Cấu trúc ưu tiên của một ứng dụng âm thanh là thiết kế máy khách/máy chủ. Ứng dụng khách là một Hoạt động trong ứng dụng của bạn bao gồm MediaBrowser, trình điều khiển nội dung nghe nhìn và giao diện người dùng. Máy chủ là một MediaBrowserService chứa trình phát và một phiên phát nội dung đa phương tiện.
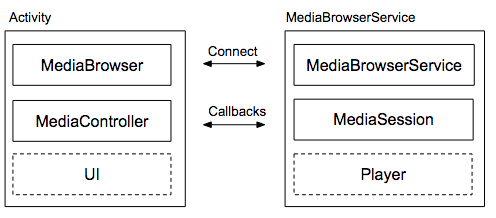
MediaBrowserService cung cấp hai tính năng chính:
- Khi bạn sử dụng
MediaBrowserService, các thành phần và ứng dụng khác cóMediaBrowsercó thể khám phá dịch vụ của bạn, tạo trình điều khiển nội dung nghe nhìn riêng, kết nối với phiên phát nội dung nghe nhìn của bạn và điều khiển trình phát. Đây là cách ứng dụng Wear OS và ứng dụng Android Auto có quyền truy cập vào ứng dụng đa phương tiện của bạn. - Dịch vụ này cũng cung cấp một API duyệt web không bắt buộc. Các ứng dụng không phải sử dụng tính năng này. API duyệt qua cho phép khách hàng truy vấn dịch vụ và xây dựng bản trình bày phân cấp nội dung của dịch vụ, có thể đại diện cho danh sách phát, thư viện nội dung nghe nhìn hoặc một số loại bộ sưu tập khác.
- Xây dựng dịch vụ trình duyệt nội dung đa phương tiện
- Cách tạo dịch vụ trình duyệt nội dung đa phương tiện có chứa một phiên phát nội dung đa phương tiện, quản lý kết nối ứng dụng và trở thành dịch vụ trên nền trước trong khi phát âm thanh.
- Xây dựng ứng dụng trình duyệt đa phương tiện
- Cách tạo hoạt động trên ứng dụng trình duyệt nội dung đa phương tiện có chứa giao diện người dùng và trình điều khiển nội dung đa phương tiện, cũng như kết nối và giao tiếp với một dịch vụ trình duyệt nội dung đa phương tiện.
- Lệnh gọi lại phiên đa phương tiện
- Mô tả cách các phương thức gọi lại phiên phát nội dung đa phương tiện quản lý phiên phát nội dung đa phương tiện, dịch vụ trình duyệt nội dung đa phương tiện và các thành phần khác của ứng dụng như thông báo và broadcast receiver.
- Mẫu Universal Android Music Player
- Mẫu GitHub này cho biết cách triển khai một ứng dụng đa phương tiện cho phép phát âm thanh ở chế độ nền và cung cấp thư viện nội dung nghe nhìn để hiển thị với các ứng dụng khác.
