Чтобы узнать, как использовать библиотеку Microbenchmark, внеся изменения в код вашего приложения, см. раздел «Быстрый старт» . Чтобы узнать, как выполнить полную настройку с более сложными изменениями в кодовой базе, см. раздел «Полная настройка проекта» .
Быстрый старт
В этом разделе показано, как провести тестирование производительности и выполнить разовые измерения без необходимости переноса кода в модули. Для получения точных результатов производительности эти шаги включают отключение отладки в вашем приложении, поэтому сохраните это в локальной рабочей копии, не внося изменения в систему контроля версий.
Для проведения разового сравнительного анализа выполните следующие действия:
Добавьте библиотеку в файл
build.gradleилиbuild.gradle.ktsвашего модуля:Котлин
dependencies { implementation("androidx.benchmark:benchmark-junit4:1.2.4") }
Классный
dependencies { implementation 'androidx.benchmark:benchmark-junit4:1.2.4' }
Вместо зависимости
androidTestImplementationиспользуйте зависимостьimplementation. Если вы используетеandroidTestImplementation, тесты производительности не будут запущены, поскольку манифест библиотеки не будет объединен с манифестом приложения.Измените тип
debugсборки так, чтобы она не была отлаживаемой:Котлин
android { ... buildTypes { debug { isDebuggable = false } } }
Классный
android { ... buildTypes { debug { debuggable false } } }
Измените значение параметра
testInstrumentationRunnerнаAndroidBenchmarkRunner:Котлин
android { ... defaultConfig { testInstrumentationRunner = "androidx.benchmark.junit4.AndroidBenchmarkRunner" } }
Классный
android { ... defaultConfig { testInstrumentationRunner "androidx.benchmark.junit4.AndroidBenchmarkRunner" } }
Добавьте экземпляр класса
BenchmarkRuleв тестовый файл в каталогеandroidTest, чтобы добавить свой бенчмарк. Для получения дополнительной информации о создании бенчмарков см. раздел «Создание класса Microbenchmark» .Следующий фрагмент кода показывает, как добавить бенчмарк в инструментальный тест:
Котлин
@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4::class) class SampleBenchmark { @get:Rule val benchmarkRule = BenchmarkRule() @Test fun benchmarkSomeWork() { benchmarkRule.measureRepeated { doSomeWork() } } }
Java
@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4.class) class SampleBenchmark { @Rule public BenchmarkRule benchmarkRule = new BenchmarkRule(); @Test public void benchmarkSomeWork() { BenchmarkRuleKt.measureRepeated( (Function1<BenchmarkRule.Scope, Unit>) scope -> doSomeWork() ); } } }
Чтобы узнать, как создать тест производительности, перейдите к разделу «Создание класса Microbenchmark» .
Полная настройка проекта
Чтобы настроить регулярное тестирование производительности, а не разовое, выделите тесты в отдельный модуль. Это поможет гарантировать, что их конфигурация, например, установка параметра debuggable в false , будет отделена от обычных тестов.
Поскольку Microbenchmark запускает ваш код напрямую, поместите код, который вы хотите протестировать, в отдельный модуль Gradle и установите зависимость от этого модуля, как показано на рисунке 1.

:app , :microbenchmark и :benchmarkable , которая позволяет Microbenchmarks проводить бенчмаркинг кода в модуле :benchmarkable . Чтобы добавить новый модуль Gradle, можно использовать мастер создания модулей в Android Studio. Мастер создаст модуль, предварительно настроенный для бенчмаркинга, с добавленным каталогом для бенчмарков и параметром debuggable установленным в значение false .
В Android Studio щелкните правой кнопкой мыши по своему проекту или модулю на панели «Проект» и выберите «Создать» > «Модуль» .
В панели «Шаблоны» выберите «Контрольный тест» .
Выберите Microbenchmark в качестве типа модуля для проведения бенчмаркинга.
Введите "microbenchmark" в качестве названия модуля.
Нажмите «Готово» .
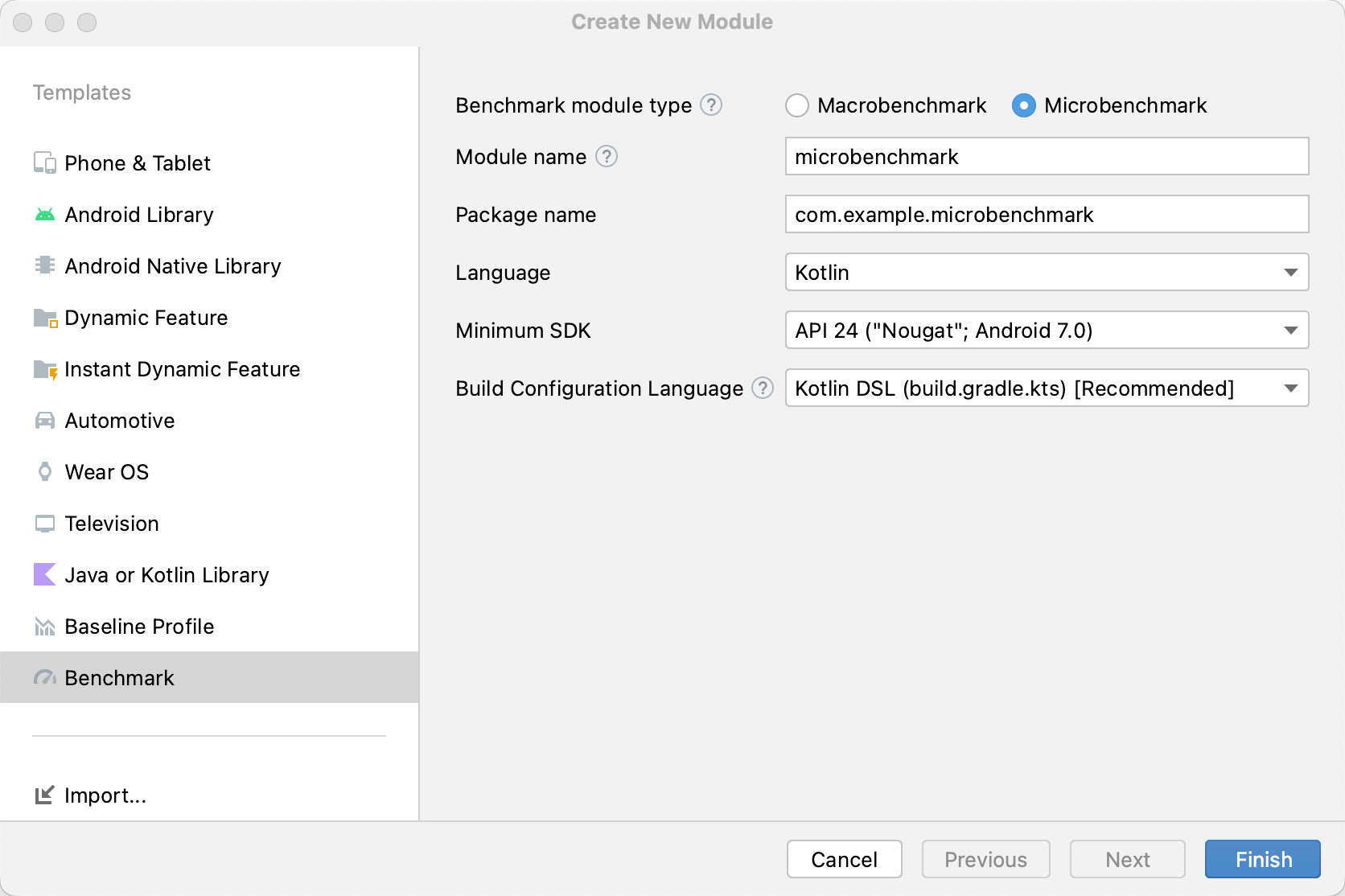
После создания модуля измените его файл build.gradle или build.gradle.kts и добавьте в модуль, содержащий код для бенчмаркинга, атрибут androidTestImplementation :
Котлин
dependencies { // The module name might be different. androidTestImplementation(project(":benchmarkable")) }
Классный
dependencies { // The module name might be different. androidTestImplementation project(':benchmarkable') }
Создайте класс Microbenchmark.
Бенчмарки — это стандартные инструментальные тесты. Для создания бенчмарка используйте класс BenchmarkRule , предоставляемый библиотекой. Для бенчмаркинга действий используйте ActivityScenario или ActivityScenarioRule . Для бенчмаркинга кода пользовательского интерфейса используйте аннотацию @UiThreadTest .
Следующий код демонстрирует пример теста производительности:
Котлин
@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4::class) class SampleBenchmark { @get:Rule val benchmarkRule = BenchmarkRule() @Test fun benchmarkSomeWork() { benchmarkRule.measureRepeated { doSomeWork() } } }
Java
@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4.class) class SampleBenchmark { @Rule public BenchmarkRule benchmarkRule = new BenchmarkRule(); @Test public void benchmarkSomeWork() { final BenchmarkState state = benchmarkRule.getState(); while (state.keepRunning()) { doSomeWork(); } } }
Отключить отсчет времени для настройки
Вы можете отключить измерение времени выполнения для тех участков кода, которые не хотите измерять, с помощью блока runWithTimingDisabled{} . Эти участки обычно представляют собой код, который необходимо выполнять на каждой итерации бенчмарка.
Котлин
// using random with the same seed, so that it generates the same data every run private val random = Random(0) // create the array once and just copy it in benchmarks private val unsorted = IntArray(10_000) { random.nextInt() } @Test fun benchmark_quickSort() { // ... benchmarkRule.measureRepeated { // copy the array with timing disabled to measure only the algorithm itself listToSort = runWithTimingDisabled { unsorted.copyOf() } // sort the array in place and measure how long it takes SortingAlgorithms.quickSort(listToSort) } // assert only once not to add overhead to the benchmarks assertTrue(listToSort.isSorted) }
Java
private final int[] unsorted = new int[10000]; public SampleBenchmark() { // Use random with the same seed, so that it generates the same data every // run. Random random = new Random(0); // Create the array once and copy it in benchmarks. Arrays.setAll(unsorted, (index) -> random.nextInt()); } @Test public void benchmark_quickSort() { final BenchmarkState state = benchmarkRule.getState(); int[] listToSort = new int[0]; while (state.keepRunning()) { // Copy the array with timing disabled to measure only the algorithm // itself. state.pauseTiming(); listToSort = Arrays.copyOf(unsorted, 10000); state.resumeTiming(); // Sort the array in place and measure how long it takes. SortingAlgorithms.quickSort(listToSort); } // Assert only once, not to add overhead to the benchmarks. assertTrue(SortingAlgorithmsKt.isSorted(listToSort)); }
Постарайтесь свести к минимуму объем работы, выполняемой внутри блока measureRepeated и внутри runWithTimingDisabled . Блок measureRepeated выполняется несколько раз, и это может повлиять на общее время, необходимое для выполнения бенчмарка. Если вам нужно проверить какие-либо результаты бенчмарка, вы можете проверить последний результат, вместо того чтобы делать это на каждой итерации бенчмарка.
Запустите тест производительности
В Android Studio запустите тест производительности так же, как и любой другой тест с @Test , используя действие в боковой панели рядом с тестовым классом или методом, как показано на рисунке 3.
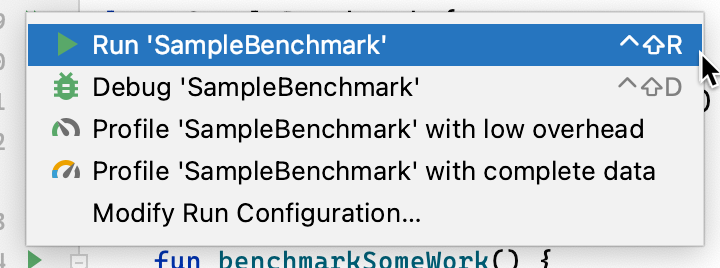
В качестве альтернативы, из командной строки запустите connectedCheck , чтобы выполнить все тесты из указанного модуля Gradle:
./gradlew benchmark:connectedCheckИли один тест:
./gradlew benchmark:connectedCheck -P android.testInstrumentationRunnerArguments.class=com.example.benchmark.SampleBenchmark#benchmarkSomeWorkРезультаты сравнительного анализа
После успешного выполнения микротеста метрики отображаются непосредственно в Android Studio, а полный отчет о результатах теста с дополнительными метриками и информацией об устройстве доступен в формате JSON.
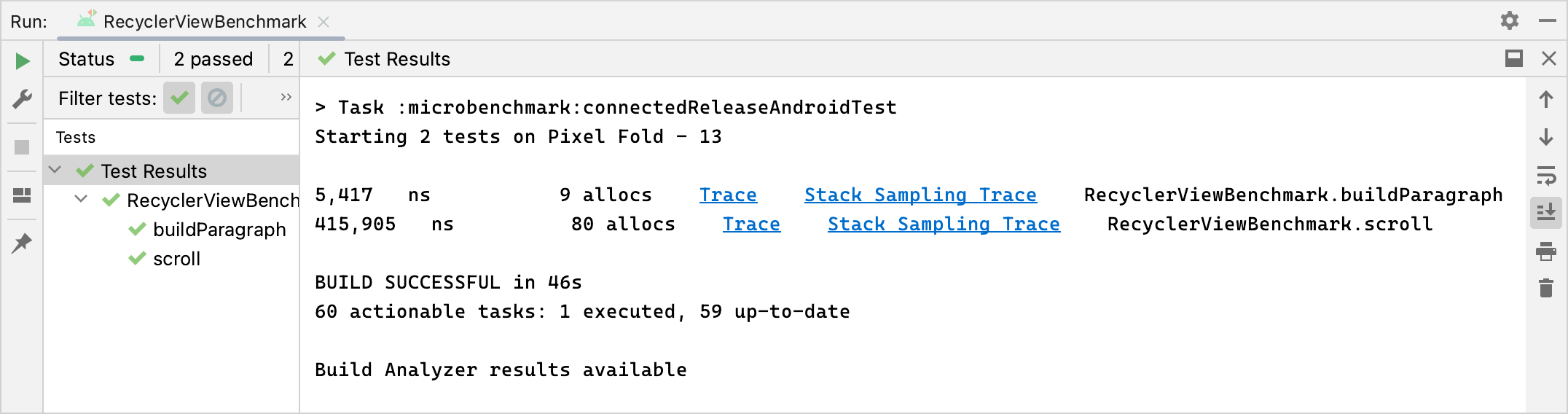
JSON-отчеты и любые трассировки профилирования также автоматически копируются с устройства на хост. На хост-машине они записываются в следующее местоположение:
project_root/module/build/outputs/connected_android_test_additional_output/debugAndroidTest/connected/device_id/
По умолчанию отчет в формате JSON записывается на диск устройства во внешнюю общую папку тестового APK-файла, которая обычно находится по адресу /storage/emulated/0/Android/media/**app_id**/**app_id**-benchmarkData.json .
Ошибки конфигурации
Библиотека определяет следующие условия, чтобы гарантировать, что ваш проект и среда настроены для обеспечения производительности, соответствующей релизной версии:
- Параметр Debuggable установлен на
false. - Используется физическое устройство — эмуляторы не поддерживаются.
- Часы блокируются, если устройство рутировано.
- Уровень заряда батареи устройства должен быть достаточным — не менее 25%.
Если какая-либо из предыдущих проверок не пройдена, программа выдает сообщение об ошибке, чтобы предотвратить неточные измерения.
Чтобы подавить определенные типы ошибок в виде предупреждений и предотвратить остановку бенчмарка из-за них, передайте тип ошибки в виде списка, разделенного запятыми, в аргумент инструментария androidx.benchmark.suppressErrors .
Это можно установить из вашего скрипта Gradle, как показано в следующем примере:
Котлин
android { defaultConfig { … testInstrumentationRunnerArguments["androidx.benchmark.suppressErrors"] = "DEBUGGABLE,LOW-BATTERY" } }
Классный
android { defaultConfig { … testInstrumentationRunnerArguments["androidx.benchmark.suppressErrors"] = "DEBUGGABLE,LOW-BATTERY" } }
Также можно подавлять ошибки из командной строки:
$ ./gradlew :benchmark:connectedCheck -P andoidtestInstrumentationRunnerArguments.androidx.benchmark.supperssErrors=DEBUGGABLE,LOW-BATTERY
Подавление ошибок позволяет запустить бенчмарк в некорректно настроенном состоянии, и выходные данные бенчмарка намеренно переименовываются путем добавления к именам тестов префикса ошибки. Например, запуск отлаживаемого бенчмарка с подавлением ошибок, как показано в предыдущем фрагменте кода, добавляет к именам тестов префикс DEBUGGABLE_ .
Рекомендуем вам
- Примечание: текст ссылки отображается, когда JavaScript отключен.
- Напишите макротест производительности
- Создавайте микротесты производительности без Gradle.
- Создание базовых профилей {:#creating-profile-rules}

