注意:本页介绍的是 Camera2 软件包。除非您的应用需要 Camera2 中的特定低级功能,否则我们建议您使用 CameraX。CameraX 和 Camera2 都支持 Android 5.0(API 级别 21)及更高版本。
Android 9(API 级别 28)中引入了多摄像头。自发布以来, 已经上市的设备都支持此 API。许多多摄像头应用场景 与特定硬件配置紧密耦合。也就是说, 所有用例都与每种设备兼容,这使得多摄像头 是针对 Play 功能 投放。
一些典型用例包括:
- 缩放:根据剪裁区域或所需的焦点在镜头之间切换 。
- 深度:使用多个镜头构建深度图。
- 焦外成像:使用推断的深度信息模拟数码单反式窄屏效果 对焦范围。
逻辑摄像头和物理摄像头的区别
了解多摄像头 API 需要了解 逻辑摄像头和物理摄像头。作为参考,我们假设有一个设备 后置摄像头。在本示例中,三个后置摄像头分别 都属于实体相机。逻辑摄像头是指 物理摄像头。逻辑的输出 摄像头可以是来自某个底层物理摄像头的视频流, 或者来自多个底层物理摄像头的融合数据流 。无论采用哪种方式,视频流都由相机硬件处理 抽象层 (HAL)。
许多手机制造商都开发了第一方相机应用,这些应用通常 但其设备上已预装了该应用要使用硬件的所有功能, 它们可能会使用私有或隐藏 API,或者从 其他应用无权访问的驱动程序实现。部分 通过提供融合数据流, 但只能传输到具有特定特权的 应用。通常情况下,只有一个物理摄像头 框架。Android 9 之前第三方开发者的情况是 如下图所示:

从 Android 9 开始,Android 应用中不再允许使用私有 API。 通过在框架中包含多摄像头支持,Android 最佳 强烈建议手机制造商公开一个逻辑摄像头, 所有物理摄像头都朝向同一方向下面介绍了 应该能在运行 Android 9 和 较高:
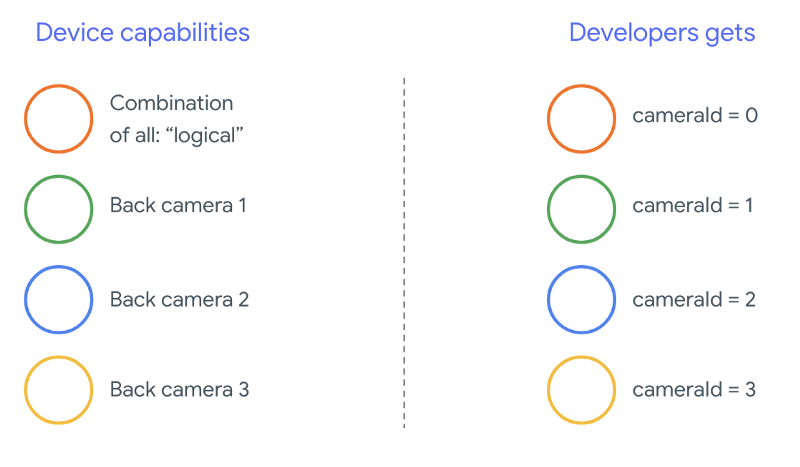
逻辑摄像头提供的内容完全取决于 OEM 实现 相机 HAL 的组件。例如,像 Pixel 3 这样的设备会实现其逻辑 让它能够根据实例选择 请求的焦距和剪裁区域。
多摄像头 API
新 API 添加了以下新常量、类和方法:
CameraMetadata.REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_LOGICAL_MULTI_CAMERACameraCharacteristics.getPhysicalCameraIds()CameraCharacteristics.getAvailablePhysicalCameraRequestKeys()CameraDevice.createCaptureSession(SessionConfiguration config)CameraCharacteritics.LOGICAL_MULTI_CAMERA_SENSOR_SYNC_TYPEOutputConfiguration和SessionConfiguration
由于 Android 兼容性定义文档 (CDD) 有所变更, 对多摄像头 API 也有一些期望。设备 Android 9 之前的版本中存在配备双摄像头,但同时打开了多个摄像头的情况 同时涉及试错。在 Android 9 及更高版本上,多摄像头 提供了一组规则,用于指定何时可以打开一对物理 属于同一逻辑摄像头的一部分。
在大多数情况下,搭载 Android 9 及更高版本的设备会公开所有 以及红外线等不太常见的传感器类型除外) 更易于使用的逻辑摄像头对于 那么属于逻辑摄像头的一个视频流就可以被替换为 来自底层物理摄像头的两个视频流。
同时观看多个直播
同时使用多个摄像头信息流
涵盖在单个摄像头中同时使用多个视频流的规则。
只要有一项值得注意的新增内容,那么同样的规则也适用于多个摄像头。
CameraMetadata.REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_LOGICAL_MULTI_CAMERA
解释了如何将逻辑 YUV_420_888 或原始流替换为两个
实体视频流也就是说,每个 YUV 或 RAW 类型的流都可替换为
两个具有相同类型和大小的数据流。你可以先从相机流开始,
单摄像头设备的以下有保证配置:
- 数据流 1:YUV 类型,来自逻辑摄像头
id = 0的MAXIMUM大小
然后,在支持多摄像头的设备上创建会话 将该逻辑 YUV 流替换为两个物理流:
- 数据流 1:YUV 类型,
MAXIMUM大小,来自物理摄像头id = 1 - 数据流 2:YUV 类型,
MAXIMUM大小,来自物理摄像头id = 2
当且仅当满足以下条件时,您才可以将 YUV 或 RAW 流替换为两个等效的流
这两台摄像头属于一个逻辑摄像头分组,该分组列于
CameraCharacteristics.getPhysicalCameraIds()。
框架提供的保证只是运行 3D 模型 同时从多个物理摄像头获取帧。其他直播 有时甚至允许打开多个实体设备 摄像头设备由于这并不能保证 框架,要做到这一点,需要使用 不断尝试和犯错。
创建具有多个物理摄像头的会话
在支持多摄像头的设备上使用物理摄像头时,打开一个
CameraDevice(逻辑摄像头),并在单个对象中与其交互
会话。使用 API 创建单个会话
CameraDevice.createCaptureSession(SessionConfiguration config),原为
此项为 API 级别 28 中的新增配置。会话配置有多个输出
每个配置都有一组输出目标,以及
所需的物理摄像头 ID。
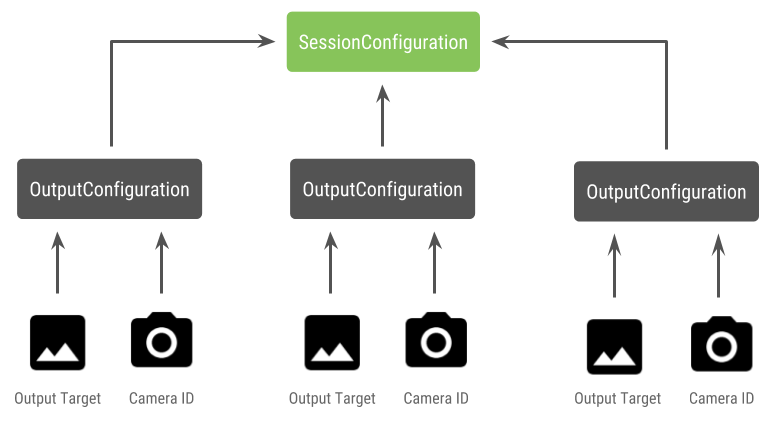
捕获请求具有与之关联的输出目标。框架 根据请求发送到哪个物理(或逻辑)摄像头 附加了哪个输出目标。如果输出目标对应于 作为输出配置与物理 摄像头 ID,然后该物理摄像头会接收并处理请求。
使用一对物理摄像头
用于多摄像头的相机 API 的另一个新增功能是识别 并找出它们背后的物理摄像头您可以定义 函数来帮助识别可以使用的可能的物理摄像头对 替换其中一个逻辑摄像头信息流:
Kotlin
/** * Helper class used to encapsulate a logical camera and two underlying * physical cameras */ data class DualCamera(val logicalId: String, val physicalId1: String, val physicalId2: String) fun findDualCameras(manager: CameraManager, facing: Int? = null): List{ val dualCameras = MutableList () // Iterate over all the available camera characteristics manager.cameraIdList.map { Pair(manager.getCameraCharacteristics(it), it) }.filter { // Filter by cameras facing the requested direction facing == null || it.first.get(CameraCharacteristics.LENS_FACING) == facing }.filter { // Filter by logical cameras // CameraCharacteristics.REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_LOGICAL_MULTI_CAMERA requires API >= 28 it.first.get(CameraCharacteristics.REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES)!!.contains( CameraCharacteristics.REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_LOGICAL_MULTI_CAMERA) }.forEach { // All possible pairs from the list of physical cameras are valid results // NOTE: There could be N physical cameras as part of a logical camera grouping // getPhysicalCameraIds() requires API >= 28 val physicalCameras = it.first.physicalCameraIds.toTypedArray() for (idx1 in 0 until physicalCameras.size) { for (idx2 in (idx1 + 1) until physicalCameras.size) { dualCameras.add(DualCamera( it.second, physicalCameras[idx1], physicalCameras[idx2])) } } } return dualCameras }
Java
/** * Helper class used to encapsulate a logical camera and two underlying * physical cameras */ final class DualCamera { final String logicalId; final String physicalId1; final String physicalId2; DualCamera(String logicalId, String physicalId1, String physicalId2) { this.logicalId = logicalId; this.physicalId1 = physicalId1; this.physicalId2 = physicalId2; } } ListfindDualCameras(CameraManager manager, Integer facing) { List dualCameras = new ArrayList<>(); List cameraIdList; try { cameraIdList = Arrays.asList(manager.getCameraIdList()); } catch (CameraAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); cameraIdList = new ArrayList<>(); } // Iterate over all the available camera characteristics cameraIdList.stream() .map(id -> { try { CameraCharacteristics characteristics = manager.getCameraCharacteristics(id); return new Pair<>(characteristics, id); } catch (CameraAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return null; } }) .filter(pair -> { // Filter by cameras facing the requested direction return (pair != null) && (facing == null || pair.first.get(CameraCharacteristics.LENS_FACING).equals(facing)); }) .filter(pair -> { // Filter by logical cameras // CameraCharacteristics.REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_LOGICAL_MULTI_CAMERA requires API >= 28 IntPredicate logicalMultiCameraPred = arg -> arg == CameraCharacteristics.REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_LOGICAL_MULTI_CAMERA; return Arrays.stream(pair.first.get(CameraCharacteristics.REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES)) .anyMatch(logicalMultiCameraPred); }) .forEach(pair -> { // All possible pairs from the list of physical cameras are valid results // NOTE: There could be N physical cameras as part of a logical camera grouping // getPhysicalCameraIds() requires API >= 28 String[] physicalCameras = pair.first.getPhysicalCameraIds().toArray(new String[0]); for (int idx1 = 0; idx1 < physicalCameras.length; idx1++) { for (int idx2 = idx1 + 1; idx2 < physicalCameras.length; idx2++) { dualCameras.add( new DualCamera(pair.second, physicalCameras[idx1], physicalCameras[idx2])); } } }); return dualCameras; }
物理摄像头的状态处理由逻辑摄像头控制。接收者 打开“双摄像头”打开与实体设备对应的逻辑摄像头 摄像头:
Kotlin
fun openDualCamera(cameraManager: CameraManager, dualCamera: DualCamera, // AsyncTask is deprecated beginning API 30 executor: Executor = AsyncTask.SERIAL_EXECUTOR, callback: (CameraDevice) -> Unit) { // openCamera() requires API >= 28 cameraManager.openCamera( dualCamera.logicalId, executor, object : CameraDevice.StateCallback() { override fun onOpened(device: CameraDevice) = callback(device) // Omitting for brevity... override fun onError(device: CameraDevice, error: Int) = onDisconnected(device) override fun onDisconnected(device: CameraDevice) = device.close() }) }
Java
void openDualCamera(CameraManager cameraManager, DualCamera dualCamera, Executor executor, CameraDeviceCallback cameraDeviceCallback ) { // openCamera() requires API >= 28 cameraManager.openCamera(dualCamera.logicalId, executor, new CameraDevice.StateCallback() { @Override public void onOpened(@NonNull CameraDevice cameraDevice) { cameraDeviceCallback.callback(cameraDevice); } @Override public void onDisconnected(@NonNull CameraDevice cameraDevice) { cameraDevice.close(); } @Override public void onError(@NonNull CameraDevice cameraDevice, int i) { onDisconnected(cameraDevice); } }); }
除了选择要打开的相机外,操作过程与打开 是相机。使用新的 Session Configuration API 指示框架将某些目标与 特定物理摄像头 ID:
Kotlin
/** * Helper type definition that encapsulates 3 sets of output targets: * * 1. Logical camera * 2. First physical camera * 3. Second physical camera */ typealias DualCameraOutputs = Triple<MutableList?, MutableList?, MutableList?> fun createDualCameraSession(cameraManager: CameraManager, dualCamera: DualCamera, targets: DualCameraOutputs, // AsyncTask is deprecated beginning API 30 executor: Executor = AsyncTask.SERIAL_EXECUTOR, callback: (CameraCaptureSession) -> Unit) { // Create 3 sets of output configurations: one for the logical camera, and // one for each of the physical cameras. val outputConfigsLogical = targets.first?.map { OutputConfiguration(it) } val outputConfigsPhysical1 = targets.second?.map { OutputConfiguration(it).apply { setPhysicalCameraId(dualCamera.physicalId1) } } val outputConfigsPhysical2 = targets.third?.map { OutputConfiguration(it).apply { setPhysicalCameraId(dualCamera.physicalId2) } } // Put all the output configurations into a single flat array val outputConfigsAll = arrayOf( outputConfigsLogical, outputConfigsPhysical1, outputConfigsPhysical2) .filterNotNull().flatMap { it } // Instantiate a session configuration that can be used to create a session val sessionConfiguration = SessionConfiguration( SessionConfiguration.SESSION_REGULAR, outputConfigsAll, executor, object : CameraCaptureSession.StateCallback() { override fun onConfigured(session: CameraCaptureSession) = callback(session) // Omitting for brevity... override fun onConfigureFailed(session: CameraCaptureSession) = session.device.close() }) // Open the logical camera using the previously defined function openDualCamera(cameraManager, dualCamera, executor = executor) { // Finally create the session and return via callback it.createCaptureSession(sessionConfiguration) } }
Java
/** * Helper class definition that encapsulates 3 sets of output targets: ** 1. Logical camera * 2. First physical camera * 3. Second physical camera */ final class DualCameraOutputs { private final List
logicalCamera; private final List firstPhysicalCamera; private final List secondPhysicalCamera; public DualCameraOutputs(List logicalCamera, List firstPhysicalCamera, List third) { this.logicalCamera = logicalCamera; this.firstPhysicalCamera = firstPhysicalCamera; this.secondPhysicalCamera = third; } public List getLogicalCamera() { return logicalCamera; } public List getFirstPhysicalCamera() { return firstPhysicalCamera; } public List getSecondPhysicalCamera() { return secondPhysicalCamera; } } interface CameraCaptureSessionCallback { void callback(CameraCaptureSession cameraCaptureSession); } void createDualCameraSession(CameraManager cameraManager, DualCamera dualCamera, DualCameraOutputs targets, Executor executor, CameraCaptureSessionCallback cameraCaptureSessionCallback) { // Create 3 sets of output configurations: one for the logical camera, and // one for each of the physical cameras. List outputConfigsLogical = targets.getLogicalCamera().stream() .map(OutputConfiguration::new) .collect(Collectors.toList()); List outputConfigsPhysical1 = targets.getFirstPhysicalCamera().stream() .map(s -> { OutputConfiguration outputConfiguration = new OutputConfiguration(s); outputConfiguration.setPhysicalCameraId(dualCamera.physicalId1); return outputConfiguration; }) .collect(Collectors.toList()); List outputConfigsPhysical2 = targets.getSecondPhysicalCamera().stream() .map(s -> { OutputConfiguration outputConfiguration = new OutputConfiguration(s); outputConfiguration.setPhysicalCameraId(dualCamera.physicalId2); return outputConfiguration; }) .collect(Collectors.toList()); // Put all the output configurations into a single flat array List outputConfigsAll = Stream.of( outputConfigsLogical, outputConfigsPhysical1, outputConfigsPhysical2 ) .filter(Objects::nonNull) .flatMap(Collection::stream) .collect(Collectors.toList()); // Instantiate a session configuration that can be used to create a session SessionConfiguration sessionConfiguration = new SessionConfiguration( SessionConfiguration.SESSION_REGULAR, outputConfigsAll, executor, new CameraCaptureSession.StateCallback() { @Override public void onConfigured(@NonNull CameraCaptureSession cameraCaptureSession) { cameraCaptureSessionCallback.callback(cameraCaptureSession); } // Omitting for brevity... @Override public void onConfigureFailed(@NonNull CameraCaptureSession cameraCaptureSession) { cameraCaptureSession.getDevice().close(); } }); // Open the logical camera using the previously defined function openDualCamera(cameraManager, dualCamera, executor, (CameraDevice c) -> // Finally create the session and return via callback c.createCaptureSession(sessionConfiguration)); }
请参阅
createCaptureSession
了解支持哪种数据流组合。合并数据流
适用于单个逻辑摄像头上的多个视频流。兼容性扩展到
使用相同的配置,并将这些数据流替换为两个数据流
属于同一个逻辑摄像头的两个物理摄像头。
使用 摄像头会话 将所需的 捕获请求。每个 捕获请求的目标从其关联的物理设备接收数据, 或者回退到逻辑摄像头。
Zoom 用例示例
可以将物理摄像头合并到单个视频流中, 用户可以切换使用不同物理摄像头 从而有效地捕获不同的“缩放级别”。
<ph type="x-smartling-placeholder">
首先选择一对物理摄像头,以便用户切换 。为了达到最佳效果,您可以选择一对 最小和最大焦距
Kotlin
fun findShortLongCameraPair(manager: CameraManager, facing: Int? = null): DualCamera? { return findDualCameras(manager, facing).map { val characteristics1 = manager.getCameraCharacteristics(it.physicalId1) val characteristics2 = manager.getCameraCharacteristics(it.physicalId2) // Query the focal lengths advertised by each physical camera val focalLengths1 = characteristics1.get( CameraCharacteristics.LENS_INFO_AVAILABLE_FOCAL_LENGTHS) ?: floatArrayOf(0F) val focalLengths2 = characteristics2.get( CameraCharacteristics.LENS_INFO_AVAILABLE_FOCAL_LENGTHS) ?: floatArrayOf(0F) // Compute the largest difference between min and max focal lengths between cameras val focalLengthsDiff1 = focalLengths2.maxOrNull()!! - focalLengths1.minOrNull()!! val focalLengthsDiff2 = focalLengths1.maxOrNull()!! - focalLengths2.minOrNull()!! // Return the pair of camera IDs and the difference between min and max focal lengths if (focalLengthsDiff1 < focalLengthsDiff2) { Pair(DualCamera(it.logicalId, it.physicalId1, it.physicalId2), focalLengthsDiff1) } else { Pair(DualCamera(it.logicalId, it.physicalId2, it.physicalId1), focalLengthsDiff2) } // Return only the pair with the largest difference, or null if no pairs are found }.maxByOrNull { it.second }?.first }
Java
// Utility functions to find min/max value in float[] float findMax(float[] array) { float max = Float.NEGATIVE_INFINITY; for(float cur: array) max = Math.max(max, cur); return max; } float findMin(float[] array) { float min = Float.NEGATIVE_INFINITY; for(float cur: array) min = Math.min(min, cur); return min; } DualCamera findShortLongCameraPair(CameraManager manager, Integer facing) { return findDualCameras(manager, facing).stream() .map(c -> { CameraCharacteristics characteristics1; CameraCharacteristics characteristics2; try { characteristics1 = manager.getCameraCharacteristics(c.physicalId1); characteristics2 = manager.getCameraCharacteristics(c.physicalId2); } catch (CameraAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return null; } // Query the focal lengths advertised by each physical camera float[] focalLengths1 = characteristics1.get( CameraCharacteristics.LENS_INFO_AVAILABLE_FOCAL_LENGTHS); float[] focalLengths2 = characteristics2.get( CameraCharacteristics.LENS_INFO_AVAILABLE_FOCAL_LENGTHS); // Compute the largest difference between min and max focal lengths between cameras Float focalLengthsDiff1 = findMax(focalLengths2) - findMin(focalLengths1); Float focalLengthsDiff2 = findMax(focalLengths1) - findMin(focalLengths2); // Return the pair of camera IDs and the difference between min and max focal lengths if (focalLengthsDiff1 < focalLengthsDiff2) { return new Pair<>(new DualCamera(c.logicalId, c.physicalId1, c.physicalId2), focalLengthsDiff1); } else { return new Pair<>(new DualCamera(c.logicalId, c.physicalId2, c.physicalId1), focalLengthsDiff2); } }) // Return only the pair with the largest difference, or null if no pairs are found .max(Comparator.comparing(pair -> pair.second)).get().first; }
一个合理的架构是
SurfaceViews - 每个数据流一个。
系统会根据用户互动替换这些 SurfaceViews,以便只替换其中一个
始终显示
以下代码展示了如何打开逻辑摄像头并配置摄像头 输出,创建一个相机会话,然后启动两个预览流:
Kotlin
val cameraManager: CameraManager = ... // Get the two output targets from the activity / fragment val surface1 = ... // from SurfaceView val surface2 = ... // from SurfaceView val dualCamera = findShortLongCameraPair(manager)!! val outputTargets = DualCameraOutputs( null, mutableListOf(surface1), mutableListOf(surface2)) // Here you open the logical camera, configure the outputs and create a session createDualCameraSession(manager, dualCamera, targets = outputTargets) { session -> // Create a single request which has one target for each physical camera // NOTE: Each target receive frames from only its associated physical camera val requestTemplate = CameraDevice.TEMPLATE_PREVIEW val captureRequest = session.device.createCaptureRequest(requestTemplate).apply { arrayOf(surface1, surface2).forEach { addTarget(it) } }.build() // Set the sticky request for the session and you are done session.setRepeatingRequest(captureRequest, null, null) }
Java
CameraManager manager = ...; // Get the two output targets from the activity / fragment Surface surface1 = ...; // from SurfaceView Surface surface2 = ...; // from SurfaceView DualCamera dualCamera = findShortLongCameraPair(manager, null); DualCameraOutputs outputTargets = new DualCameraOutputs( null, Collections.singletonList(surface1), Collections.singletonList(surface2)); // Here you open the logical camera, configure the outputs and create a session createDualCameraSession(manager, dualCamera, outputTargets, null, (session) -> { // Create a single request which has one target for each physical camera // NOTE: Each target receive frames from only its associated physical camera CaptureRequest.Builder captureRequestBuilder; try { captureRequestBuilder = session.getDevice().createCaptureRequest(CameraDevice.TEMPLATE_PREVIEW); Arrays.asList(surface1, surface2).forEach(captureRequestBuilder::addTarget); // Set the sticky request for the session and you are done session.setRepeatingRequest(captureRequestBuilder.build(), null, null); } catch (CameraAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } });
剩下要做的就是提供一个界面,供用户在这两者之间进行切换
表面,例如按钮或点按两次 SurfaceView。您甚至可以
执行某种形式的场景分析,并在两个视频流之间切换
。
镜头失真
所有镜头都会产生一定程度的失真。在 Android 中,您可以查询
透镜造成的失真
CameraCharacteristics.LENS_DISTORTION、
该版本取代了现已弃用的
CameraCharacteristics.LENS_RADIAL_DISTORTION。
对于逻辑摄像头,失真最小,您的应用可以使用
呈现不同帧数的变化。对于实体摄像头
镜头配置可能截然不同
一些设备可以通过以下方法实现自动失真校正:
CaptureRequest.DISTORTION_CORRECTION_MODE。
失真校正功能在大多数设备上默认处于启用状态。
Kotlin
val cameraSession: CameraCaptureSession = ... // Use still capture template to build the capture request val captureRequest = cameraSession.device.createCaptureRequest( CameraDevice.TEMPLATE_STILL_CAPTURE ) // Determine if this device supports distortion correction val characteristics: CameraCharacteristics = ... val supportsDistortionCorrection = characteristics.get( CameraCharacteristics.DISTORTION_CORRECTION_AVAILABLE_MODES )?.contains( CameraMetadata.DISTORTION_CORRECTION_MODE_HIGH_QUALITY ) ?: false if (supportsDistortionCorrection) { captureRequest.set( CaptureRequest.DISTORTION_CORRECTION_MODE, CameraMetadata.DISTORTION_CORRECTION_MODE_HIGH_QUALITY ) } // Add output target, set other capture request parameters... // Dispatch the capture request cameraSession.capture(captureRequest.build(), ...)
Java
CameraCaptureSession cameraSession = ...; // Use still capture template to build the capture request CaptureRequest.Builder captureRequestBuilder = null; try { captureRequestBuilder = cameraSession.getDevice().createCaptureRequest( CameraDevice.TEMPLATE_STILL_CAPTURE ); } catch (CameraAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // Determine if this device supports distortion correction CameraCharacteristics characteristics = ...; boolean supportsDistortionCorrection = Arrays.stream( characteristics.get( CameraCharacteristics.DISTORTION_CORRECTION_AVAILABLE_MODES )) .anyMatch(i -> i == CameraMetadata.DISTORTION_CORRECTION_MODE_HIGH_QUALITY); if (supportsDistortionCorrection) { captureRequestBuilder.set( CaptureRequest.DISTORTION_CORRECTION_MODE, CameraMetadata.DISTORTION_CORRECTION_MODE_HIGH_QUALITY ); } // Add output target, set other capture request parameters... // Dispatch the capture request cameraSession.capture(captureRequestBuilder.build(), ...);
在此模式下设置拍摄请求可能会影响 相机生成的图片您可以选择仅将失真校正设置为开启 静态图片捕获。
