
适用于 Wear OS 的 Material Design 可以帮助您设计引人入胜的应用体验。
了解用例
手表可以让用户一目了然地查看信息(例如查看健康与健身目标的完成进度)并迅速采取行动(例如回复即时通讯)。针对智能手表设计应用时,应重点关注此类用例。
有别于移动设备,手表界面能够支持一些独特的操作方式,其中包括:
- 可通过与身体的实际接触(通过传感器和移动侦测)进行输入。
- 快速访问一目了然的信息和操作,例如复杂功能、通知和卡片。
不过,手表也有一些限制:
- 屏幕空间较小
- 信息密度较低
- 电池续航时间较短
针对手表设计应用时,既要考虑这种平台的功能,也要考虑到它的限制。

正确做法
设计能够通过手表界面轻松完成任务的体验。
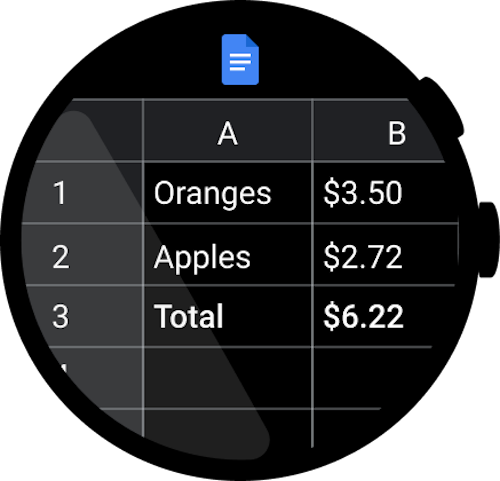
错误做法
不要创建包含电子表格等内容的复杂详细的应用,因为这样的内容在手表上难以修改和查看。
测试设计
大多数 Wear OS 设备都采用圆形屏幕,其界面空间比方形显示屏要少 22%。圆形屏幕还需要较大的边距,才能确保文字更易于阅读。
适用于 Wear OS 的 Material Design 可以帮助您设计引人入胜的应用体验。以下屏幕截图显示了几个遵循本指南中所述原则的 Wear OS 应用的图解示例。
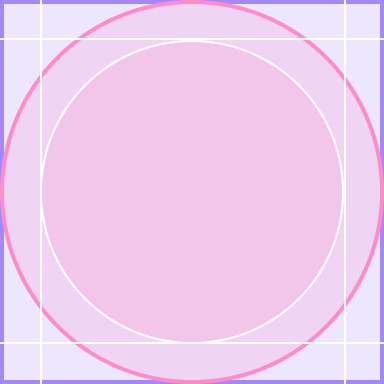
正确做法
优先针对圆形显示屏设备进行设计,确保布局能够适应尺寸限制值较小的屏幕。

错误做法
佩戴手表的人经常处于运动状态,无论他们是站着、做手势,还是跑着去赶公共汽车。在用户需要移动的情况下测试您的设计,确保设计方便用户一目了然地使用。
应用示例
适用于 Wear OS 的 Material Design 可以帮助您设计引人入胜的应用体验。以下屏幕截图显示了几个遵循本指南中所述原则的 Wear OS 应用的图解示例。
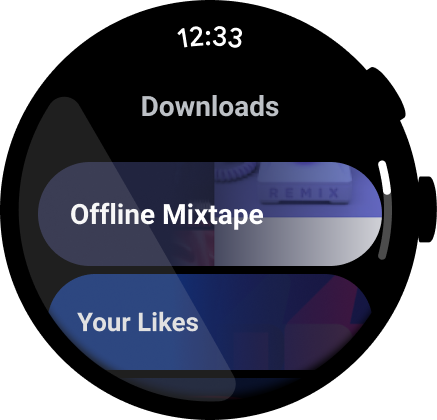
图 1. 媒体应用示例。
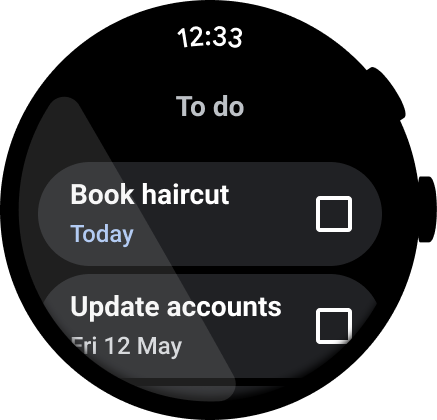
图 2. 任务管理应用示例。
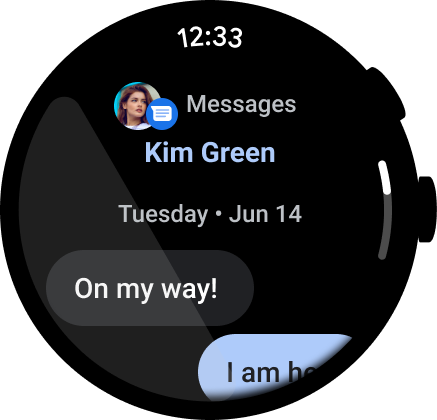
图 3. 即时通讯应用示例。

图 4. 秒表应用示例。
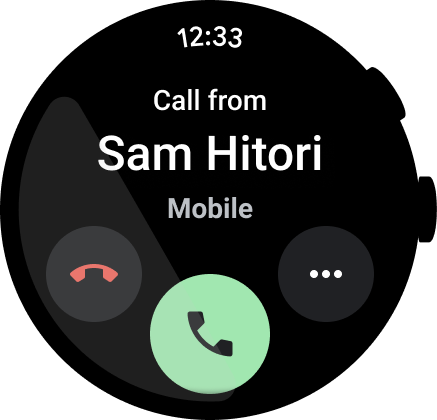
图 5. 拨号器应用示例。

图 6. 计算器应用示例。

