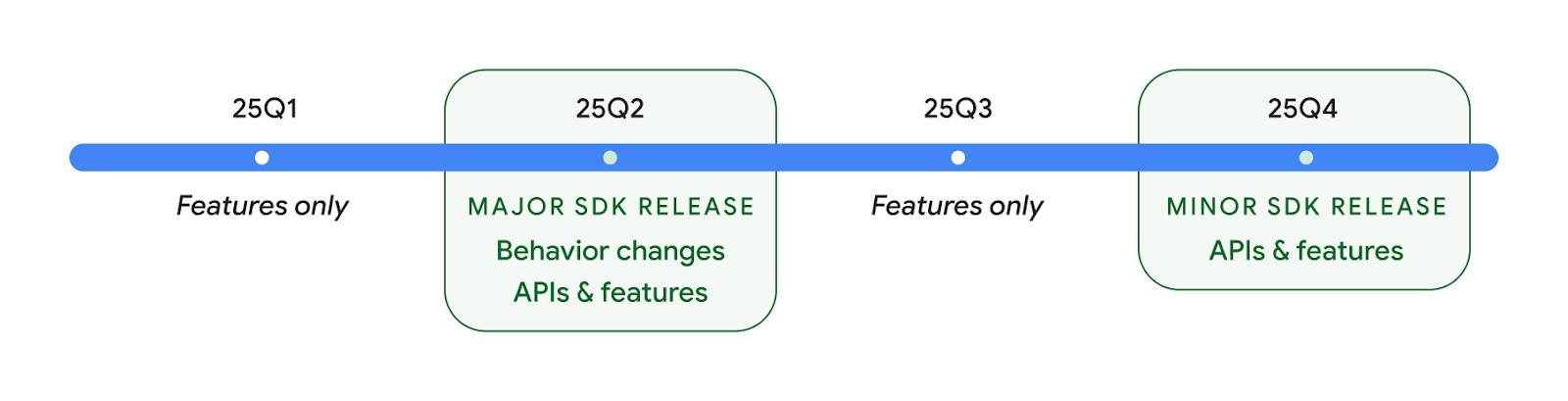
We'll continue to have quarterly Android releases. The Q1 and Q3 updates in-between the API releases will provide incremental updates to help ensure continuous quality. We're actively working with our device partners to bring the Q2 release to as many devices as possible.
Using new APIs with major and minor releases
Guarding a code block with a check for API level is done today using
the SDK_INT constant with
VERSION_CODES. This will continue
to be supported for major Android releases.
if (SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.BAKLAVA) {
// Use APIs introduced in Android 16
}
The new SDK_INT_FULL
constant can be used for API checks against both major and minor versions with
the new VERSION_CODES_FULL
enumeration.
if (SDK_INT_FULL >= VERSION_CODES_FULL.[MAJOR or MINOR RELEASE]) {
// Use APIs introduced in a major or minor release
}
You can also use the
Build.getMinorSdkVersion()
method to get just the minor SDK version.
val minorSdkVersion = Build.getMinorSdkVersion(VERSION_CODES_FULL.BAKLAVA)
These APIs have not yet been finalized and are subject to change, so please send us feedback if you have any concerns.
User Experience und System-UI
Android 16 bietet App-Entwicklern und Nutzern mehr Kontrolle und Flexibilität bei der Konfiguration ihrer Geräte.
Fortschrittsbasierte Benachrichtigungen
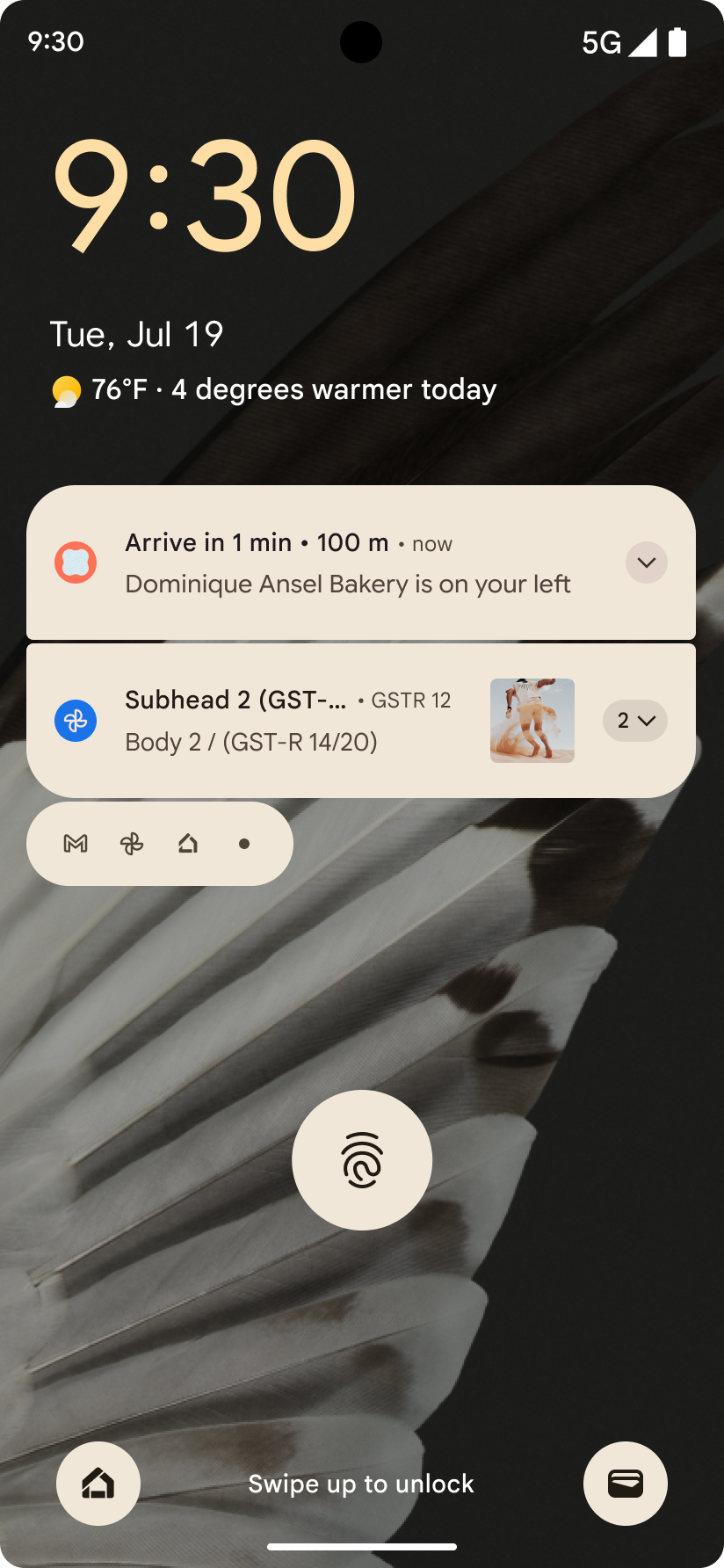
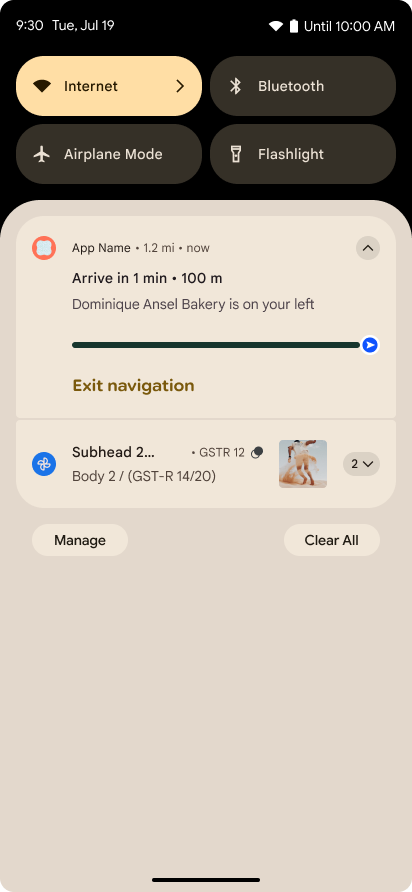
Android 16 引入了以进度为中心的通知,可帮助用户顺畅地跟踪用户发起的端到端历程。
Notification.ProgressStyle 是一种新的通知样式,可让您创建以进度为中心的通知。主要用例包括共享车辆、送货和导航。在 Notification.ProgressStyle 类中,您可以使用点和细分来表示用户体验历程中的状态和里程碑。
如需了解详情,请参阅以进度为中心的通知文档页面。
Updates für die intelligente „Zurück“-Geste
Android 16 adds new APIs to help you enable predictive back system animations in
gesture navigation such as the back-to-home animation. Registering the
onBackInvokedCallback with the new
PRIORITY_SYSTEM_NAVIGATION_OBSERVER allows your app to
receive the regular onBackInvoked call whenever the
system handles a back navigation without impacting the normal back navigation
flow.
Android 16 additionally adds the
finishAndRemoveTaskCallback() and
moveTaskToBackCallback. By registering these callbacks
with the OnBackInvokedDispatcher, the system can trigger
specific behaviors and play corresponding ahead-of-time animations when the back
gesture is invoked.
Detailliertere Haptik
自诞生之日起,Android 就提供了对触感反馈致动器的控制。
Android 11 添加了对更复杂的触感反馈效果的支持,更高级的致动器可以通过设备定义的语义基元 VibrationEffect.Compositions 支持这些效果。
Android 16 添加了触感反馈 API,让应用能够定义触感反馈效果的振幅和频率曲线,同时抽象出设备功能之间的差异。
Produktivität von Entwicklern und Tools
Die meisten unserer Bemühungen zur Steigerung Ihrer Produktivität konzentrieren sich auf Tools wie Android Studio, Jetpack Compose und die Android Jetpack-Bibliotheken. Wir suchen aber auch immer nach Möglichkeiten, Sie auf der Plattform bei der Umsetzung Ihrer Vision zu unterstützen.
Umgang mit Inhalten für Live-Hintergründe
在 Android 16 中,动态壁纸框架将获得一个新的 content API,以应对由用户驱动的动态壁纸带来的挑战。目前,包含用户提供的内容的实时壁纸需要复杂的服务专用实现。Android 16 引入了 WallpaperDescription 和 WallpaperInstance。借助 WallpaperDescription,您可以识别同一服务中的动态壁纸的不同实例。例如,如果某张壁纸同时在主屏幕和锁定屏幕上显示,则这两种情况下显示的内容可能各不相同。壁纸选择器和 WallpaperManager 会使用此元数据更好地向用户呈现壁纸,从而简化创建多样化个性化动态壁纸体验的过程。
Leistung und Akku
Mit Android 16 werden APIs eingeführt, mit denen Sie Informationen zu Ihren Apps sammeln können.
Vom System ausgelöstes Profiling
ProfilingManager wurde in Android 15 hinzugefügt. Damit können Apps die Erhebung von Profilierungsdaten mit Perfetto auf öffentlichen Geräten vor Ort anfordern.
Da dieses Profiling jedoch von der App gestartet werden muss, können kritische Abläufe wie Starts oder ANRs von Apps nur schwer oder gar nicht erfasst werden.
Dazu wird in Android 16 das systemgetriggerte Profiling für ProfilingManager eingeführt. Apps können angeben, dass sie Protokolle für bestimmte Trigger wie Kaltstarts reportFullyDrawn oder ANRs erhalten möchten. Das System startet und beendet dann im Namen der App ein Protokoll. Nach Abschluss der Aufzeichnung werden die Ergebnisse an das Datenverzeichnis der App gesendet.
Startkomponente in ApplicationStartInfo
ApplicationStartInfo 在 Android 15 中添加,可让应用查看进程启动原因、启动类型、启动时间、节流和其他实用诊断数据。Android 16 添加了 getStartComponent(),用于区分触发启动的组件类型,这有助于优化应用的启动流程。
Bessere Job-Introspektion
Die JobScheduler#getPendingJobReason() API gibt einen Grund zurück, warum ein Job möglicherweise ausstehend ist. Es kann jedoch mehrere Gründe dafür geben, dass ein Job ausstehend ist.
In Android 16 führen wir die neue API JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasons(int jobId) ein, die mehrere Gründe zurückgibt, warum ein Job aussteht, sowohl aufgrund expliziter Einschränkungen, die vom Entwickler festgelegt wurden, als auch aufgrund impliziter Einschränkungen, die vom System festgelegt wurden.
Außerdem führen wir JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory(int jobId) ein, mit dem eine Liste der letzten Änderungen an Einschränkungen zurückgegeben wird.
Wir empfehlen, die API zu verwenden, um herauszufinden, warum Ihre Jobs möglicherweise nicht ausgeführt werden. Das gilt insbesondere, wenn die Erfolgsrate bestimmter Aufgaben sinkt oder es Probleme mit der Latenz bei der Ausführung bestimmter Jobs gibt. Beispielsweise wurde die Aktualisierung von Widgets im Hintergrund nicht durchgeführt oder der Prefetch-Job wurde vor dem Start der App nicht aufgerufen.
So können Sie besser nachvollziehen, ob bestimmte Jobs aufgrund von systemdefinierten oder explizit festgelegten Einschränkungen nicht abgeschlossen werden.
Adaptive Aktualisierungsrate
Adaptive refresh rate (ARR), introduced in Android 15, enables the display refresh rate on supported hardware to adapt to the content frame rate using discrete VSync steps. This reduces power consumption while eliminating the need for potentially jank-inducing mode-switching.
Android 16 introduces hasArrSupport() and
getSuggestedFrameRate(int) while restoring
getSupportedRefreshRates() to make it easier for your apps to take
advantage of ARR. RecyclerView
1.4 internally supports ARR when it is settling from a fling or
smooth scroll, and we're continuing our work to add ARR
support into more Jetpack libraries. This frame rate article covers
many of the APIs you can use to set the frame rate so that your app can directly
use ARR.
Headroom-APIs in ADPF
The SystemHealthManager introduces the
getCpuHeadroom and
getGpuHeadroom APIs, designed to provide games and
resource-intensive apps with estimates of available CPU and GPU resources. These
methods offer a way for you to gauge how your app or game can best improve
system health, particularly when used in conjunction with other Android Dynamic
Performance Framework (ADPF) APIs that detect thermal
throttling.
By using CpuHeadroomParams and
GpuHeadroomParams on supported devices, you can
customize the time window used to compute the headroom and select between
average or minimum resource availability. This can help you reduce your CPU or
GPU resource usage accordingly, leading to better user experiences and improved
battery life.
Bedienungshilfen
Android 16 bietet neue Accessibility APIs und Funktionen, mit denen Sie Ihre App für alle Nutzer zugänglich machen können.
Verbesserte APIs für Bedienungshilfen
Android 16 添加了其他 API 来增强界面语义,这有助于为依赖于无障碍服务(例如 TalkBack)的用户提高一致性。
为文字添加轮廓,以最大限度地提高文字对比度
视力较低的用户对对比度的敏感度通常较低,因此很难将对象与背景区分开来。为了帮助这些用户,Android 16 引入了轮廓文本,取代了高对比度文本,后者会在文本周围绘制较大的对比度区域,以大大提高可辨性。
Android 16 包含新的 AccessibilityManager API,可让您的应用检查或注册监听器,以查看此模式是否已启用。这主要适用于 Compose 等界面工具包,以提供类似的视觉体验。如果您维护界面工具包库,或者您的应用执行绕过 android.text.Layout 类的自定义文本渲染,则可以使用此方法来了解何时启用轮廓文本。
向 TtsSpan 添加了时长
Android 16 使用 TYPE_DURATION 扩展了 TtsSpan,其中包含 ARG_HOURS、ARG_MINUTES 和 ARG_SECONDS。这样,您就可以直接为时长添加注释,确保通过 TalkBack 等服务获得准确且一致的文本转语音输出。
支持具有多个标签的元素
Android 目前允许界面元素从其他元素派生其无障碍功能标签,现在还支持关联多个标签,这是 Web 内容中常见的情况。通过在 AccessibilityNodeInfo 中引入基于列表的 API,Android 可以直接支持这些多标签关系。在进行这项更改的过程中,我们已弃用 AccessibilityNodeInfo#setLabeledBy 和 #getLabeledBy,改用 #addLabeledBy、#removeLabeledBy 和 #getLabeledByList。
改进了对可展开元素的支持
Android 16 添加了无障碍功能 API,可让您传达互动元素(例如菜单和展开式列表)的展开或收起状态。通过使用 setExpandedState 设置展开状态,并使用 CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_EXPANDED 内容更改类型调度 TYPE_WINDOW_CONTENT_CHANGED AccessibilityEvents,您可以确保 TalkBack 等屏幕阅读器会读出状态更改,从而提供更直观、更包容的用户体验。
不确定进度条
Android 16 添加了 RANGE_TYPE_INDETERMINATE,让您可以为确定性和不确定性 ProgressBar 微件公开 RangeInfo,从而让 TalkBack 等服务能够更一致地为进度指示器提供反馈。
三态复选框
Android 16 中的新 AccessibilityNodeInfo
getChecked 和 setChecked(int) 方法现在除了“已选中”和“未选中”之外,还支持“部分选中”状态。此字段取代了已废弃的布尔值 isChecked 和 setChecked(boolean)。
补充说明
如果无障碍服务提供关于 ViewGroup 的说明,则会将来自其子视图的内容标签合并在一起。如果您为 ViewGroup 提供 contentDescription,无障碍服务会假定您还要覆盖不可聚焦的子视图的说明。如果您想为下拉菜单等内容添加标签(例如“字体系列”),同时保留当前的无障碍功能选择(例如“Roboto”),这可能会造成问题。Android 16 添加了 setSupplementalDescription,以便您提供用于提供 ViewGroup 相关信息的文本,而不会覆盖其子项中的信息。
必填表单字段
Android 16 向 AccessibilityNodeInfo 添加了 setFieldRequired,以便应用可以告知无障碍服务需要输入表单字段。对于填写各种类型表单的用户而言,这是一个重要的场景,即使是简单的必填条款及条件复选框,也能帮助用户始终如一地识别必填字段并在必填字段之间快速导航。
Smartphone als Mikrofoneingabe für Sprachanrufe mit LEA-Hörgeräten
Mit Android 16 können Nutzer von LE Audio-Hörgeräten für Sprachanrufe zwischen den integrierten Mikrofonen der Hörgeräte und dem Mikrofon auf ihrem Smartphone wechseln. Das kann in lauten Umgebungen oder anderen Situationen hilfreich sein, in denen die Mikrofone des Hörgeräts möglicherweise nicht optimal funktionieren.
Einstellungen für die Umgebungslautstärke für Hörgeräte mit LEA
Android 16 新增了一项功能,可让 LE Audio 助听器用户调节助听器麦克风接收的环境声音的音量。在背景噪音过大或过小的情况下,这可能会很有用。
Kamera
Android 16 bietet eine verbesserte Unterstützung für professionelle Kameranutzer und ermöglicht die Hybrid-Auto-Belichtung sowie präzise Anpassungen von Farbtemperatur und Farbton. Ein neuer Nachtmodus-Indikator hilft Ihrer App, zu erkennen, wann sie in eine Kamerasitzung im Nachtmodus wechseln und wann sie diese beenden sollte. Neue Intent-Aktionen erleichtern das Aufnehmen von Bewegungsfotos. Außerdem verbessern wir UltraHDR-Bilder weiter, indem wir die HEIC-Codierung und neue Parameter aus dem ISO 21496-1-Entwurf unterstützen.
Hybride automatische Belichtung
Android 16 fügt Camera2 neue hybride Autofokusmodi hinzu, mit denen Sie bestimmte Aspekte der Belichtung manuell steuern können, während der Autofokusalgorithmus (AE) den Rest übernimmt. Sie können ISO + AE und Belichtungszeit + AE steuern. Das bietet mehr Flexibilität als der aktuelle Ansatz, bei dem Sie entweder die volle manuelle Kontrolle haben oder sich vollständig auf die automatische Belichtung verlassen.
fun setISOPriority() {
// ... (Your existing code before the snippet) ...
val availablePriorityModes = mStaticInfo.characteristics.get(
CameraCharacteristics.CONTROL_AE_AVAILABLE_PRIORITY_MODES
)
// ... (Your existing code between the snippets) ...
// Turn on AE mode to set priority mode
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE_SENSOR_SENSITIVITY_PRIORITY
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.SENSOR_SENSITIVITY,
TEST_SENSITIVITY_VALUE
)
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after the snippet) ...
}
Genaue Anpassung von Farbtemperatur und Farbton
Android 16 adds camera support for fine color temperature and tint adjustments
to better support professional video recording applications. In previous Android
versions, you could control white balance settings through
CONTROL_AWB_MODE, which contains options limited to a
preset list, such as Incandescent,
Cloudy, and Twilight. The
COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT enables the use of
COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE and
COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT for precise adjustments of
white balance based on the correlated color temperature.
fun setCCT() {
// ... (Your existing code before this point) ...
val colorTemperatureRange: Range<Int> =
mStaticInfo.characteristics[CameraCharacteristics.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE_RANGE]
// Set to manual mode to enable CCT mode
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AWB_MODE] = CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AWB_MODE_OFF
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE] = CameraMetadata.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE] = 5000
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT] = 30
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after this point) ...
}
The following examples show how a photo would look after applying different color temperature and tint adjustments:





Szenenerkennung im Nachtmodus der Kamera
To help your app know when to switch to and from a night mode camera session,
Android 16 adds EXTENSION_NIGHT_MODE_INDICATOR. If
supported, it's available in the CaptureResult within
Camera2.
This is the API we briefly mentioned as coming soon in the How Instagram enabled users to take stunning low light photos blog post. That post is a practical guide on how to implement night mode together with a case study that links higher-quality in-app night mode photos with an increase in the number of photos shared from the in-app camera.
Intent-Aktionen für die Aufnahme von Fotos mit Bewegtbild
Android 16 添加了标准 intent 操作 ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE 和 ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE_SECURE,用于请求相机应用拍摄动态照片并将其返回。
您必须传递额外的 EXTRA_OUTPUT 来控制将图片写入的位置,或者通过 Intent.setClipData(ClipData) 传递 Uri。如果您未设置 ClipData,系统会在调用 Context.startActivity(Intent) 时将其复制到该位置。
Ultra HDR-Bildoptimierung

Mit Android 16 setzen wir unsere Bemühungen fort, mit Ultra-HDR-Bildern eine beeindruckende Bildqualität zu bieten. Es wird die Unterstützung für Ultra-HDR-Bilder im HEIC-Dateiformat hinzugefügt. Diese Bilder erhalten den Typ ImageFormat HEIC_ULTRAHDR und enthalten eine eingebettete Verstärkungskarte, ähnlich wie das vorhandene UltraHDR-JPEG-Format. Wir arbeiten auch an der AVIF-Unterstützung für UltraHDR. Mehr dazu demnächst.
Außerdem werden in Android 16 zusätzliche Parameter in UltraHDR aus dem ISO 21496-1-Entwurfsstandard implementiert. Dazu gehören die Möglichkeit, den Farbraum abzurufen und festzulegen, in dem die Gainmap-Berechnung angewendet werden soll, sowie die Unterstützung für HDR-codierte Basisbilder mit SDR-Gainmaps.
Grafik
Android 16 bietet die neuesten Grafikverbesserungen, z. B. benutzerdefinierte Grafikeffekte mit AGSL.
Benutzerdefinierte grafische Effekte mit AGSL
Android 16 adds RuntimeColorFilter and
RuntimeXfermode, allowing you to author complex effects like
Threshold, Sepia, and Hue Saturation and apply them to draw calls. Since Android
13, you've been able to use AGSL to create custom
RuntimeShaders that extend Shader. The new API
mirrors this, adding an AGSL-powered RuntimeColorFilter that
extends ColorFilter, and a Xfermode effect that
lets you implement AGSL-based custom compositing and blending between source and
destination pixels.
private val thresholdEffectString = """
uniform half threshold;
half4 main(half4 c) {
half luminosity = dot(c.rgb, half3(0.2126, 0.7152, 0.0722));
half bw = step(threshold, luminosity);
return bw.xxx1 * c.a;
}"""
fun setCustomColorFilter(paint: Paint) {
val filter = RuntimeColorFilter(thresholdEffectString)
filter.setFloatUniform(0.5);
paint.colorFilter = filter
}
Konnektivität
Mit Android 16 wird die Plattform aktualisiert, damit Ihre App Zugriff auf die neuesten Fortschritte in der Kommunikations- und Funktechnologie hat.
Entfernungsmessung mit erweiterter Sicherheit
Android 16 adds support for robust security features in Wi-Fi location on supported devices with Wi-Fi 6's 802.11az, allowing apps to combine the higher accuracy, greater scalability, and dynamic scheduling of the protocol with security enhancements including AES-256-based encryption and protection against MITM attacks. This allows it to be used more safely in proximity use cases, such as unlocking a laptop or a vehicle door. 802.11az is integrated with the Wi-Fi 6 standard, leveraging its infrastructure and capabilities for wider adoption and easier deployment.
Allgemeine APIs für die Reichweite
Android 16 enthält das neue Symbol RangingManager, mit dem sich auf unterstützter Hardware die Entfernung und der Winkel zwischen dem lokalen Gerät und einem Remote-Gerät bestimmen lassen. RangingManager unterstützt die Verwendung verschiedener Technologien zur Entfernungsmessung wie BLE-Kanalabfrage, BLE-RSSI-basierte Entfernungsmessung, Ultrabreitband und WLAN-Rücklaufzeit.
Gerätepräsenz im Begleitgerätemanager
In Android 16, new APIs are being introduced for binding your companion app
service. Service will be bound when BLE is in range and Bluetooth is connected
and service will be unbound when BLE is out of range or Bluetooth is
disconnected. App will receives a new
'onDevicePresenceEvent()' callback based on various
of DevicePresenceEvent.
More details can be found in
'startObservingDevicePresence(ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)'.
Medien
Android 16 bietet eine Vielzahl von Funktionen, die die Medienwiedergabe verbessern.
Verbesserungen bei der Bildauswahl
The photo picker provides a safe, built-in way for users to grant your app access to selected images and videos from both local and cloud storage, instead of their entire media library. Using a combination of Modular System Components through Google System Updates and Google Play services, it's supported back to Android 4.4 (API level 19). Integration requires just a few lines of code with the associated Android Jetpack library.
Android 16 includes the following improvements to the photo picker:
- Embedded photo picker: New APIs that enable apps to embed the photo picker into their view hierarchy. This allows it to feel like a more integrated part of the app while still leveraging the process isolation that allows users to select media without the app needing overly broad permissions. To maximize compatibility across platform versions and simplify your integration, you'll want to use the forthcoming Android Jetpack library if you want to integrate the embedded photo picker.
- Cloud search in photo picker: New APIs that enable searching from the cloud media provider for the Android photo picker. Search functionality in the photo picker is coming soon.
Erweiterte professionelle Videoinhalte
Android 16 introduces support for the Advanced Professional Video (APV) codec which is designed to be used for professional level high quality video recording and post production.
The APV codec standard has the following features:
- Perceptually lossless video quality (close to raw video quality)
- Low complexity and high throughput intra-frame-only coding (without pixel domain prediction) to better support editing workflows
- Support for high bit-rate range up to a few Gbps for 2K, 4K and 8K resolution content, enabled by a lightweight entropy coding scheme
- Frame tiling for immersive content and for enabling parallel encoding and decoding
- Support for various chroma sampling formats and bit-depths
- Support for multiple decoding and re-encoding without severe visual quality degradation
- Support multi-view video and auxiliary video like depth, alpha, and preview
- Support for HDR10/10+ and user-defined metadata
A reference implementation of APV is provided through the OpenAPV project. Android 16 will implement support for the APV 422-10 Profile that provides YUV 422 color sampling along with 10-bit encoding and for target bitrates of up to 2Gbps.
Datenschutz
Android 16 enthält eine Vielzahl von Funktionen, die App-Entwicklern helfen, den Datenschutz der Nutzer zu schützen.
Health Connect-Updates
Health Connect adds ACTIVITY_INTENSITY, a data type defined according to World
Health Organization guidelines around moderate and vigorous activity. Each
record requires the start time, the end time, and whether the activity intensity
is moderate or vigorous.
Health Connect also contains updated APIs supporting medical records. This allows apps to read and write medical records in FHIR format with explicit user consent.
Privacy Sandbox für Android
Android 16 incorporates the latest version of the Privacy Sandbox on Android, part of our ongoing work to develop technologies where users know their privacy is protected. Our website has more about the Privacy Sandbox on Android developer beta program to help you get started. Check out the SDK Runtime which allows SDKs to run in a dedicated runtime environment separate from the app they are serving, providing stronger safeguards around user data collection and sharing.
Sicherheit
Android 16 enthält Funktionen, mit denen Sie die Sicherheit Ihrer App verbessern und die Daten Ihrer App schützen können.
API zum Teilen von Schlüsseln
Android 16 adds APIs that support sharing access to
Android Keystore keys with other apps. The new
KeyStoreManager class supports
granting and revoking access to keys
by app uid, and includes an API for apps to access shared
keys.
Formfaktoren von Geräten
Android 16 bietet Ihren Apps die Unterstützung, die sie benötigen, um die Formfaktoren von Android optimal zu nutzen.
Standardisiertes Framework für Bild- und Audioqualität für Fernseher
Das neue MediaQuality-Paket in Android 16 stellt eine Reihe standardisierter APIs für den Zugriff auf Audio- und Bildprofile sowie hardwarebezogene Einstellungen bereit. So können Streaming-Apps Profile abfragen und dynamisch auf Medien anwenden:
- Filme, die mit einem größeren dynamischen Bereich gemastert wurden, erfordern eine höhere Farbgenauigkeit, um feine Details in Schatten zu erkennen und sich an das Umgebungslicht anzupassen. Daher kann ein Profil geeignet sein, bei dem die Farbgenauigkeit der Helligkeit vorgezogen wird.
- Live-Sportveranstaltungen werden oft mit einem schmalen dynamischen Bereich gemastert, werden aber häufig bei Tageslicht angesehen. Daher kann ein Profil, bei dem die Helligkeit gegenüber der Farbrichtigkeit bevorzugt wird, bessere Ergebnisse liefern.
- Für vollständig interaktive Inhalte ist eine minimale Verarbeitung erforderlich, um die Latenz zu reduzieren, und es werden höhere Frameraten benötigt. Aus diesem Grund sind viele Fernseher mit einem Spielprofil ausgestattet.
Mit der API können Apps zwischen Profilen wechseln und Nutzer können unterstützte Fernseher so einstellen, dass sie am besten zu ihren Inhalten passen.
Lokalisierung
Android 16 bietet Funktionen und Möglichkeiten, die die Nutzerfreundlichkeit verbessern, wenn ein Gerät in verschiedenen Sprachen verwendet wird.
Vertikaler Text
Android 16 添加了对垂直渲染和测量文本的低级支持,以便为库开发者提供基本的垂直书写支持。这对于日语等通常使用竖向书写系统的语言特别有用。Paint 类中添加了一个新标志 VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG。使用 Paint.setFlags 设置此标志后,Paint 的文本测量 API 将报告垂直进度,而不是水平进度,并且 Canvas 将垂直绘制文本。
val text = "「春は、曙。」"
Box(
Modifier.padding(innerPadding).background(Color.White).fillMaxSize().drawWithContent {
drawIntoCanvas { canvas ->
val paint = Paint().apply { textSize = 64.sp.toPx() }
// Draw text vertically
paint.flags = paint.flags or VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG
val height = paint.measureText(text)
canvas.nativeCanvas.drawText(
text,
0,
text.length,
size.width / 2,
(size.height - height) / 2,
paint
)
}
}
) {}
Messsystem anpassen
Nutzer können das Maßsystem jetzt in den regionalen Einstellungen unter „Einstellungen“ anpassen. Die Nutzereinstellung ist Teil des Gebietscodes. Sie können also eine BroadcastReceiver unter ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED registrieren, um Änderungen an der Gebietskonfiguration zu verarbeiten, wenn sich die regionalen Einstellungen ändern.
Mit Formatierungsoptionen können Sie die Inhalte an die jeweilige Region anpassen. „0,5 in“ auf Englisch (USA) entspricht beispielsweise „12,7 mm“ für einen Nutzer,der sein Smartphone auf Englisch (Dänemark) eingestellt hat oder sein Smartphone auf Englisch (USA) mit dem metrischen System als bevorzugtem Maßsystem verwendet.
Öffnen Sie dazu die Einstellungen und gehen Sie zu System > Sprache und Region.
