فهرستها به کاربران اجازه میدهند یک مورد را از میان مجموعهای از گزینهها به راحتی در دستگاههای Wear OS انتخاب کنند.
کتابخانه Wearable UI شامل کلاس WearableRecyclerView است که یک پیاده سازی RecyclerView برای ایجاد لیست های بهینه شده برای دستگاه های پوشیدنی است. می توانید با ایجاد یک کانتینر جدید WearableRecyclerView از این رابط در برنامه پوشیدنی خود استفاده کنید.
از WearableRecyclerView برای فهرستی طولانی از موارد ساده، مانند راهانداز برنامه یا فهرستی از مخاطبین، استفاده کنید. هر مورد ممکن است یک رشته کوتاه و یک نماد مرتبط داشته باشد. از طرف دیگر، هر مورد ممکن است فقط یک رشته یا یک نماد داشته باشد.
توجه: از چیدمان های پیچیده خودداری کنید. کاربران فقط باید به یک آیتم نگاهی بیندازند تا بفهمند چیست، به خصوص با اندازه صفحه نمایش محدود ابزارهای پوشیدنی.
با گسترش کلاس RecyclerView موجود، API های WearableRecyclerView به طور پیش فرض لیستی از موارد قابل پیمایش عمودی را در یک لیست مستقیم نمایش می دهند. همچنین میتوانید از APIهای WearableRecyclerView برای انتخاب طرحبندی منحنی و حرکت چرخشی دایرهای در برنامههای پوشیدنی خود استفاده کنید.
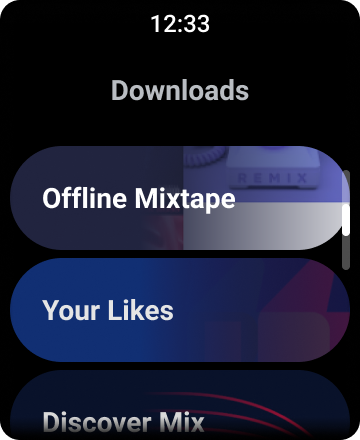
شکل 1. نمای فهرست پیش فرض در Wear OS.
این راهنما به شما نشان میدهد که چگونه از کلاس WearableRecyclerView برای ایجاد فهرستها در برنامههای Wear OS خود، نحوه انتخاب طرحبندی منحنی برای موارد قابل پیمایش خود، و نحوه سفارشیسازی ظاهر کودکان در حین پیمایش استفاده کنید.
WearableRecyclerView را با استفاده از XML به یک فعالیت اضافه کنید
طرح زیر یک WearableRecyclerView را به یک فعالیت اضافه می کند:
<androidx.wear.widget.WearableRecyclerView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/recycler_launcher_view" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:scrollbars="vertical" />
مثال زیر WearableRecyclerView اعمال شده روی یک فعالیت را نشان می دهد:
کاتلین
class MainActivity : Activity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) } ... }
جاوا
public class MainActivity extends Activity { @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } ... }
یک طرح منحنی ایجاد کنید
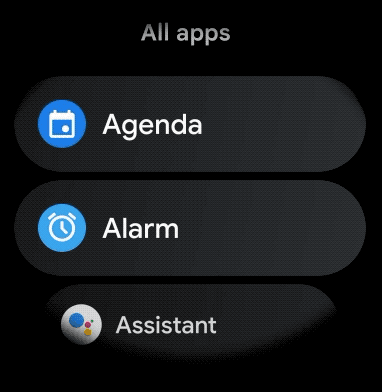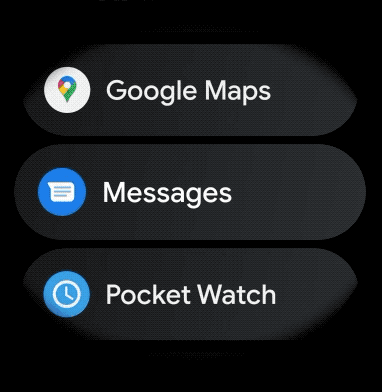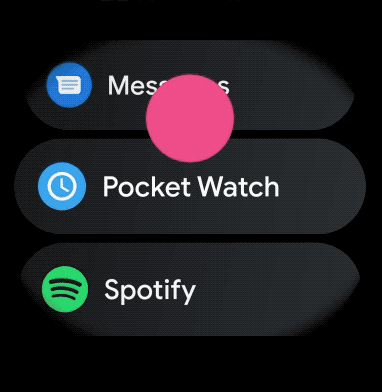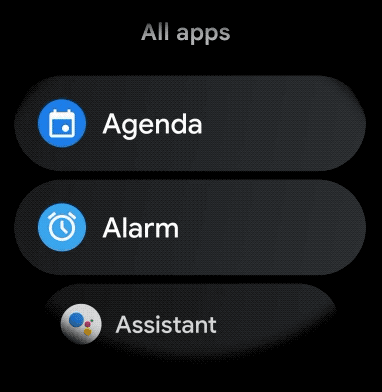
برای ایجاد یک طرح منحنی برای موارد قابل پیمایش در برنامه پوشیدنی خود، موارد زیر را انجام دهید:
- از
WearableRecyclerViewبه عنوان محفظه اصلی خود در طرح XML مربوطه استفاده کنید. - متد
setEdgeItemsCenteringEnabled(boolean)را رویtrueتنظیم کنید. این به صورت عمودی اولین و آخرین موارد موجود در لیست را روی صفحه در مرکز قرار می دهد. - از متد
WearableRecyclerView.setLayoutManager()برای تنظیم چیدمان موارد روی صفحه استفاده کنید.
کاتلین
wearableRecyclerView.apply { // To align the edge children (first and last) with the center of the screen. isEdgeItemsCenteringEnabled = true ... layoutManager = WearableLinearLayoutManager(this@MainActivity) }
جاوا
// To align the edge children (first and last) with the center of the screen. wearableRecyclerView.setEdgeItemsCenteringEnabled(true); ... wearableRecyclerView.setLayoutManager( new WearableLinearLayoutManager(this));
اگر برنامه شما دارای الزامات خاصی برای سفارشی کردن ظاهر کودکان در حین پیمایش است - به عنوان مثال، تغییر مقیاس نمادها و متن در حالی که موارد از مرکز حرکت می کنند - کلاس WearableLinearLayoutManager.LayoutCallback را گسترش دهید و روش onLayoutFinished را لغو کنید.
تکه کد زیر نمونه ای از سفارشی کردن پیمایش موارد را برای مقیاس دورتر از مرکز با گسترش کلاس WearableLinearLayoutManager.LayoutCallback نشان می دهد:
کاتلین
/** How much icons should scale, at most. */ private const val MAX_ICON_PROGRESS = 0.65f class CustomScrollingLayoutCallback : WearableLinearLayoutManager.LayoutCallback() { private var progressToCenter: Float = 0f override fun onLayoutFinished(child: View, parent: RecyclerView) { child.apply { // Figure out % progress from top to bottom. val centerOffset = height.toFloat() / 2.0f / parent.height.toFloat() val yRelativeToCenterOffset = y / parent.height + centerOffset // Normalize for center. progressToCenter = Math.abs(0.5f - yRelativeToCenterOffset) // Adjust to the maximum scale. progressToCenter = Math.min(progressToCenter, MAX_ICON_PROGRESS) scaleX = 1 - progressToCenter scaleY = 1 - progressToCenter } } }
جاوا
public class CustomScrollingLayoutCallback extends WearableLinearLayoutManager.LayoutCallback { /** How much icons should scale, at most. */ private static final float MAX_ICON_PROGRESS = 0.65f; private float progressToCenter; @Override public void onLayoutFinished(View child, RecyclerView parent) { // Figure out % progress from top to bottom. float centerOffset = ((float) child.getHeight() / 2.0f) / (float) parent.getHeight(); float yRelativeToCenterOffset = (child.getY() / parent.getHeight()) + centerOffset; // Normalize for center. progressToCenter = Math.abs(0.5f - yRelativeToCenterOffset); // Adjust to the maximum scale. progressToCenter = Math.min(progressToCenter, MAX_ICON_PROGRESS); child.setScaleX(1 - progressToCenter); child.setScaleY(1 - progressToCenter); } }
کاتلین
wearableRecyclerView.layoutManager = WearableLinearLayoutManager(this, CustomScrollingLayoutCallback())
جاوا
CustomScrollingLayoutCallback customScrollingLayoutCallback = new CustomScrollingLayoutCallback(); wearableRecyclerView.setLayoutManager( new WearableLinearLayoutManager(this, customScrollingLayoutCallback));


