穿戴式裝置通常含有多個實體按鈕 (也稱為Stem)。Wear OS 裝置至少須有一個按鈕,亦即電源按鈕。除此之外,也可能會有其他的多功能按鈕。部分裝置也提供實體旋轉側邊按鈕。
在應用程式中,您可以將多功能按鈕指派給動作,以便在應用程式於前景運作時使用。舉例來說,健身應用程式可能會使用多功能按鈕開始或暫停健身:
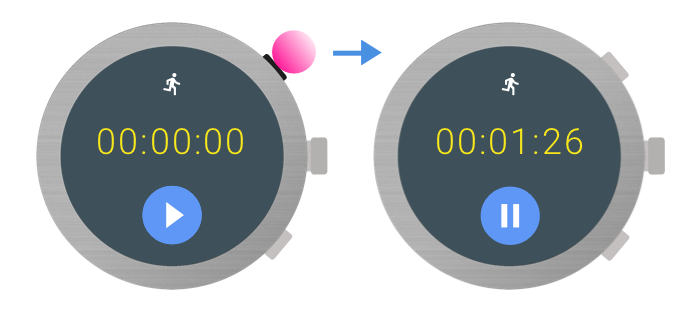
如要瞭解適合用途和設計考量,請參閱「Wear OS 設計原則」。
本文說明如何擷取裝置上多功能按鈕的相關資訊,以及如何處理按鈕的按下動作。
按鈕中繼資料
如要取得裝置上按鈕的額外資訊,請使用 Wear Input AndroidX 程式庫中定義的 API。在應用程式模組的 build.gradle 檔案中新增下列依附元件:
dependencies {
implementation "androidx.wear:wear-input:1.2.0"
}
按鈕數量
如要判斷裝置可用的按鈕數量,請使用 WearableButtons.getButtonCount() 方法。此方法傳回的按鈕數量包含電源按鈕,因此若傳回的值大於一,表示有多功能按鈕可供使用。如要準確計算可指派的多功能按鈕數量,請將按鈕總數扣除一,因為第一個按鈕一律是電源按鈕。
按下按鈕動作的的按鍵碼
每個按鈕都對應至 KeyEvent 類別中的 int 常數,如下表所示:
| 按鈕 | KeyEvent |
|---|---|
| 多功能按鈕 1 | KEYCODE_STEM_1 |
| 多功能按鈕 2 | KEYCODE_STEM_2 |
| 多功能按鈕 3 | KEYCODE_STEM_3 |
下列程式碼範例說明如何取得可用的按鈕數量:
val count = WearableButtons.getButtonCount(context) if (count > 1) { Log.d(TAG, "More than one button available") } val buttonInfo = WearableButtons.getButtonInfo( activity, KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_1 ) if (buttonInfo == null) { // KEYCODE_STEM_1 is unavailable Log.d(TAG, "KEYCODE_STEM_1 not available") } else { // KEYCODE_STEM_1 is present on the device Log.d(TAG, "KEYCODE_STEM_1 is present on the device") }
處理按鈕的按下動作
應用程式有多種可能的按鈕按鍵碼:
KEYCODE_STEM_1。KEYCODE_STEM_2。
您的應用程式可接收這些按鈕按鍵碼,並轉換為應用程式內特定動作。
如要處理按下按鈕動作,請實作 onKeyDown() 方法。
舉例來說,此實作會回應某個按下按鈕的動作,以控制應用程式中的動作:
override fun onKeyDown(keyCode: Int, event: KeyEvent?): Boolean { return if (event?.repeatCount == 0) { when (keyCode) { KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_1 -> { Log.d(TAG, "KEYCODE_STEM_1 pressed") true } KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_2 -> { Log.d(TAG, "KEYCODE_STEM_2 pressed") true } else -> { super.onKeyDown(keyCode, event) } } } else { super.onKeyDown(keyCode, event) } }
決定按鈕的位置
AndroidX 程式庫提供兩種說明按鈕位置的方法:
WearableButtons.getButtonLabel()傳回本地化字串,說明裝置上按鈕通常的位置。WearableButtons.getButtonIcon()傳回圖示,表示裝置上按鈕通常的位置。
如果這些 API 不符合您應用程式的需求,您也可以使用 WearableButtons.getButtonInfo() API 取得按鈕在畫面中的位置,並且透過自己希望的方式處理。如要進一步瞭解 API,請參閱「Wear API 參考資料」。

