实体按钮
使用集合让一切井井有条
根据您的偏好保存内容并对其进行分类。
穿戴式设备上通常会有多个实体按钮,也称为“表把按钮”。所有 Wear OS 设备都至少有一个按钮,即电源按钮。除此之外,还可能会有多个多功能按钮(也可能没有)。
在您的应用中,您可以为操作分配多功能按钮。例如,健身应用可以使用多功能按钮开始或暂停锻炼:
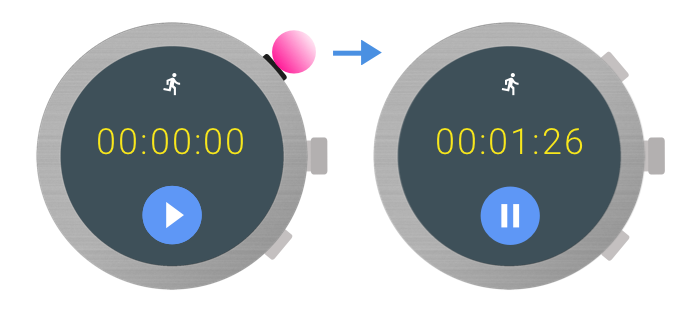
注意:Wear OS 3.0 会为操作系统预留两个按钮,而 Wear OS 2.0 则只会预留一个按钮。这样,您可以为操作分配的按钮数量便会减少。
本指南介绍了如何检索设备上可用的多功能按钮的相关信息,以及如何处理按钮按下动作。
如需获取有关设备上按钮的更多信息,请使用 Wear Input AndroidX 库中定义的 API。请在应用模块的 build.gradle 文件中添加以下依赖项:
dependencies {
implementation "androidx.wear:wear-input:1.0.0"
}
如需了解设备上可用的按钮数量,请使用 WearableButtons.getButtonCount() 方法。此方法的搜索范围包括电源按钮,因此,如果此方法返回的值大于 1,则表示有多功能按钮可供使用。将此返回的值减去 1 即为可分配的多功能按钮的准确总数,因为第一个按钮始终是电源按钮。
每个按钮都将映射到 KeyEvent 类中的一个 int 常量,如下表所示:
|
按钮
|
KeyEvent
|
| 多功能按钮 1
|
KEYCODE_STEM_1
|
| 多功能按钮 2
|
KEYCODE_STEM_2
|
| 多功能按钮 3
|
KEYCODE_STEM_3
|
以下示例代码展示了如何获取可用按钮的数量:
Kotlin
val count = WearableButtons.getButtonCount(context)
if (count > 1) {
// There are multifunction buttons available
}
val buttonInfo = WearableButtons.getButtonInfo(activity, KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_1)
if (buttonInfo == null) {
// KEYCODE_STEM_1 is unavailable
} else {
// KEYCODE_STEM_1 is present on the device
}
Java
int count = WearableButtons.getButtonCount(context);
if (count > 1) {
// There are multifunction buttons available
}
WearableButtons.ButtonInfo buttonInfo =
WearableButtons.getButtonInfo(activity, KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_1);
if (buttonInfo == null) {
// KEYCODE_STEM_1 is unavailable
} else {
// KEYCODE_STEM_1 is present on the device
}
您的应用可以处理多个可能的按钮键码,如下所示:
-
KEYCODE_STEM_1
-
KEYCODE_STEM_2
-
KEYCODE_STEM_3
您的应用可以接收这些键码并将其转换为特定的应用内操作。
如需处理按钮按下动作,请实现 onKeyDown() 方法。
例如,以下实现可响应某个按钮按下动作,以控制应用中的操作:
Kotlin
// Activity
override fun onKeyDown(keyCode: Int, event: KeyEvent): Boolean {
return if (event.repeatCount == 0) {
when (keyCode) {
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_1 -> {
// Do stuff
true
}
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_2 -> {
// Do stuff
true
}
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_3 -> {
// Do stuff
true
}
else -> {
super.onKeyDown(keyCode, event)
}
}
} else {
super.onKeyDown(keyCode, event)
}
}
Java
@Override
// Activity
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event){
if (event.getRepeatCount() == 0) {
if (keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_1) {
// Do stuff
return true;
} else if (keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_2) {
// Do stuff
return true;
} else if (keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_3) {
// Do stuff
return true;
}
}
return super.onKeyDown(keyCode, event);
}
确定按钮位置
AndroidX 库提供了两种描述按钮位置的方法:
注意:在描述按钮及其功能时,我们建议您不要使用文本描述符,而改用直观的指示符。不过,在某些情况下,描述按钮的方式可能会更有意义。
前述方法专为简单的描述而设计。如果这些 API 不符合您的应用需求,您还可以使用 WearableButtons.getButtonInfo() API 获取按钮在屏幕上的位置,并以更加个性化的方式对其进行处理。如需详细了解这些 API,请参阅 Wear API 参考文档。
本页面上的内容和代码示例受内容许可部分所述许可的限制。Java 和 OpenJDK 是 Oracle 和/或其关联公司的注册商标。
最后更新时间 (UTC):2025-07-26。
[null,null,["最后更新时间 (UTC):2025-07-26。"],[],[],null,["# Physical buttons\n\nA wearable device typically contains multiple physical buttons, also known as _stems_. Wear OS\ndevices always have, at minimum, one button: the power button. Beyond that, zero or more\nmultifunction buttons might be present.\n\n\nIn your app, you can assign multifunction buttons to actions. For example, a fitness app\nmight start or pause a workout using multifunction buttons:\n\n**Note:** Wear OS 3.0 reserves two buttons for the OS, while\nWear OS 2.0 reserves only one. This reduces the number of buttons you can assign\nactions to. \n\nFor suitable use cases and design considerations, review the\n[Wear OS design principles](/training/wearables/design).\n\n\nThis guide describes how to retrieve information about available multifunction buttons on\na device and how to process button presses.\n\nButton metadata\n---------------\n\n\nTo get extra information about the buttons on a device, use the API defined in the\n[Wear Input](/reference/androidx/wear/input/package-summary) AndroidX library. Add the\nfollowing dependency in your app module's `build.gradle` file: \n\n```groovy\ndependencies {\nimplementation \"androidx.wear:wear-input:1.0.0\"\n}\n```\n\n### Number of buttons\n\n\nTo find out how many buttons are available on the device, use the\n[`WearableButtons.getButtonCount()`](/reference/android/support/wearable/input/WearableButtons#getButtonCount(android.content.Context)) method. This method includes the power button,\nso if the method returns a value greater than one, then there are multifunction buttons available\nfor use. To get an accurate count of assignable multifunction buttons, subtract\none from the count, since the first button is always the power button.\n\n### Keycodes for button presses\n\n\nEach button is mapped to an `int` constant from the [KeyEvent](https://developer.android.com/reference/android/view/KeyEvent.html)\nclass, as shown in the following table:\n\n| Button | KeyEvent |\n|------------------------|------------------|\n| Multifunction button 1 | `KEYCODE_STEM_1` |\n| Multifunction button 2 | `KEYCODE_STEM_2` |\n| Multifunction button 3 | `KEYCODE_STEM_3` |\n\n\nThe following example code shows how to get the available button\ncount: \n\n### Kotlin\n\n```kotlin\nval count = WearableButtons.getButtonCount(context)\n\nif (count \u003e 1) {\n // There are multifunction buttons available\n}\n\nval buttonInfo = WearableButtons.getButtonInfo(activity, KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_1)\n\nif (buttonInfo == null) {\n // KEYCODE_STEM_1 is unavailable\n} else {\n // KEYCODE_STEM_1 is present on the device\n}\n```\n\n### Java\n\n```java\nint count = WearableButtons.getButtonCount(context);\n\nif (count \u003e 1) {\n // There are multifunction buttons available\n}\n\nWearableButtons.ButtonInfo buttonInfo =\n WearableButtons.getButtonInfo(activity, KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_1);\n\nif (buttonInfo == null) {\n // KEYCODE_STEM_1 is unavailable\n} else {\n // KEYCODE_STEM_1 is present on the device\n}\n```\n\nHandle button presses\n---------------------\n\n\nThere are a number of possible button keycodes that your app can handle:\n\n- `KEYCODE_STEM_1`\n- `KEYCODE_STEM_2 `\n- `KEYCODE_STEM_3`\n\n\nYour app can receive these key codes and convert them to specific in-app actions.\n\n\nTo handle a button press, implement the\n[`onKeyDown()`](/reference/android/app/Activity#onKeyDown(int,%20android.view.KeyEvent)) method.\n\n\nFor example, this implementation responds to button presses to control\nactions in an app: \n\n### Kotlin\n\n```kotlin\n// Activity\noverride fun onKeyDown(keyCode: Int, event: KeyEvent): Boolean {\n return if (event.repeatCount == 0) {\n when (keyCode) {\n KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_1 -\u003e {\n // Do stuff\n true\n }\n KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_2 -\u003e {\n // Do stuff\n true\n }\n KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_3 -\u003e {\n // Do stuff\n true\n }\n else -\u003e {\n super.onKeyDown(keyCode, event)\n }\n }\n } else {\n super.onKeyDown(keyCode, event)\n }\n}\n```\n\n### Java\n\n```java\n@Override\n// Activity\npublic boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event){\n if (event.getRepeatCount() == 0) {\n if (keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_1) {\n // Do stuff\n return true;\n } else if (keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_2) {\n // Do stuff\n return true;\n } else if (keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_3) {\n // Do stuff\n return true;\n }\n }\n return super.onKeyDown(keyCode, event);\n}\n```\n\nDetermine the button positions\n------------------------------\n\n\nThe AndroidX Library provides two methods that describe the location of a button:\n\n- [`WearableButtons.getButtonLabel()`](/reference/android/support/wearable/input/WearableButtons#getButtonLabel(android.content.Context, int)) returns a localized string describing the general placement of the button on the device.\n- [`WearableButtons.getButtonIcon()`](/reference/android/support/wearable/input/WearableButtons#getButtonIcon(android.content.Context, int)) returns an icon representing the general placement of the button on the device.\n\n**Note:** We recommend that you avoid using textual descriptors\nwhen describing buttons and their functions. Use visual indicators instead. However, there may\nbe some cases where describing a button makes more sense.\n\n\nThe previous methods were designed for simple descriptions. If these APIs don't suit your app's\nneeds, you can also use the `WearableButtons.getButtonInfo()` API to get the\nlocation of the button on the screen and handle it in a more customized way. For more\ninformation on the APIs, see the\n[Wear API reference](/reference/android/support/wearable/input/package-summary)."]]


