content provider 可以帮助应用管理对自身存储或由其他应用存储的数据的访问,并提供与其他应用共享数据的方法。它们封装数据,并提供用于定义数据安全性的机制。content provider 是将一个进程中的数据与另一个进程中运行的代码连接的标准接口。
实现 content provider 有诸多优势。最重要的是,您可以配置 content provider,让其他应用安全地访问和修改您的应用数据,如图 1 所示。
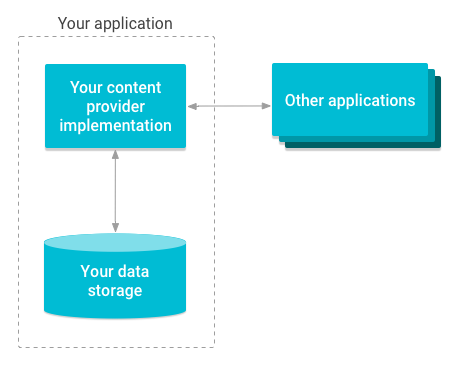
图 1. 内容提供程序如何管理对存储空间的访问权限的概览图。
如果您打算共享数据,请使用内容提供程序。如果您不打算共享数据,则不必使用它们,但您可以选择使用它们,因为它们提供的抽象让您可以修改应用的数据存储实现,而不会影响依赖于访问数据的其他应用。
在这种情况下,只有您的内容提供程序会受到影响,访问该提供程序的应用不会受到影响。例如,您可以将 SQLite 数据库换成其他存储空间,如图 2 所示。
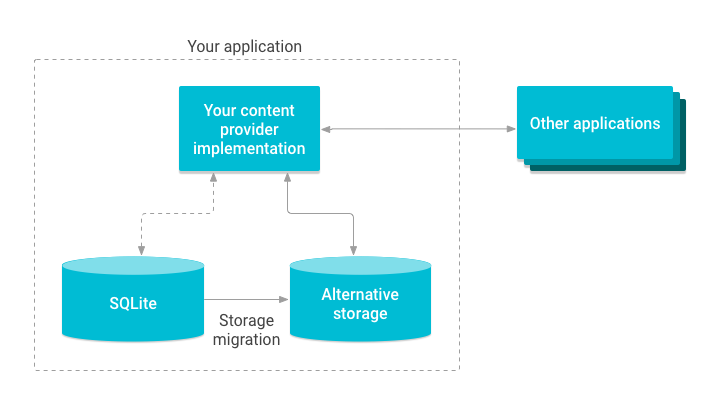
图 2. 图示:迁移 content provider 存储空间。
许多其他类依赖于 ContentProvider 类:
如果您使用这些类中的任何一个,则需要在应用中实现 content provider。使用同步适配器框架时,您还可以创建桩内容提供器作为替代方案。如需了解详情,请参阅创建桩内容提供器。此外,在以下情况下,您还需要使用自己的内容提供程序:
- 在您的应用中实现自定义搜索建议。
- 向 widget 公开应用数据。
- 将复杂的数据或文件从您的应用复制并粘贴到其他应用。
Android 框架包括一些 content provider,可管理音频、视频、图片和个人联系信息等数据。android.provider
软件包的参考文档中列出了其中一些选项。任何 Android 应用都可以访问这些提供程序,但会受到某些限制。
content provider 可用于管理对各种数据存储源的访问,包括结构化数据(如 SQLite 关系型数据库)或非结构化数据(如图片文件)。如需详细了解 Android 上可用的存储类型,请参阅数据和文件存储概览以及 设计数据存储。
内容提供程序的优点
content provider 可精细控制数据访问权限。您可以选择仅允许您访问自己应用中的内容提供程序、授予访问其他应用的数据的一揽子权限,或配置读取和写入数据的不同权限。如需详细了解如何安全地使用 content provider,请参阅 有关数据存储的安全提示和 Content Provider 权限。
您可以使用 content provider 来抽象化处理中用于访问应用中不同数据源的详细信息。例如,您的应用可能会将结构化记录以及视频和音频文件存储在一个 SQLite 数据库中。您可以使用 content provider 来访问所有这些数据。
此外,CursorLoader 对象依赖 content provider 运行异步查询,然后将结果返回到应用中的界面层。如需详细了解如何使用 CursorLoader 在后台加载数据,请参阅
加载器。
以下主题更详细地介绍了 content provider:
- Content Provider 基础知识
- 如何使用现有 content provider 访问和更新数据。
- 创建 content provider
- 如何设计和实现您自己的 content provider。
- 日历提供程序概览
- 如何访问 Android 平台中的日历提供程序。
- 联系人提供程序
- 如何访问作为 Android 平台一部分的联系人提供程序。
