O Android 16 introduz ótimos recursos e APIs novos para desenvolvedores. As seções a seguir resumem esses recursos para ajudar você a começar a usar as APIs relacionadas.
Para uma lista detalhada das APIs novas, modificadas e removidas, leia o Relatório de diferenças da API. Para ver detalhes sobre as novas APIs, acesse a Referência da API do Android. As APIs novas estão em destaque para melhor visibilidade.Você também precisa analisar as áreas em que as mudanças na plataforma podem afetar seus apps. Para mais informações, consulte as seguintes páginas:
- Mudanças de comportamento que afetam apps destinados ao Android 16
- Mudanças de comportamento que afetam todos os apps, independentemente da
targetSdkVersion.
Principal recurso
O Android inclui novas APIs que expandem os recursos principais do sistema Android.
Dois lançamentos de API do Android em 2025
- Esta visualização é para a próxima versão principal do Android, com lançamento previsto no segundo trimestre de 2025. Esta versão é semelhante a todas as versões de API do passado, em que podemos ter mudanças de comportamento planejadas que geralmente são vinculadas a uma targetSdkVersion.
- Estamos planejando o lançamento principal um trimestre antes (segundo trimestre em vez do terceiro trimestre em anos anteriores) para alinhar melhor com a programação de lançamentos de dispositivos em todo o ecossistema, para que mais dispositivos possam receber a versão principal do Android mais cedo. Com o lançamento principal no segundo trimestre, você precisará fazer o teste anual de compatibilidade alguns meses antes do que nos anos anteriores para garantir que seus apps estão prontos.
- Planejamos lançar outra versão no 4º trimestre de 2025, que também vai incluir novas APIs para desenvolvedores. A versão principal do segundo trimestre será a única em 2025 a incluir mudanças de comportamento planejadas que podem afetar apps.
Além das novas APIs para desenvolvedores, a versão secundária do Q4 vai incluir atualizações de recursos, otimizações e correções de bugs. Ela não vai incluir mudanças de comportamento que afetam o app.
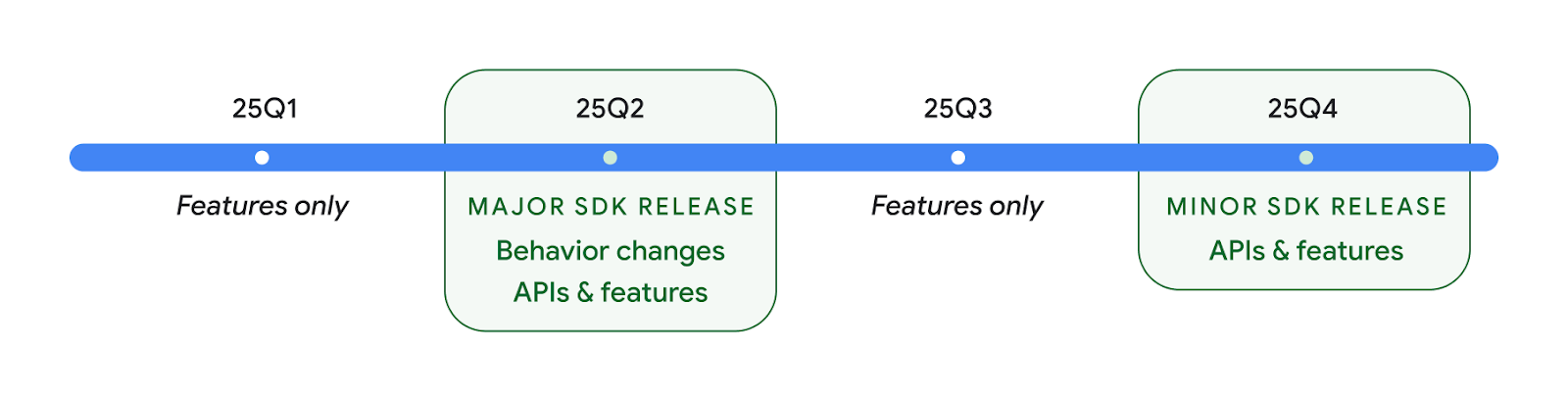
Vamos continuar lançando versões do Android trimestralmente. As atualizações do Q1 e do Q3 entre as versões da API vão oferecer atualizações incrementais para ajudar a garantir qualidade contínua. Estamos trabalhando ativamente com nossos parceiros de dispositivos para disponibilizar a versão do segundo trimestre no maior número possível de dispositivos.
Como usar novas APIs com versões principais e secundárias
Hoje, a proteção de um bloco de código com uma verificação do nível da API é feita usando
a constante SDK_INT com
VERSION_CODES. Esse suporte
vai continuar sendo oferecido para as principais versões do Android.
if (SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.BAKLAVA) {
// Use APIs introduced in Android 16
}
A nova constante SDK_INT_FULL
pode ser usada para verificações de API em relação a versões principais e secundárias com
a nova enumeração VERSION_CODES_FULL.
if (SDK_INT_FULL >= VERSION_CODES_FULL.[MAJOR or MINOR RELEASE]) {
// Use APIs introduced in a major or minor release
}
Você também pode usar o método
Build.getMinorSdkVersion()
para acessar apenas a versão secundária do SDK.
val minorSdkVersion = Build.getMinorSdkVersion(VERSION_CODES_FULL.BAKLAVA)
Essas APIs ainda não foram finalizadas e estão sujeitas a alterações. Envie feedback se tiver alguma dúvida.
Experiência do usuário e interface do sistema
O Android 16 oferece aos desenvolvedores de apps e usuários mais controle e flexibilidade para configurar o dispositivo de acordo com as necessidades.
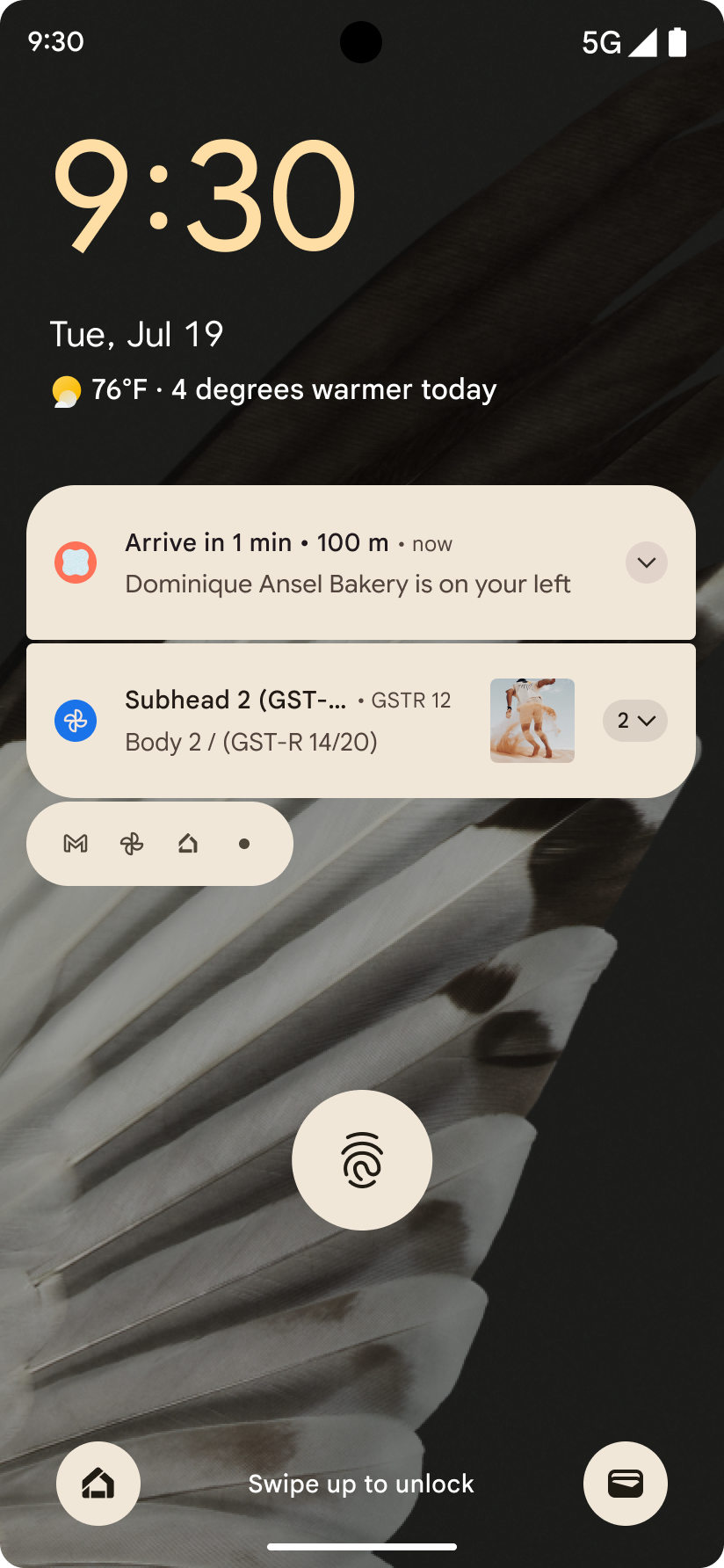
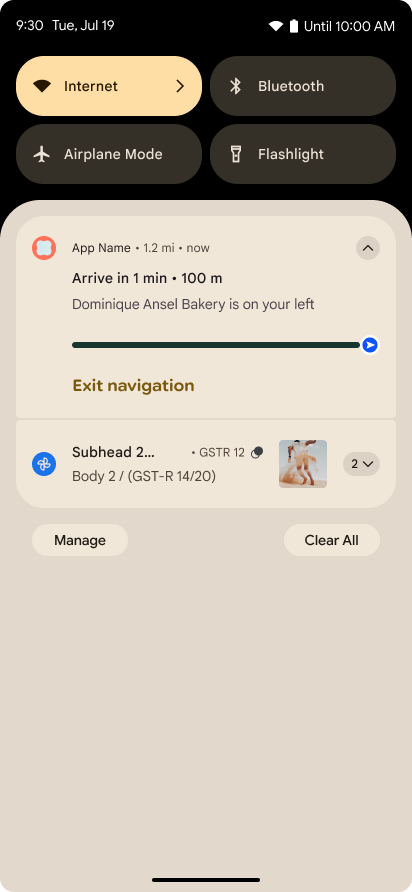
Notificações focadas no progresso
O Android 16 apresenta notificações com foco no progresso para ajudar os usuários a acompanhar as jornadas iniciadas pelo usuário do início ao fim.
Notification.ProgressStyle é um novo estilo
de notificação que permite criar notificações com foco no progresso. Os principais casos de uso incluem
compartilhamento de viagens, entrega e navegação. Na classe Notification.ProgressStyle, é possível denotar estados e marcos em uma jornada do usuário usando
pontos e segmentos.
Para saber mais, consulte a página de documentação Notificações centradas no progresso.
Atualizações da volta preditiva
O Android 16 adiciona novas APIs para ajudar a ativar animações de volta preditiva do sistema na
navegação por gestos, como a animação de volta à tela inicial. Registrar o
onBackInvokedCallback com o novo
PRIORITY_SYSTEM_NAVIGATION_OBSERVER permite que o app
receba a chamada onBackInvoked normal sempre que o
sistema processa uma navegação de retorno sem afetar o fluxo normal de navegação
de retorno.
O Android 16 também adiciona o
finishAndRemoveTaskCallback() e o
moveTaskToBackCallback. Ao registrar esses callbacks
com o OnBackInvokedDispatcher, o sistema pode acionar
comportamentos específicos e reproduzir animações antecipadas correspondentes quando o gesto
de voltar é invocado.
Retorno tátil mais avançado
O Android expõe o controle do atuador háptico desde o início.
O Android 11 adicionou suporte a efeitos hápticos mais complexos que atuadores
mais avançados podem oferecer com
VibrationEffect.Compositions de primitivas semânticas
definidas pelo dispositivo.
O Android 16 adiciona APIs hápticas que permitem que os apps definam as curvas de amplitude e frequência de um efeito háptico, abstraindo as diferenças entre os recursos do dispositivo.
Produtividade e ferramentas para desenvolvedores
Embora a maior parte do nosso trabalho para melhorar sua produtividade se concentre em ferramentas como o Android Studio, o Jetpack Compose e as bibliotecas do Android Jetpack, sempre buscamos maneiras na plataforma de ajudar você a realizar sua visão.
Processamento de conteúdo para planos de fundo interativos
No Android 16, o framework de plano de fundo interativo está recebendo uma nova API de conteúdo para
resolver os desafios de planos de fundo dinâmicos e orientados pelo usuário. Atualmente, os planos de fundo
dinâmicos que incorporam conteúdo fornecido pelo usuário exigem implementações complexas
e específicas para o serviço. O Android 16 apresenta
WallpaperDescription e
WallpaperInstance. A WallpaperDescription permite
identificar instâncias distintas de um plano de fundo interativo do mesmo serviço. Por
exemplo, um plano de fundo que tem instâncias na tela inicial e na tela de
bloqueio pode ter conteúdo exclusivo em ambos os lugares. O seletor de plano de fundo e o
WallpaperManager usam esses metadados para apresentar melhor
os planos de fundo aos usuários, simplificando o processo para você criar experiências
diversas e personalizadas de plano de fundo animado.
Desempenho e bateria
O Android 16 apresenta APIs que ajudam a coletar insights sobre seus apps.
Criação de perfis acionada pelo sistema
O ProfilingManager foi
adicionado no Android 15, permitindo que os apps
solicitem a coleta de dados de perfil usando o Perfetto em dispositivos públicos no campo.
No entanto, como esse perfil precisa ser iniciado pelo app, fluxos críticos, como
inicializações ou ANRs, seriam difíceis ou impossíveis de capturar.
Para ajudar com isso, o Android 16 apresenta a criação de perfil acionado pelo sistema para
ProfilingManager. Os apps podem registrar interesse em receber rastros de determinados
gatilhos, como inicialização a frio reportFullyDrawn
ou ANRs. Em seguida, o sistema inicia e interrompe um rastro em nome do app. Depois
que o rastreamento for concluído, os resultados serão enviados para o diretório de dados do app.
Iniciar componente em ApplicationStartInfo
ApplicationStartInfo foi adicionado no Android
15, permitindo que um app mostre os motivos
para a inicialização do processo, o tipo de inicialização, os horários de inicialização, o controle de demanda e outros dados de diagnóstico
úteis. O Android 16 adiciona
getStartComponent()
para distinguir qual tipo de componente acionou a inicialização, o que pode ser útil para
otimizar o fluxo de inicialização do app.
Melhor introspecção de tarefas
A API JobScheduler#getPendingJobReason() retorna um motivo pelo qual um job
pode estar pendente. No entanto, um job pode ficar pendente por vários motivos.
No Android 16, estamos lançando uma nova API
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasons(int jobId), que retorna vários
motivos para um job estar pendente, devido a restrições explícitas definidas pelo
desenvolvedor e restrições implícitas definidas pelo sistema.
Também estamos lançando
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory(int jobId), que retorna uma lista
das mudanças de restrição mais recentes.
Recomendamos usar a API para depurar por que seus jobs não estão sendo executados, principalmente se você notar taxas de sucesso reduzidas de determinadas tarefas ou tiver bugs na latência de determinada conclusão de job. Por exemplo, a atualização de widgets em segundo plano não ocorreu ou o job de pré-busca não foi chamado antes do início do app.
Isso também pode ajudar a entender melhor se determinados jobs não estão sendo concluídos devido a restrições definidas pelo sistema em vez de restrições definidas explicitamente.
Taxa de Atualização Adaptativa
A taxa de atualização adaptativa (ARR, na sigla em inglês), introduzida no Android 15, permite que a taxa de atualização da tela em hardwares com suporte se adapte à taxa de frames do conteúdo usando passos discretos de VSync. Isso reduz o consumo de energia e elimina a necessidade de alternar entre modos que podem causar instabilidade.
O Android 16 apresenta hasArrSupport() e
getSuggestedFrameRate(int), além de restaurar
getSupportedRefreshRates() para facilitar o uso do ARR
nos apps. O RecyclerView
1.4 oferece suporte interno ao ARR quando ele é definido por um movimento rápido ou
rolagem suave. Continuamos trabalhando para adicionar suporte
ao ARR em mais bibliotecas do Jetpack. Este artigo sobre frame rate aborda
muitas das APIs que podem ser usadas para definir a frame rate para que o app possa usar
diretamente o ARR.
APIs de headroom na ADPF
O SystemHealthManager apresenta as APIs
getCpuHeadroom e
getGpuHeadroom, projetadas para fornecer jogos e
apps com uso intensivo de recursos com estimativas de recursos disponíveis de CPU e GPU. Esses
métodos oferecem uma maneira de avaliar como seu app ou jogo pode melhorar
a integridade do sistema, principalmente quando usado com outras APIs do Android Dynamic
Performance Framework (ADPF, na sigla em inglês) que detectam o
throttling térmico.
Ao usar CpuHeadroomParams e
GpuHeadroomParams em dispositivos compatíveis, você pode
personalizar a janela de tempo usada para calcular o headroom e selecionar a
disponibilidade de recursos média ou mínima. Isso pode ajudar a reduzir o uso de recursos da CPU ou
da GPU, o que leva a uma melhor experiência do usuário e
à melhoria da duração da bateria.
Acessibilidade
O Android 16 adiciona novas APIs e recursos de acessibilidade que podem ajudar você a levar seu app para todos os usuários.
APIs de acessibilidade aprimoradas
O Android 16 adiciona APIs adicionais para melhorar a semântica da interface, o que ajuda a melhorar a consistência para usuários que dependem de serviços de acessibilidade, como o TalkBack.
Contorno do texto para máximo contraste
Os usuários com visão reduzida geralmente têm sensibilidade reduzida ao contraste, o que dificulta a distinção de objetos do plano de fundo. Para ajudar esses usuários, o Android 16 apresenta texto com contorno, substituindo o texto de alto contraste, que desenha uma área de contraste maior ao redor do texto para melhorar muito a legibilidade.
O Android 16 tem novas APIs AccessibilityManager para permitir que
os apps verifiquem ou registrem um listener para
verificar se esse modo está ativado. Isso é principalmente para que kits de ferramentas de interface, como o Compose,
ofereçam uma experiência visual semelhante. Se você mantém uma biblioteca do kit de ferramentas de IU ou se o
app executa renderização de texto personalizada que ignora a classe
android.text.Layout, use isso para saber
quando o texto de contorno está ativado.
Duração adicionada ao TtsSpan
O Android 16 estende TtsSpan com um TYPE_DURATION,
que consiste em ARG_HOURS, ARG_MINUTES
e ARG_SECONDS. Isso permite anotar diretamente a duração
do tempo, garantindo uma saída de texto para fala precisa e consistente com serviços
como o TalkBack.
Suporte a elementos com vários rótulos
Atualmente, o Android permite que elementos da interface derivem o rótulo de acessibilidade de
outro e agora oferece a capacidade de associar vários rótulos, um
cenário comum no conteúdo da Web. Ao introduzir uma API baseada em lista em
AccessibilityNodeInfo, o Android pode oferecer suporte direto a essas
relacionamentos com vários rótulos. Como parte dessa mudança, suspendemos o uso de
AccessibilityNodeInfo#setLabeledBy e
#getLabeledBy em favor de
#addLabeledBy, #removeLabeledBy e
#getLabeledByList.
Melhoria no suporte a elementos expansíveis
O Android 16 adiciona APIs de acessibilidade que permitem transmitir o estado aberto ou
fechado de elementos interativos, como menus e listas expansíveis. Ao
definir o estado expandido usando setExpandedState e
enviar TYPE_WINDOW_CONTENT_CHANGED AccessibilityEvents
com um tipo de mudança de conteúdo CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_EXPANDED,
é possível garantir que leitores de tela como o TalkBack anunciem
mudanças de estado, oferecendo uma experiência do usuário mais intuitiva e inclusiva.
Barras de progresso indeterminadas
O Android 16 adiciona RANGE_TYPE_INDETERMINATE, oferecendo uma maneira de
exibir RangeInfo para widgets ProgressBar determinados e
indeterminados, permitindo que serviços como o
TalkBack forneçam feedback mais consistente para indicadores
de progresso.
Caixa de seleção de três estados
Os novos métodos AccessibilityNodeInfo
getChecked e setChecked(int)
no Android 16 agora oferecem suporte a um estado "parcialmente verificado", além de
"verificado" e "não verificado". Isso substitui os booleanos
isChecked e setChecked(boolean), que foram descontinuados.
Descrições complementares
Quando um serviço de acessibilidade descreve um ViewGroup, ele
combina marcadores de conteúdo das visualizações filhas. Se você fornecer um
contentDescription para o ViewGroup, os serviços de acessibilidade vão assumir que você
também está substituindo a descrição de visualizações filhas não focalizáveis. Isso pode ser
um problema se você quiser rotular itens como um menu suspenso (por exemplo, "Família
de fontes") e preservar a seleção atual para acessibilidade (por exemplo,
"Roboto"). O Android 16 adiciona setSupplementalDescription para
que você possa fornecer texto que ofereça informações sobre um ViewGroup sem
substituir as informações dos filhos.
Campos obrigatórios do formulário
O Android 16 adiciona setFieldRequired a
AccessibilityNodeInfo para que os apps possam informar a um serviço de
acessibilidade que a entrada em um campo de formulário é obrigatória. Esse é um cenário importante
para os usuários que preenchem muitos tipos de formulários, mesmo coisas simples como uma caixa de seleção de termos e condições, ajudando os usuários a identificar e
navegar rapidamente entre os campos obrigatórios.
Usar o smartphone como microfone para chamadas de voz com aparelhos auditivos LEA
O Android 16 adiciona a capacidade de usuários de aparelhos auditivos de áudio LE alternarem entre os microfones integrados nos aparelhos auditivos e o microfone no smartphone para ligações. Isso pode ser útil em ambientes barulhentos ou em outras situações em que os microfones do aparelho auditivo não funcionam bem.
Controles de volume ambiente para aparelhos auditivos LEA
O Android 16 adiciona a capacidade de os usuários de aparelhos auditivos de áudio LE ajustarem o volume do som ambiente captado pelos microfones do aparelho. Isso pode ser útil em situações em que o ruído de fundo está muito alto ou muito baixo.
Câmera
O Android 16 melhora o suporte para usuários de câmeras profissionais, permitindo a exposição automática híbrida, além de ajustes precisos de temperatura e tonalidade de cor. Um novo indicador de modo noturno ajuda o app a saber quando alternar para uma sessão de câmera no modo noturno e vice-versa. Novas ações de Intent facilitam a captura de fotos em movimento, e continuamos a melhorar as imagens UltraHDR com suporte à codificação HEIC e novos parâmetros do padrão ISO 21496-1.
Exposição automática híbrida
O Android 16 adiciona novos modos híbridos de exposição automática à Camera2, permitindo que você controle manualmente aspectos específicos da exposição enquanto deixa o algoritmo de exposição automática (AE, na sigla em inglês) cuidar do restante. É possível controlar ISO + AE e tempo de exposição + AE, oferecendo maior flexibilidade em comparação com a abordagem atual, em que você tem controle manual total ou depende totalmente da exposição automática.
fun setISOPriority() {
// ... (Your existing code before the snippet) ...
val availablePriorityModes = mStaticInfo.characteristics.get(
CameraCharacteristics.CONTROL_AE_AVAILABLE_PRIORITY_MODES
)
// ... (Your existing code between the snippets) ...
// Turn on AE mode to set priority mode
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE_SENSOR_SENSITIVITY_PRIORITY
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.SENSOR_SENSITIVITY,
TEST_SENSITIVITY_VALUE
)
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after the snippet) ...
}
Ajustes precisos de temperatura e tonalidade da cor
O Android 16 adiciona suporte à câmera para ajustes de temperatura de cor e matiz
para oferecer melhor suporte a aplicativos profissionais de gravação de vídeo. Em versões anteriores do
Android, era possível controlar as configurações de balanço de branco usando
CONTROL_AWB_MODE, que contém opções limitadas a uma
lista predefinida, como Incandescent,
Cloudy e Twilight. O
COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT permite o uso de
COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE e
COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT para ajustes precisos do
equilíbrio de branco com base na temperatura de cor correlacionada.
fun setCCT() {
// ... (Your existing code before this point) ...
val colorTemperatureRange: Range<Int> =
mStaticInfo.characteristics[CameraCharacteristics.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE_RANGE]
// Set to manual mode to enable CCT mode
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AWB_MODE] = CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AWB_MODE_OFF
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE] = CameraMetadata.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE] = 5000
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT] = 30
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after this point) ...
}
Os exemplos a seguir mostram como uma foto ficaria após aplicar diferentes ajustes de temperatura e matiz de cor:





Detecção de cena no modo noturno da câmera
Para ajudar o app a saber quando alternar para e de uma sessão de câmera no modo noturno,
o Android 16 adiciona EXTENSION_NIGHT_MODE_INDICATOR. Se
tiver suporte, ele estará disponível no CaptureResult no
Camera2.
Essa é a API que mencionamos brevemente como em breve na postagem do blog Como o Instagram permitiu que os usuários tirassem fotos incríveis em ambientes com pouca luz. Essa postagem é um guia prático sobre como implementar o Modo noturno com um estudo de caso que relaciona fotos de alta qualidade no Modo noturno do app a um aumento no número de fotos compartilhadas pela câmera do app.
Ações de intent de captura de fotos com movimento
O Android 16 adiciona ações padrão da intent,
ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE e
ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE_SECURE, que solicitam que
o aplicativo de câmera capture e retorne uma
foto com movimento.
É necessário transmitir um EXTRA_OUTPUT extra para controlar
onde a imagem será gravada ou um Uri por
Intent.setClipData(ClipData). Se você não definir um
ClipData, ele será copiado para você ao chamar
Context.startActivity(Intent).
Melhorias de imagem UltraHDR

O Android 16 continua nosso trabalho para oferecer uma qualidade de imagem incrível com imagens
UltraHDR. Ele adiciona suporte a imagens UltraHDR no formato de arquivo
HEIC. Essas imagens vão receber o tipo ImageFormat
HEIC_ULTRAHDR e vão conter um mapa de ganho incorporado semelhante
ao formato JPEG UltraHDR. Também estamos trabalhando no suporte a AVIF para UltraHDR.
Fique de olho.
Além disso, o Android 16 implementa outros parâmetros no UltraHDR do draft standard ISO 21496-1 (link em inglês), incluindo a capacidade de receber e definir o espaço de cor em que a matemática do mapa de ganho precisa ser aplicada, além de suportar imagens de base codificadas em HDR com mapas de ganho SDR.
Gráficos
O Android 16 inclui as melhorias gráficas mais recentes, como efeitos gráficos personalizados com a AGSL.
Efeitos gráficos personalizados com a AGSL
O Android 16 adiciona RuntimeColorFilter e
RuntimeXfermode, permitindo que você crie efeitos complexos, como
Threshold, Sepia e Hue Saturation, e os aplique a chamadas de exibição. Desde o Android
13, é possível usar a AGSL para criar RuntimeShaders personalizados que estendem Shader. A nova API
reflete isso, adicionando um RuntimeColorFilter com tecnologia AGSL que
amplia ColorFilter e um efeito Xfermode que
permite implementar a composição e a mesclagem personalizadas com base na AGSL entre os pixels de origem e
de destino.
private val thresholdEffectString = """
uniform half threshold;
half4 main(half4 c) {
half luminosity = dot(c.rgb, half3(0.2126, 0.7152, 0.0722));
half bw = step(threshold, luminosity);
return bw.xxx1 * c.a;
}"""
fun setCustomColorFilter(paint: Paint) {
val filter = RuntimeColorFilter(thresholdEffectString)
filter.setFloatUniform(0.5);
paint.colorFilter = filter
}
Conectividade
O Android 16 atualiza a plataforma para dar ao seu app acesso aos mais recentes avanços em tecnologias de comunicação e sem fio.
Intervalo com segurança reforçada
O Android 16 adiciona suporte a recursos de segurança robustos na localização do Wi-Fi em dispositivos com suporte ao 802.11az do Wi-Fi 6, permitindo que os apps combinem a maior precisão, maior escalonabilidade e programação dinâmica do protocolo com aprimoramentos de segurança, incluindo criptografia baseada em AES-256 e proteção contra ataques MITM. Isso permite que ele seja usado com mais segurança em casos de uso de proximidade, como desbloquear um laptop ou uma porta de veículo. O 802.11az é integrado ao padrão Wi-Fi 6, aproveitando a infraestrutura e os recursos dele para uma adoção mais ampla e uma implantação mais fácil.
APIs de intervalo genérico
O Android 16 inclui o novo RangingManager, que oferece
maneiras de determinar a distância e o ângulo no hardware com suporte entre o dispositivo
local e um dispositivo remoto. O RangingManager oferece suporte ao uso de várias
tecnologias de medição, como a detecção de canal BLE, a medição baseada em RSSI BLE, a banda ultralarga e o tempo de ida e volta do Wi-Fi.
Presença do dispositivo gerenciador de dispositivos complementares
No Android 16, novas APIs estão sendo introduzidas para vincular o serviço do app
complementar. O serviço será vinculado quando o BLE estiver no alcance e o Bluetooth estiver conectado
e será desvinculado quando o BLE estiver fora do alcance ou o Bluetooth estiver
desconectado. O app vai receber um novo callback
'onDevicePresenceEvent()' com base em vários
DevicePresenceEvent.
Confira mais detalhes em
'startObservingDevicePresence(ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)'.
Mídia
O Android 16 inclui vários recursos que melhoram a experiência de mídia.
Melhorias no seletor de fotos
O seletor de fotos oferece uma maneira segura e integrada para os usuários concederem ao app acesso a imagens e vídeos selecionados do armazenamento local e da nuvem, em vez de toda a biblioteca de mídia. Usando uma combinação de componentes modulares do sistema pelas Atualizações do sistema do Google e os Serviços do Google Play, ele tem suporte ao Android 4.4 (nível 19 da API). A integração requer apenas algumas linhas de código com a biblioteca Android Jetpack associada.
O Android 16 inclui as seguintes melhorias no seletor de fotos:
- Seletor de fotos incorporado: novas APIs que permitem que os apps incorporem o seletor de fotos à hierarquia de visualização. Isso permite que ela pareça uma parte mais integrada do app, aproveitando o isolamento de processos que permite que os usuários selecionem mídia sem que o app precise de permissões muito amplas. Para maximizar a compatibilidade entre as versões da plataforma e simplificar a integração, use a próxima biblioteca Jetpack do Android se quiser integrar o seletor de fotos incorporado.
- Pesquisa na nuvem no seletor de fotos: novas APIs que permitem a pesquisa do provedor de mídia na nuvem para o seletor de fotos do Android. A funcionalidade de pesquisa no seletor de fotos será lançada em breve.
Vídeo profissional avançado
O Android 16 apresenta suporte ao codec Advanced Professional Video (APV, na sigla em inglês), que foi projetado para ser usado em gravação de vídeo e pós-produção de alta qualidade de nível profissional.
O padrão de codec APV tem os seguintes recursos:
- Qualidade de vídeo sem perdas perceptível (próxima da qualidade de vídeo bruto)
- Baixa complexidade e codificação intra-frame com alto throughput (sem previsão de domínio de pixels) para melhor suporte a fluxos de trabalho de edição
- Suporte a um intervalo de taxa de bits alto de até alguns Gbps para conteúdo de resolução 2K, 4K e 8K, ativado por um esquema de codificação de entropia leve
- Dividir o frame em blocos para conteúdo imersivo e ativar a codificação e decodificação paralelas
- Suporte a vários formatos de amostragem de cromatismo e profundidades de bits
- Suporte a várias decodificações e recodificações sem degradação severa da qualidade visual
- Oferecer suporte a vídeos com várias visualizações e vídeos auxiliares, como profundidade, Alfa e visualização
- Suporte a HDR10/10+ e metadados definidos pelo usuário
Uma implementação de referência do APV é fornecida pelo projeto OpenAPV. O Android 16 vai implementar suporte ao perfil APV 422-10, que oferece amostragem de cores YUV 422 com codificação de 10 bits e para taxas de bits de destino de até 2 Gbps.
Privacidade
O Android 16 inclui vários recursos que ajudam os desenvolvedores de apps a proteger a privacidade dos usuários.
Atualizações do app Conexão Saúde
A Conexão Saúde adiciona ACTIVITY_INTENSITY, um tipo de dados definido de acordo com as diretrizes da
Organização Mundial da Saúde sobre atividade moderada e vigorosa. Cada
registro exige o horário de início, o horário de término e se a intensidade da atividade
é moderada ou intensa.
A Conexão Saúde também tem APIs atualizadas com suporte a históricos médicos. Isso permite que os apps leiam e gravem registros médicos no formato FHIR com consentimento explícito do usuário.
Sandbox de privacidade no Android
O Android 16 incorpora a versão mais recente do Sandbox de privacidade no Android, parte do nosso trabalho contínuo para desenvolver tecnologias em que os usuários sabem que a privacidade deles está protegida. Nosso site tem mais informações sobre o programa Beta do Sandbox de privacidade para desenvolvedores Android para ajudar você a começar. Confira o SDK Runtime, que permite que os SDKs sejam executados em um ambiente de execução dedicado separado do app que eles estão oferecendo, oferecendo proteções mais fortes em relação à coleta e ao compartilhamento de dados do usuário.
Segurança
O Android 16 inclui recursos que ajudam a melhorar a segurança do app e proteger os dados dele.
API de compartilhamento de chaves
O Android 16 adiciona APIs que oferecem suporte ao compartilhamento de acesso a
chaves do Keystore do Android com outros apps. A nova classe
KeyStoreManager oferece suporte a
acesso e revogação de chaves
por uid do app e inclui uma API para que os apps acessem chaves
compartilhadas.
Formatos de dispositivos
O Android 16 oferece aos seus apps o suporte necessário para aproveitar ao máximo os formatos do Android.
Estrutura padronizada de qualidade de imagem e áudio para TVs
O novo pacote
MediaQuality no Android 16 expõe
um conjunto de APIs padronizadas para acesso a perfis de áudio e imagem e
configurações relacionadas ao hardware. Isso permite que os apps de streaming consultem perfis e
os apliquem à mídia de forma dinâmica:
- Filmes masterizados com um intervalo dinâmico mais amplo exigem maior precisão de cor para ver detalhes sutis nas sombras e se ajustar à luz ambiente. Portanto, um perfil que prioriza a precisão de cor em vez do brilho pode ser adequado.
- Eventos esportivos ao vivo geralmente são masterizados com um intervalo dinâmico estreito, mas são assistidos durante o dia. Portanto, um perfil que prioriza o brilho em vez da precisão de cores pode gerar resultados melhores.
- O conteúdo totalmente interativo exige um processamento mínimo para reduzir a latência e taxas de quadros mais altas. É por isso que muitas TVs são enviadas com um perfil de jogo.
A API permite que os apps alternem entre perfis, e os usuários podem ajustar as TVs compatíveis para se adequar melhor ao conteúdo.
Internacionalização
O Android 16 adiciona recursos e funcionalidades que complementam a experiência do usuário quando um dispositivo é usado em diferentes idiomas.
Texto vertical
O Android 16 adiciona suporte de baixo nível para renderização e medição de texto verticalmente para
oferecer suporte básico de escrita vertical para desenvolvedores de bibliotecas. Isso é
especialmente útil para idiomas como o japonês, que costumam usar sistemas de escrita
vertical. Uma nova flag,
VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG,
foi adicionada à classe Paint. Quando
essa flag é definida usando
Paint.setFlags, as APIs de medição de texto
do Paint vão informar avanços verticais em vez de horizontais, e Canvas vai desenhar o texto
verticalmente.
val text = "「春は、曙。」"
Box(
Modifier.padding(innerPadding).background(Color.White).fillMaxSize().drawWithContent {
drawIntoCanvas { canvas ->
val paint = Paint().apply { textSize = 64.sp.toPx() }
// Draw text vertically
paint.flags = paint.flags or VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG
val height = paint.measureText(text)
canvas.nativeCanvas.drawText(
text,
0,
text.length,
size.width / 2,
(size.height - height) / 2,
paint
)
}
}
) {}
Personalização do sistema de medidas
Os usuários agora podem personalizar o sistema de medição nas preferências regionais nas
Configurações. A preferência do usuário é incluída como parte do código de localidade. Assim, é possível
registrar um BroadcastReceiver em
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED para processar mudanças de configuração de localidade quando
as preferências regionais mudarem.
O uso de formatadores pode ajudar a corresponder à experiência local. Por exemplo, "0,5 pol" em inglês (Estados Unidos) é "12,7 mm" para um usuário que definiu o smartphone como inglês (Dinamarca) ou que usa o smartphone em inglês (Estados Unidos) com o sistema métrico como a preferência de sistema de medição.
Para encontrar essas configurações, abra o app Configurações e navegue até Sistema > Idiomas e região.
