您可以按照本指南中的步骤,从 Java 代码获取应用的资源包。
针对 Kotlin 和 Java 构建
您可以按照以下步骤将 Play Asset Delivery 内置到项目的 Android App Bundle 中。您无需使用 Android Studio 即可执行这些步骤。
在项目的
build.gradle文件中将 Android Gradle 插件的版本更新为4.0.0或更高版本。在项目的顶级目录中,为资源包创建一个目录。此目录名称将用作资源包名称。资源包名称必须以字母开头,并且只能包含字母、数字和下划线。
在资源包目录中,创建一个
build.gradle文件并添加以下代码。请务必指定资源包的名称,并且仅指定一种分发类型:Groovy
// In the asset pack's build.gradle file: plugins { id 'com.android.asset-pack' } assetPack { packName = "asset-pack-name" // Directory name for the asset pack dynamicDelivery { deliveryType = "[ install-time | fast-follow | on-demand ]" } }
Kotlin
// In the asset pack's build.gradle.kts file: plugins { id("com.android.asset-pack") } assetPack { packName.set("asset-pack-name") // Directory name for the asset pack dynamicDelivery { deliveryType.set("[ install-time | fast-follow | on-demand ]") } }
在项目的应用
build.gradle文件中,添加项目中每个资源包的名称,如下所示:Groovy
// In the app build.gradle file: android { ... assetPacks = [":asset-pack-name", ":asset-pack2-name"] }
Kotlin
// In the app build.gradle.kts file: android { ... assetPacks += listOf(":asset-pack-name", ":asset-pack2-name") }
在项目的
settings.gradle文件中,添加项目中的所有资源包,如下所示:Groovy
// In the settings.gradle file: include ':app' include ':asset-pack-name' include ':asset-pack2-name'
Kotlin
// In the settings.gradle.kts file: include(":app") include(":asset-pack-name") include(":asset-pack2-name")
在资源包目录中,创建以下子目录:
src/main/assets。将资源放置在
src/main/assets目录中。您也可以在此处创建子目录。应用的目录结构现在应如下所示:build.gradlesettings.gradleapp/asset-pack-name/build.gradleasset-pack-name/src/main/assets/your-asset-directories
使用 Gradle 构建 Android App Bundle。在生成的 app bundle 中,根级目录现在包含以下内容:
asset-pack-name/manifest/AndroidManifest.xml:此目录用于配置资源包的标识符和分发模式asset-pack-name/assets/your-asset-directories:此目录包含作为资源包的一部分分发的所有资源
Gradle 会为每个资源包生成清单,并为您输出
assets/目录。(可选)如果您计划使用快速跟进式分发和按需分发,请添加 Play Asset Delivery 库
Groovy
implementation "com.google.android.play:asset-delivery:2.3.0" // For Kotlin use asset-delivery-ktx implementation "com.google.android.play:asset-delivery-ktx:2.3.0"
Kotlin
implementation("com.google.android.play:asset-delivery:2.3.0") // For Kotlin use core-ktx implementation("com.google.android.play:asset-delivery-ktx:2.3.0")
(可选)配置 app bundle 以支持不同的纹理压缩格式。
与 Play Asset Delivery API 集成
Play Asset Delivery Java API 提供了用于请求资源包、管理下载内容和获取资源的 AssetPackManager 类。请务必先将 Play Asset Delivery 库添加到您的项目中。
您可以根据希望获取的资源包的分发类型来实现此 API。这些步骤如以下流程图所示。
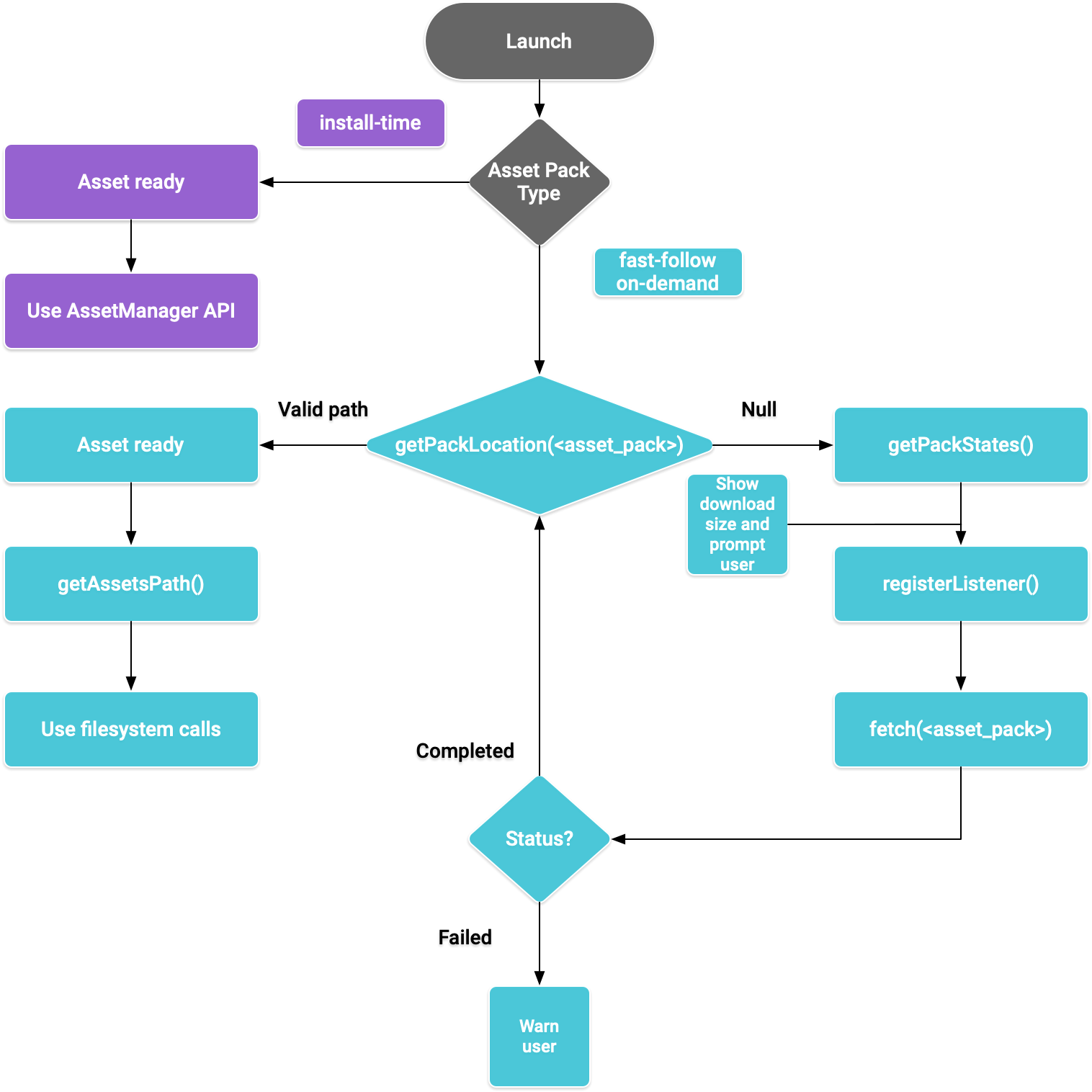
图 1. 获取资源包的流程图
安装时分发
配置为 install-time 的资源包可以在应用启动后立即使用。使用 Java AssetManager API 获取在此模式下提供的资源:
Kotlin
import android.content.res.AssetManager ... val context: Context = createPackageContext("com.example.app", 0) val assetManager: AssetManager = context.assets val stream: InputStream = assetManager.open("asset-name")
Java
import android.content.res.AssetManager; ... Context context = createPackageContext("com.example.app", 0); AssetManager assetManager = context.getAssets(); InputStream is = assetManager.open("asset-name");
快速跟进式分发和按需分发
以下几部分介绍了如何在下载资源包前获取其相关信息、如何调用 API 以开始下载,以及之后如何获取已下载的资源包。这几部分适用于 fast-follow 和 on-demand Asset Pack。
查看状态
每个资源包都存储于应用的内部存储空间内单独的文件夹中。使用 getPackLocation() 方法确定资源包的根文件夹。此方法会返回以下值:
| 返回值 | 状态 |
|---|---|
有效的 AssetPackLocation 对象 |
资源包根文件夹位于 assetsPath(),现在可直接访问 |
null |
未知 Asset Pack 或资产无法使用 |
获取有关资源包的下载信息
在提取资源包之前,应用必须披露下载内容的大小。使用 requestPackStates() 或 getPackStates() 方法确定下载内容的大小,以及资源包是否已在下载。
Kotlin
suspend fun requestPackStates(packNames: List<String>): AssetPackStates
Java
Task<AssetPackStates> getPackStates(List<String> packNames)
requestPackStates() 是一个返回 AssetPackStates 对象的挂起函数,而 getPackStates() 是一个返回 Task<AssetPackStates> 的异步方法。AssetPackStates 对象的 packStates() 方法会返回一个 Map<String,
AssetPackState>。此映射包含所请求的每个资源包的状态,按其名称进行键控:
Kotlin
AssetPackStates#packStates(): Map<String, AssetPackState>
Java
Map<String, AssetPackState> AssetPackStates#packStates()
最终请求如下所示:
Kotlin
const val assetPackName = "assetPackName" coroutineScope.launch { try { val assetPackStates: AssetPackStates = manager.requestPackStates(listOf(assetPackName)) val assetPackState: AssetPackState = assetPackStates.packStates()[assetPackName] } catch (e: RuntimeExecutionException) { Log.d("MainActivity", e.message) } }
Java
final String assetPackName = "myasset"; assetPackManager .getPackStates(Collections.singletonList(assetPackName)) .addOnCompleteListener(new OnCompleteListener<AssetPackStates>() { @Override public void onComplete(Task<AssetPackStates> task) { AssetPackStates assetPackStates; try { assetPackStates = task.getResult(); AssetPackState assetPackState = assetPackStates.packStates().get(assetPackName); } catch (RuntimeExecutionException e) { Log.d("MainActivity", e.getMessage()); return; })
以下 AssetPackState 方法提供了资源包的大小、截至目前已下载的数据量(如已请求),以及已传输到应用的数据量:
如需获取资源包的状态,请使用 status() 方法,该方法以整数形式返回与 AssetPackStatus 类中某个常量字段相对应的状态。尚未安装的资源包状态为 AssetPackStatus.NOT_INSTALLED。
如果请求失败,请使用 errorCode() 方法,该方法的返回值与 AssetPackErrorCode 类中的某个常量字段相对应。
安装
使用 requestFetch() 或 fetch() 方法首次下载资源包,或要求进行资源包更新以完成操作:
Kotlin
suspend fun AssetPackManager.requestFetch(packs: List<String>): AssetPackStates
Java
Task<AssetPackStates> fetch(List<String> packNames)
此方法会返回一个 AssetPackStates 对象,其中包含资源包列表及其初始下载状态和大小。如果通过 requestFetch() 或 fetch() 请求的资源包已经在下载,就会返回下载状态,并且不会启动其他下载。
监控下载状态
您应实现 AssetPackStateUpdatedListener 以跟踪资源包的安装进度。状态更新按资源包细分,以支持跟踪各资源包的状态。在请求的其他所有下载完成之前,您就可以开始使用可用的资源包。
Kotlin
fun registerListener(listener: AssetPackStateUpdatedListener) fun unregisterListener(listener: AssetPackStateUpdatedListener)
Java
void registerListener(AssetPackStateUpdatedListener listener) void unregisterListener(AssetPackStateUpdatedListener listener)
下载内容较大
如果下载内容超过 200 MB 并且用户未连接到 Wi-Fi,那么在用户明确同意使用移动网络连接继续下载前,下载不会开始。同样,如果下载内容较大并且用户与 WLAN 的连接断开,下载会暂停,需要用户明确同意才能使用移动网络连接继续下载。已暂停的资源包状态为 WAITING_FOR_WIFI。如需触发界面流程以提示用户同意,请使用 showConfirmationDialog() 方法。
请注意,如果应用不调用此方法,下载会暂停,并且只有当用户重新连接到 Wi-Fi 时才会自动恢复下载。
需要用户确认
如果包的状态为 REQUIRES_USER_CONFIRMATION,则在用户接受显示 showConfirmationDialog() 的对话框之前,下载不会继续进行。
如果 Play 无法识别应用(例如,应用是旁加载的),则可能会出现此状态。
请注意,在这种情况下调用 showConfirmationDialog() 会导致应用更新。更新后,您需要重新请求相应资产。
以下是监听器的一个实现示例:
Kotlin
private val activityResultLauncher = registerForActivityResult( ActivityResultContracts.StartIntentSenderForResult() ) { result -> if (result.resultCode == RESULT_OK) { Log.d(TAG, "Confirmation dialog has been accepted.") } else if (result.resultCode == RESULT_CANCELED) { Log.d(TAG, "Confirmation dialog has been denied by the user.") } } assetPackManager.registerListener { assetPackState -> when(assetPackState.status()) { AssetPackStatus.PENDING -> { Log.i(TAG, "Pending") } AssetPackStatus.DOWNLOADING -> { val downloaded = assetPackState.bytesDownloaded() val totalSize = assetPackState.totalBytesToDownload() val percent = 100.0 * downloaded / totalSize Log.i(TAG, "PercentDone=" + String.format("%.2f", percent)) } AssetPackStatus.TRANSFERRING -> { // 100% downloaded and assets are being transferred. // Notify user to wait until transfer is complete. } AssetPackStatus.COMPLETED -> { // Asset pack is ready to use. Start the game. } AssetPackStatus.FAILED -> { // Request failed. Notify user. Log.e(TAG, assetPackState.errorCode()) } AssetPackStatus.CANCELED -> { // Request canceled. Notify user. } AssetPackStatus.WAITING_FOR_WIFI, AssetPackStatus.REQUIRES_USER_CONFIRMATION -> { if (!confirmationDialogShown) { assetPackManager.showConfirmationDialog(activityResultLauncher); confirmationDialogShown = true } } AssetPackStatus.NOT_INSTALLED -> { // Asset pack is not downloaded yet. } AssetPackStatus.UNKNOWN -> { Log.wtf(TAG, "Asset pack status unknown") } } }
Java
assetPackStateUpdateListener = new AssetPackStateUpdateListener() { private final ActivityResultLauncher<IntentSenderRequest> activityResultLauncher = registerForActivityResult( new ActivityResultContracts.StartIntentSenderForResult(), new ActivityResultCallback<ActivityResult>() { @Override public void onActivityResult(ActivityResult result) { if (result.getResultCode() == RESULT_OK) { Log.d(TAG, "Confirmation dialog has been accepted."); } else if (result.getResultCode() == RESULT_CANCELED) { Log.d(TAG, "Confirmation dialog has been denied by the user."); } } }); @Override public void onStateUpdate(AssetPackState assetPackState) { switch (assetPackState.status()) { case AssetPackStatus.PENDING: Log.i(TAG, "Pending"); break; case AssetPackStatus.DOWNLOADING: long downloaded = assetPackState.bytesDownloaded(); long totalSize = assetPackState.totalBytesToDownload(); double percent = 100.0 * downloaded / totalSize; Log.i(TAG, "PercentDone=" + String.format("%.2f", percent)); break; case AssetPackStatus.TRANSFERRING: // 100% downloaded and assets are being transferred. // Notify user to wait until transfer is complete. break; case AssetPackStatus.COMPLETED: // Asset pack is ready to use. Start the game. break; case AssetPackStatus.FAILED: // Request failed. Notify user. Log.e(TAG, assetPackState.errorCode()); break; case AssetPackStatus.CANCELED: // Request canceled. Notify user. break; case AssetPackStatus.WAITING_FOR_WIFI: case AssetPackStatus.REQUIRES_USER_CONFIRMATION: if (!confirmationDialogShown) { assetPackManager.showConfirmationDialog(activityResultLauncher); confirmationDialogShown = true; } break; case AssetPackStatus.NOT_INSTALLED: // Asset pack is not downloaded yet. break; case AssetPackStatus.UNKNOWN: Log.wtf(TAG, "Asset pack status unknown") break; } } }
或者,您也可以使用 getPackStates() 方法获取当前下载的状态。AssetPackStates 包含下载进度、下载状态和任何失败的错误代码。
获取资源包
在下载请求达到 COMPLETED 状态后,您可以使用文件系统调用获取资源包。使用 getPackLocation() 方法获取资源包的根文件夹。
资源存储于资源包根目录内的 assets 目录下。您可以使用便捷方法 assetsPath() 获取 assets 目录的路径。使用以下方法获取特定资源的路径:
Kotlin
private fun getAbsoluteAssetPath(assetPack: String, relativeAssetPath: String): String? { val assetPackPath: AssetPackLocation = assetPackManager.getPackLocation(assetPack) // asset pack is not ready ?: return null val assetsFolderPath = assetPackPath.assetsPath() // equivalent to: FilenameUtils.concat(assetPackPath.path(), "assets") return FilenameUtils.concat(assetsFolderPath, relativeAssetPath) }
Java
private String getAbsoluteAssetPath(String assetPack, String relativeAssetPath) { AssetPackLocation assetPackPath = assetPackManager.getPackLocation(assetPack); if (assetPackPath == null) { // asset pack is not ready return null; } String assetsFolderPath = assetPackPath.assetsPath(); // equivalent to: FilenameUtils.concat(assetPackPath.path(), "assets"); String assetPath = FilenameUtils.concat(assetsFolderPath, relativeAssetPath); return assetPath; }
其他 Play Asset Delivery API 方法
以下是您可能希望在应用中使用的一些其他 API 方法。
取消请求
您可以使用 cancel() 取消有效的资源包请求。请注意,此请求是尽力而为的操作。
移除资源包
使用 requestRemovePack() 或 removePack() 安排移除资源包。
获取多个资源包的位置
使用 getPackLocations() 批量查询多个资源包的状态,此方法将返回资源包与其位置的映射。getPackLocations() 返回的映射包含当前已下载且为最新状态的每个 Asset Pack 的条目。
后续步骤
在本地以及通过 Google Play 测试 Play Asset Delivery。
