La piattaforma Android 16 include modifiche al comportamento che potrebbero influire sulla tua app.
Le seguenti modifiche al comportamento si applicano a tutte le app quando vengono eseguite su Android 16,
indipendentemente dal targetSdkVersion. Devi testare la tua app e poi modificarla
in base alle necessità per supportare queste modifiche, ove applicabile.
Assicurati di esaminare anche l'elenco delle modifiche al comportamento che interessano solo le app che hanno come target Android 16.
Funzionalità di base
Android 16 (livello API 36) include le seguenti modifiche che modificano o espandono varie funzionalità di base del sistema Android.
Ottimizzazioni delle quote di JobScheduler
A partire da Android 16, stiamo modificando la quota di runtime per l'esecuzione di job regolari e rapidi in base ai seguenti fattori:
- In quale bucket standby app si trova l'applicazione: in Android 16, i bucket standby attivi inizieranno a essere applicati da una generosa quota di runtime.
- Se l'esecuzione del job inizia mentre l'app è in primo piano: in Android 16, i job avviati mentre l'app è visibile all'utente e continuano dopo che l'app diventa invisibile, rispettano la quota di runtime del job.
- Se il job viene eseguito durante l'esecuzione di un servizio in primo piano: in Android 16, i job eseguiti contemporaneamente a un servizio in primo piano rispettano la quota di runtime del job. Se utilizzi i job per il trasferimento di dati avviato dall'utente, valuta la possibilità di utilizzare i job di trasferimento di dati avviato dall'utente.
Questa modifica influisce sulle attività pianificate utilizzando WorkManager, JobScheduler e
DownloadManager. Per eseguire il debug del motivo per cui un job è stato interrotto, ti consigliamo di registrare il motivo per cui il job è stato interrotto chiamando WorkInfo.getStopReason() (per i job JobScheduler, chiama JobParameters.getStopReason()).
Per informazioni su come lo stato dell'app influisce sulle risorse che può utilizzare, consulta Limiti delle risorse di gestione dell'alimentazione. Per ulteriori informazioni sulle best practice per l'ottimizzazione della batteria, consulta le indicazioni su come ottimizzare l'utilizzo della batteria per le API di pianificazione delle attività.
Ti consigliamo inoltre di utilizzare la nuova API
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory introdotta in
Android 16 per capire perché un job non è stato eseguito.
Test
Per testare il comportamento della tua app, puoi attivare l'override di alcune ottimizzazioni della quota di job purché l'app sia in esecuzione su un dispositivo Android 16.
Per disattivare l'applicazione di "top state will adhere to job runtime quota", esegui il seguente comando adb:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Per disattivare l'applicazione di "i job in esecuzione contemporaneamente a un servizio in primo piano rispetteranno la quota di runtime del job", esegui questo comando adb:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Per testare il comportamento di determinati bucket di standby delle app, puoi impostare il bucket di standby delle app
della tua app utilizzando il seguente comando adb:
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
Per capire in quale bucket di standby dell'app si trova la tua app, puoi recuperare il bucket di standby dell'app utilizzando il seguente comando adb:
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Motivo di interruzione dei processi vuoti abbandonati
Un job abbandonato si verifica quando l'oggetto JobParameters associato al job è stato sottoposto a garbage collection, ma JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) non è stato chiamato per segnalare il completamento del job. Ciò indica che il job potrebbe essere in esecuzione e essere riprogrammato senza che l'app lo sappia.
Le app che si basano su JobScheduler non mantengono un riferimento forte all'oggettoJobParameters e ora al timeout verrà concesso il nuovo motivo di interruzione del jobSTOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED, anziché STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT.
Se si verificano spesso casi del nuovo motivo di interruzione dell'abbandono, il sistema prenderà provvedimenti per ridurre la frequenza dei job.
Le app devono utilizzare il nuovo motivo di interruzione per rilevare e ridurre i job abbandonati.
Se utilizzi WorkManager, AsyncTask o DownloadManager, non sono interessati perché queste API gestiscono il ciclo di vita dei job per conto della tua app.
Ritiro completo di JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground
Il metodo JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean) indica l'importanza di un job quando l'app di pianificazione è in primo piano o quando è temporaneamente esente dalle limitazioni in background.
Questo metodo è stato ritirato da Android 12 (livello API 31). A partire da Android 16, non funziona più in modo efficace e la chiamata di questo metodo verrà ignorata.
Questa rimozione di funzionalità si applica anche a
JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground(). A partire da Android
16, se il metodo viene chiamato, restituisce false.
L'ambito della priorità di trasmissione ordinata non è più globale
Le app per Android possono definire le priorità per i ricevitori di trasmissione per controllare
l'ordine in cui i ricevitori ricevono ed elaborano la trasmissione. Per i gestori dichiarati nel file manifest, le app possono utilizzare l'attributo android:priority per definire la priorità e per i gestori registrati nel contesto, le app possono utilizzare l'API IntentFilter#setPriority() per definire la priorità. Quando viene inviata una trasmissione, il sistema la consegna ai ricevitori in ordine di priorità, dalla più alta alla più bassa.
In Android 16, l'ordine di invio delle trasmissioni che utilizzano l'attributo android:priority o IntentFilter#setPriority() in diversi processi non sarà garantito. Le priorità di trasmissione verranno rispettate solo all'interno della stessa procedura di applicazione e non in tutte le procedure.
Inoltre, le priorità di trasmissione verranno automaticamente limitate all'intervallo
(SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1,
SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1). Solo i componenti di sistema potranno impostare SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY come priorità di trasmissione.
La tua app potrebbe essere interessata se esegue una delle seguenti azioni:
- La tua applicazione ha dichiarato più processi con lo stesso intento di trasmissione e si aspetta di ricevere questi intent in un determinato ordine in base alla priorità.
- La procedura di applicazione interagisce con altri processi e ha aspettative sulla ricezione di un'intenzione di trasmissione in un determinato ordine.
Se le procedure devono coordinarsi tra loro, devono comunicare utilizzando altri canali di coordinamento.
Modifiche interne ad ART
Android 16 include gli aggiornamenti più recenti all'ambiente di runtime Android (ART) che migliorano le prestazioni dell'ambiente di runtime Android (ART) e forniscono il supporto di funzionalità Java aggiuntive. Tramite gli aggiornamenti di sistema di Google Play, questi miglioramenti sono disponibili anche per oltre un miliardo di dispositivi con Android 12 (livello API 31) e versioni successive.
Man mano che queste modifiche vengono rilasciate, le librerie e il codice delle app che si basano sulle strutture interne di ART potrebbero non funzionare correttamente sui dispositivi con Android 16 e sulle versioni precedenti di Android che aggiornano il modulo ART tramite gli aggiornamenti di sistema di Google Play.
Fare affidamento su strutture interne (ad esempio interfacce non SDK) può sempre portare a problemi di compatibilità, ma è particolarmente importante evitare di fare affidamento su codice (o librerie contenenti codice) che sfrutta strutture ART interne, poiché le modifiche ART non sono legate alla versione della piattaforma su cui è in esecuzione il dispositivo e vengono rilasciate su oltre un miliardo di dispositivi tramite gli aggiornamenti di sistema di Google Play.
Tutti gli sviluppatori devono verificare se la loro app è interessata testando le proprie app in modo approfondito su Android 16. Inoltre, controlla i problemi noti per verificare se la tua app dipende da librerie che abbiamo identificato come basate su strutture ART interne. Se hai dipendenze di codice dell'app o della libreria che sono interessate, cerca alternative API pubbliche, se possibile, e richiedi API pubbliche per nuovi casi d'uso creando una richiesta di funzionalità nel nostro issue tracker.
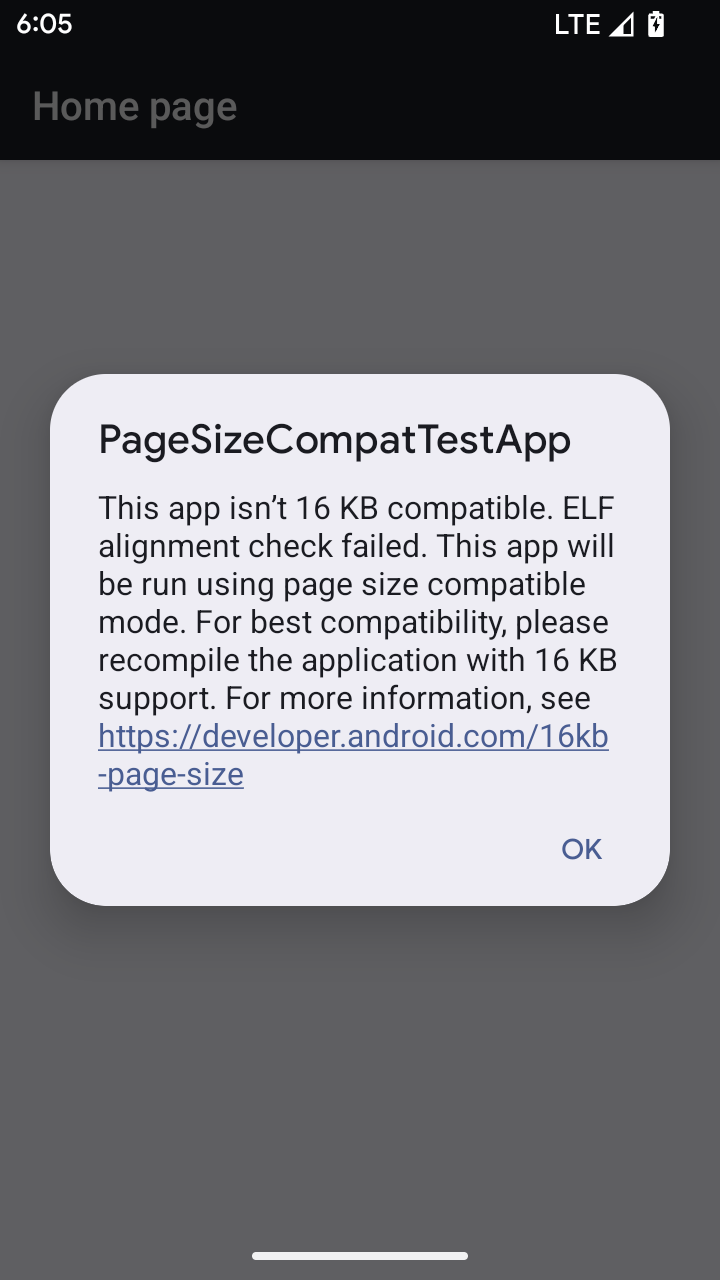
Modalità di compatibilità con le dimensioni pagina di 16 kB
Android 15 ha introdotto il supporto per le pagine di memoria da 16 KB per ottimizzare le prestazioni della piattaforma. Android 16 aggiunge una modalità di compatibilità, che consente ad alcune app create per pagine di memoria da 4 KB di essere eseguite su un dispositivo configurato per pagine di memoria da 16 KB.
Quando la tua app viene eseguita su un dispositivo con Android 16 o versioni successive, se Android rileva che la tua app ha pagine di memoria allineate a 4 KB, utilizza automaticamente la modalità di compatibilità e mostra una finestra di dialogo di notifica all'utente. L'impostazione della proprietà android:pageSizeCompat in AndroidManifest.xml per attivare la modalità di compatibilità con le versioni precedenti impedisce la visualizzazione della finestra di dialogo al momento dell'avvio dell'app. Per utilizzare la proprietà android:pageSizeCompat, compila l'app
utilizzando l'SDK Android 16.
Per ottenere le migliori prestazioni, affidabilità e stabilità, la tua app deve comunque essere allineata a 16 KB. Per ulteriori dettagli, consulta il nostro recente post del blog sull'aggiornamento delle app per supportare le pagine di memoria di 16 KB.
Esperienza utente e UI di sistema
Android 16 (livello API 36) include le seguenti modifiche volte a creare un'esperienza utente più coerente e intuitiva.
Ritiro degli annunci di accessibilità invasivi
Android 16 ritira gli annunci di accessibilità, caratterizzati dall'utilizzo di
announceForAccessibility o dall'invio di
TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT eventi di accessibilità. Ciò può creare esperienze utente incoerenti per gli utenti di TalkBack e dello screen reader di Android e le alternative soddisfano meglio una gamma più ampia di esigenze degli utenti in una serie di tecnologie per la disabilità di Android.
Esempi di alternative:
- Per modifiche significative all'interfaccia utente, come le modifiche alle finestre, utilizza
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)esetAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence). In Scrivi, usaModifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" } - Per informare l'utente delle modifiche all'interfaccia utente di importanza critica, utilizza
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int). In Scrivi, usaModifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}. Questi annunci devono essere utilizzati con parsimonia, in quanto potrebbero generare annunci ogni volta che una visualizzazione viene aggiornata. - Per notificare gli utenti degli errori, invia un
AccessibilityEventdi tipoAccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORe impostaAccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence)oppure utilizzaTextView#setError(CharSequence).
La documentazione di riferimento per l'API announceForAccessibility obsoleta include ulteriori dettagli sulle alternative suggerite.
Supporto della navigazione con tre pulsanti
Android 16 introduce il supporto del pulsante Indietro predittivo alla navigazione con tre pulsanti per le app che hanno effettuato correttamente la migrazione al pulsante Indietro predittivo. Se premi a lungo il pulsante Indietro, viene avviata un'animazione di Indietro predittiva che ti mostra un'anteprima della destinazione del gesto Indietro.
Questo comportamento si applica a tutte le aree del sistema che supportano le animazioni Indietro predittive, incluse le animazioni di sistema (torna alla schermata Home, passaggio da un'attività all'altra e così via).
Icone delle app a tema automatiche
A partire da Android 16 QPR 2, Android applica automaticamente i temi alle icone delle app per creare un'esperienza coerente nella schermata Home. Ciò si verifica se un'app non fornisce la propria icona dell'app a tema. Le app possono controllare il design dell'icona dell'app a tema includendo un livello monocromatico nell'icona adattiva e visualizzando l'aspetto dell'icona dell'app in Android Studio.
Fattori di forma dei dispositivi
Android 16 (livello API 36) include le seguenti modifiche per le app quando vengono proiettate sui display dai proprietari di dispositivi virtuali.
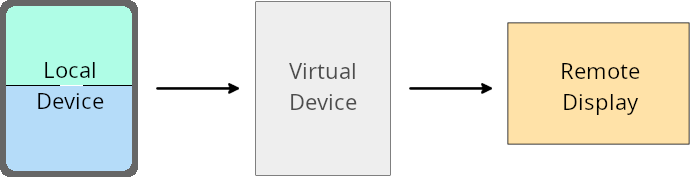
Override del proprietario del dispositivo virtuale
Un proprietario di dispositivo virtuale è un'app attendibile o con privilegi che crea e gestisce un dispositivo virtuale. I proprietari di dispositivi virtuali eseguono app su un dispositivo virtuale e poi proiettano le app sul display di un dispositivo remoto, come un computer personale, un dispositivo di realtà virtuale o un sistema di infotainment per auto. Il proprietario del dispositivo virtuale si trova su un dispositivo locale, ad esempio un cellulare.
Override per app
Sui dispositivi con Android 16 (livello API 36), i proprietari di dispositivi virtuali possono ignorare le impostazioni delle app su determinati dispositivi virtuali che gestiscono. Ad esempio, per migliorare il layout delle app, il proprietario di un dispositivo virtuale può ignorare le limitazioni di orientamento, proporzioni e ridimensionamento durante la proiezione delle app su un display esterno.
Modifiche che provocano un errore comuni
Il comportamento di Android 16 potrebbe influire sulla UI della tua app su fattori di forma con schermi di grandi dimensioni, come display per auto o Chromebook, in particolare sui layout progettati per piccoli display in orientamento verticale. Per scoprire come rendere la tua app adattabile a tutti i fattori di forma dei dispositivi, consulta Informazioni sui layout adattabili.
Riferimenti
Streaming di app complementari
Sicurezza
Android 16 (livello API 36) include modifiche che promuovono la sicurezza del sistema per proteggere app e utenti da app dannose.
Maggiore sicurezza contro gli attacchi di reindirizzamento degli intent
Android 16 offre una sicurezza predefinita contro gli attacchi di reindirizzamento Intent generali, con modifiche minime alla compatibilità e allo sviluppo richieste.
Stiamo introducendo soluzioni di rafforzamento della sicurezza per impostazione predefinita per gli exploit di reindirizzamento Intent. Nella maggior parte dei casi, le app che utilizzano intent non
riscontrano problemi di compatibilità. Abbiamo raccolto metriche durante il nostro
processo di sviluppo per monitorare quali app potrebbero riscontrare interruzioni.
Il reindirizzamento degli intent in Android si verifica quando un malintenzionato può controllare parzialmente o completamente i contenuti di un intent utilizzato per avviare un nuovo componente nel contesto di un'app vulnerabile, mentre l'app vittima avvia un intent di livello secondario non attendibile in un campo extra di un intent ("di primo livello"). Ciò può portare l'app malintenzionata ad avviare componenti privati nel contesto dell'app vittima, ad attivare azioni privilegiate o a ottenere l'accesso URI a dati sensibili, con conseguente furto di dati ed esecuzione di codice arbitrario.
Disattivare la gestione del reindirizzamento intent
Android 16 introduce una nuova API che consente alle app di disattivare le protezioni di sicurezza all'avvio. Ciò potrebbe essere necessario in casi specifici in cui il comportamento di sicurezza predefinito interferisce con casi d'uso legittimi dell'app.
Per le applicazioni compilate con l'SDK Android 16 (livello API 36) o versioni successive
Puoi utilizzare direttamente il metodo removeLaunchSecurityProtection() sull'oggetto Intent.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
Per le applicazioni compilate su Android 15 (livello API 35) o versioni precedenti
Anche se non è consigliato, puoi utilizzare la reflection per accedere al metodo removeLaunchSecurityProtection().
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
Le app complementari non ricevono più notifiche relative ai timeout di rilevamento
Android 16 introduce un nuovo comportamento durante il percorso di accoppiamento del dispositivo complementare per proteggere la privacy della posizione dell'utente dalle app dannose. Tutte le app complementari in esecuzione su Android 16 non ricevono più una notifica diretta del timeout di rilevamento utilizzando RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT. L'utente viene invece informato degli eventi di timeout con una finestra di dialogo visiva. Quando l'utente chiude la finestra di dialogo, l'app viene avvisata dell'errore di associazione con RESULT_USER_REJECTED.
La durata della ricerca è stata estesa rispetto ai 20 secondi iniziali e la ricerca del dispositivo può essere interrotta dall'utente in qualsiasi momento durante la ricerca. Se viene rilevato almeno un dispositivo nei primi 20 secondi dall'avvio della ricerca, il CDM interrompe la ricerca di altri dispositivi.
Connettività
Android 16 (livello API 36) include le seguenti modifiche nello stack Bluetooth per migliorare la connettività con i dispositivi periferici.
Gestione migliorata della perdita di cauzione
A partire da Android 16, lo stack Bluetooth è stato aggiornato per migliorare la sicurezza e l'esperienza utente quando viene rilevata una perdita del legame remoto. In precedenza, il sistemarimuoveva automaticamente il legame e avviava una nuova procedura di accoppiamento, che poteva portare a un'accoppiata non intenzionale. In molti casi abbiamo notato che le app non gestiscono l'evento di perdita del legame in modo coerente.
Per unificare l'esperienza, Android 16 ha migliorato la gestione della perdita del legame con il sistema. Se un dispositivo Bluetooth accoppiato in precedenza non può essere autenticato al nuovo collegamento, il sistema scollega il link, conserva le informazioni sull'accoppiamento locale e mostra una finestra di dialogo di sistema che informa gli utenti della perdita dell'accoppiamento e li invita a eseguire nuovamente l'accoppiamento.
