ในอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ Android 8.0 (API ระดับ 26) ขึ้นไป การจับคู่อุปกรณ์เสริมจะทำการสแกนบลูทูธหรือ Wi-Fi ของอุปกรณ์ที่อยู่ใกล้เคียงในนามของแอปโดยไม่ต้องมีสิทธิ์ ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION
ซึ่งจะช่วยเพิ่มการปกป้องความเป็นส่วนตัวของผู้ใช้ให้ได้มากที่สุด ใช้วิธีนี้เพื่อ
กำหนดค่าเริ่มต้นของอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ร่วมกัน เช่น สมาร์ทวอทช์ที่รองรับ BLE นอกจากนี้ การจับคู่อุปกรณ์เสริมยังต้องเปิดใช้บริการตำแหน่งด้วย
การจับคู่อุปกรณ์เสริมไม่ได้สร้างการเชื่อมต่อด้วยตัวเองและไม่ได้เปิดใช้ การสแกนอย่างต่อเนื่อง แอปสามารถใช้ API การเชื่อมต่อบลูทูธหรือ Wi-Fi เพื่อ สร้างการเชื่อมต่อได้
หลังจากจับคู่อุปกรณ์แล้ว อุปกรณ์จะใช้สิทธิ์
REQUEST_COMPANION_RUN_IN_BACKGROUND
และ
REQUEST_COMPANION_USE_DATA_IN_BACKGROUND
เพื่อเริ่มแอปจากพื้นหลังได้ แอปยังใช้สิทธิ์
REQUEST_COMPANION_START_FOREGROUND_SERVICES_FROM_BACKGROUND
เพื่อเริ่มบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าจากเบื้องหลังได้ด้วย
ผู้ใช้สามารถเลือกอุปกรณ์จากรายการและให้สิทธิ์แอปในการเข้าถึง
อุปกรณ์ ระบบจะเพิกถอนสิทธิ์เหล่านี้หากคุณถอนการติดตั้งแอปหรือโทรหา
disassociate()
แอปที่ใช้ร่วมกันมีหน้าที่ล้างการเชื่อมโยงของตัวเองหากผู้ใช้ไม่ต้องการใช้การเชื่อมโยงนั้นอีกต่อไป เช่น เมื่อผู้ใช้บันทึกการออกจากระบบหรือนำอุปกรณ์ที่เชื่อมโยงออก
ใช้การจับคู่อุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ร่วมกัน
ส่วนนี้จะอธิบายวิธีใช้ CompanionDeviceManager เพื่อจับคู่แอปกับอุปกรณ์เสริมผ่านบลูทูธ, BLE และ Wi-Fi
ระบุอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ร่วมกัน
ตัวอย่างโค้ดต่อไปนี้แสดงวิธีเพิ่มแฟล็ก
<uses-feature> ลงใน
ไฟล์ Manifest ซึ่งจะบอกระบบว่าแอปของคุณต้องการตั้งค่าอุปกรณ์
คู่
<uses-feature android:name="android.software.companion_device_setup"/>
แสดงรายการอุปกรณ์ตาม DeviceFilter
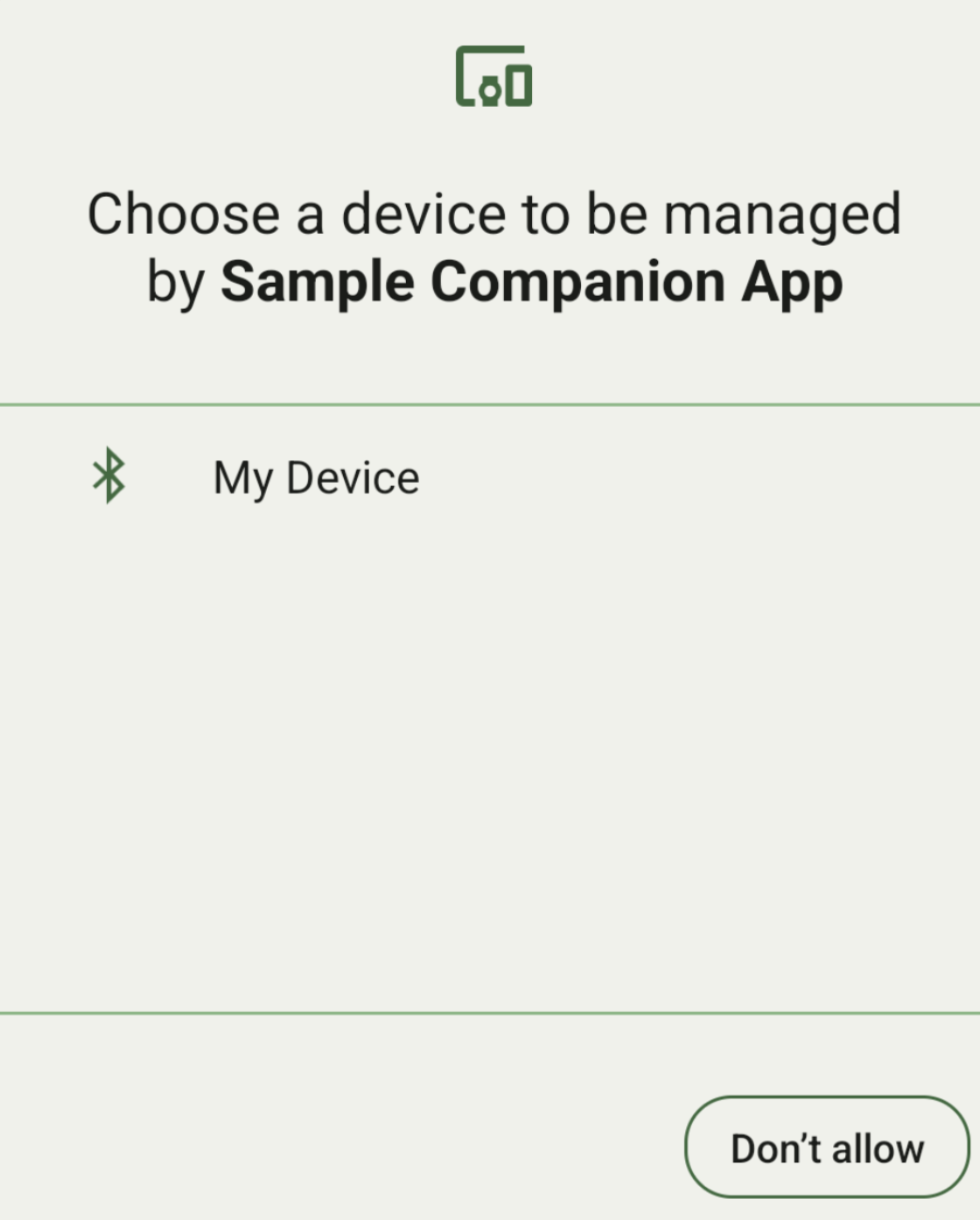
คุณสามารถแสดงอุปกรณ์คู่ที่อยู่ในช่วงทั้งหมดซึ่งตรงกับ
DeviceFilter
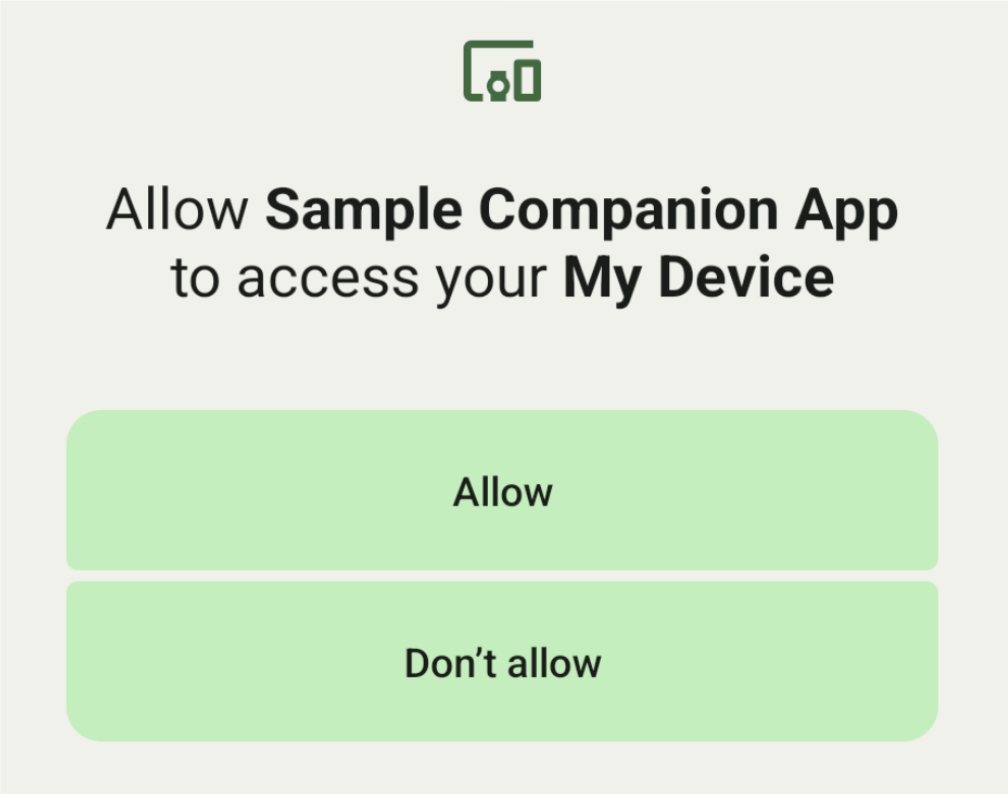
ที่คุณระบุ (แสดงในรูปที่ 1) หากต้องการจำกัดการสแกนไว้ที่อุปกรณ์เดียว ให้setSingleDevice()
ไปที่true (แสดงในรูปที่ 2)
ต่อไปนี้คือคลาสย่อยของ DeviceFilter ที่
ระบุได้ใน AssociationRequest
ทั้ง 3 คลาสย่อยมีตัวสร้างที่ช่วยให้การกำหนดค่าตัวกรองมีประสิทธิภาพมากขึ้น
ในตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้ อุปกรณ์จะสแกนหาอุปกรณ์บลูทูธที่มี
BluetoothDeviceFilter
Kotlin
val deviceFilter: BluetoothDeviceFilter = BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() // Match only Bluetooth devices whose name matches the pattern. .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) // Match only Bluetooth devices whose service UUID matches this pattern. .addServiceUuid(ParcelUuid(UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build()
Java
BluetoothDeviceFilter deviceFilter = new BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() // Match only Bluetooth devices whose name matches the pattern. .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) // Match only Bluetooth devices whose service UUID matches this pattern. .addServiceUuid(new ParcelUuid(new UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build();
ตั้งค่า DeviceFilter ให้กับ AssociationRequest เพื่อให้ CompanionDeviceManager ระบุประเภทอุปกรณ์ที่จะค้นหาได้
Kotlin
val pairingRequest: AssociationRequest = AssociationRequest.Builder() // Find only devices that match this request filter. .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) // Stop scanning as soon as one device matching the filter is found. .setSingleDevice(true) .build()
Java
AssociationRequest pairingRequest = new AssociationRequest.Builder() // Find only devices that match this request filter. .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) // Stop scanning as soon as one device matching the filter is found. .setSingleDevice(true) .build();
หลังจากที่แอปเริ่มต้น AssociationRequest แล้ว ให้เรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน
associate()
ใน CompanionDeviceManager ฟังก์ชัน associate()
รับ AssociationRequest และ Callback
Callback จะแสดง IntentSender ใน onAssociationPending เมื่อ CompanionDeviceManager ค้นหาอุปกรณ์
และพร้อมที่จะเปิดกล่องโต้ตอบความยินยอมของผู้ใช้
หลังจากที่ผู้ใช้ยืนยันอุปกรณ์แล้ว ระบบจะส่งคืนAssociationInfo
ของอุปกรณ์ใน onAssociationCreated
หากแอปไม่พบอุปกรณ์ใดๆ Callback จะแสดง onFailure
พร้อมข้อความแสดงข้อผิดพลาด
ในอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ Android 13 (API ระดับ 33) ขึ้นไป ให้ทำดังนี้
Kotlin
val deviceManager = requireContext().getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) val executor: Executor = Executor { it.run() } deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, executor, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user // can select the device they want to pair with. override fun onAssociationPending(intentSender: IntentSender) { intentSender?.let { startIntentSenderForResult(it, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } } override fun onAssociationCreated(associationInfo: AssociationInfo) { // An association is created. } override fun onFailure(errorMessage: CharSequence?) { // To handle the failure. } })
Java
CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE); Executor executor = new Executor() { @Override public void execute(Runnable runnable) { runnable.run(); } }; deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { executor, // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user can // select the device they want to pair with. @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult( chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0 ); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { Log.e("MainActivity", "Failed to send intent"); } } @Override public void onAssociationCreated(AssociationInfo associationInfo) { // An association is created. } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence errorMessage) { // To handle the failure. });
ในอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ Android 12L (API ระดับ 32) หรือต่ำกว่า (เลิกใช้งานแล้ว) ให้ทำดังนี้
Kotlin
val deviceManager = requireContext().getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user // can select the device they want to pair with. override fun onDeviceFound(chooserLauncher: IntentSender) { startIntentSenderForResult(chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } override fun onFailure(error: CharSequence?) { // To handle the failure. } }, null)
Java
CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE); deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user can // select the device they want to pair with. @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult( chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0 ); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { Log.e("MainActivity", "Failed to send intent"); } } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence error) { // To handle the failure. } }, null);
ระบบจะส่งผลลัพธ์ของการเลือกผู้ใช้กลับไปยัง Fragment ใน
onActivityResult()
ของกิจกรรม จากนั้นคุณจะเข้าถึงอุปกรณ์ที่เลือกได้
เมื่อผู้ใช้เลือกอุปกรณ์บลูทูธ ให้คาดหวังBluetoothDevice
เมื่อผู้ใช้เลือกอุปกรณ์ Bluetooth LE คุณจะเห็นandroid.bluetooth.le.ScanResult
เมื่อผู้ใช้เลือกอุปกรณ์ Wi-Fi ให้คาดหวังว่าจะมี
android.net.wifi.ScanResult
Kotlin
override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) { when (requestCode) { SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE -> when(resultCode) { Activity.RESULT_OK -> { // The user chose to pair the app with a Bluetooth device. val deviceToPair: BluetoothDevice? = data?.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE) deviceToPair?.let { device -> device.createBond() // Continue to interact with the paired device. } } } else -> super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data) } }
Java
@Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) { if (resultCode != Activity.RESULT_OK) { return; } if (requestCode == SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE && data != null) { BluetoothDevice deviceToPair = data.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE); if (deviceToPair != null) { deviceToPair.createBond(); // Continue to interact with the paired device. } } else { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); } }
ดูตัวอย่างที่สมบูรณ์
ในอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ Android 13 (API ระดับ 33) ขึ้นไป ให้ทำดังนี้
Kotlin
private const val SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0 class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { private val deviceManager: CompanionDeviceManager by lazy { getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) as CompanionDeviceManager } val mBluetoothAdapter: BluetoothAdapter by lazy { val java = BluetoothManager::class.java getSystemService(java)!!.adapter } val executor: Executor = Executor { it.run() } override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) // To skip filters based on names and supported feature flags (UUIDs), // omit calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid() // respectively, as shown in the following Bluetooth example. val deviceFilter: BluetoothDeviceFilter = BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid(ParcelUuid(UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build() // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of them appears. val pairingRequest: AssociationRequest = AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build() // When the app tries to pair with a Bluetooth device, show the // corresponding dialog box to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, executor, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user // can select the device they want to pair with. override fun onAssociationPending(intentSender: IntentSender) { intentSender?.let { startIntentSenderForResult(it, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } } override fun onAssociationCreated(associationInfo: AssociationInfo) { // AssociationInfo object is created and get association id and the // macAddress. var associationId: int = associationInfo.id var macAddress: MacAddress = associationInfo.deviceMacAddress } override fun onFailure(errorMessage: CharSequence?) { // Handle the failure. } ) override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) { when (requestCode) { SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE -> when(resultCode) { Activity.RESULT_OK -> { // The user chose to pair the app with a Bluetooth device. val deviceToPair: BluetoothDevice? = data?.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE) deviceToPair?.let { device -> device.createBond() // Maintain continuous interaction with a paired device. } } } else -> super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data) } } }
Java
class MainActivityJava extends AppCompatActivity { private static final int SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0; Executor executor = new Executor() { @Override public void execute(Runnable runnable) { runnable.run(); } }; @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService( Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE ); // To skip filtering based on name and supported feature flags, // do not include calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid(), // respectively. This example uses Bluetooth. BluetoothDeviceFilter deviceFilter = new BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid( new ParcelUuid(new UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null ) .build(); // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of device names is presented to the user as // pairing options. AssociationRequest pairingRequest = new AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build(); // When the app tries to pair with the Bluetooth device, show the // appropriate pairing request dialog to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { executor, // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user can // select the device they want to pair with. @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult( chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0 ); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { Log.e("MainActivity", "Failed to send intent"); } } @Override public void onAssociationCreated(AssociationInfo associationInfo) { // AssociationInfo object is created and get association id and the // macAddress. int associationId = associationInfo.getId(); MacAddress macAddress = associationInfo.getDeviceMacAddress(); } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence errorMessage) { // Handle the failure. }); } @Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) { if (resultCode != Activity.RESULT_OK) { return; } if (requestCode == SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE) { if (resultCode == Activity.RESULT_OK && data != null) { BluetoothDevice deviceToPair = data.getParcelableExtra( CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE ); if (deviceToPair != null) { deviceToPair.createBond(); // ... Continue interacting with the paired device. } } } else { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); } } }
ในอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ Android 12L (API ระดับ 32) หรือต่ำกว่า (เลิกใช้งานแล้ว) ให้ทำดังนี้
Kotlin
private const val SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0 class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { private val deviceManager: CompanionDeviceManager by lazy { getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) as CompanionDeviceManager } override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) // To skip filters based on names and supported feature flags (UUIDs), // omit calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid() // respectively, as shown in the following Bluetooth example. val deviceFilter: BluetoothDeviceFilter = BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid(ParcelUuid(UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build() // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of them appears. val pairingRequest: AssociationRequest = AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build() // When the app tries to pair with a Bluetooth device, show the // corresponding dialog box to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { override fun onDeviceFound(chooserLauncher: IntentSender) { startIntentSenderForResult(chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } override fun onFailure(error: CharSequence?) { // Handle the failure. } }, null) } override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) { when (requestCode) { SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE -> when(resultCode) { Activity.RESULT_OK -> { // The user chose to pair the app with a Bluetooth device. val deviceToPair: BluetoothDevice? = data?.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE) deviceToPair?.let { device -> device.createBond() // Maintain continuous interaction with a paired device. } } } else -> super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data) } } }
Java
class MainActivityJava extends AppCompatActivity { private static final int SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0; @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService( Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE ); // To skip filtering based on name and supported feature flags, // don't include calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid(), // respectively. This example uses Bluetooth. BluetoothDeviceFilter deviceFilter = new BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid( new ParcelUuid(new UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null ) .build(); // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of device names is presented to the user as // pairing options. AssociationRequest pairingRequest = new AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build(); // When the app tries to pair with the Bluetooth device, show the // appropriate pairing request dialog to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult(chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { // failed to send the intent } } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence error) { // handle failure to find the companion device } }, null); } @Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) { if (requestCode == SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE) { if (resultCode == Activity.RESULT_OK && data != null) { BluetoothDevice deviceToPair = data.getParcelableExtra( CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE ); if (deviceToPair != null) { deviceToPair.createBond(); // ... Continue interacting with the paired device. } } } else { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); } } }
โปรไฟล์อุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ร่วมกัน
ใน Android 12 (API ระดับ 31) ขึ้นไป แอปที่ใช้ร่วมกันซึ่งจัดการอุปกรณ์ต่างๆ เช่น นาฬิกา จะใช้โปรไฟล์อุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ร่วมกันเพื่อเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพกระบวนการตั้งค่าได้โดยการให้สิทธิ์ที่จำเป็นเมื่อจับคู่ ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่โปรไฟล์อุปกรณ์เสริม
เปิดแอปที่ใช้ร่วมกันไว้
ตั้งแต่ Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) เป็นต้นไป
CompanionDeviceManager.startObservingDevicePresence(String)
และ
CompanionDeviceService.onDeviceAppeared()
เลิกใช้งานแล้ว
คุณควรใช้
CompanionDeviceManager.startObservingDevicePresence (ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)เพื่อ จัดการการเชื่อมโยงCompanionDeviceServiceที่ติดตั้งใช้งานโดยอัตโนมัติ- ระบบจะจัดการสถานะการเชื่อมโยงของ
CompanionDeviceServiceโดยอัตโนมัติ ตามสถานะการตรวจหาอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ร่วมกันที่เชื่อมโยงอยู่ ดังนี้- บริการจะผูกมัดเมื่ออุปกรณ์คู่หูอยู่ในช่วง BLE หรือ เชื่อมต่อโดยใช้บลูทูธ
- บริการจะยกเลิกการเชื่อมต่อเมื่ออุปกรณ์คู่ย้ายออก นอกช่วง BLE หรือการเชื่อมต่อบลูทูธสิ้นสุดลง
- ระบบจะจัดการสถานะการเชื่อมโยงของ
แอปจะได้รับการเรียกกลับตาม
DevicePresenceEventต่างๆดูรายละเอียดได้ที่
CompanionDeviceService.onDeviceEvent()

