Android は、USB アクセサリと USB ホストの 2 つのモードで、さまざまな USB 周辺機器と Android USB アクセサリ(Android アクセサリ プロトコルを実装しているハードウェア)をサポートしています。USB アクセサリ モードでは、外部 USB ハードウェアが USB ホストとして機能します。アクセサリの例:
- ロボット工学 コントローラ
- ドッキング ステーション
- 診断、音楽機器
- キオスク
- カードリーダー
その他多数。これにより、ホスト機能を持たない Android 搭載デバイスで USB ハードウェアを操作できます。Android USB アクセサリは、Android 搭載デバイスと連携するように設計され、Android アクセサリの通信プロトコルに準拠している必要があります。USB ホストモードでは、Android 搭載デバイスがホストとして機能します。デバイスの例としては、デジタルカメラ、キーボード、マウス、ゲーム コントローラなどがあります。さまざまなアプリや環境向けに設計された USB デバイスでも、デバイスと正しく通信できる Android アプリとやり取りできます。
図 1 は 2 つのモードの違いを示しています。Android 搭載デバイスがホストモードのときは、USB ホストとして機能し、バスに電力を供給します。Android 搭載デバイスが USB アクセサリ モードの場合、接続された USB ハードウェア(この場合は Android USB アクセサリ)がホストとして機能し、バスに電力を供給します。
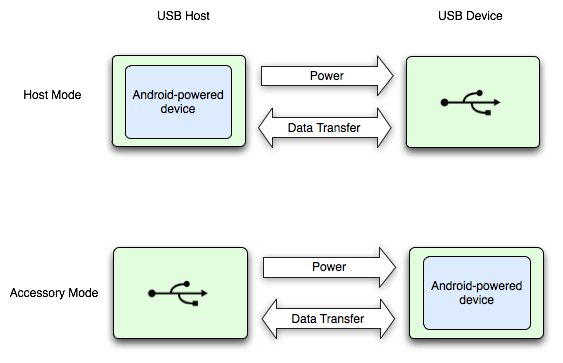
図 1. USB ホストモードとアクセサリ モード
USB アクセサリとホストモードは、Android 3.1(API レベル 12)以降のプラットフォームで直接サポートされます。また、USB アクセサリ モードは、アドオン ライブラリとして Android 2.3.4(API レベル 10)にバックポートされており、幅広いデバイスをサポートしています。デバイス メーカーは、デバイスのシステム イメージにアドオン ライブラリを含めるかどうかを選択できます。
注: USB ホストモードとアクセサリ モードのサポートは、プラットフォーム レベルに関係なく、最終的にはデバイスのハードウェアに依存します。<uses-feature> 要素を使用すると、USB ホストとアクセサリをサポートするデバイスをフィルタできます。詳しくは、USB アクセサリとホストのドキュメントをご覧ください。
デバッグに関する考慮事項
USB アクセサリまたはホスト機能を使用するアプリをデバッグする場合、USB ハードウェアを Android 搭載デバイスに接続していることがよくあります。これにより、USB を使用して Android 搭載デバイスに adb 接続できなくなります。adb にはネットワーク接続を介して引き続きアクセスできます。ネットワーク接続経由で adb を有効にするには:
- USB を使用して Android 搭載デバイスをパソコンに接続します。
- SDK の
platform-tools/ディレクトリで、コマンド プロンプトに「adb tcpip 5555」と入力します。 - 「
adb connect <device-ip-address>:5555」と入力します。Android 搭載デバイスに接続され、adb logcatなどの通常のadbコマンドを発行できます。 - USB をリッスンするようにデバイスを設定するには、
adb usbと入力します。
