使用 3D 模型时,Jetpack XR SDK 支持 glTF 2.0 开放标准。当 Android XR 渲染使用 Jetpack XR SDK 构建的应用时,3D 模型将使用 glTF 2.0 标准中指定的基于物理的渲染 (PBR) 技术(以及受支持的扩展程序)进行渲染。大多数数字内容创作 (DCC) 工具(例如 Autodesk Maya、Maxon ZBrush、Blender 和 Spline)都可以将 3D 模型导出为 glTF 格式(.gltf 或 .glb 文件)。
如果用户或您的应用指定了 SpatialEnvironment 天空盒,3D 模型将根据环境天空盒提供的光照信息进行照明。反射性材质和镜面高光也会反射环境天空盒。如果透视功能已启用,则光照、反射和镜面高光将基于一个简单的明亮房间,其中包含一个定向光源。
如需快速了解支持的材质,请参阅 Khronos 网站上的 glTF PBR 属性。
使用 Jetpack XR SDK 构建的应用可以通过两种主要方式加载 3D 模型。
- 按照将 3D 模型放入
ActivitySpace中中的说明,将其加载到ActivitySpace中 - 通过 intent 使用内置的 Scene Viewer
将 3D 模型放置到 ActivitySpace 中
获得 glTF 文件后,下一步是在 Android Studio 中将其添加到 assets 目录。我们建议您创建一个 models 目录,以便更好地整理您的资产类型。
如需加载 glTF 模型,请调用 GltfModel.create()。
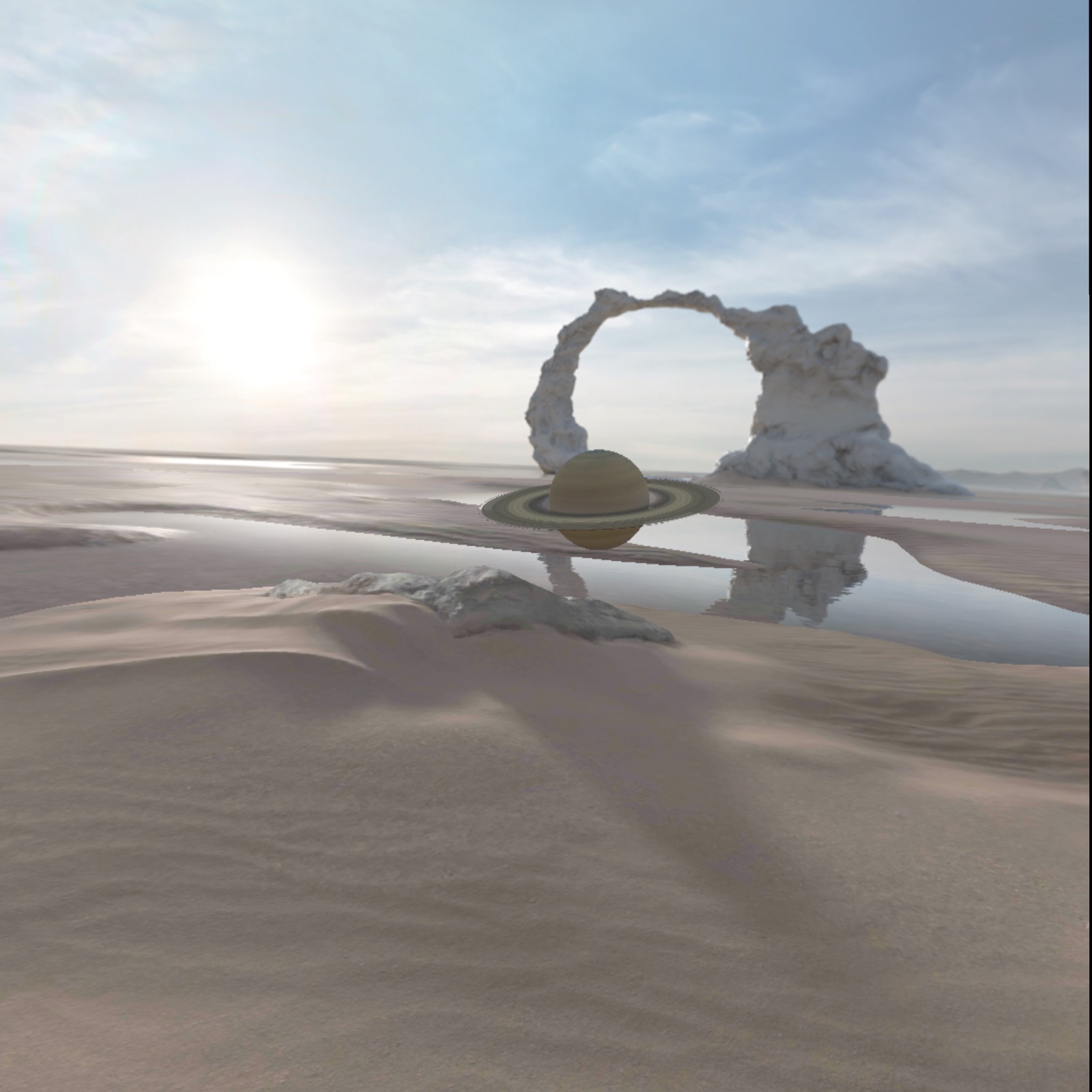
val gltfModel = GltfModel.create(session, Paths.get("models", "saturn_rings.glb"))
此时,模型已加载到内存中,但尚未渲染。 如果您要加载许多 3D 模型,或者您的模型很大,最好提前异步加载它们。这样,用户就不必等待模型加载到内存中。
我们需要将 glTF 添加到 ActivitySpace 中。调用 GltfModelEntity.create 以创建实体并将其放入 ActivitySpace 中。最佳实践是,您应检查应用是否处于允许使用空间功能的状态。
if (session.scene.spatialCapabilities.contains(SpatialCapability.SPATIAL_3D_CONTENT)) { val gltfEntity = GltfModelEntity.create(session, gltfModel) }
现在,运行应用时,您应该会看到已加载的 3D 模型。

将 3D 模型放置到 Compose SceneCoreEntity 中
虽然您仍需使用 GltfModel.create() 将 glTF 加载到内存中,但如果您使用 Jetpack Compose for XR 创建界面,则可以将 3D 模型放置在 SceneCoreEntity 中。
请参阅使用 SceneCoreEntity 在布局中放置 3D 对象。
为 3D 模型添加动画效果
根据 glTF 规范,3D 模型可以嵌入动画。
Jetpack XR SDK 支持骨骼(绑定)、刚性、变形目标(混合形状)动画。系统还支持使用 KHR_animation_pointer glTF 扩展创建的 Material 动画。
如需播放动画,请调用 startAnimation() 并指定动画的名称。您可以选择指定动画是否应无限循环播放。
gltfEntity.startAnimation(loop = true, animationName = "Walk")
再次调用 startAnimation 时,当前动画将停止,并开始播放新动画。
您可以通过 getAnimationState() 查询动画的当前状态。
如果在调用 startAnimation() 时指定的动画名称不存在,则调用会静默失败,所有正在运行的动画都会停止,并且 getAnimationState() 会返回 STOPPED。
使用场景查看器加载 3D 模型
如果您想以最简单的方式加载具有基本互动功能的 3D 模型,可以选择像在移动设备上一样使用 Scene Viewer。Android XR 设备上的 Scene Viewer 与移动设备上的 Scene Viewer 之间的主要区别在于,Scene Viewer 仅支持指向 glTF 文件的文件 URI 参数,而忽略所有其他参数。
Scene Viewer 是一个单独的应用,通过 intent 调用,并在全沉浸空间模式下运行。因此,当您调用它时,您的应用将不再可见,而 Scene Viewer 将获得焦点。您可能更改过的任何环境都将重置为用户的系统偏好设置。
以下示例展示了如何在 Android XR 上使用 Intent 在 Scene Viewer 中查看 glTF 文件:
val url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/KhronosGroup/glTF-Sample-Models/master/2.0/Avocado/glTF/Avocado.gltf" val sceneViewerIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW) val intentUri = Uri.parse("https://arvr.google.com/scene-viewer/1.2") .buildUpon() .appendQueryParameter("file", url) .build() sceneViewerIntent.setData(intentUri) try { startActivity(sceneViewerIntent) } catch (e: ActivityNotFoundException) { // There is no activity that could handle the intent. }
如需详细了解 Scene Viewer 的互动选项,请参阅我们的3D 模型设计文档。
glTF 扩展
Jetpack XR SDK 支持多种可扩展 3D 模型功能的 glTF 扩展。您可以通过 GltfModelEntity 和 Scene Viewer 使用这些功能。
KHR_animation_pointerKHR_draco_mesh_compressionKHR_lights_punctualKHR_materials_clearcoatKHR_materials_sheenKHR_materials_unlitKHR_materials_variantsKHR_mesh_quantizationKHR_texture_basisuKHR_texture_transformEXT_texture_webp


