如果需要在應用程式中顯示靜態圖片,可以使用 Drawable 類別及其子類別來繪製形狀和
所以映像檔較小Drawable 是以下項目的一般抽象化機制:
可以繪製的事物各種子類別可協助您處理特定圖片
您可以擴充這些情境,定義自己的可繪項目物件
能夠以獨特的方式運作
除了使用類別建構函式,您也可以用兩種方式定義和例項化 Drawable:
- 加載儲存在專案中的圖片資源 (點陣圖檔案)。
- 加載定義可繪項目屬性的 XML 資源。
注意: 建議您改用向量可繪項目,以定義圖片的 點、線和曲線,以及相關色彩資訊。如此一來,向量可繪項目 但不會影響畫質詳情請參閱「向量 可繪項目總覽。
根據資源圖片建立可繪項目
您可以參照 專案資源支援的檔案類型包括 PNG (建議)、JPG (可接受)、 和 GIF (不建議)。應用程式圖示、標誌和其他圖像,例如 非常適合採用這種技巧
如要使用圖片資源,請將檔案新增至 res/drawable/
目標專案目錄在專案中
您可以參照
從程式碼或 XML 版面配置中移除資源無論選擇哪種方式,一律採用
資源 ID,即不含檔案類型副檔名的檔案名稱。適用對象
例如,將 my_image.png 稱為 my_image。
注意:放在
可能會透過以下項目自動最佳化 res/drawable/ 目錄:
在建構期間使用 aapt 工具進行無損圖片壓縮
上傳資料集之後,您可以運用 AutoML
自動完成部分資料準備工作例如,真實色彩 PNG,而且只能使用 256 種顏色
可以使用調色盤轉換為 8 位元 PNG。這會產生一張圖片
但需要較少記憶體因此,映像檔的二進位檔
此目錄中的所有項目可能會在建構時變更。如果您想閱讀
才能轉換為點陣圖,將圖片放在
改為 res/raw/ 資料夾,但 aapt 工具沒有
進行修改。
下列程式碼片段說明如何建立 ImageView,以使用
從可繪製資源建立的圖片並新增至版面配置:
Kotlin
private lateinit var constraintLayout: ConstraintLayout override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Instantiate an ImageView and define its properties val i = ImageView(this).apply { setImageResource(R.drawable.my_image) contentDescription = resources.getString(R.string.my_image_desc) // set the ImageView bounds to match the Drawable's dimensions adjustViewBounds = true layoutParams = ViewGroup.LayoutParams( ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) } // Create a ConstraintLayout in which to add the ImageView constraintLayout = ConstraintLayout(this).apply { // Add the ImageView to the layout. addView(i) } // Set the layout as the content view. setContentView(constraintLayout) }
Java
ConstraintLayout constraintLayout; protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Create a ConstraintLayout in which to add the ImageView constraintLayout = new ConstraintLayout(this); // Instantiate an ImageView and define its properties ImageView i = new ImageView(this); i.setImageResource(R.drawable.my_image); i.setContentDescription(getResources().getString(R.string.my_image_desc)); // set the ImageView bounds to match the Drawable's dimensions i.setAdjustViewBounds(true); i.setLayoutParams(new ViewGroup.LayoutParams( ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT)); // Add the ImageView to the layout and set the layout as the content view. constraintLayout.addView(i); setContentView(constraintLayout); }
在其他情況下,建議您將圖片資源處理為 Drawable 物件,如下所示
範例:
Kotlin
val myImage: Drawable = ResourcesCompat.getDrawable(context.resources, R.drawable.my_image, null)
Java
Resources res = context.getResources(); Drawable myImage = ResourcesCompat.getDrawable(res, R.drawable.my_image, null);
警告:專案中的每個不重複資源
無論您建立多少不同的物件
例項化。舉例來說,假設您從同一圖片資源將兩個 Drawable 物件例項化,並
變更一個物件的屬性 (例如 Alpha 值),但也會影響
另一個處理映像檔資源的多個執行個體時
才能直接轉換 Drawable 物件,您應執行
前青少年
動畫。
以下 XML 程式碼片段說明如何在 XML 版面配置中,將可繪製資源新增至 ImageView:
<ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:src="@drawable/my_image" android:contentDescription="@string/my_image_desc" />
如要進一步瞭解如何使用專案資源,請參閱「資源和資產」。
注意事項:使用圖片資源做為可繪項目來源時, 確認圖片尺寸適用於各種像素密度。如果 圖像不正確時,系統會將圖片調整為適當大小,導致可繪項目失真。 詳情請參閱透過 像素密度。
從 XML 資源建立可繪項目
如果有 Drawable
要建立的物件,一開始並沒有依賴由
然後在 XML 中定義 Drawable 是個不錯的方法平均
如果您希望 Drawable 在使用者互動期間變更屬性,請這麼做
您應考慮使用 XML 定義物件,因為您可以在
已為物件執行個體化
在 XML 中定義 Drawable 後,請將檔案儲存在
專案的 res/drawable/ 目錄。以下範例顯示
會定義
TransitionDrawable
繼承自 Drawable 的資源:
<!-- res/drawable/expand_collapse.xml --> <transition xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <item android:drawable="@drawable/image_expand"/> <item android:drawable="@drawable/image_collapse"/> </transition>
然後,透過呼叫
Resources#getDrawable()
並傳送 XML 檔案的資源 ID不限
Drawable 子類別
支援 inflate() 方法,且可在 XML 中定義並例項化
。
每個支援 XML 加載作業的可繪項目類別都會使用特定的 XML 屬性
這些內容會用於定義物件屬性下方程式碼會將
TransitionDrawable
並將其設為
ImageView 物件:
Kotlin
val transition= ResourcesCompat.getDrawable( context.resources, R.drawable.expand_collapse, null ) as TransitionDrawable val image: ImageView = findViewById(R.id.toggle_image) image.setImageDrawable(transition) // Description of the initial state that the drawable represents. image.contentDescription = resources.getString(R.string.collapsed) // Then you can call the TransitionDrawable object's methods. transition.startTransition(1000) // After the transition is complete, change the image's content description // to reflect the new state.
Java
Resources res = context.getResources(); TransitionDrawable transition = (TransitionDrawable) ResourcesCompat.getDrawable(res, R.drawable.expand_collapse, null); ImageView image = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.toggle_image); image.setImageDrawable(transition); // Description of the initial state that the drawable represents. image.setContentDescription(getResources().getString(R.string.collapsed)); // Then you can call the TransitionDrawable object's methods. transition.startTransition(1000); // After the transition is complete, change the image's content description // to reflect the new state.
如要進一步瞭解支援的 XML 屬性,請參閱 。
形狀可繪項目
ShapeDrawable 物件
當您想動態繪製 2D 圖形時你可以
透過程式輔助方式在 ShapeDrawable 物件上繪製原始形狀
並套用應用程式所需的樣式
ShapeDrawable 是 Drawable 的子類別。因此,您可以使用
ShapeDrawable 應位於 Drawable 的位置。適用對象
例如,您可以使用 ShapeDrawable 物件來設定背景
的檢視畫面,方法是將其傳遞至檢視區塊的 setBackgroundDrawable() 方法。也可以繪製形狀
並新增至應用程式中的版面配置。
由於 ShapeDrawable 有專屬的 draw() 方法,您可以
可繪製 ShapeDrawable 的 View 子類別
物件,如onDraw()
以下程式碼範例:
Kotlin
class CustomDrawableView(context: Context) : View(context) { private val drawable: ShapeDrawable = run { val x = 10 val y = 10 val width = 300 val height = 50 contentDescription = context.resources.getString(R.string.my_view_desc) ShapeDrawable(OvalShape()).apply { // If the color isn't set, the shape uses black as the default. paint.color = 0xff74AC23.toInt() // If the bounds aren't set, the shape can't be drawn. setBounds(x, y, x + width, y + height) } } override fun onDraw(canvas: Canvas) { drawable.draw(canvas) } }
Java
public class CustomDrawableView extends View { private ShapeDrawable drawable; public CustomDrawableView(Context context) { super(context); int x = 10; int y = 10; int width = 300; int height = 50; setContentDescription(context.getResources().getString( R.string.my_view_desc)); drawable = new ShapeDrawable(new OvalShape()); // If the color isn't set, the shape uses black as the default. drawable.getPaint().setColor(0xff74AC23); // If the bounds aren't set, the shape can't be drawn. drawable.setBounds(x, y, x + width, y + height); } protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { drawable.draw(canvas); } }
您可以在程式碼範例中使用 CustomDrawableView 類別
方法就跟使用其他自訂檢視模式一樣舉例來說:
透過程式輔助方式將函式新增至應用程式活動,如下所示
範例:
Kotlin
private lateinit var customDrawableView: CustomDrawableView override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) customDrawableView = CustomDrawableView(this) setContentView(customDrawableView) }
Java
CustomDrawableView customDrawableView; protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); customDrawableView = new CustomDrawableView(this); setContentView(customDrawableView); }
如果您想改為在 XML 版面配置中使用自訂檢視區塊,請
CustomDrawableView 類別必須覆寫 View(Context, AttributeSet) 建構函式,系統會在類別發生時呼叫該建構函式
由 XML 加載。以下範例說明如何宣告
XML 版面配置中的 CustomDrawableView:
<com.example.shapedrawable.CustomDrawableView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
ShapeDrawable 類別,和其他許多
android.graphics.drawable 套件中的可繪項目類型,可讓您
使用公開方法定義物件的各種屬性。一些例子
建議調整的屬性包括 Alpha 透明度、色彩濾鏡
顏色、透明度和顏色。
您也可以使用 XML 資源定義原始可繪項目形狀。如要 資訊,請參閱 中的形狀可繪項目 可繪製資源類型。
NinePatch 可繪項目
NinePatchDrawable 圖形是一個
可延展點陣圖圖片,可做為檢視畫面的背景。Android 版
自動調整圖像大小,以配合檢視畫面的內容。一個
NinePatch 圖像的使用範例為標準 Android 使用的背景
按鈕:按鈕必須延伸,才能容納各種長度的字串。A 罩杯
NinePatch 圖像是標準的 PNG 圖片,其中包含額外的 1 像素邊框。
必須使用 9.png 擴充功能儲存 (位於
專案的 res/drawable/ 目錄。
使用邊框來定義圖片的可延展和靜態區域。 繪製一個 (或更多個) 1 像素寬,即可指出可延展區塊 框線的左側和上半部黑線 (其他邊框像素) 必須是完全透明或白色的內容)。可以延展的部分數量 視需要調整設定可延展部分的相對大小維持不變 最大的區塊永遠是最大的
您也可以為圖片定義選用的可繪項目部分 (實際上
也就是在右側繪製線條,並在底部繪製線條。如果
View 物件會將 NinePatch 圖像設為背景
然後指定檢視區塊的文字,並延展到所有文字
只會佔用右側和底部程式碼指定的區域 (如有)。
如果沒有邊框間距,Android 會使用左側和上行
會定義此可繪項目區域
為了清楚區分兩條線的差異,左側和上行會定義 允許複製的圖像像素來延展 圖片。底部和右線會定義圖片中的相對區域 檢視畫面的內容可供佔用。
圖 1 範例顯示用來定義按鈕的 NinePatch 圖像:
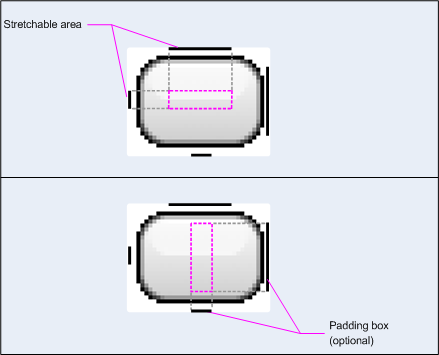
圖 1:NinePatch 圖像範例 定義按鈕的
此 NinePatch 圖像定義了一個可延展區域,左側和頂部為一個可延展區域 而可繪項目區域以及底部和右側線條在頂端圖片中 灰色虛線代表複製的圖像區域 以便延展圖片底部圖片中的粉紅色矩形代表了 系統允許檢視區塊內容的區域。如果內容 會延展圖片,將圖片調整為合適大小。
繪製 9-patch 工具提供 用 WYSIWYG 圖形製作 NinePatch 圖像非常方便的方法 編輯。如為可延展範圍定義區域,它甚至會引發警告 可能導致系統產生繪圖失真 複製功能
以下版面配置 XML 示範如何新增 NinePatch 圖像
移到兩個按鈕上NinePatch 圖像會儲存至
res/drawable/my_button_background.9.png。
<Button android:id="@+id/tiny" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:text="Tiny" android:textSize="8sp" android:background="@drawable/my_button_background"/> <Button android:id="@+id/big" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:text="Biiiiiiig text!" android:textSize="30sp" android:background="@drawable/my_button_background"/>
請注意,layout_width 和 layout_height
將屬性設為 wrap_content,讓按鈕更美觀
文字周圍
圖 2 顯示透過 XML 和 NinePatch 圖像轉譯的兩個按鈕 如上所示。請注意按鈕的寬度和高度會如何隨文字改變 而且背景圖片會配合尺寸延展

圖 2:使用 XML 轉譯的按鈕 資源和 NinePatch 圖像
自訂可繪項目
如要建立自訂繪圖,您可以擴充 Drawable 類別 (或其任何子類別)。
最重要的實作方法為 draw(Canvas)
因為此方法會提供您需要使用的 Canvas 物件
擷取繪圖指示
以下程式碼顯示 Drawable 的簡易子類別
來繪製圓形:
Kotlin
class MyDrawable : Drawable() { private val redPaint: Paint = Paint().apply { setARGB(255, 255, 0, 0) } override fun draw(canvas: Canvas) { // Get the drawable's bounds val width: Int = bounds.width() val height: Int = bounds.height() val radius: Float = Math.min(width, height).toFloat() / 2f // Draw a red circle in the center canvas.drawCircle((width / 2).toFloat(), (height / 2).toFloat(), radius, redPaint) } override fun setAlpha(alpha: Int) { // This method is required } override fun setColorFilter(colorFilter: ColorFilter?) { // This method is required } override fun getOpacity(): Int = // Must be PixelFormat.UNKNOWN, TRANSLUCENT, TRANSPARENT, or OPAQUE PixelFormat.OPAQUE }
Java
public class MyDrawable extends Drawable { private final Paint redPaint; public MyDrawable() { // Set up color and text size redPaint = new Paint(); redPaint.setARGB(255, 255, 0, 0); } @Override public void draw(Canvas canvas) { // Get the drawable's bounds int width = getBounds().width(); int height = getBounds().height(); float radius = Math.min(width, height) / 2; // Draw a red circle in the center canvas.drawCircle(width/2, height/2, radius, redPaint); } @Override public void setAlpha(int alpha) { // This method is required } @Override public void setColorFilter(ColorFilter colorFilter) { // This method is required } @Override public int getOpacity() { // Must be PixelFormat.UNKNOWN, TRANSLUCENT, TRANSPARENT, or OPAQUE return PixelFormat.OPAQUE; } }
接著,您可以視需求新增可繪項目,例如
ImageView,如下所示:
Kotlin
val myDrawing = MyDrawable() val image: ImageView = findViewById(R.id.imageView) image.setImageDrawable(myDrawing) image.contentDescription = resources.getString(R.string.my_image_desc)
Java
MyDrawable mydrawing = new MyDrawable(); ImageView image = findViewById(R.id.imageView); image.setImageDrawable(mydrawing); image.setContentDescription(getResources().getString(R.string.my_image_desc));
在 Android 7.0 (API 級別 24) 以上版本中,您也可以定義自訂可繪項目的執行個體 以下列方式使用 XML:
- 使用完整的類別名稱做為 XML 元素名稱。就這個方法而言
可繪項目類別必須是公開的頂層類別:
<com.myapp.MyDrawable xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:color="#ffff0000" />
- 使用
drawable做為 XML 標記名稱,並指定完整類別 從類別屬性中移除名稱這個方法適用於公開頂層類別和 公開靜態內部類別:<drawable xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" class="com.myapp.MyTopLevelClass$MyDrawable" android:color="#ffff0000" />
為可繪項目新增色調
在 Android 5.0 (API 級別 21) 以上版本中,您可以對點陣圖和 nine-patch 定義
使用 Alpha 遮罩可使用色彩資源或解析為顏色的主題屬性來配色
(例如 ?android:attr/colorPrimary)。您通常會建立這些素材資源
而且只會依照主題自動調整顏色。
可套用色調至 BitmapDrawable、NinePatchDrawable 或 VectorDrawable
建立含有 setTint() 方法的物件你可以
您也可以使用 android:tint 和
android:tintMode 屬性。
從圖片擷取顯著色彩
Android 支援資料庫包含 Palette 類別,可讓您從圖片中擷取醒目的顏色。
您可以將可繪項目載入為 Bitmap,並傳遞至 Palette 來存取顏色。
如需瞭解更多資訊,請參閱選擇色彩
Palette API。

