במסמך הזה מוצגים שלבי ההגדרה הבסיסיים ותהליך העבודה של הכלי נכונה ל-Bearstats והסקריפט של 'היסטוריית הסוללה'. כדי ללמוד איך להשתמש ב'היסטוריית הסוללה': לבדיקת דפוסי צריכת הסוללה, אפשר לעיין במאמר ניתוח השימוש בסוללה באמצעות סוללה היסטוריון.
ניצול הסוללה הוא כלי שכלול במסגרת של Android שאוספת נתוני סוללה
במכשיר שלכם. אפשר להשתמש ב-adb כדי להשליך את
שאספו נתוני סוללה למכונת הפיתוח שלך ויוצרים דוח שאפשר
לנתח באמצעות 'היסטוריית סוללה'. התכונה 'היסטוריית סוללה' ממירה את הדוח מ-
נתוני סוללה להדמיה של HTML שניתנת להצגה בדפדפן.
נתונים של 'סוללה' ו'היסטוריית סוללה' שימושיים לצרכים הבאים:
- מראה לך איפה ואיך התהליכים שולפים את הסוללה מהסוללה.
- לזהות משימות באפליקציה שאפשר לדחות או להסיר כדי לשפר אותן חיי הסוללה.
התקנת היסטוריית סוללה
אפשר להשתמש ב-Docker כדי להתקין את הגדרת סוללה. להתקנה חלופית כולל בנייה ממקור, README ב- בדף של הפרויקט ב-GitHub. כדי להתקין באמצעות Docker, מבצעים את הפעולות הבאות:
מתקינים את Docker לפי ההוראות אתר Docker. כלשהו סוג המינוי ל-subscription עובד, כולל מינוי אישי בחינם.
כדי לוודא ש-Docker מותקן כראוי, פותחים את שורת הפקודה ו מזינים את הפקודה הבאה:
docker run hello-worldאם Docker מותקן כראוי, הוא מציג פלט כזה:
Unable to find image 'hello-world:latest' locally latest: Pulling from library/hello-world 78445dd45222: Pull complete Digest: sha256:c5515758d4c5e1e838e9cd307f6c6a0d620b5e07e6f927b07d05f6d12a1ac8d7 Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest Hello from Docker! This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly. To generate this message, Docker took the following steps: 1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon. 2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub. 3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the executable that produces the output you are currently reading. 4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it to your terminalמפעילים את אפליקציית Docker Desktop – חזית GUI של Docker – לפני שמריצים את התמונה של היסטוריית הסוללה. הרצת הפקודה הזו מפעילה את ה-Docker הכלים שלנו. היסטוריית הסוללה תפעל רק אחרי שמבצעים את הפעולה הזו לפחות פעם אחת.
הרצת היסטוריית הסוללה משורת הפקודה כשמריצים אותה בפעם הראשונה בזמן האימון. אפליקציית Docker Desktop לא מאפשרת לציין את היציאה להפעלת האינטרנט השרת מופעל. אפשר לעשות את זה רק משורת הפקודה. אבל אחרי להריץ את הקונטיינר משורת הפקודה, נוצרת רשומה ב- Docker Desktop, ולאחר מכן אפשר להפעיל אותו באמצעות אותה יציאת Listener מ-Docker Desktop.
מריצים את קובץ האימג' של 'היסטוריית הסוללה' באמצעות הפקודה הבאה:
docker run -p port_number:9999 gcr.io/android-battery-historian/stable:3.1 --port 9999
התכונה 'היסטוריי סוללה' משתמשת ביציאה שבחרת, כפי שצוין באמצעות
port_numberצריך לעבור אל 'היסטוריית הסוללה' בדפדפן כדי לוודא שהיא פועלת. הכתובת משתנה בהתאם למערכת ההפעלה שלך:
- ב-Linux וב-Mac השירות 'היסטורית סוללה' של
- זמין בשעה
http://localhost:port_number. - ל-Windows
- אחרי שמפעילים את Docker, הוא מציין את כתובת ה-IP של המכונה
בשימוש. לדוגמה, אם כתובת ה-IP היא 123.456.78.90, סוללה
היסטוריית הנתונים זמינה בכתובת
http://123.456.78.90:port_number
לאחר מכן מוצג דף ההתחלה של היסטוריית הסוללה, שבו אפשר להעלות וגם להציג את הנתונים הסטטיסטיים של הסוללה.
איור 1. דף הפתיחה של הסוללה היסטוריון.
איסוף נתונים באמצעות הסוללהstats
כדי לאסוף נתונים מהמכשיר באמצעות הסוללהstats ולפתוח אותם במצב 'סוללה' היסטורי, מבצעים את הפעולות הבאות:
מחברים את המכשיר הנייד למחשב.
מחלון טרמינל, משביתים את שרת
adbהפעיל על ידי הרצת הפקודה הבאה:adb kill-serverצריך להפעיל מחדש את
adbולבדוק אם יש מכשירים מחוברים על ידי הרצת השלבים הבאים הפקודה.adb devicesהיא מציגה את רשימת המכשירים שלכם, בדומה לפלט לדוגמה הבא.

איור 2. הפלט של adb devices, מוצג מכשיר מחובר אחדאם לא מופיעים מכשירים, צריך לוודא שהטלפון מחובר וב-USB ניפוי באגים מופעל, צריך להפסיק ולהפעיל מחדש את
adb.כדי לאפס את איסוף נתוני הסוללה, מריצים את הפקודה הבאה:
adb shell dumpsys batterystats --resetהמכשיר תמיד אוסף נתוני סוללה ומידע אחר על ניפוי באגים ברקע. איפוס מוחק את הנתונים הקודמים של איסוף הסוללה. אם לא תאפס, הפלט עלול להיות גדול מאוד.
נתקו את המכשיר מהמחשב כדי שתוכלו רק לשרטט מסוללת המכשיר.
משתמשים באפליקציה ומבצעים פעולות שעבורן רוצים לאסוף נתונים. עבור לדוגמה: התנתקות מה-Wi-Fi ושליחת נתונים לענן.
מחברים מחדש את הטלפון.
ודאו שהטלפון שלכם מזוהה ומריצים את הפקודה הבאה:
adb devicesמוחקים את כל נתוני הסוללה על ידי הרצת הפקודה הבאה. הפעולה הזו עשויה להימשך בזמן הזה.
adb shell dumpsys batterystats > [path/]batterystats.txt
הקובץ
batterystats.txtנוצר בספרייה שציינתם באמצעות את ארגומנט הנתיב האופציונלי. אם לא תציינו נתיב, הקובץ שנוצרו בספריית הבית שלכם.יצירת דוח מנתונים גולמיים.
- במכשירים עם Android מגרסה 7.0 ואילך:
-
adb bugreport [path/]bugreport.zip
- במכשירים עם Android מגרסה 6.0 ומטה:
-
adb bugreport [path/]bugreport.txt
מילוי הדוח על הבאג עשוי להימשך כמה דקות. אל תנתקו את במכשיר או לבטל את התהליך עד לסיום.
בדומה ל-
batterystats.txt, הקבצים האלה נוצרים בספרייה לציין באמצעות הארגומנט האופציונליpath. אם לא מציינים נתיב, הם נוצרים בספריית הבית שלכם.אם היא עדיין לא פועלת, מריצים את התכונה 'היסטוריית סוללה' באמצעות הפקודה:
docker run -p port_number:9999 gcr.io/android-battery-historian/stable:3.1 --port 9999
כדי להציג את הנתונים ב'היסטוריית הסוללה', צריך לפתוח את 'היסטוריית הסוללה' ב בדפדפן. ב-Mac וב-Linux, היסטוריית הסוללה פועלת ב-
http://localhost:port_numberב-Windows, סוללה היסטוריון רץ ב-http://your_IP_address:port_numberלוחצים על עיון ובוחרים את קובץ הדוח על הבאג שיצרתם.
לוחצים על שליחה. התכונה 'היסטוריית סוללה' פותחת תרשים שנוצר נתוני סוללה.
הצגת נתונים באמצעות תרשימים של היסטוריית הסוללה
התרשים 'היסטוריית הסוללה' מציג אירועים רלוונטיים לצריכת חשמל לאורך זמן.
כל שורה מציגה פלח עמודות צבעוני כשרכיב מערכת פעיל, הרשאה לזרם של הסוללה. בתרשים לא מוצגת רמת הטעינה של הסוללה משמש את הרכיב – רק אם האפליקציה פעילה. התרשימים מאורגנים לפי קטגוריה, שמציגה סרגל לכל קטגוריה לאורך זמן, כפי שמוצג בדף וציר x בתרשים.
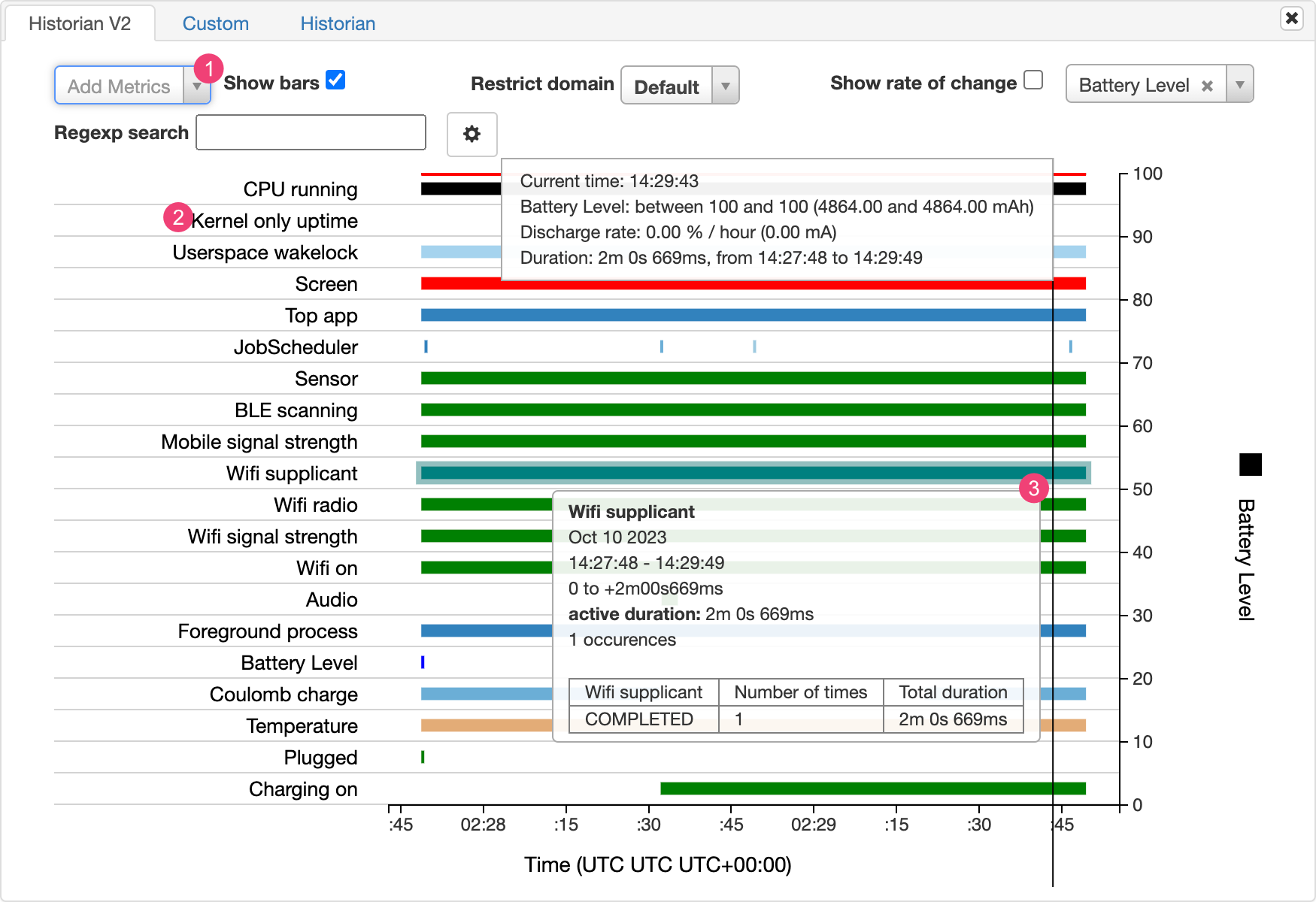
- מוסיפים מדדים מהרשימה הנפתחת.
- מעבירים את העכבר מעל שם המדד כדי לראות מידע נוסף על כל מדד, כולל מפתח לצבעים של התרשים.
- מעבירים את הסמן מעל לעמודה כדי לראות מידע מפורט יותר על הנושא ואת הנתונים הסטטיסטיים של הסוללה בנקודה ספציפית בציר הזמן.
פלט נוסף של Budgetstats
אפשר להציג מידע נוסף מהקובץ batterystats.txt ב
של הנתונים הסטטיסטיים שאחרי התרשים של היסטוריית הסוללה.
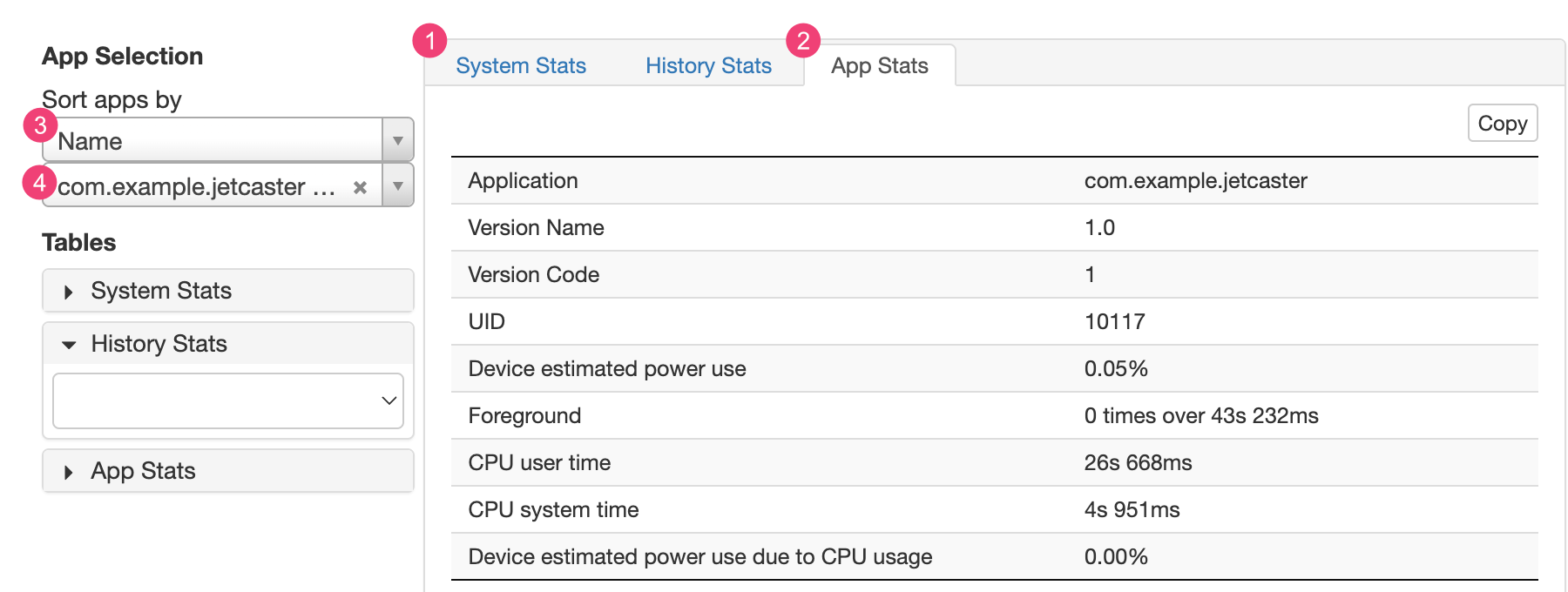
הכרטיסייה 1 נתונים סטטיסטיים של המערכת כוללת את כל המערכת נתונים סטטיסטיים, כמו רמות האות הסלולרי ובהירות המסך. המידע הזה מספקת תמונה כללית של מה שקורה במכשיר. הדבר שימושי במיוחד כדי לוודא שאין אירועים חיצוניים שמשפיעים על הבדיקה.
הכרטיסייה 2 נתונים סטטיסטיים של אפליקציות כוללת מידע על באפליקציות ספציפיות. אפשר למיין את רשימת האפליקציות באמצעות 3 ברשימה הנפתחת מיון אפליקציות לפי בחלונית בחירת האפליקציות. שלך הם יכולים לבחור אפליקציה ספציפית כדי לראות נתונים סטטיסטיים לגבי השימוש רשימה נפתחת של 4 אפליקציות.

