Android 15 面向开发者引入了一些出色的功能和 API。以下各部分总结了这些功能,可帮助您开始使用相关 API。
如需查看新增、修改和移除的 API 的详细列表,请参阅 API 差异报告。如需详细了解添加的 API,请访问 Android API 参考文档。对于 Android 15,请查找在 API 级别 35 中添加的 API。如需了解平台变更可能会在哪些方面影响您的应用,请务必查看会影响以 Android 15 为目标平台的应用和所有应用的 Android 15 行为变更。
摄像头和媒体
Android 15 包含各种功能,可改善相机和媒体体验,并让您能够使用工具和硬件来帮助创作者在 Android 上实现自己的创意。
如需详细了解 Android 媒体和相机方面的最新功能和开发者解决方案,请观看 Google I/O 大会上的打造现代 Android 媒体和相机体验讲座。
弱光增强
Android 15 引入了弱光增强功能,这是一种自动曝光模式,适用于 Camera 2 和夜间模式相机扩展。“弱光增强”功能可在光线昏暗的环境下调整预览画面的曝光度。这与夜间模式相机扩展程序创建静态图片的方式不同,因为夜间模式会将一系列照片组合起来,以创建一张经过增强的单张图片。虽然夜间模式非常适合拍摄静态图片,但无法创建连续的帧流,而“低光增强”功能可以。因此,弱光增强功能可启用相机功能,例如:
- 提供增强型图片预览,以便用户更好地取景拍摄低光照片
- 在光线不足的情况下扫描二维码
如果您启用“弱光增强”功能,该功能会在光线较弱时自动开启,在光线较强时关闭。
应用可以在光线昏暗的环境下录制预览画面,以保存经过亮度提升的视频。
如需了解详情,请参阅弱光增强。
应用内相机控件
Android 15 添加了一个扩展程序,可让您更好地控制支持的设备上的相机硬件及其算法:
HDR 余量控制
Android 15 会选择适合底层设备功能和面板位深的 HDR 余量。对于包含大量 SDR 内容的网页(例如显示单个 HDR 缩略图的消息应用),此行为最终可能会对 SDR 内容的感知亮度产生不利影响。在 Android 15 中,您可以使用 setDesiredHdrHeadroom 控制 HDR 余量,以便在 SDR 内容和 HDR 内容之间取得平衡。

响度控制

Android 15 引入了对 CTA-2075 响度标准的支持,可帮助您避免音频响度不一致,并确保用户在切换内容时不必不断调整音量。系统利用输出设备(头戴式耳机和扬声器)的已知特性以及 AAC 音频内容中提供的响度元数据,智能调整音频响度和动态范围压缩级别。
如需启用此功能,您需要确保 AAC 内容中提供响度元数据,并在应用中启用平台功能。为此,您可以通过使用关联的 AudioTrack 中的音频会话 ID 调用其 create 工厂方法来实例化 LoudnessCodecController 对象;这会自动开始应用音频更新。您可以传递 OnLoudnessCodecUpdateListener 来修改或过滤响度参数,然后再将其应用于 MediaCodec。
// Media contains metadata of type MPEG_4 OR MPEG_D
val mediaCodec = …
val audioTrack = AudioTrack.Builder()
.setSessionId(sessionId)
.build()
...
// Create new loudness controller that applies the parameters to the MediaCodec
try {
val lcController = LoudnessCodecController.create(mSessionId)
// Starts applying audio updates for each added MediaCodec
}
AndroidX media3 ExoPlayer 也将更新,以使用
LoudnessCodecController API,可实现无缝应用集成。
虚拟 MIDI 2.0 设备
Android 13 添加了对使用 USB 连接 MIDI 2.0 设备的支持,这些设备使用通用 MIDI 数据包 (UMP) 进行通信。Android 15 将 UMP 支持扩展到了虚拟 MIDI 应用,使作曲应用能够像使用 USB MIDI 2.0 设备一样,将虚拟 MIDI 2.0 设备用作控制合成器应用的设备。
更高效的 AV1 软件解码

dav1d 是 VideoLAN 推出的热门 AV1 软件解码器,适用于不支持硬件 AV1 解码的 Android 设备。与旧版 AV1 软件解码器相比,dav1d 的性能最高可提升 3 倍,让更多用户(包括一些低端和中端设备)能够播放高清 AV1 视频。
您的应用需要选择启用 dav1d,方法是通过名称 "c2.android.av1-dav1d.decoder" 调用它。在后续更新中,dav1d 将成为默认的 AV1 软件解码器。此支持已标准化,并向后移植到收到 Google Play 系统更新的 Android 11 设备。
开发者工作效率和工具
虽然我们的大部分工作都是围绕 Android Studio、Jetpack Compose 和 Android Jetpack 库等工具来提高您的工作效率,但我们始终在寻找平台中的方法,以帮助您更轻松地实现自己的愿景。
OpenJDK 17 更新
Android 15 将继续更新 Android 的核心库,以与最新 OpenJDK LTS 版本中的功能保持一致。
其中包含以下主要功能和改进:
- 改进了 NIO 缓冲区的使用体验
- 数据流
- 其他
math和strictmath方法 util软件包更新,包括顺序的collection、map和setDeflater中的ByteBuffer支持- 安全更新,例如
X500PrivateCredential和安全密钥更新
这些 API 会通过 Google Play 系统更新在搭载 Android 12(API 级别 31)及更高版本的 10 亿多部设备上更新,以便您以最新的编程功能为目标平台。
PDF 改进
Android 15 对 PdfRenderer API 进行了重大改进。应用可以整合呈现等高级功能
受密码保护的文件、注释、表单编辑、
searching,而 selection 则包含副本。支持线性化 PDF 优化,此功能可加快本地 PDF 查看速度并减少资源使用量。Jetpack PDF 库使用这些 API 来简化 PDF 的添加
查看功能。

PdfRenderer 已移至一个可使用 Google
Play 系统更新独立于平台版本,并且我们支持
将这些变更还原到 Android 11(API 级别 30),方法是创建兼容的
Android 15 之前版本的 API Surface,称为
PdfRendererPreV。
自动切换语言功能的改进
Android 14 在音频中添加了设备端多语言识别功能,并支持在语言之间自动切换,但这可能会导致丢失字词,尤其是当两次语音之间语言切换的间隔时间较短时。Android 15 添加了其他控件,以帮助应用根据其用例调整此切换。EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_INITIAL_ACTIVE_DURATION_TIME_MILLIS 会将自动切换限制在音频会话开始时,而 EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_MATCH_SWITCHES 会在发生指定次数的切换后停用语言切换。如果您预计会话期间只会使用一种语言,并且该语言应被自动检测到,这些选项会特别有用。
改进的 OpenType Variable Font API
Android 15 提高了 OpenType 可变字体的易用性。您可以创建
来自可变字体的 FontFamily 实例,而不指定粗细轴
使用 buildVariableFamily API。文本渲染程序会替换 wght 轴的值,以匹配显示的文本。
使用该 API 可以大大简化创建 Typeface 的代码:
Kotlin
val newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build()
Java
Typeface newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build();
以前,如需创建相同的 Typeface,您需要更多代码:
Kotlin
val oldTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build()) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ).build() ).build()
Java
Typeface oldTypeface = new Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ) .build() ).build();
以下示例展示了同时使用旧版和新版 API 创建的 Typeface 的呈现方式:
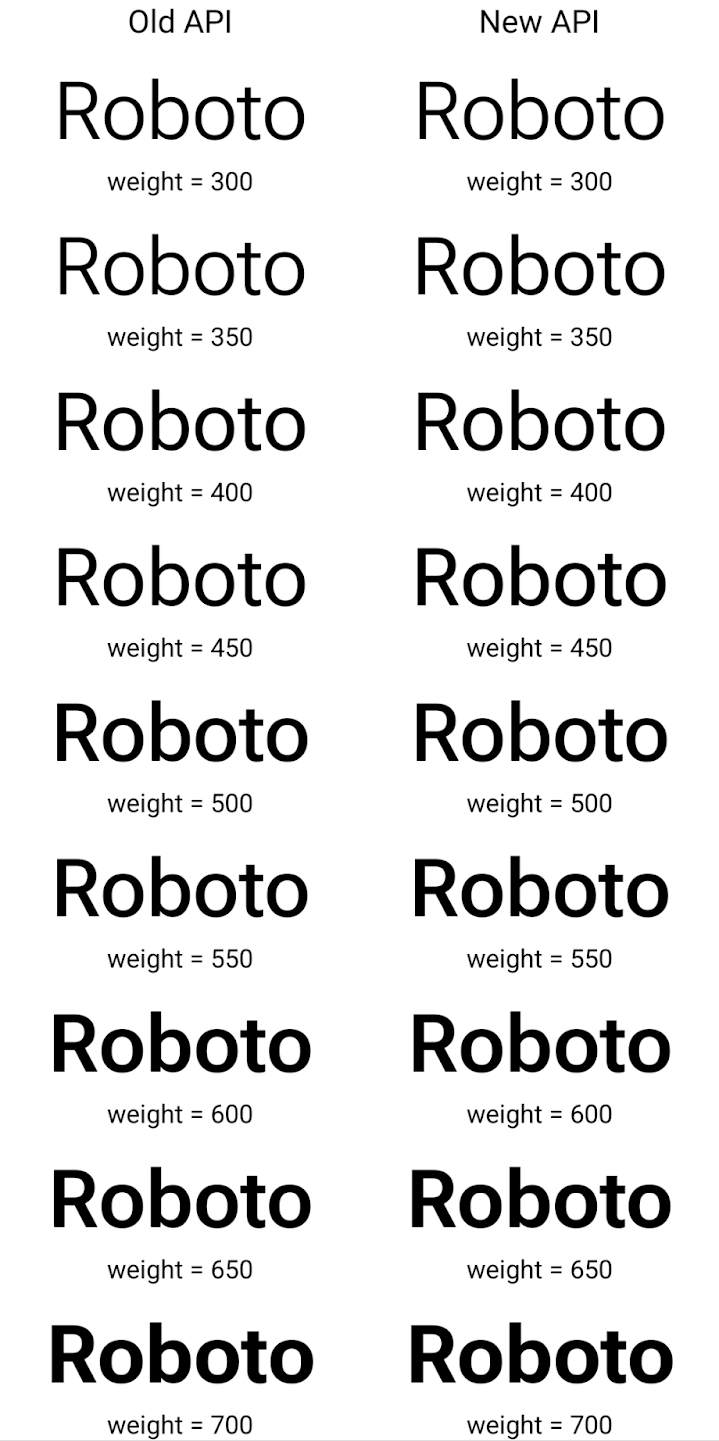
在此示例中,使用旧 API 创建的 Typeface 不包含
为 350、450、550 和 650 创建准确的字体粗细
Font 实例,因此渲染程序会回退到最接近的权重。在
在此示例中,系统会渲染 300 而不是 350,渲染 400 而不是 450,
依此类推。相比之下,使用新 API 创建的 Typeface 会为给定重量动态创建 Font 实例,因此系统也会为 350、450、550 和 650 呈现准确的重量。
精细的换行控制
从 Android 15 开始,TextView 和底层行断开符可以将给定部分文本保留在同一行中,以提高可读性。您可以通过在字符串资源或 createNoBreakSpan 中使用 <nobreak> 标记来充分利用此换行符自定义功能。同样,您可以使用 <nohyphen> 标记或 createNoHyphenationSpan 来防止对字词进行分词。
例如,以下字符串资源不包含换行符,在呈现时,文本“Pixel 8 Pro”会在不合适的位置换行:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind Pixel 8 Pro.</string>
</resources>
相比之下,此字符串资源包含 <nobreak> 标记,该标记会将字词“Pixel 8 Pro”换行,并防止换行:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind <nobreak>Pixel 8 Pro.</nobreak></string>
</resources>
以下图片展示了这些字符串呈现方式的差异:

<nobreak> 标记换行。
<nobreak> 标记封装“Pixel 8 Pro.”短语的同一行文本的布局。应用归档
Android 和 Google Play 宣布支持最后的应用归档功能 年,这让用户可以通过移除部分内容来释放空间 通过 Android 应用发布的设备中不常用的应用 前往 Google Play 下载套装。Android 15 在操作系统级别支持应用归档和解压缩,让所有应用商店都能更轻松地实现归档和解压缩。
具有 REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES 权限的应用可以调用
PackageInstaller requestArchive 方法请求归档
已安装的应用软件包,这会移除 APK 和所有缓存的文件,但会保留
用户数据已归档的应用会通过 LauncherApps API 作为可显示的应用返回;用户会看到一个界面处理,以突出显示这些应用已归档。如果用户点按已归档的应用,负责安装的应用会收到解除归档请求,并且可以通过 ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED 广播监控恢复过程。
使用开发者选项在设备上启用 16 KB 模式

切换以 16KB 页面大小启动设备开发者选项,以在 16 KB 模式下启动设备。
在 Android 15 的 QPR 版本中,您可以使用某些设备上提供的开发者选项,以 16 KB 模式启动设备并执行设备端测试。在使用开发者选项之前,请依次前往设置 > 系统 > 软件更新,并应用所有可用的更新。
此开发者选项适用于以下设备:
Pixel 8 和 Pixel 8 Pro(搭载 Android 15 QPR1 或更高版本)
Pixel 8a(搭载 Android 15 QPR1 或更高版本)
Pixel 9、9 Pro 和 9 Pro XL(搭载 Android 15 QPR2 或更高版本)
Pixel 9a(搭载 Android 16 或更高版本)
图形
Android 15 带来了最新的图形改进,包括 ANGLE 和对 Canvas 图形系统的添加。
实现 Android GPU 访问的现代化

与早期相比,Android 硬件已经有了很大的进步。早期,核心操作系统在单个 CPU 上运行,并且使用基于固定功能流水线的 API 访问 GPU。从 Android 7.0(API 级别 24)开始,NDK 中就提供了 Vulkan® 图形 API,其较低级别的抽象更好地反映了现代 GPU 硬件,可更好地扩缩以支持多个 CPU 核心,并可降低 CPU 驱动程序开销,从而提升应用性能。所有现代游戏引擎都支持 Vulkan。
Vulkan 是 Android 与 GPU 的首选接口。因此,Android 15 包含 ANGLE 作为可选层,用于在 Vulkan 基础上运行 OpenGL® ES。改用 ANGLE 将标准化 Android OpenGL 实现,提高兼容性,在某些情况下还有助于提升性能。在 Android 15 中,您可以依次前往设置 -> 系统 -> 开发者选项 -> 实验性功能:启用 ANGLE,启用开发者选项,以便通过 ANGLE 测试 OpenGL ES 应用的稳定性和性能。
Android ANGLE on Vulkan 路线图

为了简化 GPU 堆栈,我们今后将在更多新设备上将 ANGLE 作为 GL 系统驱动程序提供,未来 OpenGL/ES 将只能通过 ANGLE 获得支持。尽管如此,我们计划继续在所有设备上支持 OpenGL ES。
建议的后续措施
使用开发者选项为 OpenGL ES 选择 ANGLE 驱动程序,然后测试您的应用。对于新项目,我们强烈建议您为 C/C++ 使用 Vulkan。
Canvas 方面的改进
Android 15 继续对 Android 的 Canvas 图形系统进行现代化改造,并新增了以下功能:
Matrix44提供一个 4x4 矩阵来转换坐标,当您想在 3D 中操控画布时,应使用此矩阵。clipShader会将当前剪裁区域与指定的着色器相交,而clipOutShader会将剪裁区域设为当前剪裁区域与着色器的差值,每个操作都会将着色器视为一个 Alpha 遮罩。这支持高效地绘制复杂形状。
性能和电池
Android 将继续专注于帮助您提升应用的性能和质量。Android 15 引入了多项 API,可帮助您更高效地执行应用中的任务、优化应用性能,并收集有关应用的分析洞见。
如需了解省电的最佳实践、调试网络和电源使用情况,以及我们如何在 Android 15 和最新版 Android 中提高后台工作的电池效率,请观看 Google I/O 大会上的提高 Android 上后台工作的电池效率讲座。
ApplicationStartInfo API
在以前的 Android 版本中,应用启动一直是个谜。在应用中确定应用是从冷启动、温启动还是热启动状态启动很困难。您还很难了解应用在各种启动阶段(分叉进程、调用 onCreate、绘制第一个帧等)所花的时间。在 Application 类被实例化时,您无法知道应用是通过广播、content provider、作业、备份、启动完成、闹钟还是 Activity 启动的。
Android 15 上的 ApplicationStartInfo API 提供了所有这些功能,以及更多功能。您甚至可以选择在流程中添加自己的时间戳,以便在一个位置收集时间数据。除了收集指标之外,您还可以使用 ApplicationStartInfo 直接优化应用启动;例如,您可以消除在应用因广播而启动时在 Application 类中实例化与界面相关的库所带来的高昂开销。
详细的应用大小信息
从 Android 8.0(API 级别 26)开始,Android 包含 StorageStats.getAppBytes API,该 API 会将应用的安装大小总结为一个字节数,该数值是 APK 大小、从 APK 中提取的文件的大小以及在设备上生成的文件(例如提前编译 [AOT] 代码)的总和。此数字对于了解应用的存储空间使用情况而言,没有太大帮助。
Android 15 添加了 StorageStats.getAppBytesByDataType([type]) API,可让您深入了解应用如何使用所有这些空间,包括 APK 文件分块、AOT 和加速相关代码、DEX 元数据、库和引导式配置文件。
由应用管理的性能分析
Android 15 包含 ProfilingManager 类,可让您从应用内部收集性能分析信息,例如堆转储、堆分析报告、堆栈采样等。它使用提供的标记为您的应用提供回调,以标识输出文件,该文件将传递给应用的文件目录。该 API 会进行速率限制,以尽可能降低对性能的影响。
为了简化在应用中构建性能分析请求的过程,我们建议您使用 Core 1.15.0-rc01 或更高版本中的相应 Profiling AndroidX API。
SQLite 数据库方面的改进
Android 15 引入了 SQLite API,这些 API 可公开底层 SQLite 引擎的高级功能,以解决可能在应用中出现的特定性能问题。将 SQLite 更新到版本 3.44.3。
开发者应参阅 SQLite 性能最佳实践 以便充分利用其 SQLite 数据库,尤其是在处理大型 或运行对延迟敏感的查询时
- 只读延迟事务:在发出
只读(不包括写入语句),请使用
beginTransactionReadOnly()和beginTransactionWithListenerReadOnly(SQLiteTransactionListener)发出只读的DEFERRED事务。此类事务 如果数据库处于 WAL 模式 与IMMEDIATE或EXCLUSIVE事务并发运行。 - 行数和 ID:添加了 API 以检索已更改的行数和 ID
行或最后插入的行 ID 而不发出额外的查询。
getLastChangedRowCount()会返回当前事务中最近的 SQL 语句插入、更新或删除的行数,而getTotalChangedRowCount()会返回当前连接的计数。getLastInsertRowId()返回最后一行的rowid以便在当前连接中插入 - 原始语句:发出原始 SQlite 语句,从而绕过便利 及其可能产生的任何额外处理开销。
Android 动态性能框架更新
Android 15 继续投资于 Android 动态性能框架 (ADPF),这是一组 API,可让游戏和性能密集型应用更为直接地与 Android 设备的电源和散热系统进行互动。在受支持的设备上,Android 15 添加了 ADPF 功能:
- 针对提示会话的节能模式,用于指明其关联的线程应优先节能而非性能,非常适合长时间运行的后台工作负载。
- 系统可以在提示会话中报告 GPU 和 CPU 工作时长,以便同时调整 CPU 和 GPU 频率,以最佳方式满足工作负载需求。
- 热余量阈值,用于根据余量预测来解读可能的热节流状态。
如需详细了解如何在应用和游戏中使用 ADPF,请参阅相关文档。
隐私权
Android 15 包含多种功能,可帮助应用开发者保护用户隐私。
屏幕录制检测
Android 15 增加了对应用的支持,以检测 正在录制。每当应用转换时,系统都会调用回调 在屏幕录制内容中处于可见与隐藏状态之间。如果正在记录注册进程的 UID 拥有的 activity,则系统会将应用视为可见。这样一来,如果您的应用执行敏感操作,您就可以告知用户正在录制他们的操作。
val mCallback = Consumer<Int> { state ->
if (state == SCREEN_RECORDING_STATE_VISIBLE) {
// We're being recorded
} else {
// We're not being recorded
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val initialState =
windowManager.addScreenRecordingCallback(mainExecutor, mCallback)
mCallback.accept(initialState)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
windowManager.removeScreenRecordingCallback(mCallback)
}
扩展了 IntentFilter 功能
Android 15 通过 UriRelativeFilterGroup 支持更精确的 Intent 解析,UriRelativeFilterGroup 包含一组 UriRelativeFilter 对象,这些对象构成一组必须满足的 Intent 匹配规则,包括网址查询参数、网址片段以及屏蔽或排除规则。
您可以在 AndroidManifest XML 文件中使用 <uri-relative-filter-group> 标记来定义这些规则,该标记可以包含 android:allow 标记。这些代码可以包含使用现有数据代码属性以及 android:query 和 android:fragment 属性的 <data> 代码。
下面是一个 AndroidManifest 语法示例:
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="astore.com" />
<uri-relative-filter-group>
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="region=na" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="mobileoptout=true" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:fragmentPrefix="faq" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
</intent-filter>
私密空间
借助私密空间,用户可以在设备上创建一个单独的空间,在额外的身份验证层保护下,防止敏感应用遭到窥探。私密空间使用单独的用户个人资料。用户可以选择使用设备锁定方式或为私密空间使用单独的锁定方式。
私密空间中的应用会显示在启动器的单独容器中,并且当私密空间处于锁定状态时,这些应用不会显示在“最近用过”视图、通知、“设置”和其他应用中。用户生成的内容和下载的内容(例如媒体内容或文件)以及账号在私密空间和主空间之间是分开的。在私密空间处于解锁状态时,您可以使用系统 Sharesheet 和照片选择器向应用授予对各个空间中内容的访问权限。
用户无法将现有应用及其数据移至私密空间。相反,用户可以在私密空间中选择安装选项,以便使用他们偏好的任意应用商店安装应用。私密空间中的应用会作为主空间中任何应用的单独副本进行安装(同一应用的新副本)。
当用户锁定私密空间时,系统会停止该个人资料。在个人资料停止运行时,私密空间中的应用将不再处于活动状态,无法执行前台或后台活动,包括显示通知。
我们建议您使用私密空间测试应用,以确保应用能按预期运行,尤其是当您的应用属于以下某一类别时:
- 具有工作资料逻辑的应用:假定其应用的任何已安装副本(不在主资料中)均位于工作资料中。
- 医疗应用
- 启动器应用
- 应用商店应用
查询用户最近一次针对“选择的照片访问权限”做出的选择
现在,如果应用获得了部分访问权限,则只能突出显示最近选择的照片和视频。此功能可以改善频繁请求访问照片和视频的应用的用户体验。如需在应用中使用此功能,请在通过 ContentResolver 查询 MediaStore 时启用 QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY 参数。
Kotlin
val externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external") val mediaColumns = arrayOf( FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE, ) val queryArgs = bundleOf( // Return only items from the last selection (selected photos access) QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY to true, // Sort returned items chronologically based on when they were added to the device's storage QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER to "${FileColumns.DATE_ADDED} DESC", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION to "${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ? OR ${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ?", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS to arrayOf( FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE.toString(), FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.toString() ) )
Java
Uri externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external"); String[] mediaColumns = { FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE }; Bundle queryArgs = new Bundle(); queryArgs.putBoolean(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, true); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER, FileColumns.DATE_ADDED + " DESC"); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION, FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ? OR " + FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ?"); queryArgs.putStringArray(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS, new String[] { String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE), String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) });
Privacy Sandbox on Android
Android 15 包含最新的 Android 广告服务扩展,其中包含最新版本的 Privacy Sandbox on Android。我们一直致力于开发可更好地保护用户隐私,并为移动应用打造高效的个性化广告体验的技术,此次添加新功能就是其中的一项举措。我们的 Privacy Sandbox 页面详细介绍了 Privacy Sandbox on Android 开发者预览版和 Beta 版计划,可帮助您上手使用。
健康数据共享
Android 15 集成了与 Health Connect by Android 相关的最新扩展程序。Health Connect by Android 是一个安全的集中式平台,可用于管理和共享应用收集的健康与健身数据。此次更新 增加了对健身、 营养、体表温度、训练计划等。
体表温度追踪功能让用户可以更精确地存储和分享体表温度 来自穿戴式设备或其他跟踪设备的体温数据。
训练计划是一种结构化的锻炼计划,可帮助用户实现健身目标。训练计划支持各种完成和表现目标:
如需详细了解 Android 中 Health Connect 的最新更新,请参阅 利用 Android 打造自适应体验 健康演讲。
应用屏幕共享
Android 15 支持应用屏幕共享,因此用户可以仅共享或录制应用窗口,而不是整个设备屏幕。此功能首次在 Android 14 QPR2 中启用,包含 MediaProjection 回调,可让您的应用自定义应用屏幕共享体验。请注意,对于以 Android 14(API 级别 34)或更高版本为目标平台的应用,每个 MediaProjection 捕获会话都需要征得用户同意。
用户体验和系统界面
Android 15 为应用开发者和用户提供了更多控制权和灵活性,以便他们根据自己的需求配置设备。
如需详细了解如何利用 Android 15 中的最新改进来提升应用的用户体验,请观看 Google I/O 大会上的提升 Android 应用的用户体验讲座。
通过“生成的预览”API 获得更丰富的 widget 预览
在 Android 15 之前,提供微件选择器预览的唯一方法是指定静态图片或布局资源。这些预览通常与放置在主屏幕上的实际 widget 的外观大不相同。此外,由于无法使用 Jetpack Glance 创建静态资源,因此“资讯一览” 开发者必须为其微件截屏或创建 XML 布局, 微件预览。
Android 15 添加了对生成的预览的支持。这意味着,应用微件提供程序可以生成 RemoteViews 以用作选择器预览,而不是静态资源。

推送 API
应用可以通过推送 API 提供生成的预览。应用可以提供
预览,并且不会收到明确的请求,
以提供预览。预览会保留在 AppWidgetService 中,并且主持人可以按需请求预览。以下示例加载了一个 XML 微件
并将其设置为预览:
AppWidgetManager.getInstance(appContext).setWidgetPreview(
ComponentName(
appContext,
SociaLiteAppWidgetReceiver::class.java
),
AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN,
RemoteViews("com.example", R.layout.widget_preview)
)
预期的流程如下:
- 任何时候,widget 提供程序都会调用
setWidgetPreview。提供的预览会与其他提供方信息一起保留在AppWidgetService中。 setWidgetPreview会通过AppWidgetHost.onProvidersChanged回调。作为回应,微件宿主会重新加载其所有提供方信息。- 显示微件预览时,主机会检查
AppWidgetProviderInfo.generatedPreviewCategories,如果所选类别可用,则调用AppWidgetManager.getWidgetPreview以返回此提供程序的已保存预览。
何时调用 setWidgetPreview
由于没有用于提供预览的回调,因此应用可以选择在运行期间的任何时间发送预览。预览的更新频率取决于微件的用例。
以下列表介绍了两大类预览用例:
- 在 widget 预览中显示真实数据(例如个性化数据)的提供程序 或最新信息。这些提供商可以设置预览 已登录 Google 账号或已在其应用中完成初始配置。之后 可以设置一项定期任务,按照所选的节奏更新预览。 此类 widget 的示例包括照片、日历、天气或新闻 widget。
- 在预览中显示静态信息或不显示任何数据的快捷操作 widget 的提供程序。这些提供程序可以在应用首次启动时设置预览一次。例如,快速开车便是此类微件的示例 操作 widget 或 Chrome 快捷方式 widget。
某些提供商可能会在基座接入模式选择器上显示静态预览,但真实的 信息。这些提供商应遵循指南 设置预览
画中画
Android 15 引入了画中画 (PiP) 方面的变更,确保实现 更流畅的过渡效果。对于在主界面上叠加界面元素的应用,这将非常有用,因为这些界面元素会进入 PiP。
开发者使用 onPictureInPictureModeChanged 回调来定义逻辑
用于切换叠加界面元素的可见性。此回调是
在画中画进入或退出动画播放完毕时触发。距离开始还有
Android 15 中,PictureInPictureUiState 类包含另一种状态。
在此界面状态下,以 Android 15(API 级别 35)为目标平台的应用将遵守
使用以下参数调用 Activity#onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged 回调:
isTransitioningToPip()。还有
在画中画模式下,有很多与应用无关的界面元素,
包含建议、
评分和标题当应用进入画中画模式时,请使用
onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged 回调以隐藏这些界面元素。当
应用从画中画窗口进入全屏模式,使用
onPictureInPictureModeChanged 回调以取消隐藏这些元素,如
请参阅以下示例:
override fun onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged(pipState: PictureInPictureUiState) {
if (pipState.isTransitioningToPip()) {
// Hide UI elements
}
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean) {
if (isInPictureInPictureMode) {
// Unhide UI elements
}
}
不相关界面元素的快速可见性切换(适用于画中画窗口)有助于 确保画中画播放动画更流畅、无闪烁。
改进了“勿扰”规则
AutomaticZenRule 允许应用自定义注意力机制
管理(勿扰)规则,并确定何时启用或停用
。Android 15 极大地增强了这些规则,旨在提高
用户体验。其中包含以下增强功能:
- 向
AutomaticZenRule添加类型,让系统能够应用特殊类型 对某些规则的处理 - 向
AutomaticZenRule添加图标,使模式更加丰富 易于识别。 - 将
triggerDescription字符串添加到AutomaticZenRule,用于描述 规则应当对用户生效的条件。 - 已添加
ZenDeviceEffects更改为AutomaticZenRule,从而允许规则触发灰度等操作 显示、夜间模式或调暗壁纸。
为通知渠道设置 VibrationEffect
Android 15 支持为传入的通知设置丰富的振动,方法是
频道使用的是NotificationChannel.setVibrationEffect,因此
您的用户可以区分不同类型的通知
不需要看他们的设备
媒体投影状态栏条状标签和自动停止
媒体投放可能会泄露用户的私密信息。一个醒目的新状态栏条状标签可让用户了解任何正在进行的屏幕投影。用户可以点按该条状标签停止投屏、共享或录制屏幕。此外,为了提供更直观的用户体验,当设备屏幕锁定后,所有正在进行的屏幕投影都会自动停止。

大屏设备和外形规格
Android 15 为您的应用提供支持,让它们能够充分利用 Android 的设备类型,包括大屏设备、翻盖设备和可折叠设备。
改进了大屏设备上的多任务处理
Android 15 为用户提供了在大屏设备上更好地进行多任务处理的方式。对于 例如,用户可以保存自己喜爱的分屏应用组合, 访问并固定屏幕上的任务栏,以便在应用之间快速切换。这意味着 让应用具备自适应能力比以往任何时候都更加重要。
Google I/O 大会上有一些关于构建自适应 Android 的会议 应用和使用 Material 3 构建界面 自适应库 我们的文档中提供了更多帮助信息,帮助您针对大型语言 。
支持封面屏幕
您的应用可以声明一个属性,Android 15 会使用该属性来允许您的 Application 或 Activity 显示在受支持的可翻转设备的小封面屏幕上。这些屏幕太小,无法被视为适合运行 Android 应用的兼容目标平台,但您的应用可以选择支持它们,从而让您的应用在更多平台上可用。
连接
Android 15 更新了平台,让您的应用能够使用通信和无线技术方面的最新进展。
卫星支持
Android 15 继续扩大对卫星连接的平台支持,并包含一些界面元素,以确保在整个卫星连接环境中提供一致的用户体验。
应用可以使用 ServiceState.isUsingNonTerrestrialNetwork() 执行以下操作:
检测设备是否连接到卫星,让他们更清楚地了解
可能会导致完全网络服务不可用的原因此外,Android 15 支持短信和彩信应用以及预加载的 RCS 应用,以便使用卫星连接发送和接收消息。

更顺畅的 NFC 体验
Android 15 正在努力打造更顺畅、更可靠的感应式付款体验,同时继续支持 Android 强大的 NFC 应用生态系统。在受支持的设备上,应用可以请求 NfcAdapter 进入观察模式,在该模式下,设备会监听但不会响应 NFC 读卡器,并将应用的 NFC 服务 PollingFrame
对象发送以进行处理。PollingFrame 对象可用于在与 NFC 读卡器进行首次通信之前进行身份验证,在许多情况下,这支持一触式交易。
此外,应用可以在受支持的设备上注册过滤器,以便在有轮询循环活动时收到通知,从而能够与多个感知 NFC 的应用顺畅运行。
钱包角色
Android 15 引入了钱包角色,可与用户的首选钱包应用更紧密地集成。此角色会取代 NFC 默认的感应式付款设置。用户可以前往设置 > 应用 > 默认应用,管理钱包角色持有者。
在为在付款类别中注册的 AID 路由 NFC 感应式付款时,系统会使用钱包角色。点按操作始终会转到 Google 钱包角色持有者,除非有已注册相同 AID 的其他应用在前台运行。
此角色还用于确定“Google 钱包”快速访问功能块在启用后应显示在何处。将角色设为“无”时,“快速访问”功能块不可用,并且支付类别 NFC 点按仅传送到前台应用。
安全
Android 15 可帮助您增强应用安全性、保护应用数据,并让用户更清楚地了解并更好地控制自己的数据。如需详细了解我们为改进用户保护措施和保护您的应用免遭新威胁侵扰而采取的措施,请观看 Google I/O 大会上的在 Android 上保障用户安全讲座。
将 Credential Manager 与自动填充功能集成
从 Android 15 开始,开发者可以将用户名或密码字段等特定视图与 Credential Manager 请求相关联,从而更轻松地在登录过程中提供量身定制的用户体验。当用户聚焦于其中一个视图时,系统会向 Credential Manager 发送相应请求。系统会汇总来自各个提供商的凭据,并在自动填充后备界面(例如内嵌建议或下拉菜单建议)中显示这些凭据。Jetpack androidx.credentials 库是开发者首选的端点,很快将在 Android 15 及更高版本中推出,以进一步增强此功能。
将一键注册和登录与生物识别提示集成
Credential Manager将生物识别提示集成到凭据创建过程中 和登录流程,这样提供商就无需管理 生物识别提示。因此,凭据提供程序只需专注于创建和获取流程的结果,并辅以生物识别流程结果。这一简化的流程创建了更高效、更精简的凭据 创建和检索过程。
端到端加密的密钥管理
我们将在 Android 15 中引入 E2eeContactKeysManager,它通过提供用于存储加密公钥的操作系统级 API,有助于在 Android 应用中实现端到端加密 (E2EE)。
E2eeContactKeysManager 旨在与平台通讯录应用集成,以便用户集中管理和验证通讯录联系人的公钥。
对内容 URI 的权限检查
Android 15 引入了一组用于对内容 URI 执行权限检查的 API:
Context.checkContentUriPermissionFull:此选项会对内容 URI 执行完整权限检查。Activity清单属性requireContentUriPermissionFromCaller:此属性会在 activity 启动时对提供的内容 URI 强制执行指定权限。Activity调用方的ComponentCaller类:此类表示启动 activity 的应用。
无障碍
Android 15 新增了一些功能,可提升用户无障碍体验。
更好的盲文体验
在 Android 15 中,我们让 TalkBack 能够支持通过 USB 和安全蓝牙使用 HID 标准的盲文显示屏。
此标准与鼠标和键盘使用的标准非常相似,将有助于 Android 随着时间的推移支持更多类型的盲文显示屏。
国际化
Android 15 新增了多项功能,可在设备以不同语言使用时提升用户体验。
CJK 可变字体
从 Android 15 开始,面向中文、日文和韩文 (CJK) 语言的字体文件 NotoSansCJK 现在是可变字体。可变字体为中日韩语言的创意排版提供了更多可能性。设计师可以探索更多样式的排版,并制作出以前难以实现或根本无法实现的视觉效果出色的布局。

字符间两端对齐
从 Android 15 开始,可以通过
使用 JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER。“字词间的理由”原为
最初是在 Android 8.0(API 级别 26)中引入的,
Justifications 功能为使用
例如中文、日语等。

JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE 的日语文本布局。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE 的英语文本布局。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD 的日语文本布局。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD 的英语文本布局。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER 的日语文本布局。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER 的英语文本布局。自动换行配置
Android 从以下语言开始支持基于短语的日语和韩语换行:
Android 13(API 级别 33)。不过,虽然基于短语的行分隔符可以提高短文本行的可读性,但对于长文本行,效果并不理想。在 Android 15 中,应用只能使用 LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO 选项,针对短文本行应用基于短语的行分隔符。此选项会为文本选择最佳字词样式选项。
对于短文本行,则使用基于短语的换行符,功能相同
为 LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE,如
以下图片:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
应用基于短语的换行符,以提高文本的可读性。
这与应用
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE。对于较长的文本行,LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO 会使用 no
换行字词样式,
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE,如
以下图片:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
应用不换行的字词样式,以提高文本的可读性。
这与应用
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE。其他日语变体假名字体
在 Android 15 中,旧版日语平假名(也称为 Hentaigana)字体文件 捆绑在一起半形人物的独特形状可以增加 风格或设计独特的风格 传播和理解古代日本文件的能力。

VideoLAN 圆锥图标 版权所有 (c) 1996-2010 VideoLAN。任何人都可以使用此徽标或修改版徽标来提及 VideoLAN 项目或 VideoLAN 团队开发的任何产品,但这并不表示该项目对其表示认可。
Vulkan 和 Vulkan 徽标是 Khronos Group Inc.的注册商标。
OpenGL 是注册商标,OpenGL ES 徽标是 Hewlett Packard Enterprise 的商标,已获得 Khronos 的许可。
