Android 16 平台包含可能對應用程式造成影響的行為變更。無論 targetSdkVersion 為何,當應用程式在 Android 16 上執行時,下列行為變更將會套用至所有應用程式。您應測試應用程式,並視需要修改,以便在適當情況下支援這些變更。
另請務必查看僅對指定 Android 16 為目標版本的應用程式造成影響的行為變更。
核心功能
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 包含下列變更,可修改或擴充 Android 系統的各種核心功能。
JobScheduler 配額最佳化
Starting in Android 16, we're adjusting regular and expedited job execution runtime quota based on the following factors:
- Which app standby bucket the application is in: in Android 16, active standby buckets will start being enforced by a generous runtime quota.
- If the job starts execution while the app is in a top state: in Android 16, Jobs started while the app is visible to the user and continues after the app becomes invisible, will adhere to the job runtime quota.
- If the job is executing while running a Foreground Service: in Android 16, jobs that are executing concurrently with a foreground service will adhere to the job runtime quota. If you're leveraging jobs for user initiated data transfer, consider using user initiated data transfer jobs instead.
This change impacts tasks scheduled using WorkManager, JobScheduler, and
DownloadManager. To debug why a job was stopped, we recommend logging why your
job was stopped by calling WorkInfo.getStopReason() (for
JobScheduler jobs, call JobParameters.getStopReason()).
For information about how your app's state affects the resources it can use, see Power management resource limits. For more information on battery-optimal best practices, refer to guidance on optimize battery use for task scheduling APIs.
We also recommend leveraging the new
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory API introduced in
Android 16 to understand why a job has not executed.
Testing
To test your app's behavior, you can enable override of certain job quota optimizations as long as the app is running on an Android 16 device.
To disable enforcement of "top state will adhere to job runtime quota", run the
following adb command:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
To disable enforcement of "jobs that are executing while concurrently with a
foreground service will adhere to the job runtime quota", run the following
adb command:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
To test certain app standby bucket behavior, you can set the app standby bucket
of your app using the following adb command:
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
To understand the app standby bucket your app is in, you can get the app standby
bucket of your app using the following adb command:
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
放棄空白工作停止原因
如果与作业关联的 JobParameters 对象已被垃圾回收,但尚未调用 JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) 来指示作业已完成,则会发生作业被废弃的情况。这表示作业可能会在应用不知情的情况下运行和重新调度。
依赖于 JobScheduler 的应用不会维护对 JobParameters 对象的强引用,并且超时现在将获得新的作业停止原因 STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED,而不是 STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT。
如果新的作业被废弃停止原因频繁出现,系统会采取缓解措施来降低作业频率。
应用应使用新的停止原因来检测和减少被废弃的作业。
如果您使用的是 WorkManager、AsyncTask 或 DownloadManager,则不会受到影响,因为这些 API 会代表您的应用管理作业生命周期。
完全淘汰 JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground
JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean) 方法會在排程應用程式處於前景或暫時豁免背景限制時,指出工作的重要性。
自 Android 12 (API 級別 31) 起,此方法已淘汰。自 Android 16 起,這項方法不再有效,系統會忽略呼叫此方法的行為。
這項功能移除作業也適用於 JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground()。自 Android 16 起,如果呼叫該方法,該方法會傳回 false。
已排序的廣播優先順序範圍不再是全域
Android 应用可以为广播接收器定义优先级,以控制接收器接收和处理广播的顺序。对于清单声明的接收器,应用可以使用 android:priority 属性来定义优先级;对于上下文注册的接收器,应用可以使用 IntentFilter#setPriority() API 来定义优先级。发送广播时,系统会按接收器的优先级(从高到低)将其传送给接收器。
在 Android 16 中,无法保证使用 android:priority 属性或 IntentFilter#setPriority() 在不同进程中传送广播的顺序。广播优先级仅在同一应用进程内有效,而不会跨所有进程有效。
此外,广播优先级将自动限制在 (SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1) 的范围内。只有系统组件才能将 SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY、SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY 设置为广播优先级。
如果您的应用执行以下任一操作,可能会受到影响:
- 您的应用声明了具有相同广播 intent 的多个进程,并且希望根据优先级以特定顺序接收这些 intent。
- 您的应用进程与其他进程交互,并期望以特定顺序接收广播 intent。
如果进程需要相互协调,则应使用其他协调渠道进行通信。
ART 內部變更
Android 16 includes the latest updates to the Android Runtime (ART) that improve the Android Runtime's (ART's) performance and provide support for additional Java features. Through Google Play System updates, these improvements are also available to over a billion devices running Android 12 (API level 31) and higher.
As these changes are released, libraries and app code that rely on internal structures of ART might not work correctly on devices running Android 16, along with earlier Android versions that update the ART module through Google Play system updates.
Relying on internal structures (such as non-SDK interfaces) can always lead to compatibility problems, but it's particularly important to avoid relying on code (or libraries containing code) that leverages internal ART structures, since ART changes aren't tied to the platform version the device is running on and they go out to over a billion devices through Google Play system updates.
All developers should check whether their app is impacted by testing their apps thoroughly on Android 16. In addition, check the known issues to see if your app depends on any libraries that we've identified that rely on internal ART structures. If you do have app code or library dependencies that are affected, seek public API alternatives whenever possible and request public APIs for new use cases by creating a feature request in our issue tracker.
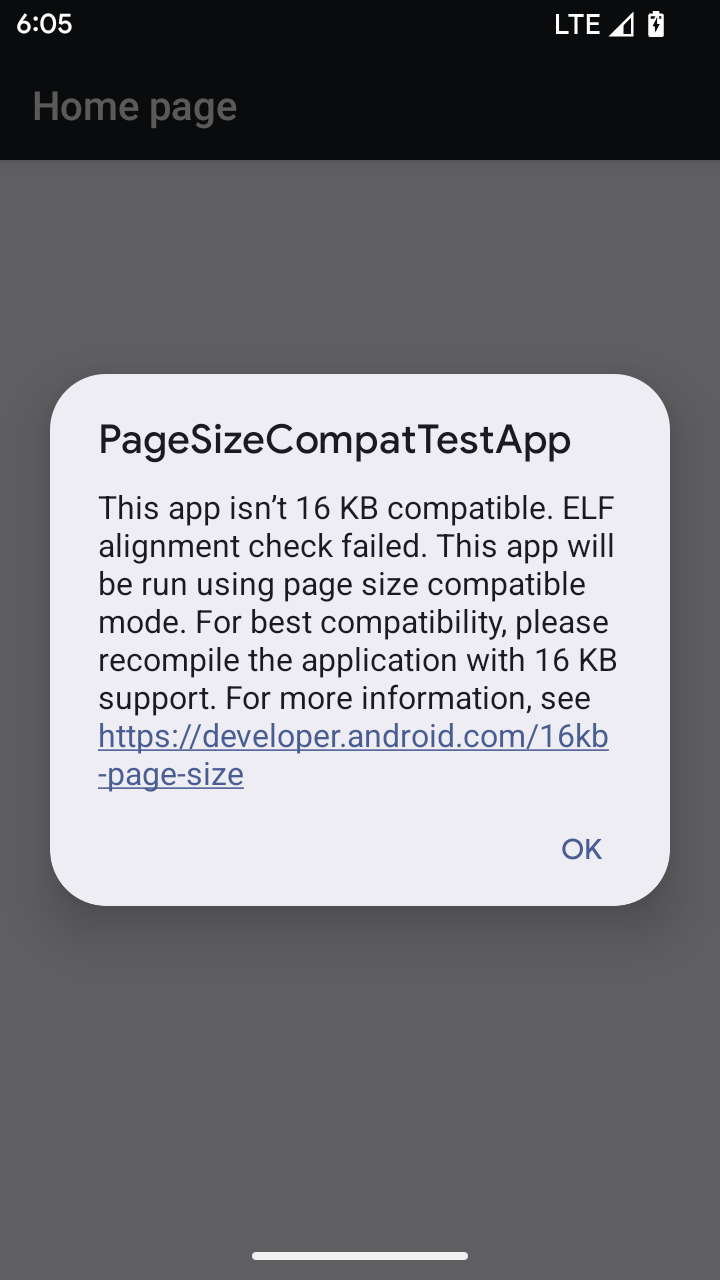
16 KB 頁面大小相容模式
Android 15 推出了 16 KB 記憶體分頁支援功能,以提升平台效能。Android 16 新增了相容模式,可讓為 4 KB 記憶體分頁建構的部分應用程式,在針對 16 KB 記憶體分頁設定的裝置上執行。
當應用程式在搭載 Android 16 以上版本的裝置上執行時,如果 Android 偵測到應用程式有 4 KB 對齊的記憶體分頁,就會自動使用相容性模式,並向使用者顯示通知對話方塊。在 AndroidManifest.xml 中設定 android:pageSizeCompat 屬性以啟用向後相容性模式,可防止應用程式啟動時顯示對話方塊。如要使用 android:pageSizeCompat 屬性,請使用 Android 16 SDK 編譯應用程式。
為獲得最佳效能、可靠性和穩定性,應用程式仍應以 16 KB 對齊。如要進一步瞭解如何更新應用程式以支援 16 KB 記憶體分頁,請參閱近期的網誌文章。
使用者體驗和系統 UI
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 包含下列變更,旨在打造更一致、直覺的使用者體驗。
淘汰令人混淆的無障礙工具公告
Android 16 已淘汰無障礙公告,這類公告的特色是使用 announceForAccessibility 或調度 TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT 無障礙事件。這可能會為 TalkBack 和 Android 螢幕閱讀器的使用者帶來不一致的使用者體驗,而替代方案可在各種 Android 輔助技術中,滿足更廣泛的使用者需求。
替代方案範例:
- 如要進行重大的 UI 變更 (例如變更視窗),請使用
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)和setAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence)。在 Compose 中使用Modifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" } - 如要通知使用者關鍵 UI 的變更,請使用
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int)。在 Compose 中使用Modifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}。這些事件應謹慎使用,因為每次 View 更新時,這些事件都可能產生通知。 - 如要通知使用者錯誤,請傳送
AccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERROR類型的AccessibilityEvent,並設定AccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence),或使用TextView#setError(CharSequence)。
如要進一步瞭解建議的替代方案,請參閱已淘汰的 announceForAccessibility API 參考說明文件。
支援三按鈕操作模式
Android 16 为已正确迁移到预测性返回的应用的三按钮导航栏引入了预测性返回支持。长按返回按钮会启动预测性返回动画,让您预览返回滑动手势会打开的界面。
此行为适用于系统中支持预测性返回动画的所有区域,包括系统动画(返回主屏幕、跨任务和跨 activity)。
自動套用主題色應用程式圖示
Beginning with Android 16 QPR 2, Android automatically applies themes to app icons to create a cohesive home screen experience. This occurs if an app does not provide its own themed app icon. Apps can control the design of their themed app icon by including a monochrome layer within their adaptive icon and previewing what their app icon will look like in Android Studio.
裝置板型規格
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 包含以下變更,適用於虛擬裝置擁有者將應用程式投放到螢幕時。
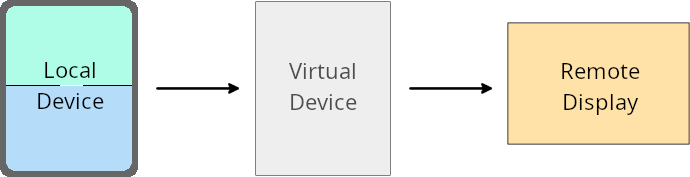
虛擬裝置擁有者覆寫
虚拟设备所有者是创建和管理虚拟设备的受信任应用或特权应用。虚拟设备所有者在虚拟设备上运行应用,然后将应用投影到远程设备的显示屏上,例如个人电脑、虚拟现实设备或车载信息娱乐系统。虚拟设备所有者位于本地设备上,例如手机。
按应用替换项
在搭载 Android 16(API 级别 36)的设备上,虚拟设备所有者可以替换其管理的特定虚拟设备上的应用设置。例如,为了改进应用布局,虚拟设备所有者在将应用投影到外部显示屏上时,可以忽略屏幕方向、宽高比和可调整大小性限制。
常见的重大更改
Android 16 的行为可能会影响应用在汽车显示屏或 Chromebook 等大屏幕设备上的界面,尤其是那些专为竖屏小显示屏设计的布局。如需了解如何让应用适应所有设备类型,请参阅自适应布局简介。
参考文档
安全性
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 包含多項異動,可提升系統安全性,協助保護應用程式和使用者免受惡意應用程式侵害。
安全性提高,避免意圖重新導向攻擊
Android 16 provides default security against general Intent redirection
attacks, with minimum compatibility and developer changes required.
We are introducing by-default security hardening solutions to Intent
redirection exploits. In most cases, apps that use intents normally won't
experience any compatibility issues; we've gathered metrics throughout our
development process to monitor which apps might experience breakages.
Intent redirection in Android occurs when an attacker can partly or fully control the contents of an intent used to launch a new component in the context of a vulnerable app, while the victim app launches an untrusted sub-level intent in an extras field of an ("top-level") Intent. This can lead to the attacker app launching private components in the context of the victim app, triggering privileged actions, or gaining URI access to sensitive data, potentially leading to data theft and arbitrary code execution.
Opt out of Intent redirection handling
Android 16 introduces a new API that allows apps to opt out of launch security protections. This might be necessary in specific cases where the default security behavior interferes with legitimate app use cases.
For applications compiling against Android 16 (API level 36) SDK or higher
You can directly use the removeLaunchSecurityProtection() method on the Intent
object.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
For applications compiling against Android 15 (API level 35) or lower
While not recommended, you can use reflection to access the
removeLaunchSecurityProtection() method.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
隨附應用程式不會再收到探索逾時通知
Android 16 在配件裝置配對流程中導入了新行為,以保護使用者的所在位置隱私,避免遭到惡意應用程式竊取。所有在 Android 16 上執行的隨附應用程式,都不再直接透過 RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT 收到發現逾時的通知。而是透過視覺對話方塊通知使用者逾時事件。當使用者關閉對話方塊時,應用程式會收到關於 RESULT_USER_REJECTED 關聯失敗的警示。
搜尋時間也從原本的 20 秒延長,使用者可在搜尋期間的任何時間停止裝置探索。如果在開始搜尋的頭 20 秒內發現至少一台裝置,CDM 就會停止搜尋其他裝置。
連線能力
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 包含藍牙堆疊的下列變更,可提升與周邊裝置的連線能力。
改善債券損失處理方式
Starting in Android 16, the Bluetooth stack has been updated to improve security and user experience when a remote bond loss is detected. Previously, the system would automatically remove the bond and initiate a new pairing process, which could lead to unintentional re-pairing. We have seen in many instances apps not taking care of the bond loss event in a consistent way.
To unify the experience, Android 16 improved the bond loss handling to the system. If a previously bonded Bluetooth device could not be authenticated upon reconnection, the system will disconnect the link, retain local bond information, and display a system dialog informing users of the bond loss and directing them to re-pair.
